Jetpack-Compose
![]()
![]()
一、什么都不如官网来的直接
Jetpack Compose去年写了一些列表布局就丢下了,以前一个小兄弟说“什么都不如官网来的直接”这是他的博客打算用Compose写玩安卓大家可以去好好学习一波,接下来我们跟着官网走,原理案例基于官网,写的效果高于官网。Flutter,SwiftUI对比这些众说风云,人云亦云,我不多说,XML相对于当前流行的前段或者移动端布局组建框架都不在是优势,既然Google推出的那我们就学。
二、环境
1.AndroidSdio Beta 4.2版本或者Canary版本
版本提供有好的界面预览-即时预览 Compose 界面
2.确保您在项目中使用的是Kotlin 1.4.21 或更高版本
项目build.gradle里面配置:
buildscript {
ext {
compose_version = '1.0.0-alpha04'
}
//大于1.4.12版本
ext.kotlin_version = "1.4.30"
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:4.2.0-beta05'
classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:$kotlin_version"
}
}
3.app下面的build.gradle配置如下:
最低 API 级别设置为 21 或更高级别
并在应用的 build.gradle 文件中启用 Jetpack Compose
添加 Jetpack Compose 工具包依赖项
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
id 'kotlin-android'
}
android {
compileSdkVersion 30
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.example.jetpackcompose"
minSdkVersion 21//最低 API 级别设置为 21 或更高级别
targetSdkVersion 30
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = '1.8'
useIR = true
}
buildFeatures {
compose true//并在应用的 build.gradle 文件中启用 Jetpack Compose
}
composeOptions {
kotlinCompilerExtensionVersion compose_version
kotlinCompilerVersion '1.4.10'
}
}
dependencies {
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:$kotlin_version"
implementation 'androidx.core:core-ktx:1.3.1'
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.2.0'
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.2.1'
implementation "androidx.compose.ui:ui:$compose_version"
implementation "androidx.compose.material:material:$compose_version"
implementation "androidx.ui:ui-tooling:$compose_version"
implementation 'androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.3.0-alpha06'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.+'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.2'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.3.0'
}
创建项目
MainActivity.class
package com.example.jetpackcompose
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.compose.foundation.*
import androidx.compose.ui.platform.setContent
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
Text("Hello World")
}
}
}
三、Layouts
官网地址组件学习
- 接下来我们学习-如何使用Compose构建简单的UI布局,如
文本,图片之类的组件以及列和行之类的容器布局组件,不管是Flutter、SwiftUI、HTML、Compose…只要学会最基本的行和列加个Stack,基本就能够搞定所有的布局样式了,至于细节和不常用的组建看属性、看官网、看百度即可直接上手。
Jetpack Compose 是围绕可组合函数构建的,所有的部件都是Compose,只需
将 @Composable 注释添加到函数名称中即可。
一、文字相关属性和案例
- 我们来看看官方库提供的
Text被@Composeable也注解成为可组合组建。内部定义了很多我们熟悉的属性提供开发者设置。
@Composable
fun Text(
text: String,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
color: Color = Color.Unset,
fontSize: TextUnit = TextUnit.Inherit,
fontStyle: FontStyle? = null,
fontWeight: FontWeight? = null,
fontFamily: FontFamily? = null,
letterSpacing: TextUnit = TextUnit.Inherit,
textDecoration: TextDecoration? = null,
textAlign: TextAlign? = null,
lineHeight: TextUnit = TextUnit.Inherit,
overflow: TextOverflow = TextOverflow.Clip,
softWrap: Boolean = true,
maxLines: Int = Int.MAX_VALUE,
onTextLayout: (TextLayoutResult) -> Unit = {
},
style: TextStyle = currentTextStyle()
) {
Text(
AnnotatedString(text),
modifier,
color,
fontSize,
fontStyle,
fontWeight,
fontFamily,
letterSpacing,
textDecoration,
textAlign,
lineHeight,
overflow,
softWrap,
maxLines,
emptyMap(),
onTextLayout,
style
)
}
- 到现在是不是迫不及待的想写一个TextView呢?
class ComposeStudy_01 : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent{
Text("Hello World")
}
}
}
既然提供了这么多的属性我们不妨试一试常用的颜色、字体大小、边框、字体样式、间距、加粗等
⭐️ 这里需要注意的是属性默认可以不写参数名称按照参数顺序从上到下,但是如果你要跳级设置其中两三个或多个需要写参数名哦,这样才能对应负值,给初学者的提示。
class ComposeStudy_01 : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
Text(
text = " Hello World",
//`边框`
modifier = Modifier.border(
border = BorderStroke(
width = 3.dp,
color = Color(0xFF999999),
),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(20f, 60f, 20f, 160f),
),
//`颜色`、
color = Color.Green,
//`字体大小`、
fontSize = TextUnit.Sp(66),
//字形的厚度
fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold,
//斜体
fontStyle = FontStyle.Italic,
fontFamily = FontFamily.Default,
//字体水平间隔
letterSpacing = TextUnit.Em(0),
//在文本上方绘制一条水平线
textDecoration = TextDecoration.LineThrough
)
}
}
}
二、文字分装
- 既然Jetpack Compose是围绕可组合函数构建的。那我们接下来写个通用的文字组建通过
@Compose
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
myText(" Hello World")
}
}
@Composable
private fun myText(text:String) {
Text(
text = text,
//`边框`
modifier = Modifier.border(
border = BorderStroke(
width = 3.dp,
color = Color(0xFF999999),
),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(20f, 60f, 20f, 160f),
),
//`颜色`、
color = Color.Green,
//`字体大小`、
fontSize = TextUnit.Sp(66),
//字形的厚度
fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold,
//斜体
fontStyle = FontStyle.Italic,
fontFamily = FontFamily.Default,
//字体水平间隔
letterSpacing = TextUnit.Em(0),
//在文本上方绘制一条水平线
textDecoration = TextDecoration.LineThrough
)
}
是不是觉得这样写Activity还不是和Flutter一样套娃娃,当然不管是Compose还是Flutter或者SwiftUI我们都可以将其放在其他文件中进行分离封装。如下我们新建文件和类夹专门放置我们的UI。
三、Modifier
- 当我用到
Modifier的时候我很惊叹,这不是SwiftUI么?于是我快速的打开了Xcode
Modifier用于装饰Compose UI元素或向其添加行为。例如,背景,填充和单击事件侦听器可修饰行或添加行,文本或按钮的行为。
1.Modifier来添加点击事件
- 当我点击时候修改当前字体的颜色,我们看到Modifier可以设置clickable,接下来我们进行Modifier的探究。当我
双击时候为红色,单机时候为绿色。
如下代码
1.设置了局部变量color默认为绿色
2.当单机时候设置为黄色
3.双击为红色
@Composable
fun myText(text: String) {
var color = Color.Green
Text(
text = text,
//`边框`
modifier = Modifier.border(
border = BorderStroke(
width = 3.dp,
color = Color(0xFF999999),
),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(20f, 60f, 20f, 160f),
).clickable(
onClick = {
color = Color.Yellow },
onDoubleClick = {
color = Color.Red }
)...
}
运行代码,点击效果如下:并不能修改效果呀!此时很多学习过Flutter和SwiftUI的人都明白你并没有刷新UI咋么可能有所改变呢。那在Compose里面是否有提供如Flutter setState一样的组件。
我想对于有基础的同学modifier我就不多啰嗦了。到这里我终于可以认真的说一句真的很SwiftUI至于是否自定义也和SwiftUI一直这个我们后面章节再讨论和深究,如果没有了很好的自定义画布这些API的提供也就走上了和SwiftUI一样的道路,这一点让我深恶痛绝。
modifier = Modifier.clickable(
onClick = {
nameState.value=Color.Yellow
},
onDoubleClick = {
//2.点击之后事件向上流动修改状态值
nameState.value=Color.Red
}
).background(Color.Gray,shape = RectangleShapes)
.offset(x = Dp(10f),y=Dp(10f))
.drawShadow(elevation = Dp(10f)),
@Stable
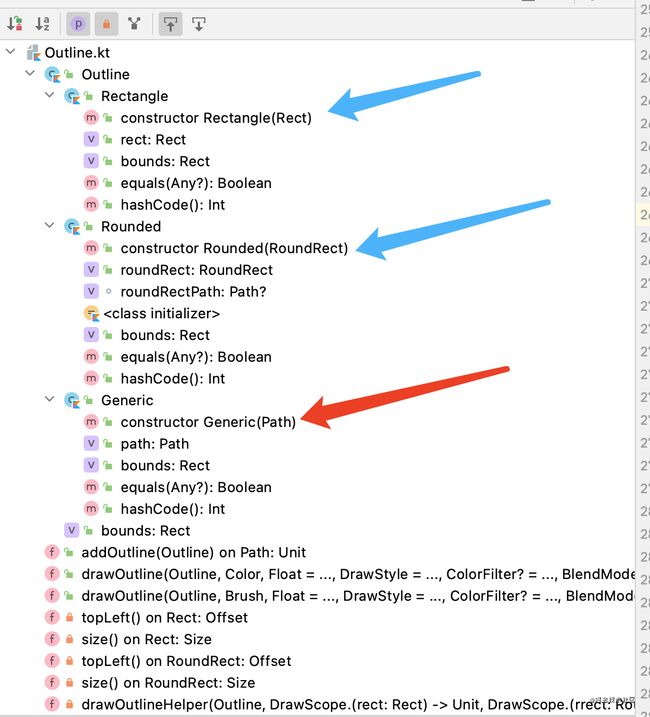
val RectangleShapes: Shape = object : Shape {
val roudRect= RoundRect(10f,0f,1110f,910f,930f,160f)
override fun createOutline(size: Size, density: Density) = Outline.Rounded(roudRect)
}
四、UI刷新-State的过渡
- 原生android JetPack使用过的人都知道LiveData和databinding都可以进行和UI同步刷新,
Flutter过来的人都明白Flutter有setState我们Compose也提供了State等来刷新UI组件。由于文字篇幅问题但是又必须刷新UI所以我们这里先使用State进行刷新UI,之后的有机会详细讲解UI的跟新。
在 Compose 应用中使用的常见可观察类型包括
State、LiveData、StateFlow、Flow和Observable
由于Flutter的习惯,不禁让人想到State,这里于是我跟着找到了State且去了官网果不其然。
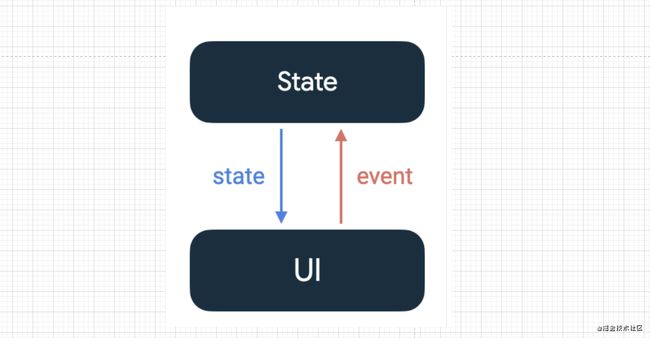
✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨在 Jetpack Compose 中,状态和事件是分开的。状态表示可更改的值,而事件表示有情况发生的通知。通过将状态与事件分开,可以将状态的显示与状态的存储和更改方式解耦。✨✨✨✨✨✨`
- Compose 专为单向数据流而打造。这是一种状态向下流动而事件向上流动的设计。
上面话如何理解呢?我们借助一下官网图片
违代码如下:
1.状态即为可更改的值【数据,类,集合…】
2.事件【各种点击事件,滑动事件,运行时,延迟执行等…】
3.状态【可更改的状态】必须肯定定义在例如Text之上吧?
//1.状态 等待事件向上流动修改状态。然后状态向下流动去修改颜色
val nameState: MutableState<Color> = remember {
mutableStateOf(Color.Green) }
Text(
name,
//跟新UI
color = nameState.value,
...
//2.事件 点击之后向上流动去修改1中的状态
onclick(`nameState.value=Color.RED`)
)
这里的nameState就是状态,而onclick就是事件,当点击事件触发之后通过nameState.value事件向上流动去修改状态。然后状态向下流动到UI修改字体颜色。
下面的
nameState就是状态,而onclick就是事件,当点击事件触发之后通过nameState.value事件向上流动去修改状态。然后状态向下流动到UI修改字体颜色。
@Composable
fun myText(text: String) {
//1.可改变的状态
val nameState: MutableState<Color> = remember {
mutableStateOf(Color.Green) }
//3.修改状态之后状态向下流动去修改4.中的UI
Text(
text = text,
//`边框`
modifier = Modifier.border(
border = BorderStroke(
width = 3.dp,
color = Color(0xFF999999),
),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(20f, 60f, 20f, 160f),
).clickable(
onClick = {
//2.点击之后事件向上流动修改状态值
nameState.value=Color.Yellow
},
onDoubleClick = {
//2.点击之后事件向上流动修改状态值
nameState.value=Color.Red
}
),
//`颜色`、
//4.状态流动下来修改UI显示UI
color = nameState.value,
//`字体大小`、
fontSize = TextUnit.Sp(66),
//字形的厚度
fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold,
//斜体
fontStyle = FontStyle.Italic,
fontFamily = FontFamily.Default,
//字体水平间隔
letterSpacing = TextUnit.Em(0),
//在文本上方绘制一条水平线
textDecoration = TextDecoration.LineThrough
)
}
效果:可以看到双击变为红色,单机变为黄色
五、图片
- 图片常用于我们开发中,我们接下来体验一波Image。之前我们先来看看
@Preview的强大。
@Preview 注解的@Compose都会在预览中一一显示,这让我们开发过程中可以单独局部的处理某一处和整体布局分离显示,提供了更好的单独管理和显示方式。

1.Image
@Preview(name = "studyImage")
@Composable
fun StudyImageView() {
val imageBitmap: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.head_god)
Image(
bitmap = imageBitmap,
contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.app_name),
)
}
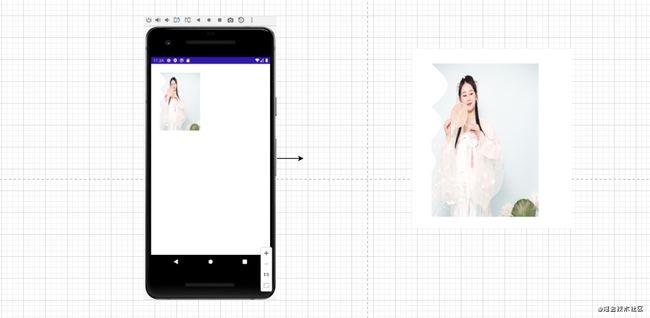
2.Image大小裁剪
@Composable
fun Image(
bitmap: ImageBitmap,
contentDescription: String?,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
alignment: Alignment = Alignment.Center,
contentScale: ContentScale = ContentScale.Fit,
alpha: Float = DefaultAlpha,
colorFilter: ColorFilter? = null
)
=
- 源码中并没有发现
大小和裁剪等。这部分设置我们之前提到过通过modifier来设置吧,那我们来小试牛刀。
@Preview(name = "studyImage")
@Composable
fun StudyImageView() {
val imageBitmap: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.meinv)
Image(
bitmap = imageBitmap,
contentScale= ContentScale.FillBounds,
contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.app_name),
modifier = Modifier
.height(260.dp)
.width(200.dp)
.padding(horizontal = 30.dp,vertical = 30.dp)
.clip(
RoundedCornerShape(
topEnd = 30.dp,
topStart = 30.dp,
bottomEnd = 30.dp,
bottomStart = 30.dp
)
)
)
}
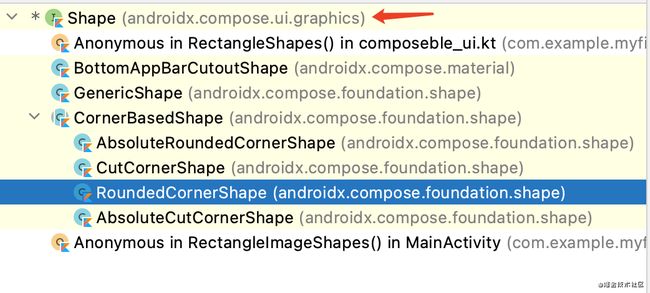
我们点击源码可以看到提供的裁剪clip完全和SwiftUI一样。到这里我很担心没有提供自定义View那一套,Google开发人员是写IOS的吧。再看Shape发现有很多实现类,大家可以一个个测试下一效果,上面我用了RoundedCornerShape,当然了大家最关心的自定义裁剪是否可以,当然没问题的,通过实现Shaper来看看。
@Stable
fun Modifier.clip(shape: Shape) = graphicsLayer(shape = shape, clip = true)
我们发现有很多字面意思提供圆角、边框线等也看到了Generic提供路径裁剪。那我们来试一试
@Preview(name = "studyImage")
@Composable
fun StudyImageView() {
val imageBitmap: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.meinv)
Image(
bitmap = imageBitmap,
contentScale= ContentScale.FillBounds,
contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.app_name),
modifier = Modifier
.height(260.dp)
.width(200.dp)
.padding(horizontal = 30.dp,vertical = 30.dp)
.clip(
RectangleImageShapes
)
)
}
@Stable
val RectangleImageShapes: Shape = object : Shape {
override fun createOutline(
size: Size,
layoutDirection: LayoutDirection,
density: Density
): Outline {
val path= Path()
path.moveTo(0f,0f)
path.relativeLineTo(20f,20f)
path.relativeCubicTo(40f,40f,60f,60f,-20f,130f)
path.relativeCubicTo(40f,40f,60f,60f,-20f,130f)
path.relativeCubicTo(40f,40f,60f,60f,-20f,130f)
path.relativeCubicTo(40f,40f,60f,60f,-20f,130f)
path.relativeCubicTo(40f,40f,60f,60f,-20f,130f)
path.relativeCubicTo(40f,40f,60f,60f,-20f,130f)
path.lineTo(size.width,size.height)
path.lineTo(size.width,0f)
path.close()
return Outline.Generic(path)
}
}
效果如下,到此-裁剪屌不屌你说了算。
3.Image 和 其他部件 旋转、平移、缩放、扭曲变换、修饰、点击拖拽等
当然了图片或者其他部件旋转、平移、缩放、扭曲变换、修饰、点击拖拽等都可以通过Modifer去进行。接下来我们来进行旋转和拖拽的小操作。
代码中以后会常常出现一堆的Modifer咋么办?抽取分装出来更舒服
@Preview(name = "studyImage")
@Composable
fun StudyImageView() {
val draggerOffset:MutableState<Float> = remember{
mutableStateOf(0f) }
val imageBitmap: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.meinv)
Image(
bitmap = imageBitmap,
contentScale = ContentScale.FillBounds,
contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.app_name),
modifier = Modifier.ImageModifier(draggerOffset)
)
}
private fun Modifier.ImageModifier(draggerOffset: MutableState<Float>):Modifier =
composed {
Modifier
.height(260.dp)
.width(200.dp)
.padding(horizontal = 30.dp, vertical = 30.dp)
.clip(
RectangleImageShapes
)
.rotate(10f)
.draggable(state = DraggableState(onDelta = {
draggerOffset.value = +it
Log.e("ondelta", "StudyImageView: " + draggerOffset.value)
}), orientation = Orientation.Horizontal)
.offset(x = draggerOffset.value.dp)
}
效果如下:
六、布局的摆放
1、Row行作为排布容器组件,是每一个移动端API简单而使用率最高的一些组件。内部将水平方向从左到右排布。
@Preview(name = "text1")
@Composable
fun StudyLayoutViews() {
Row() {
Text("第一列",fontSize = 22.sp,color = Color.White,modifier = Modifier.background(Color.Red))
Text("第二列",fontSize = 22.sp,color = Color.White,modifier = Modifier.background(Color.Green))
Text("第三列?",fontSize = 22.sp,color = Color.White,modifier = Modifier.background(Color.Blue))
}
}
2、Row行作为排布容器组件,是每一个移动端API简单而使用率最高的一些组件。内部将竖直方向从上到下排布。
Column() {
Text( "第一列",fontSize = 22.sp,color = Color.White,modifier = Modifier.background(Color.Red))
Text( "第二列",fontSize = 22.sp,color = Color.White,modifier = Modifier.background(Color.Green))
Text( "第三列",fontSize = 22.sp,color = Color.White,modifier = Modifier.background(Color.Blue))
}
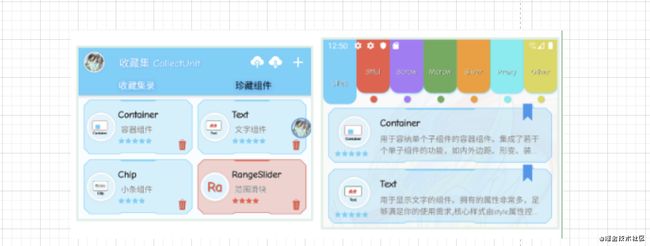
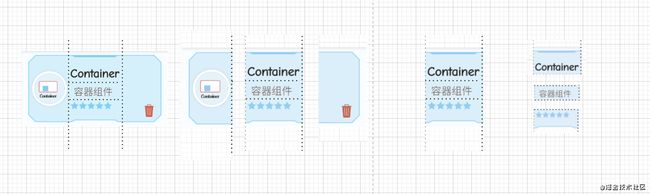
3、张风捷特烈之 FlutterUnit
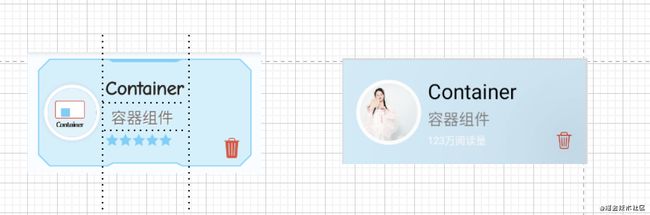
这个Item从Row和Colum分析,Row分为三个内容图片、Colunm、Icon。中间的Colunm分为三行。
@Preview(name = "text1")
@Composable
fun StudyLayoutViews() {
val imageBitmap: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.meinv)
val delectedIcon: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.delected_icon)
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.background(Color(206, 236, 250))
.padding(10.dp)
) {
Row(verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically) {
Image(
bitmap = imageBitmap,
contentDescription = "w",
contentScale = ContentScale.FillBounds,
modifier = Modifier
.height(50.dp)
.width(50.dp)
.background(Color.White, shape = CircleShape)
.padding(3.dp)
.clip(
CircleShape
)
.shadow(elevation = 150.dp, clip = true)
)
Column(modifier = Modifier.padding(start = 5.dp)) {
Text(
"Container",
fontSize = 16.sp,
color = Color.Black,
)
Text(
"容器组件",
modifier = Modifier.padding(top = 3.dp, bottom = 3.dp),
fontSize = 12.sp,
color = Color.Gray,
)
Text(
"123万阅读量",
fontSize = 8.sp,
color = Color.White,
)
}
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.height(60.dp)
.padding(start = 30.dp),
contentAlignment = Alignment.BottomCenter
) {
Image(
bitmap = delectedIcon,
contentDescription = "w",
contentScale = ContentScale.FillBounds,
modifier = Modifier
.height(20.dp)
.width(20.dp)
.shadow(elevation = 150.dp, clip = true)
)
}
}
}
}
到这里我们已经学会了基本的布局排列,当然边框目前还是有差距的,必定是自定义绘制裁剪的边框。接下来我们来再体验一下Compose的裁剪。
Shaper中提供的Size即整个组件的大小,我们通过相对形成对应的框最后裁剪画布即可。
至于自定义不熟练的可以看看张风捷特烈或者我的文章
@Stable
val BoxClipShapes: Shape = object : Shape {
override fun createOutline(
size: Size,
layoutDirection: LayoutDirection,
density: Density
): Outline {
val path = Path()
path.moveTo(20f, 0f)
path.relativeLineTo(-20f, 20f)
path.relativeLineTo(0f,size.height - 40f)
path.relativeLineTo(20f, 20f)
path.relativeLineTo(size.width / 3f-20, 0f)
path.relativeLineTo(15f, -20f)
path.relativeLineTo(size.width / 3f-30, 0f)
path.relativeLineTo(15f, 20f)
path.relativeLineTo(size.width / 3f-20, 0f)
path.relativeLineTo(20f, -20f)
path.relativeLineTo(0f, -(size.height - 40f))
path.relativeLineTo(-20f, -20f)
path.close()
return Outline.Generic(path)
}
}
是不是迫不及待看效果呢?
里面的星星我就不画了。我意思是到这里裁剪都练会了吧?不对好像上面也不一样。搞一波上部吧。
@Stable
val BoxClipShapes: Shape = object : Shape {
override fun createOutline(
size: Size,
layoutDirection: LayoutDirection,
density: Density
): Outline {
val path = Path()
path.moveTo(20f, 0f)
path.relativeLineTo(-20f, 20f)
path.relativeLineTo(0f,size.height - 40f)
path.relativeLineTo(20f, 20f)
path.relativeLineTo(size.width / 3f-20, 0f)
path.relativeLineTo(15f, -20f)
path.relativeLineTo(size.width / 3f-30, 0f)
path.relativeLineTo(15f, 20f)
path.relativeLineTo(size.width / 3f-20, 0f)
path.relativeLineTo(20f, -20f)
path.relativeLineTo(0f, -(size.height - 40f))
path.relativeLineTo(-20f, -20f)
path.relativeLineTo(-(size.width / 3f-20),0f)
path.relativeLineTo(-15f,20f)
path.relativeLineTo(-(size.width / 3f-30), 0f)
path.relativeLineTo(-15f, -20f)
path.close()
return Outline.Generic(path)
}
}
效果如下 当然了可以无比骚,看设计人员能设计出个花来都能行。
- 我们看着有深色的边框。我们试一试
容器盒子Box的Modifier设置border。
Box(modifier = Modifier.padding(20.dp)
.clip(BoxClipShapes)
.background(Color(206, 236, 250))
.border(width=1.dp,color = Color.Blue))
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️效果如下,这效果太low了吧。为嘛中间和两边没有呢?我们看看border源码,它就是个矩形,只是被我们无情的裁剪掉了中间和两边角。⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
我们既然进行了裁剪那么而且border提供了裁剪shaper那么我们是不是可以进行将Box的裁剪设置到Border和裁剪一致呢?
Box(modifier = Modifier.padding(20.dp)
.clip(BoxClipShapes)
.background(Color(206, 236, 250))
.border(width=1.dp,color = Color(79, 129, 160),shape = BoxBorderClipShape)){
内容
}
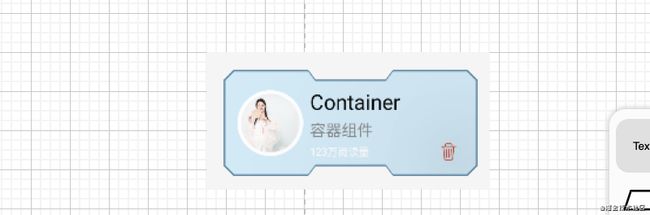
肯定还有人说不一样的。上代码看效果:
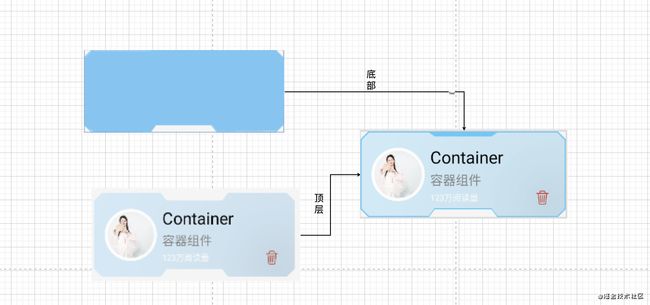
我们看到上部有部分蓝色,其实整体观察底部又一个也是裁剪但是上部没有裁剪同步的Box,内部再装一个上下都进行裁剪的Box是不是就完成了这个效果。
@Preview(name = "text1")
@Composable
fun StudyLayoutViews() {
val imageBitmap: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.meinv)
val delectedIcon: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.delected_icon)
Box(modifier = Modifier.clip(BoxBorderClipShape)
.background(Color(89, 199, 249))) {
Box(
modifier = Modifier.padding(0.dp).clip(BoxClipShapes)
.background(Color(206, 236, 250))
.border(width = 1.dp, color = Color(89, 199, 249), shape = BoxClipShapes)
) {
Row(
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically,
modifier = Modifier.padding(10.dp)
) {
Image(
bitmap = imageBitmap,
contentDescription = "w",
contentScale = ContentScale.FillBounds,
modifier = Modifier
.height(50.dp)
.width(50.dp)
.background(Color.White, shape = CircleShape)
.padding(3.dp)
.clip(
CircleShape
)
.shadow(elevation = 150.dp, clip = true)
)
Column(modifier = Modifier.padding(start = 5.dp)) {
Text(
"Container",
fontSize = 16.sp,
color = Color.Black,
)
Text(
"容器组件",
modifier = Modifier.padding(top = 3.dp, bottom = 3.dp),
fontSize = 12.sp,
color = Color.Gray,
)
Text(
"123万阅读量",
fontSize = 8.sp,
color = Color.White,
)
}
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.height(60.dp)
.padding(start = 30.dp, end = 5.dp),
contentAlignment = Alignment.BottomCenter
) {
Image(
bitmap = delectedIcon,
contentDescription = "w",
modifier = Modifier
.height(16.dp)
.width(13.dp)
.shadow(elevation = 150.dp, clip = true)
)
}
}
}
}
}
到这里我们应该对SwiftUi花里胡哨的裁剪没什么问题了吧,说错了Compose?有问题也是你对自定义不熟悉。当然了你可以去看看我博客或者其他作者的都ok。你以为到这里就结束了么?接下来才要进入正题自定义绘制,裁剪在开发中是远远满足不了需求的例如曲线或者折线图表等。
三、Compose-自定义绘制
- 对于自定义基础和相关的API大家不熟悉的可以看看我的博客
在Compose中大部分的API都在
androidx.compose.ui.graphics下,有兴趣的可以多看看。
1.Android自定义-曲线渐变填充
2.Android自定义-手势缩放折线图
3.Android自定义-手势滑动缩放渐变填充曲线折线图表
4.艺术在于绘制
5.绘制相关API…
- 你以为我会和上面这些博客一样,面面具到么?上代码。没忍住写了点提示文字
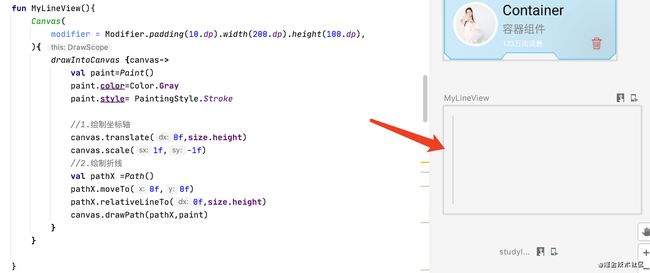
@Preview(name = "MyLineView")
@Composable
fun MyLineView(){
Canvas(
modifier = Modifier.padding(10.dp).width(200.dp).height(100.dp),
){
drawIntoCanvas {canvas->
val paint=Paint()
paint.color=Color.Gray
paint.style= PaintingStyle.Stroke
//1.变换坐标轴
canvas.translate(0f,size.height)
canvas.scale(1f,-1f)
//2.绘制Y轴
val pathY =Path()
pathY.moveTo(0f,0f)
pathY.relativeLineTo(0f,size.height)
canvas.drawPath(pathY,paint)
}
}
}
绘制X轴
绘制折线
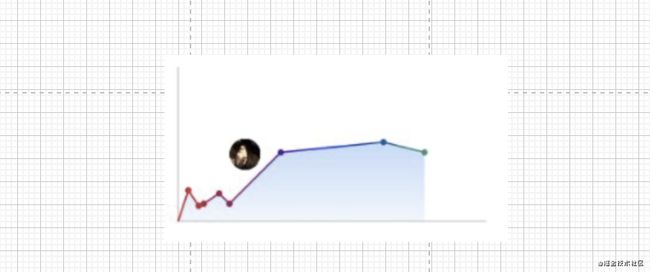
- 绘制也大致浏览了一遍基本的绘制还是有的。绘制文字没找到…尴尬到不行
@Preview(name = "MyLineView")
@Composable
fun MyLineView(bitmap: ImageBitmap){
Canvas(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(10.dp)
.width(200.dp)
.height(100.dp),
){
drawIntoCanvas {canvas->
val paint=Paint()
paint.color=Color(208,208,208)
paint.style= PaintingStyle.Stroke
paint.strokeWidth=3f
val paintFill=Paint()
paintFill.color=Color.Gray
paintFill.style= PaintingStyle.Stroke
paintFill.strokeWidth=3f
//1.绘制坐标轴
canvas.translate(0f,size.height)
canvas.scale(1f,-1f)
//2.绘制x轴
val pathY =Path()
pathY.moveTo(0f,0f)
pathY.relativeLineTo(0f,size.height)
canvas.drawPath(pathY,paint)
//2.绘制y轴
val pathX =Path()
pathX.moveTo(0f,0f)
pathX.relativeLineTo(size.width,0f)
canvas.drawPath(pathX,paint)
val dataList:MutableList = mutableListOf(Offset(20f,60f),Offset(40f,30f),Offset(50f,34f),Offset(80f,54f),Offset(100f,34f),Offset(200f,134f),Offset(400f,154f),Offset(480f,134f))
val linePath=Path()
paint.color=Color.Blue
val colors:MutableList = mutableListOf(Color.Red,Color.Blue,Color.Green)
paint.shader= LinearGradientShader(Offset(0f,0f),Offset(size.width,0f),colors,null,TileMode.Clamp)
paint.isAntiAlias=true
//3.绘制折线填充
for (index in 0 until dataList.size){
linePath.lineTo(dataList[index].x,dataList[index].y)
}
linePath.lineTo(dataList[dataList.size-1].x,0f)
linePath.close()
//绘制填充
paintFill.style= PaintingStyle.Fill
paintFill.shader= LinearGradientShader(Offset(0f,size.height),Offset(0f,0f), arrayListOf(Color(59,157,254,161),Color(59,157,254,21)),null,TileMode.Clamp)
canvas.drawPath(linePath,paintFill)
//2绘制折线2
val line =Path()
for (index in 0 until dataList.size){
line.lineTo(dataList[index].x,dataList[index].y)
}
paint.style= PaintingStyle.Stroke
canvas.drawPath(line,paint)
//3绘制圆圈
paint.style= PaintingStyle.Fill
for (index in 0 until dataList.size){
canvas.drawCircle(Offset(dataList[index].x,dataList[index].y),6f,paint)
}
canvas.drawImage(image = bitmap, Offset(100f,100f),paint)
}
}
}
到这里我们不仅学会了布局的摆放,还学会了自定义部件。我想当你的产品UI提出再变态的样式你应该不在话下。
四、列表
官网地址组件学习
- Compose中可以通过Column和Row结合
repate进行遍历形成列表,默认Column和Row超出屏幕是不可以滑动的,当然可以配合Modifer的verticalScroll和horizontalScroll进行滑动内容设置。
@Composable
fun ListStudy() {
//设置滑动
val scrollState = rememberScrollState()
Column(modifier = Modifier.verticalScroll(scrollState)) {
//遍历循环内部Item部件
repeat(100) {
Row(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(10.dp)
.fillMaxWidth(),
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceBetween
) {
StudyLayoutViews()
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 5.dp))
StudyLayoutViews()
}
}
}
}
LazyColumn
数据够多变大导致列表性能出现问题,这时候我们可以使用LazyColumn。
使用如下:
LazyColumn(state = scrollState) {
items(100) {
内容.....
}
}
@Composable
fun ListStudy() {
//设置滑动
val scrollState = rememberScrollState()
val scrollLazyState = rememberLazyListState()
LazyColumn(state = scrollLazyState) {
//遍历循环内部Item部件
items(100) {
Row(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(10.dp)
.fillMaxWidth(),
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceBetween
) {
StudyLayoutViews()
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 5.dp))
StudyLayoutViews()
}
}
}
}
到这里我们结合官网不仅学会了基本的UI组件和容器列表组件而且搞了一波自定义裁剪和绘制。当然了Compose里面还有很多需要我们去尝试的内容,动画,状态的跟新等等…最后我们写个案例完美结束。
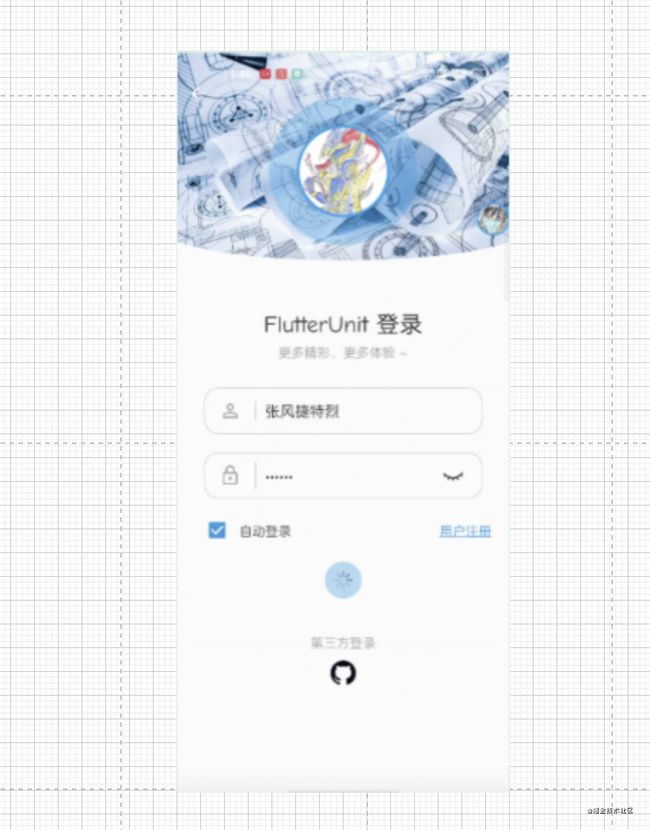
五、案例
- 学完了上文下面界面10分钟能搞定不?可能不行,好像又有自定义部分了。接下来我们进行案例开始。
1.上部图片部分
1.一个有弧度的图片上部有个发射性圆圈。
2.底部弧度图片裁剪。
3.顶部的发射性圆盘。
- 弧度图片
@Stable
class QureytoImageShapes(var hudu: Float = 100f) : Shape {
override fun createOutline(
size: Size,
layoutDirection: LayoutDirection,
density: Density
): Outline {
val path = Path()
path.moveTo(0f, 0f)
path.lineTo(0f, size.height-hudu)
path.quadraticBezierTo(size.width/2f, size.height, size.width, size.height-hudu)
path.lineTo(size.width,0f)
path.close()
return Outline.Generic(path)
}
}
@Preview(name = "login")
@Composable
fun LoginPage() {
val imageBitmap: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.head_god)
val delectedIcon: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.hean_lhc)
Box(contentAlignment = Alignment.Center) {
Image(
bitmap = imageBitmap,
contentDescription = "",
contentScale=ContentScale.FillWidth,
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth().height(280.dp).clip(QureytoImageShapes(160f))
)
Image(bitmap = delectedIcon, contentDescription = "")
}
}
- 顶部的发射性圆盘
底部半透明上色圆,顶部裁剪的圆形图片有Border上面写过的。再来一遍
@Preview(name = "login")
@Composable
fun LoginPage() {
val imageBitmap: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.head_god)
val delectedIcon: ImageBitmap = ImageBitmap.imageResource(R.drawable.hean_lhc)
Box(contentAlignment = Alignment.Center) {
Image(
bitmap = imageBitmap,
contentDescription = "",
contentScale=ContentScale.FillWidth,
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth().height(230.dp).clip(QureytoImageShapes(160f))
)
Box(
contentAlignment=Alignment.Center,
modifier = Modifier
.padding(0.dp)
.clip(CicleImageShape)
.background(Color(206, 236, 250,121))
.width(130.dp)
.height(130.dp)
){
Image(
bitmap = imageBitmap,
contentDescription = "w",
contentScale = ContentScale.FillBounds,
modifier = Modifier
.height(80.dp)
.width(80.dp)
.background(color = Color(0XFF0DBEBF), shape = CircleShape)
.padding(3.dp)
.clip(
CircleShape
)
.shadow(elevation = 150.dp, clip = true)
)
}
}
}
2.中间文字部分
Box(contentAlignment = Alignment.Center,modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(top =20.dp)) {
Column(horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally) {
Text(text = "ComposeUnit 登陆",fontSize = 18.sp)
Text(text = "更多精彩,更多体验 ~",fontSize = 12.sp,color = Color.Gray)
}
}
3.输入框部分
Box(contentAlignment = Alignment.Center, modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(top = 30.dp)
) {
TextField(
value = " ConmposeUnit",
onValueChange = {
},
shape = RoundedCornerShape(18.dp),
colors = textFieldColors(
unfocusedIndicatorColor = Color.Transparent,
backgroundColor = Color.White
),
modifier = Modifier.border(
1.dp,
Color(111, 111, 111, 66),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(18.dp)
),
leadingIcon = {
Icon(bitmap = deIcon, contentDescription = "") })
}
4.选中状态和下文字划线的设置
- 文字我们可以从背景裁剪入手。别打问号看代码
Box( modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(top = 20.dp)
) {
Row(
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceBetween, modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding( horizontal = 50.dp ,vertical = 20.dp)) {
Checkbox(
checked = true,
onCheckedChange = {
},
colors = CheckboxDefaults.colors(checkedColor = Color(0XFF0DBEBF))
)
Text("用户注册",color=Color(0XFF0DBEBF),modifier = Modifier.border(1.dp,color=Color(0XFF0DBEBF),shape = LineUndFunction))
}
}
下划线设置
val LineUndFunction:Shape = object :Shape{
override fun createOutline(
size: Size,
layoutDirection: LayoutDirection,
density: Density
): Outline {
val path=Path()
path.moveTo(0f,size.height-2f)
path.lineTo(size.width,size.height-2f)
path.lineTo(size.width,size.height)
path.lineTo(0f,size.height)
path.close()
return Outline.Generic(path)
}
}
![]()
总结
Compose今天走了一遍,基本就是SwiftUI又像极了Flutter,它的却可以创造出和Flutter一样的效率,支持版本兼容性优秀与SwiftUI,但Kotlin高阶函数的各种套让初学者不易读懂源码,后期会认真写系列文章,你如果今天学到了一些东西或者我写的有问题请你点赞评论,希望一起学习。鄙人QQ学习裙730772561