webpack 从入门到精通
小实验
我们一步步打包一个小项目看看 webpack 是如何工作的。
-
先写一个 hello.js
function hello(messgae){ alert(messgae); } -
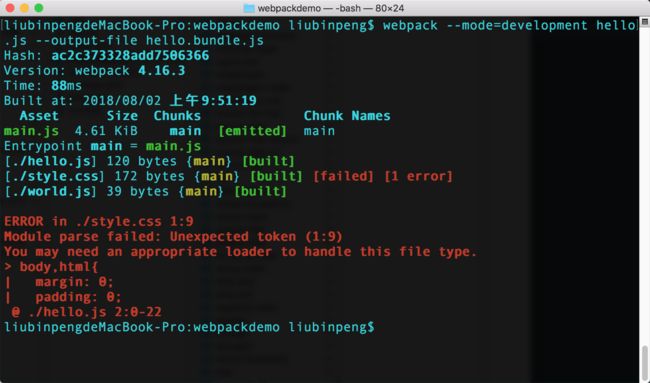
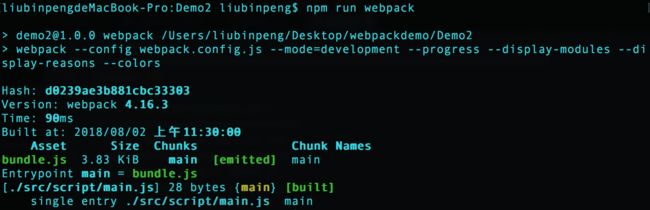
然后对其打包,发现终端报错。解决后知道在 webpack 2.0 的时候,我们打包一个 js 文件可能是这样的,比如将 hello.js 打包为 hello.bundle.js 。
webpack hello.js hello.bundle.js但是在现在 webpack 4.5.0 的时候就需要指定 mode 和输出路径
webpack --mode=development hello.js --output-file hello.bundle.jsmode 有指定的3种值, development、production、none。区别在于 development 打包出来的东西是没压缩的、可读的,production 打包出来的是压缩的、不可读的。
-
然后编写一个 world.js 和 一个 style.css ,然后进行打包
require('./world.js'); require('./style.css'); function hello(messgae){ alert(messgae); } hello("hello webpack");通过报错信息知道, webpack 对于 css 文件并不是默认支持的,需要指定相应的 loader 对其打包。
-
所以我们继续安装 css-loader、style-loader。然后指定 css 文件的 loader 为 css-loader
require('./world.js'); require('css-loader!./style.css'); function hello(messgae){ alert(messgae); } hello("hello webpack"); -
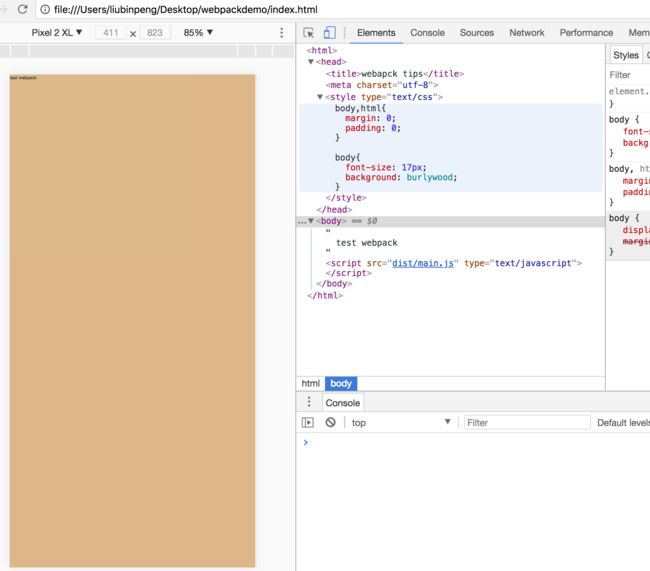
接下来设置页面的背景颜色,发现网页并没有生效。这是因为 webpack 并不知道我们的样式如何作用到 html 中,所以我们需要指定 style-loader
//style.css body,html{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } body{ font-size: 17px; background: burlywood; }//hello.js require('./world.js'); require('style-loader!css-loader!./style.css'); function hello(messgae){ alert(messgae); } hello("hello webpack"); -
查看网页效果。发现函数确实执行了,背景颜色也生效了,我们写的 css 代码新建了一个 style标签 被直接写入到 html 中了。
-
说说2个 loader 的作用。
- css-loader 就是 webpack 可以处理 css 文件。
- style-loader 的作用就是将 css-loader 处理完的文件新建一个 style 标签插入到 html 中
-
很多人会想 require(‘style-loader!css-loader!./style.css’); 我每次写一个 css 文件,那么都需要在前面加入 style-loader、css-loader 吗?显然不是,webpack 还为我们提供了简单写法
require('./world.js'); // require('style-loader!css-loader!./style.css'); require('./style.css'); function hello(messgae){ alert(messgae); } hello("hello webpack");webpack-cli 写法为
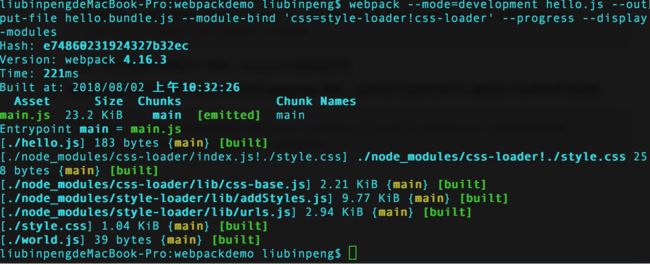
webpack --mode=development hello.js --output-file hello.bundle.js --module-bind 'css=style-loader!css-loader' -
之前的做法还存在一个弊端,就是每次修改了代码,我们都需要在终端重新运行打包命令,十分繁琐。这里强大的 webpack 为我们提供了一个 option,可以监听代码改变然后自动打包。如下
webpack --mode=development hello.js --output-file hello.bundle.js --module-bind 'css=style-loader!css-loader' --watch这样,我们在源代码每次一修改,webpack 会自动打包
-
如果你想看到打包过程,那么可以使用 pregress 参数。这样在打包的时候可以看到左下角有构件的进度
webpack --mode=development hello.js --output-file hello.bundle.js --module-bind 'css=style-loader!css-loader' --progress -
如果像看到打包的模块,可以使用 –display-modules
webpack --mode=development hello.js --output-file hello.bundle.js --module-bind 'css=style-loader!css-loader' --progress --display-modules -
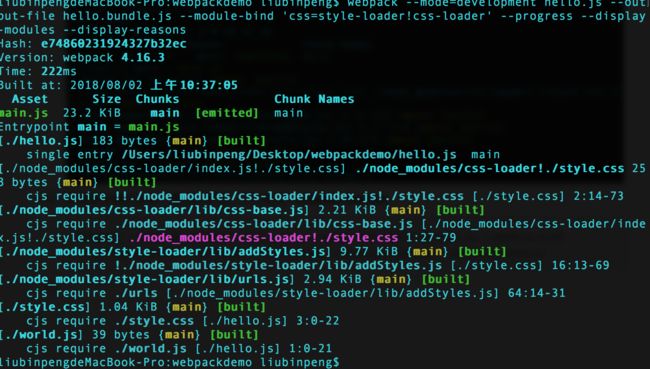
如果想知道打包某个模块的原因,可以使用 –display-reasons
webpack --mode=development hello.js --output-file hello.bundle.js --module-bind 'css=style-loader!css-loader' --progress --display-modules --display-reasons
用 webpack.config.js 完成上述步骤
-
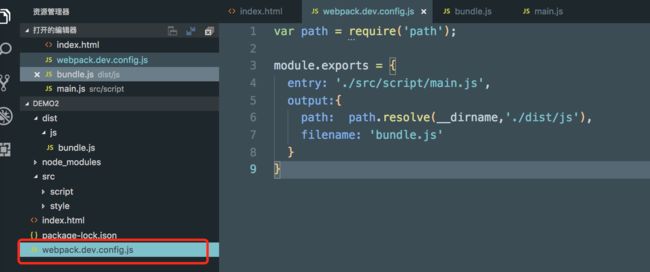
初始化项目,编辑 webpack.config.js
var path = require('path'); module.exports = { entry: './src/script/main.js', output:{ path: path.resolve(__dirname,'./dist/js'), filename: 'bundle.js' } } -
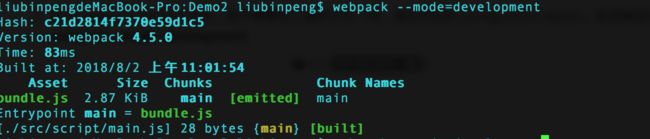
有了 webpack.config.js 文件,就不需要和上面的方式一样,指定对应的 configuration option。在终端运行 **webpack --mode=development **
-
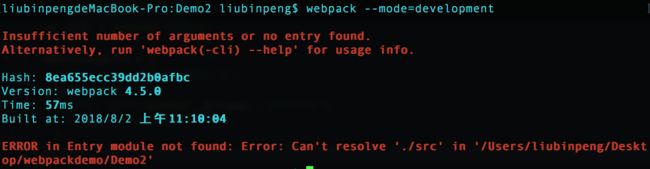
注意:如果我们将 webpack.config.js 改名为 webpack.dev.config.js ,然后在命令行打包,会发现没效果。
要将 webpack.dev.config.js 同样生效,我们需要在命令行使用下面命令。
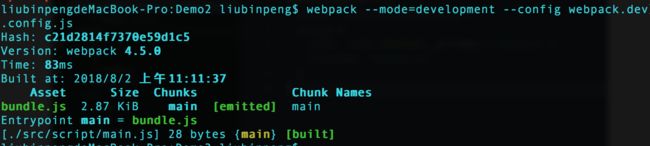
webpack --mode=development --config webpack.dev.config.js -
如果想像上个实验一样,看到打包时候的一些信息,怎么办呢?
可以配合 npm 的 package.json 文件中的 scripts 标签,在下面添加 key 为 webpack 的项,然后将命令写到后边。然后在命令行运行 npm run webpack
"scripts": { "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1", "webpack": "webpack --config webpack.config.js --mode=development --progress --display-modules --display-reasons --colors" }, -
对于 webpack 的 entrt 主要有3种写法,每种写法都有不同区别。
-
如果 webpack 只有单一入口,那么就可以是字符串。
entry: './src/script/main.js', -
如果 webpack 有多个入口,那么就可以是数组。
entry: ['./src/script/main.js','./src/script/a.js'], -
如果 webpack 有多个入口,那么可以用对象。
entry: { main: './src/script/main.js', a : './src/script/a.js' },
-
-
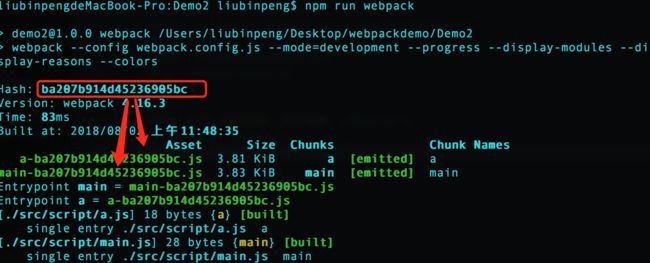
如果指定了多个入口,那么执行打包会报错,因为 webpack 文档说如果多个 entry,且只有一个 output 的 filename,那么打包的结果会覆盖。所以我们需要设置如下
When combining with the
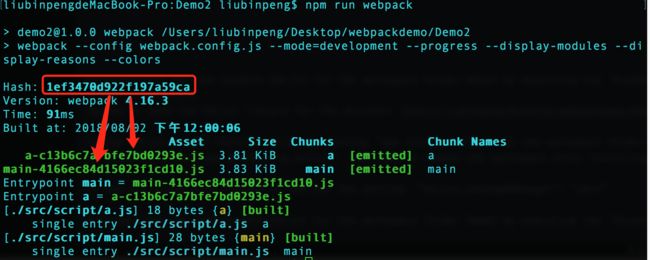
output.libraryoption: If an array is passed only the last item is exported.var path = require('path'); module.exports = { entry: { main: './src/script/main.js', a : './src/script/a.js' }, output:{ path: path.resolve(__dirname,'./dist/js'), filename: '[name]-[hash].js' } }将文件修改为 filename: '[name]-[chunkhash].js’
会发现 hash 和 chunkhash 的输出的文件名并不一样
说明: chunkhash 是根据文件的内容生成的唯一标示(类似于md5生成的唯一标示、文件版本号)。如果一个资源在打包前后文本没有变过的话,二次打包的生成的 chunkhash 是一致的。
生成项目中 html 页面文件
对于生成的的 js,我们 html 如何使用呢?难道每次一打包,html 中的 script 需要修改 src 吗?不是的,webpack 提供了 html-webpack-plugin
-
安装
npm install html-webpack-plugin --save-dev -
然后运行命令,将现有的 js 打包引入到 html 文件中
var htmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin'); //... plugins: [ new htmlWebpackPlugin() ]然后生成的文件是 webpack 帮我们生成的 html 文件。当然我们可以新建一个自己的 html 作为模版。
plugins: [ new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html' }) ]//模版 <html> <head> <titile>webpack demotitile> head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> body> <script type="text/javascript" src="./dist/js/bundle.js" >script> html> //打包生成的 <html> <head> <titile>webpack demotitile> head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> <script type="text/javascript" src="main-4166ec84d15023f1cd10.js">script><script type="text/javascript" src="a-c13b6c7a7bfe7bd0293e.js">script>body> <script type="text/javascript" src="./dist/js/bundle.js" >script> html>说明:上面选中的 template 写了 index.html 就会找到合适的文件是因为 webpack 有个上下文参数 context,会根据上下文找到对应的 html(这里就是根目录)
-
上述的缺点是生成的 html 也会放在 dist/js 目录下。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-0rhV8wwB-1585763543195)(https://github.com/FantasticLBP/knowledge-kit/raw/master/[email protected])]
需要做到的效果就是 html 放在根目录, js 放在 dist 目录下的 js 目录下。需要对 webpack.config.js 的 output 属性做修改
-
output:{ path: path.resolve(__dirname,'./dist'), filename: 'js/[name]-[chunkhash].js' }, -
plugins 的参数很多可以自定义
plugins: [ new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'index-[hash].html', inject: 'head' }) ]- template: 指定生成 html 的模版
- filename:指定生成 html 的命名规则
- inject :指定生成 js 的 script 插入的位置。head、body
-
如果想通过 plugins 传值到 生成的 html,怎么办?
- htmlWebpackPlugin.options 对象就可以拿到传递过来的值
- <%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %> 模版语法来拿值
//webpack.config.js plugins: [ new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'index.html', inject: 'head', title: 'Webpack is awesome', date : new Date() }) ]// 模版 html <html> <head> <titile><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %>titile> head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> <h3>时间:<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.date %>h3> body> html> //生成的html <html> <head> <titile>Webpack is awesometitile> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/main-82c7521f0a4a776cc00b.js">script><script type="text/javascript" src="js/a-273641522fd044fc27c7.js">script>head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> <h3>时间:Thu Aug 02 2018 15:40:50 GMT+0800 (CST)h3> body> html> -
我们很好奇 html-webpack-plugin 可以传递什么参数?或者这个对象包含什么信息。做个测试就知道了
//模版 html <% for (var key in htmlWebpackPlugin){ %> <%= key %> <% } %> //生成的 html files options看到最外层的节点就2个:files、options。那么我们分别对这2个节点遍历输出。因为遍历出的 value (**htmlWebpackPlugin.files[key] **)可能是对象、数组。所以用 JSON.Stringfy(htmlWebpackPlugin.files[key]) 打印
<html> <head> <titile><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %>titile> head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> <h3>时间:<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.date %>h3> <% for (var key in htmlWebpackPlugin.files){ %> <%= key %> <%= JSON.stringify(htmlWebpackPlugin.files[key]) %> <% } %> <hr> <% for (var key in htmlWebpackPlugin.options){ %> <%= key %> <%= JSON.stringify(htmlWebpackPlugin.options[key]) %> <% } %> body> html> //生成的 html <html> <head> <titile>Webpack is awesometitile> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/main-82c7521f0a4a776cc00b.js">script><script type="text/javascript" src="js/a-273641522fd044fc27c7.js">script>head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> <h3>时间:Thu Aug 02 2018 15:51:27 GMT+0800 (CST)h3> publicPath "" chunks {"main":{"size":28,"entry":"js/main-82c7521f0a4a776cc00b.js","hash":"82c7521f0a4a776cc00b","css":[]},"a":{"size":18,"entry":"js/a-273641522fd044fc27c7.js","hash":"273641522fd044fc27c7","css":[]} } js ["js/main-82c7521f0a4a776cc00b.js","js/a-273641522fd044fc27c7.js"] css [] manifest <hr> template "/Users/liubinpeng/Desktop/webpackdemo/Demo2/node_modules/html-webpack-plugin/lib/loader.js!/Users/liubinpeng/Desktop/webpackdemo/Demo2/index.html" templateParameters filename "index.html" hash false inject "head" compile true favicon false minify false cache true showErrors true chunks "all" excludeChunks [] chunksSortMode "auto" meta {} title "Webpack is awesome" xhtml false date "2018-08-02T07:51:27.110Z" body> html> -
有时候我们想把部分 js 放到 head ,部分 js 放到 body 中。单独通过 webpack.config.js 是没办法实现这个目的,结合上面的成果,我们可以拿到 htmlWebpackPlugin.files.chunks 属性,比如将 a.js 放到 head 标签,main.js 放到 body 标签。
plugins: [ new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'index.html', inject: false, title: 'Webpack is awesome', date : new Date() }) ]//模版 html <html> <head> <titile><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %>titile> <script type="text/javascript" src="<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.files.chunks.a.entry %>">script> head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> <h3>时间:<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.date %>h3> <script type="text/javascript" src="<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.files.chunks.a.entry %>">script> body> html>//生成 html <html> <head> <titile>Webpack is awesometitile> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/a-273641522fd044fc27c7.js">script> head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> <h3>时间:Thu Aug 02 2018 15:58:56 GMT+0800 (CST)h3> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/a-273641522fd044fc27c7.js">script> body> html>需要注意的是当自定义 js 文件的位置的时候,需要将 webpack.config.js 中 plugins 下的 inject 设置为 false
-
接下来看到的这种需求绝对很有料。前面我们看到的都是相对路径,但是我们的产品需要上线,所以我们的 js 文件资源路径需要改变。如下:
//webpack.config.js output:{ path: path.resolve(__dirname,'./dist'), filename: 'js/[name]-[chunkhash].js', publicPath: 'http://test.lbp.com' },//生成的 html <html> <head> <titile>Webpack is awesometitile> <script type="text/javascript" src="http://test.lbp.com/js/a-502c14d352874172253c.js">script> head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> <h3>时间:Thu Aug 02 2018 16:25:12 GMT+0800 (CST)h3> <script type="text/javascript" src="http://test.lbp.com/js/a-502c14d352874172253c.js">script> body> html> -
利用 webpack 我们还可以打包好的 html 做一些优化,比如删除注释、去掉空格.
修改 webpack.config.js 中 plugins 节点下的 htmlWebpackPlugin 的 minify 属性
plugins: [ new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'index.html', inject: false, title: 'Webpack is awesome', date : new Date(), minify:{ removeComments: true, collapseWhitespace: true } }) ],我们对 模版 html 写一些注释,运行 npm run webpack 后看到生成的页面中注释、空格都被去掉了。
-
如果想打包生成多个 html 怎么办?可能使用 plugins 下的 new htmlWebpackPlugin() 多来几组配置项
plugins: [ new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'a.html', title: 'this is a.html', chunks: ['main','a'], inject: 'body' }), new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'b.html', title: 'this is b.html', chunks: ['main','b'], inject: 'body' }), new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'c.html', title: 'this is c.html', chunks: ['main','c'], inject: 'body' }) ]注意:这里我们可以指定每个生成的 filename 以及 title。实现上述需求关键点在于 chunks 这个属性。用一个数组的形式来指定需要引用的 chunk。
-
上面只是实现了 a、b、c 3个页面,如果多了的话按照上面的写法要烦死人的。 webpack 为我们提供了 excludeChunks 这个属性,它指定了不需要包含的chunk。上面写法的另一种写法
plugins: [ new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'a.html', title: 'this is a.html', // chunks: ['main','a'], inject: 'body', excludeChunks: ['b','c'] }), new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'b.html', title: 'this is b.html', //chunks: ['main','b'], inject: 'body', excludeChunks: ['a','c'] }), new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'c.html', title: 'this is c.html', // chunks: ['main','c'], inject: 'body', excludeChunks: ['a','b'] }) ], -
有种需求是:当我们需要减小首页 HTTP 请求(提高首页的渲染速度),也就是将一些首页必须用到的 JS 文件用内联的方式写在首页 html 的 script 标签里面,不重要的 js 文件通过 script 的 src 引入。要怎么做呢?webpack 在设计之初没想到这种需求,很多人在 github 提了很多 issue ,官方认识到这种需求,所以在后期更新的 demo 中看到了解决方案。
-
htmlWebpackPlugin.files.chunks 对象拿到的是我们在 webpack.config.js 设置过 publicPath 生成的完整路径
-
通过截取字符串子串的方式拿到文件地址。 **htmlWebpackPlugin.files.chunks.main.entry.substr(htmlWebpackPlugin.files.publicPath.length) **
-
官方的解决方案
compilation.assets[jsFile.substr(htmlWebpackPlugin.files.publicPath.length)].source()
在我们的项目中加以改造,为生成的每个页面的 header 里面加入 main.js。在 body 部分加入除了 main.js 之外的其他 js。
//模版html <html> <head> <title><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %>title> <script type="text/javascript"> <%= compilation.assets[htmlWebpackPlugin.files.chunks.main.entry.substr(htmlWebpackPlugin.files.publicPath.length)].source() %> script> head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> <% for(var key in htmlWebpackPlugin.files.chunks){ %> <% if( key !== 'main'){ %> <script type="text/javascript" src="<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.files.chunks[key].entry %>">script> <% } %> <% } %> body> html>//webpack.config.js var htmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin'); var path = require('path'); module.exports = { // entry: './src/script/main.js', // entry: ['./src/script/main.js','./src/script/a.js'], entry: { main: './src/script/main.js', a : './src/script/a.js', b : './src/script/b.js', c : './src/script/c.js' }, output:{ path: path.resolve(__dirname,'./dist'), filename: 'js/[name]-[hash].js', publicPath: 'http://test.lbp.com' }, plugins: [ new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'a.html', title: 'this is a.html', inject: false, excludeChunks: ['b','c'] }), new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'b.html', title: 'this is b.html', inject: false, excludeChunks: ['a','c'] }), new htmlWebpackPlugin({ template: 'index.html', filename: 'c.html', title: 'this is c.html', inject: false, excludeChunks: ['a','b'] }) ], }为了验证生效,我将 main.js 加入了 alert
//main.js function helloworld(msg){ alert(msg); } helloworld("hello webpack");看看打包后生成的 a.html
<html> <head> <title>this is a.htmltitle> <script type="text/javascript"> /******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap /******/ // The module cache /******/ var installedModules = { }; /******/ /******/ // The require function /******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { /******/ /******/ // Check if module is in cache /******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) { /******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports; /******/ } /******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache) /******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = { /******/ i: moduleId, /******/ l: false, /******/ exports: { } /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Execute the module function /******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__); /******/ /******/ // Flag the module as loaded /******/ module.l = true; /******/ /******/ // Return the exports of the module /******/ return module.exports; /******/ } /******/ /******/ /******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__) /******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules; /******/ /******/ // expose the module cache /******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules; /******/ /******/ // define getter function for harmony exports /******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) { /******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) { /******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { enumerable: true, get: getter }); /******/ } /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // define __esModule on exports /******/ __webpack_require__.r = function(exports) { /******/ if(typeof Symbol !== 'undefined' && Symbol.toStringTag) { /******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, Symbol.toStringTag, { value: 'Module' }); /******/ } /******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, '__esModule', { value: true }); /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // create a fake namespace object /******/ // mode & 1: value is a module id, require it /******/ // mode & 2: merge all properties of value into the ns /******/ // mode & 4: return value when already ns object /******/ // mode & 8|1: behave like require /******/ __webpack_require__.t = function(value, mode) { /******/ if(mode & 1) value = __webpack_require__(value); /******/ if(mode & 8) return value; /******/ if((mode & 4) && typeof value === 'object' && value && value.__esModule) return value; /******/ var ns = Object.create(null); /******/ __webpack_require__.r(ns); /******/ Object.defineProperty(ns, 'default', { enumerable: true, value: value }); /******/ if(mode & 2 && typeof value != 'string') for(var key in value) __webpack_require__.d(ns, key, function(key) { return value[key]; }.bind(null, key)); /******/ return ns; /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules /******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) { /******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ? /******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } : /******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; }; /******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter); /******/ return getter; /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call /******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); }; /******/ /******/ // __webpack_public_path__ /******/ __webpack_require__.p = "http://test.lbp.com"; /******/ /******/ /******/ // Load entry module and return exports /******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "./src/script/main.js"); /******/ }) /************************************************************************/ /******/ ({ /***/ "./src/script/main.js": /*!****************************!*\ !*** ./src/script/main.js ***! \****************************/ /*! no static exports found */ /***/ (function(module, exports) { eval("function helloworld(msg){\n alert(msg);\n}\n\n\nhelloworld(\"hello webpack\");\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/script/main.js?"); /***/ }) /******/ }); script> head> <body> <h2>我是 webpack 生成 html 的模版h2> <script type="text/javascript" src="http://test.lbp.com/js/a-4caa8a542ab497f63bf8.js">script> body> html>在浏览器调试后发现页面是可以正常弹出“hello webpack”
-
loader
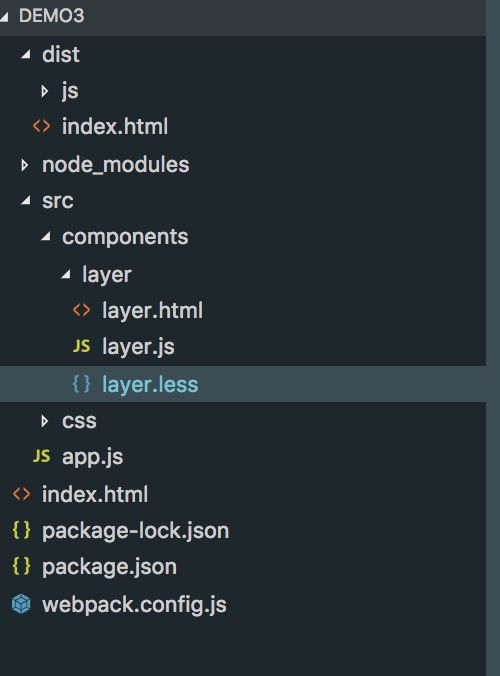
新建项目,一步步认识 loader
-
Js loader
我们写的项目中会用 es6,但是并不是所有的浏览器都支持 es6(虽然各个浏览器厂商每年在不断新增对 es6 的支持),所以我们需要使用 babel 将 es6 转换为浏览器都支持的 es2015 。所以使用 babel-loader 的时候需要指定 babel 转换的模式。loader 官方给出了2种方式
-
可以直接像 url 的 get 形式一样,将参数传递在后面。
//方式1 require("babel-loader?presets=latest"); //方式2 { test: /\.png$/, loader: 'url-loader?presets=latest' } -
写在 query 参数里面
{ test: /\.js$/, loader: 'babel', query: { presets: ['latest'] } } -
其实还有一种方式:在 package.json 文件里面添加一个 key 为 babel。
"babel": { presets: ['latest'] }
注意:webpack 现在已经是4.5.0了。以前的版本的写法是
module: { loaders: [ { test: /\.js$/, loader: 'babel-loader', query: { presets: ['latest'] } } ] },现在的写法为
module: { rules: [ { test: /\.js$/, loader: 'babel-loader', options: { presets: ['latest'] } } ] },注意:我们工程如果安装的依赖非常多,node_modules 文件非常多,babel 转换会很慢,这时候需要指定2个参数可以显著提高速度
module: { rules: [ { test: /\.js$/, loader: 'babel-loader', options: { presets: ['latest'] }, exclude: path.resolve(__dirname,'./node_modules/'), include: path.resolve(__dirname,'./src') } ] }, -
-
css loader
打包 css 经常会用到 css-loader、style-loader。我们经常写 flex 的时候很多浏览器兼容性不一致,所以我们需要加前缀,这时候需要使用 postcss-loader、autoprefixer
官网给出2种写法
-
loader
{ test: /\.css$/, loader: 'style-loader!css-loader!postcss-loader' } -
loaders
{ test: /\.css$/, loaders: ['style-loader','css-loader','postcss-loader'] }
如果项目中不只是使用了 css 的话,比如还使用了 less 和 sass 的话,我们需要将 css 加额外的设置
{ test: /\.css$/, use:[ 'style-loader', { loader: 'css-loader', options: { importLoaders: 1} }, { loader: 'postcss-loader', options:{ plugins:function(){ return [ require('postcss-import')(), require('autoprefixer')({ browsers:['last 5 versions']}) ] } } } ] }, { test: /\.less$/, use:[ 'style-loader', { loader: 'css-loader', options: { importLoaders: 1} }, { loader: 'postcss-loader', options:{ plugins:function(){ return [ require('postcss-import')(), require('autoprefixer')({ browsers:['last 5 versions']}) ] } } }, 'less-loader' ] }, -
-
处理模版
在 webpack 经常打包处理的时候会遇到模版。有普通的 html 模版,也会有 ejs 模式下的 tpl 模版
- html 模版
<html> <head> <title><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %>title> head> <body> <div id="app"> div> body> html>//layer.js import './layer.less' import tpl from './layer.html' function layer(){ return { name: 'layer', tpl: tpl } } export default layer; //app.js import Layer from './components/layer/layer.js'; import './css/common.css'; const App = function(){ var dom = document.getElementById("app"); var layer = new Layer(); dom.innerHTML = layer.tpl; } new App()-
ejs 模版
//layer.tpl <div class="layer"> <div>this is <%= name %> layr</div> <% for(var i=0;i < arr.length; i++){ %> <%= arr[i] %> <% } %> </div> //layer.js import './layer.less' import tpl from './layer.tpl' function layer(){ return { name: 'layer', tpl: tpl } } export default layer; //app.js import Layer from './components/layer/layer.js'; import './css/common.css'; const App = function(){ var dom = document.getElementById("app"); var layer = new Layer(); dom.innerHTML = layer.tpl({ name: 'john', arr: ['swift','Objective-C','JS','python'] }); } new App()