震惊:Netty竟然对ThreadLocal做出这种事...
目录
1、ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal内存泄露?
既然是ThreadLocal的弱引用导致了内存泄漏,那为什么不使用强引用?
最佳实践
源码
2、FastThreadLocal
优化1:不需要手动remove
优化2:利用字节填充避免伪共享问题
优化3:使用常量下标在数组中定位元素替代ThreadLocal通过哈希和哈希表
源码
1、ThreadLocal
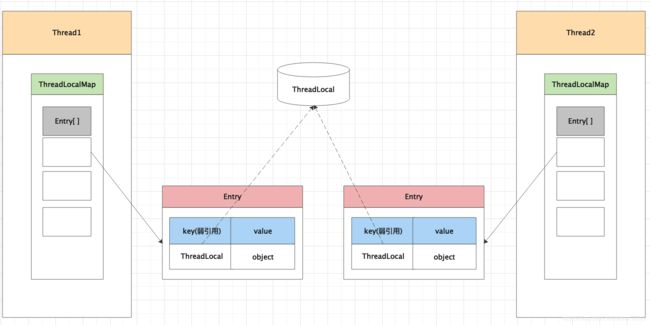
ThreadLocal类提供了线程局部 (thread-local) 变量。这些变量与普通变量不同,每个线程都可以通过其 get 或 set方法来访问自己的独立初始化的变量副本。
Thread类中包含ThreadLocalMap对象,ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的静态内部类,ThreadLocalMap中的对象都是以ThreadLocal对象作为key存储对应的value。
ThreadLocal内存泄露?
ThreadLocalMap使用ThreadLocal的弱引用作为key,如果一个ThreadLocal没有外部强引用,系统GC时这个ThreadLocal就会被回收,ThreadLocalMap中就出现了key为null的Entry,如果线程不结束,这些Entry的value就会存在一条强引用链:Thread -> ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap -> Entry[] -> Enrty -> value,造成内存泄漏。
ThreadLocalMap针对此做了一些优化,比如在调用ThreadLocal的get()、set()、remove()时都会清理ThreadLocalMap中所有key为null的value。但不能避免内存泄漏的发生,比如分配使用了ThreadLocalMap后不再调用get()、set()、remove()方法。
java对象的引用包括 : 强引用、软引用、弱引用、虚引用
- 强引用:我们平时一般都是这种引用,当一个对象被一个或一个以上的引用变量所引用时,它处于可达状态,不可能被系统垃圾回收机制回收。
- 软引用:软引用需要通过SoftReference类来实现,当系统内存空间足够时,它不会被系统回收,当系统内存空间不够时,系统可能回收它。
- 弱引用:弱引用通过WeakReference类实现,当系统垃圾回收机制运行时,不管系统内存是否足够,总会回收该对象所占用的内存。
- 虚引用:虚引用通过PhantomReference类实现,虚应用完全类似于没有引用。虚引用主要用来跟踪对象被垃圾回收器回收的活动。
既然是ThreadLocal的弱引用导致了内存泄漏,那为什么不使用强引用?
ThreadLocalMap本身并没有为外界提供取出和存放数据的API,我们所能获得数据的方式只有通过ThreadLocal类提供的API来间接的从ThreadLocalMap取出数据,所以,当我们用不了key(ThreadLocal对象)的API也就无法从ThreadLocalMap里取出指定的数据。使用强引用的话,如果引用ThreadLocal的对象已经回收了,我们就无法在get到ThreadLocalMap中的数据,也就是说已经有部分数据无效了,但ThreadLocalMap还持有对ThreadLocal的强引用,引用链Thread -> ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap -> Entry[] -> Enrty -> key,当这个线程还未结束时,他持有的强引用,包括递归下去的所有强引用都不会被垃圾回收器回收,导致Entry内存泄漏。
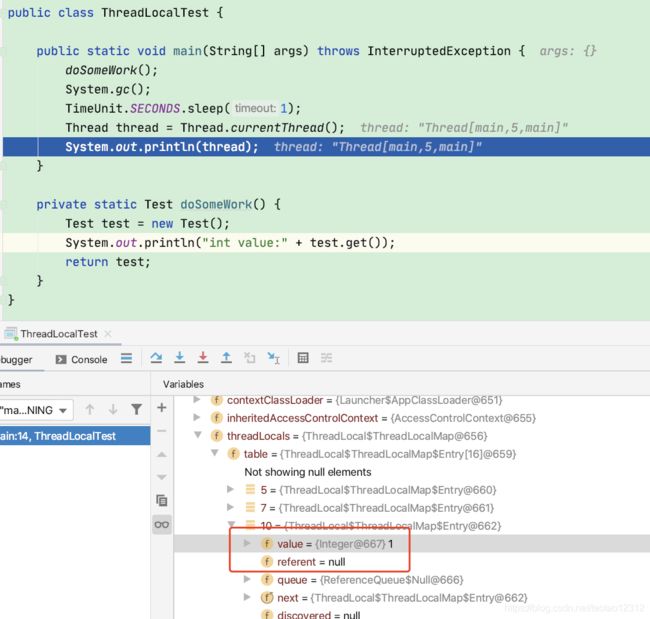
比如下面这个例子,当Test对象被回收时,没法通过get方法使用ThreadLocalMap中的数据了,那保存数据的Entry对象就没用了,所以要想办法让系统自动回收对应的Entry对象。
但是让Entry对象或其中的value对象做为弱引用都是非常不合理的。所以,让key(threadLocal对象)为弱引用,自动被垃圾回收,key就变为null了,下次,我们就可以通过Entry不为null,而key为null来判断该Entry对象该被清理掉了。
public class ThreadLocalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
doSomeWork(); //如果给它一个引用,比如Test test = doSomeWork(),System.gc()就不会回收threadLocal,直到方法结束才可能会被回收
System.gc();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread);
}
private static Test doSomeWork() {
Test test = new Test();
System.out.println("int value:" + test.get());
return test;
}
}
class Test {
private ThreadLocal threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> 1);
public Integer get() {
return threadLocal.get();
}
} 最佳实践
- 每次使用完ThreadLocal,调用remove()进行清理。
try {
// 业务逻辑,threadLocal#get, threadLocal#set
} finally {
threadLocal.remove();
}阿里规范:
15.【参考】 ThreadLocal 无法解决共享对象的更新问题, ThreadLocal 对象建议使用 static
修饰。这个变量是针对一个线程内所有操作共享的,所以设置为静态变量,所有此类实例共享
此静态变量 ,也就是说在类第一次被使用时装载,只分配一块存储空间,所有此类的对象 ( 只
要是这个线程内定义的 ) 都可以操控这个变量。源码
Entry节点,key弱引用
static class Entry extends WeakReference> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
HashMap是使用拉链法解决hash冲突的,ThreadLocalMap是使用线性探测解决hash冲突的(内部只维护Entry数组,没有链表)
set方法:
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}get方法:
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}源码中在清除泄漏的Entry时,会进行rehash,防止数组的当前位置为null后,有hash冲突的Entry访问不到的问题。
remove方法:
private void remove(ThreadLocal key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// expunge entry at staleSlot
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}
2、FastThreadLocal
优化1:不需要手动remove
构造FastThreadLocalThread的时候,通过FastThreadLocalRunnable对Runnable对象进行了包装,FastThreadLocalRunnable在执行完之后都会调用FastThreadLocal.removeAll()。
如果使用FastThreadLocal就不要使用普通线程,而应该构建FastThreadLocalThread,若使用普通线程,还是需要手动remove。
public class FastThreadLocalThread extends Thread {
public FastThreadLocalThread(Runnable target) {
super(FastThreadLocalRunnable.wrap(target));
cleanupFastThreadLocals = true;
}
}final class FastThreadLocalRunnable implements Runnable {
private final Runnable runnable;
private FastThreadLocalRunnable(Runnable runnable) {
this.runnable = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(runnable, "runnable");
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
runnable.run();
} finally {
FastThreadLocal.removeAll();
}
}
static Runnable wrap(Runnable runnable) {
return runnable instanceof FastThreadLocalRunnable ? runnable : new FastThreadLocalRunnable(runnable);
}
}优化2:利用字节填充避免伪共享问题
伪共享概念可以参考美团在Disruptor中的解释:https://tech.meituan.com/2016/11/18/disruptor.html
InternalThreadLocalMap中填充了9个long类型数据,至于为什么是9个,github上也有讨论:https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/9284
结论是这可能是个bug,这些填充数据已经标记为了废弃,在新推出的版本5中对InternalThreadLocalMap进行了重构
优化3:使用常量下标在数组中定位元素替代ThreadLocal通过哈希和哈希表
ThreadLocalMap中的Entry数组通过哈希来定位元素,并通过线性探测法解决hash冲突,所以get、set时时间复杂度并非o(1)。
而FastThreadLocal引入了InternalThreadLocalMap这种新的数据结构,内部不再是Entry数组,而是只用来存储value的Object数组。数组下标在创建FastThreadLocal就以CAS的形式分配好了。
public class FastThreadLocal {
private final int index;
public FastThreadLocal() {
index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
}
public static int nextVariableIndex() {
int index = nextIndex.getAndIncrement();
if (index < 0) {
nextIndex.decrementAndGet();
throw new IllegalStateException("too many thread-local indexed variables");
}
return index;
}
} 所以在get或set时,只需要根据下标从数组中取就可以了,时间复杂度为o(1)。
原先是拿ThreadLocal对象从Entry数组中进行hash查找,现在变成了直接拿ThreadLocal对象中的数组下标在valur数组中查找。
源码
get方法:
// 先获取InternalThreadLocalMap对象,然后根据FastThreadLocal存储的数组下标去取数据
public final V get() {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index);
if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
return (V) v;
}
return initialize(threadLocalMap);
}
//若线程为FastThreadLocalThread,执行fastGet
//若为普通线程,执行slowGet
public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);
} else {
return slowGet();
}
}
//fastGet过程
private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());
}
return threadLocalMap;
}
public final InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap() {
return threadLocalMap;
}
private InternalThreadLocalMap() {
indexedVariables = newIndexedVariableTable();
}
private static Object[] newIndexedVariableTable() {
Object[] array = new Object[INDEXED_VARIABLE_TABLE_INITIAL_SIZE];
Arrays.fill(array, UNSET);
return array;
}
//slowGet过程
private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() {
InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get();
if (ret == null) {
ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap();
slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret);
}
return ret;
}
private static final ThreadLocal slowThreadLocalMap =
new ThreadLocal(); 可以看到,如果是普通线程,会借助原生ThreadLocal来实现,将InternalThreadLocalMap对象作为value存储在ThreadLocalMap中,相当于在原来的基础上又套了一层逻辑,所以会降低效率。
因此如果在使用FastThreadLocal时一定要搭配FastThreadLocalThread来使用。
set方法:
public final void set(V value) {
if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
setKnownNotUnset(threadLocalMap, value);
} else {
remove();
}
}
private void setKnownNotUnset(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, V value) {
if (threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, value)) {
addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
}
}
public boolean setIndexedVariable(int index, Object value) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
if (index < lookup.length) {
Object oldValue = lookup[index];
lookup[index] = value;
return oldValue == UNSET;
} else {
expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(index, value);
return true;
}
}
//扩容为2的n次方
private void expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(int index, Object value) {
Object[] oldArray = indexedVariables;
final int oldCapacity = oldArray.length;
int newCapacity = index;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 1;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 2;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 4;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 8;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 16;
newCapacity ++;
Object[] newArray = Arrays.copyOf(oldArray, newCapacity);
Arrays.fill(newArray, oldCapacity, newArray.length, UNSET);
newArray[index] = value;
indexedVariables = newArray;
}
//addToVariablesToRemove方法会将 FastThreadLocal 对象存放到 threadLocalMap 中的一个集合中
//这个集合用于在需要的时候集中销毁 FastThreadLocal
private static void addToVariablesToRemove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, FastThreadLocal variable) {
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);
Set> variablesToRemove;
if (v == InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET || v == null) {
variablesToRemove = Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap, Boolean>());
threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex, variablesToRemove);
} else {
variablesToRemove = (Set>) v;
}
variablesToRemove.add(variable);
} remove方法:
public final void remove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
return;
}
Object v = threadLocalMap.removeIndexedVariable(index);
removeFromVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
try {
onRemoval((V) v);
} catch (Exception e) {
PlatformDependent.throwException(e);
}
}
}