vue笔记(四)注册组件,路由,vuex
官网
一、项目中的组件注册
二、路由
三、vuex
一、项目中的组件注册
1. 全局
import Loading from '@/components/loading';//封装的loading组件
Vue.component('Loading',Loading);
2. 局部
<loading/>
important loading from './components/loading'
components:{
loading}
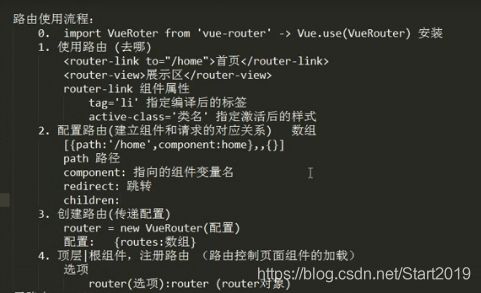
二、路由
1、路由配置
2、路由传参
3、接收参数和数据
4、组件内部实现路由跳转
5、路由导航
路由配置
import reg from './components/reg.vue'
routes = [
{
path:"/reg",
component: reg
},
{
path:'/product',
component:xx,
children:[
{
path: 'detail',//不加 '/',默认会 父路由path/子路由path
component:xx
}
]
}
]
路由传参
1. 路由参数配置
{path: 'xx/:参数变量', component: xx}
let routes = [
{
path: '/product',
component: product,
children: [
{
path: 'detail/:aid',
component: detail
}
]
}
]
2. 页面传参:
(1)router-link to="xx/参数?a=1&b=2"
<h3>商品页</h3>
<router-link to="/product/detail/001">商品001</router-link>
<router-link to="/product/detail/002">商品002</router-link>
<router-link :to="'/product/detail/002'">商品002</router-link>
(2)router-link :to="{name:'xx', params:{}, query:{}}"
params:数据,query:参数
<router-link :to="{name: 'detail', params:{aid: '003'}, query:{a:11,b22}}"
注意:用这种方式传参时,路由配置中需要添加一个 name,指向相同 name 值的路径。
let routes = [
{
path: '/product',
component: product,
children: [
{
path: 'detail/:aid',
name:'detail',
component: detail
}
]
}
]
接收参数和数据
{ {this.$route.params/query/path}}
this.$route 返回的是当前所有的路由信息
watch:(){
$route(to,from){
console.log(this.$route)
}
}
组件内部实现路由跳转
1. this.$router.push()
这个方法会向 history 栈添加一个新的记录,所以,当用户点击浏览器后退按钮时,则回到之前的 URL。
// 字符串
router.push('/home')
// 对象
router.push({
path: '/home' })
// 命名的路由
router.push({
name: 'user', params: {
userId: '123' }})
// 带查询参数,变成 /register?plan=private
router.push({
path: 'register', query: {
plan: 'private' }})
注意:如果提供了 path,那么 params 会被忽略,上述例子中的 query 并不属于这种情况。取而代之的是下面例子的做法,你需要提供路由的 name 或手写完整的带有参数的 path:
const userId = '123'
router.push({
name: 'user', params: {
userId }}) // -> /user/123
router.push({
path: `/user/${
userId}` }) // -> /user/123
// 这里的 params 不生效
router.push({
path: '/user', params: {
userId }}) // -> /user
2. this.$router.replace()
跟 router.push 很像,唯一的不同就是,它不会向 history 添加新记录,而是跟它的方法名一样 —— 替换掉当前的 history 记录。
| 声明式 | 编程式 |
|---|---|
| < router-link :to="…" replace > | router.replace(…) |
3. router.go(n)
这个方法的参数是一个整数,意思是在 history 记录中向前或者后退多少步,类似 window.history.go(n)。
// 在浏览器记录中前进一步,等同于 history.forward()
router.go(1)
// 后退一步记录,等同于 history.back()
router.go(-1)
// 前进 3 步记录
router.go(3)
// 如果 history 记录不够用,那就默默地失败呗
router.go(-100)
router.go(100)
路由导航
全局守卫、路由独享的守卫、组件内守卫
注意: 参数或查询的改变并不会触发进入/离开的导航守卫。 你可以通过观察 $route 对象来应对这些变化,或使用 beforeRouteUpdate 的组件内守卫。
1. 全局守卫: router.beforeEach
任何时候都会被守卫;应用场景:用户在未登录的时候进入任意页面,我们就让用户跳转到登录页面,在已登录的时候让用户正常跳转到点击的页面。demo
//常在 main.js 或 route.js 中写
router.beforeEach((to,from,next) => {
next()
})
2. 路由独享守卫
在路由配置上直接定义 beforeEnter 守卫:
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/foo',
component: Foo,
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
// ...
}
}
]
})
//或者
let detail = (to,from,next) =>{
// ...
}
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/foo',
component: Foo,
beforeEnter: detail
}
]
})
3. 组件内守卫
beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) {
//在渲染该组件的对应路由被 confirm 前调用
// 不!能!获取组件实例 `this`
// 因为当守卫执行前,组件实例还没被创建
},
beforeRouteUpdate (to, from, next) {
// 在当前路由改变,但是该组件被复用时调用
// 举例来说,对于一个带有动态参数的路径 /foo/:id,在 /foo/1 和 /foo/2 之间跳转的时候,
// 由于会渲染同样的 Foo 组件,因此组件实例会被复用。而这个钩子就会在这个情况下被调用。
// 可以访问组件实例 `this`
},
beforeRouteLeave (to, from, next) {
// 导航离开该组件的对应路由时调用
// 可以访问组件实例 `this`
}
示例:
<script>
export default {
beforeRouteEnter (to,from,next){
console.log("组件内部前置守卫");
// 同步条件: cookie,localstorage,vuex
if(true){
next(true);
} else {
next('/login');
}
// 异步条件
axios({
url:'xxx'}).then( res =>{
//通过路由的 query 传参
to.query.userData = data;
})
}
}
</script>
因为拿不到实例,所以不能直接赋值传参,可以通过 1. 路由传参; 2.next。
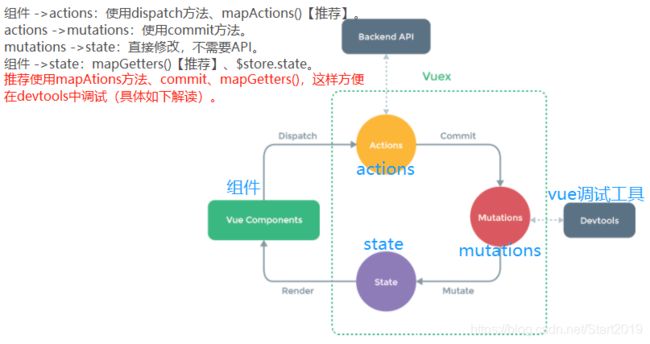
三、Vuex
集中式数据管理,一处修改,多处使用。适用于中大型项目;
图片解读:你不能直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地 提交 (commit) mutation。这样使得我们可以方便地跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够实现一些工具帮助我们更好地了解我们的应用。
一句话来说:当要修改state中的值,不建议用直接赋值的方法, 这样不方便调试。
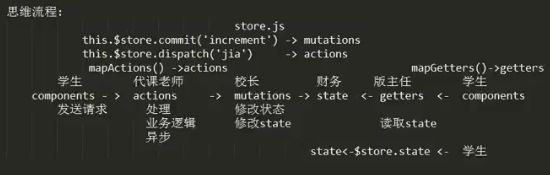
1. 通讯方式推荐使用: mapActions()(组件和 actions) 和 dispatch()(组件 和 actions);
this.$stroe.dispatch(类型, 数据/也叫“负载”):组件 - actions
commit:actions - mutations
mapActions
mapGetters
mapMutations
mapState
2. 简单示例1 [组件 - actions - mutations - state]:
在 store 中对 count 进行加一。
(1)准备工作,目录结构
(2)代码:
main.js ↓
import store from './store'
new Vue({
router,
store, //注册
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
store 文件夹下 index.js ↓
类似 router 中的 index.js,可以合并在一个 index.js 一起写,也可以分成几个文件或文件夹引入到 index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import actions from './actions'
import mutations from './mutations'
import state from './state'
import getters from './getters'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
// modules
})
| 文件名 | 代码 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| state.js | let state = {
count:0;
}
export default state;
|
state是一个仓库,常用来写初始值/默认值 |
| app.vue | < button @click="jia">按钮+< /button> count:{
{this.$store.state.count}}
methods: {
jia(){
this.$store.dispatch('jia');
}
}
|
用 $store 中的 dispatch 方法将"jia"这个类型(方法)传递到 actions 中。`dispatch(类型,负载/数据)` |
| actions.js | let actions = {
//与mutations的通讯方法,所以mutations.js中要有increment方法
// 写法: jia:function(){}
// 或者jia(){}
jia:(obj,payload)=>{
let {commit,state} = obj;
commit("increment","数据");
}
//或者
//jia: ({commit,state}, payload)=>{
// commit("increment", payload)
//}
}
export default actions;
|
actions 用来处理业务逻辑。从组件中接受过来的方法,参数有两个,第一个:返回 commit,dispatch,getters等方法;第二个:负载数据,接收在组件中的dispatch传过来的数据 |
| mutations.js | let mutations = {
increment: (state,payload){
state.count++;
//在actions中通过commit到mutations中,逻辑在mutations中处理
}
}
export default mutations;
|
做突变的。拿到从component或者 actions 中传过来的数据,然后修改数据,传到 state 中。有两个参数,第一个:state仓库;第二个:payload传过来的数据 |
(3)案例小结 :
- 在组件中,用
$store.dispatch(方法A, 数据A)将方法和数据传递到 actions 中。 - (在 actions.js 中) 此时 actions 接收到的函数(函数名是“方法A”)携带了两个参数,一个是用来传递到 mutations 的方法,一个是由组件传递过来的 数据A。经过逻辑处理,然后使用第一个参数中的
commit(方法名B, 数据B)将 方法B 和数据传递到 mutations 中。 - (在 mutations.js 中) 在 mutations 中可以接收到来自 actions 传递过来的函数(函数名为“方法B”),这个函数携带了两个参数,第一个参数是 store仓库,第二个是组件传递过来的数据A或 actions 传递过来的 数据B。这里可以对在store中定义的变量值进行处理。
- 回到组件,在组件中可以通过
this.$store.state获取到在state中定义的变量的值。
除了上面在组件中使用 dispatch 方法,还可以在组件中直接通过 commit 方法到 mutations中,省略了actions.js这一部分的操作,但是不建议使用这个方法。
app.vue
jia(){
this.$store.commit('increment','数据');
//commit方法是组件发到mutations的通讯方法
}
(4)还有 mapActions() 方法
这里如果要携带数据,直接在方法中传参 @click = "jia('数据12')";
app.vue
import {
mapActions,mapGetters} from 'vuex'
//methods:mapActions([类型1,类型2,类型3])
//mapActions调用后,返回对象,类型做key,函数做值
methods:mapActions(["jia"]) //相当于第一种方法,同时定义了同名的方法名和dispatch中的类型
当页面中既要写自己的代码,又使用到 vuex 时,使用 ... 拓展运算符和 [] 解构解析。
//下述中的 ... 是拓展运算符, 使用 [] 是解构赋值
methods: {
...mapActions(["jia"]),// 将 jia()方法 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('jia')
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 add()方法 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
}),
handleClick(){
console.log("自己在组件中写的方法");
}
}
3. 简单示例2 [组件 - getters - state]:
mapGetters 辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性:
| 文件名 | 代码 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| state.js |
let state= {
num: 10
};
export default state;
|
在 state 中初始化变量 |
| app.vue |
< button @click="getNum">+< /button>{
{num}}
//script部分
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
computed: mapGetters(['num']),
|
类似写计算属性的过程。在mapGetters中定义变量名,模板中进行使用。使用方法:`mapGetters(["类型1","类型2","类型3"])`。 |
| getters.js |
let getters= {
num: (state){
return state.num;
}
};
export default getters;
|
因为在app.vue中使用了mapGetters['num'],所以在 getters.js 中需要一个 num 函数。效果与计算属性相同:computed: {
num(){
return this.$store.state.num;
}
}
|
| 总结:`mapGetters['类型']`与计算属性一样,都依赖元数据,且要有返回值。在 getters.js 中可以对数据进行简单的操作,比如过滤 | ||
getters.js ↓
//这个getters.js 就是将原来通过 组件-action-mutation- state 后得到数据(这里最终的数据就是mutations中的样子),然后再进行修改。
//mapGetters['count']
let getters = {
count: (state) => {
//当 state.count < 10 时,依次+1,>=10 时,显示 “超过10”
if(state.count<10){
return state.count;
} else {
return "超过10";
}
}
}
export default getters;
4. 示例3-异步处理
简单来讲,vuex 中的异步处理,就是将异步请求放到 actions 中,过程与 示例1 相似。
| 文件名 | 代码 |
|---|---|
| app.vue |
< button @click="getData({pageNo:1, pageSize:10})">异步处理< /button>
//script部分
import { mapActions } from 'vuex';
methods: mapActions(['initDate'])
|
| actions.js |
import axios from 'axios';
let actions = {
initDate: ({commit, state}, paylod) => {
axios({url:'接口地址'}).then(
res => { commit('initData', res.data.count); }
)
}
};
export default actions;
|
| mutations.js |
let mutations = {
initData: (state, paylod){
state.count += paylod;
}
};
export default mutations;
|
5. 个人理解 : Vuex 是一个状态管理模式,在 vuex 中的 state 中定义变量和值。类似于我们熟悉的 localStorage 和 sessionStorage。这里就拿sessionStorage和vuex来作一下对比:
| 名称 | sessionStorage | vuex |
|---|---|---|
| 存储 | 直接在组件中: sessionStorage.setItem("key", "value"); |
在 state 中定义 key 和 key的初始值 value。 |
| 修改 | sessionStorage 的修改与它的存储类似:sessionStorage.setItem("key", "newValue"); |
为了方便在 devtools 中调试,我们要通过 “组件 -> actions -> mutations” 这一系列步骤去修改在 state 中定义的 key值。具体方法: ①在组件中,使用this.$store.dispatch(方法名A, 数据A) 或 mapActions(方法名A);②在 actions 中可以获取到 方法名A 中携带的 数据A。对 数据A 进行操作,操作后的数据B使用 commit(方法名B, 数据B);③在 mutations 中,以 方法名B 命名的函数可以获取到 state 中定义的 key 和它的初始值value以及 数据B。常将修改好的 数据B 赋值给 state中定义的 key。 |
| 获取 | 直接在组件中: sessionStorage.getItem("key"); |
在组件中可以使用 this.$store.state.key 来获取值。如果是在模板中获取,为了减少对模板的操作,可以使用 mapGetters() 来获取初始值或者修改后的值。 |
| 删除 | ①删除指定键的数据语法: sessionStorage.removeItem("key");;②删除所有数据:sessionStorage.clear(); |
通过上面的 修改 步骤去改变 state 中定义的key,让它变成初始值。 |
| 区别 | 用于临时保存同一窗口(或标签页)的数据,在关闭窗口或标签页之后将会删除这些数据。 | 当页面刷新时,使用 vuex 定义的数据都会变成初始值。 |