Java读取文件(字节流,缓存流,字符流的使用)
Java流
流是一个很重要的概念。这里的话不阐述,就简单说说文件的读。这里的话我们尽可能的和python的文件的读进行比较,写出一个类似的功能。
在Java中对于文件的操作有对应的两种流,一种是字节流,另一种是字符流。前者适合读取二进制文件比如图片,后者适合读取文本文件。
文件字节流的读取
读文件直接使用read方法
但是,这个方法的调用没有python那么简单。现在我们先演示一下。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Fileread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
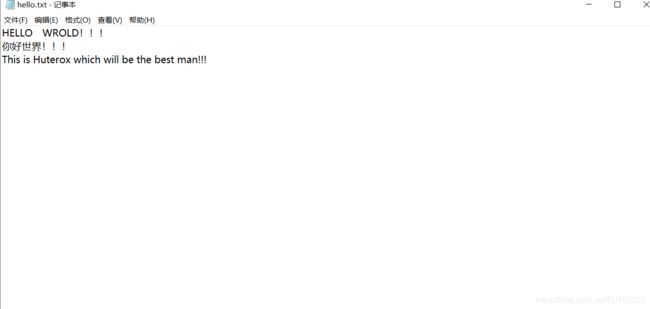
String path = "C:\\Users\\31395\\Desktop\\test\\hello.txt";
try {
FileInputStream fls = new FileInputStream(path);
int n = 0;
while(true){
n = fls.read();//文件结束的时候返回的是-1,此外注意异常接受
System.out.print((char)n);//这里强制转换为char显然中文是会乱码的
if(n==-1){
break;}
}
fls.close()//不要忘了要关掉
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
此外你可以使用一个字节数组来接收
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Fileread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "C:\\Users\\31395\\Desktop\\test\\hello.txt";
try {
FileInputStream fls = new FileInputStream(path);
byte[] a = new byte[100];
//fls.read(a,1,5);1,5是指对a操作在a[1]开始存数据。存5个
fls.read(a);//可以处理中文问题
String get = new String(a);
System.out.println(get);
fls.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
此外你还可以使用字节数组和read()混合使用,好处是可以做到逐行读取
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Fileread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "C:\\Users\\31395\\Desktop\\test\\hello.txt";
try {
FileInputStream fls = new FileInputStream(path);
byte[] a = new byte[100];
int n = 0;
int i = 0;
while(true){
n = fls.read()
if(n!=-1){
a[i] = (byte)n;
i++;
}
else{
break;
}
}
String get = new String(a);
System.out.println(get);
fls.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文件逐行读取
这个我觉得是很重要的
因为python的readline()我觉得的很不错。但是在Java中,如图:
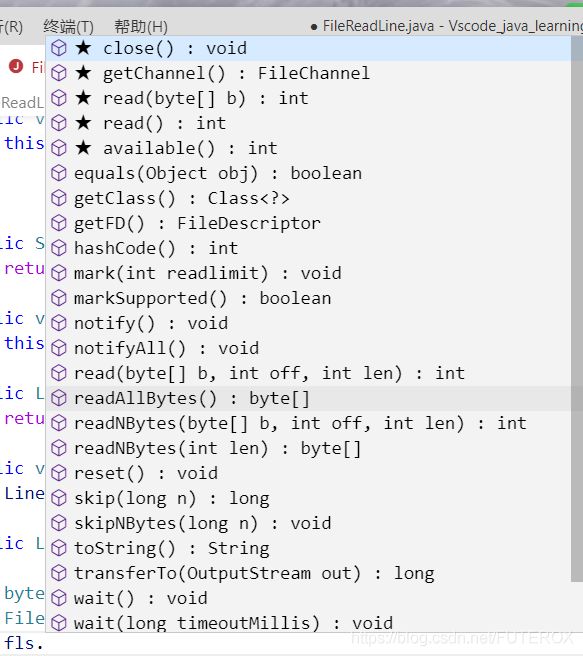
没有找到类似的方法,这个时候就不得不自己动脑子想一想了。
结合read()和字节数组可以找到一个思路,那就是逐一提取,判断(char)n !=’\n’。
这里的话我直接写了一个类。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class FileReadLine {
private String path = null;
List<String> Line_String = new ArrayList<String>();
public FileReadLine(){
}
public FileReadLine(String path){
this.setPath(path);
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
File file = new File(path);
if(file.exists()){
this.path = path;}
else{
this.path = null;
}
}
public List<String> getLine_String() {
return Line_String;
}
public void setLine_String(List<String> line_String) {
Line_String = line_String;
}
public List<String> GetLine() {
String path = this.getPath();
if(path==null){
return Line_String;
}
byte line[] = new byte[100];
FileInputStream fls=null;
int n = 0;
try {
fls = new FileInputStream(path);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
int i = 0;
while(true){
try {
n = fls.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
if((char)n!='\n'){
line[i]=(byte)n;
i++;//这里的i显然统计了多少个元素
}
else{
String get = new String(line);
Line_String.add(get);
i=0;
line = new byte[100];
}
if(n==-1){
line[i-1]=0;
String get = new String(line);
Line_String.add(get);
break;
}
}
return Line_String;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "C:\\Users\\31395\\Desktop\\test\\hello.txt";
FileReadLine FileLines = new FileReadLine(path);
List<String> Line_String = FileLines.GetLine();
for(String Line:Line_String){
System.out.println(Line);
}
}
}

接下来还有很多方法没有实现,我觉得可以试着去慢慢实现,把它做成一个比较厉害的工具类。
文件字节流的写入
写入的话需要使用到另一个类FileOutputStream。
同样的写入的话也需要通过byte 数组或者一个一个写入。但是要注意的是这里是字节流所以写入时如果写入了字符都是以ASCII编码来写入的。如果你想要使用字节流来进行写入中文的话同样只能通过字节数组来实现。下面举一个简单的例子来复制我们的hello文件。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "C:\\Users\\31395\\Desktop\\test\\hello.txt";
String pathcopy = "C:\\Users\\31395\\Desktop\\test\\hello1.txt";
try {
byte a[] = new byte[100];
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(pathcopy);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
int n = 0;
while(true){
n = fis.read(a);
if(n==-1){
break;
}
fos.write(a,0,n);//当n != -1时n为当前数组中正真有存有数据的个数,为了防止把多余的部分写入文件,限制数组的偏移。当然你可以直接使用write(a)但是复制出来的文件会大一点
}
//fos.write("Hello")是会直接报错的原因就是上面的
fos.close();
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
缓存输入输出流
前面那几个是直接在硬盘中读取文件的,速度有些许慢,我们可以选择使用缓存来提高速度。
具体使用很简单见下面的例子
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "C:\\Users\\31395\\Desktop\\test\\hello.txt";
String pathcopy = "C:\\Users\\31395\\Desktop\\test\\hello1.txt";
try {
byte a[] = new byte[100];
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(pathcopy);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
BufferedInputStream bfis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedOutputStream bfos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
int n = 0;
long star = System.currentTimeMillis();//计时对时间进行对比
while(true){
n = bfis.read(a);
if(n==-1){
break;
}
bfos.write(a,0,(n));//当n != -1时n为当前数组中正真有存有数据的个数,为了防止把多余的部分写入文件,限制数组的偏移。当然你可以直接使用write(a)但是复制出来的文件会大一点
}
wfos.write("Hello");
wfos.flush();//写入时当缓存区域满了就会写入文件,但是如果没有慢的话就不会写入,为了防止数据遗失使用这个方法强行写入。当然colse后也可以强行写入,但是此时已关闭。
Thread.sleep(1000);
//fos.close();
//fis.close();这里要注意关闭最外层就可以了,要对比没有用缓存的时候可以把下面的注释了把这个恢复,当然也可以不注释。保持这个样子不动。
bfis.close();
bfos.close();
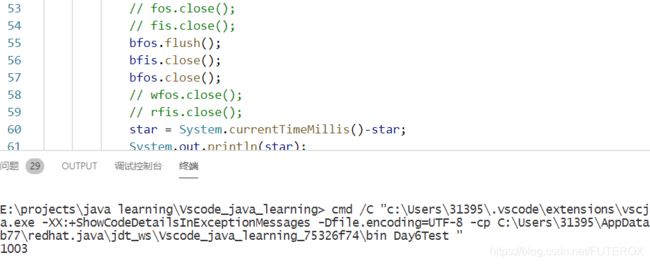
star = System.currentTimeMillis()-star;
System.out.println(star);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
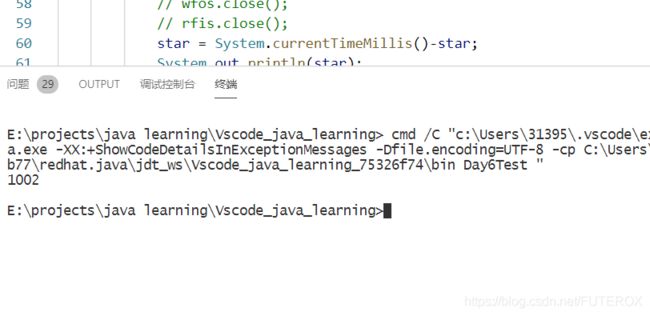
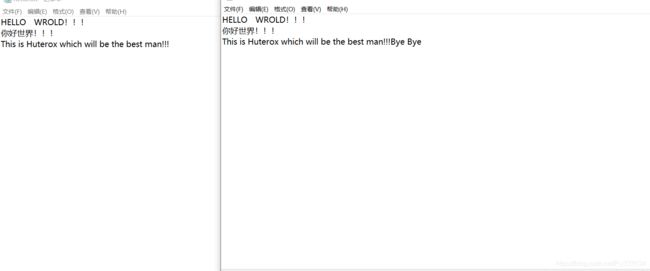
查看上面的代码,我写了一个计时程序用来计时。现在就可以分别比对一下,效果如下:
字符流
这个其实是对字节流的进一步封装,类似的它也可以使用缓存。
其用法和前面的几乎一致,只是可以设置字符编码同时它的write()方法也终于可以直接写字符串进去了。当然这里注意此时使用的时字符数组。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Day6Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "C:\\Users\\31395\\Desktop\\test\\hello.txt";
String pathcopy = "C:\\Users\\31395\\Desktop\\test\\hello1.txt";
try {
char[] a = new char[100];
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(pathcopy);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
BufferedInputStream bfis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedOutputStream bfos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
InputStreamReader rfis = new InputStreamReader(bfis,"utf-8");
OutputStreamWriter wfos = new OutputStreamWriter(bfos,"utf-8");
int n = 0;
long star = System.currentTimeMillis();
while(true){
n = rfis.read(a);
System.out.println(n);
if(n==-1){
break;
}
wfos.write(a,0,(n));
}
wfos.write("Bye Bye");
Thread.sleep(1000);
wfos.close();
rfis.close();
star = System.currentTimeMillis()-star;
System.out.println(star);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(pathcopy);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
BufferedInputStream bfis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedOutputStream bfos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
InputStreamReader rfis = new InputStreamReader(bfis,"utf-8");
OutputStreamWriter wfos = new OutputStreamWriter(bfos,"utf-8");
其实可以写成这样:
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(pathcopy);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
InputStreamReader rfis = new InputStreamReader(fis,"utf-8");
OutputStreamWriter wfos = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"utf-8");
BufferedReader brfis= new BufferedReader(rfis);
BufferedWriter bwfos = new BufferedWriter(wfos);
然后你对 brfis bwfos 进行读写就OK了。