GDB内存调试初探五
Memory Accessing beyond valid range (2)
Problem description
I presented a problem in the last blog article, in which an invalid memory write occurs beyond a chunk of memory range (here); at the end of article, I concluded that the method used sometimes fails to help us find the bug, due to some technical limitations. In this article, I present another method to tackle the problem, without setting chunks of memory regions to read-only via mprotect system call. The method, I think, is also very efficient in solving problems of this particular type. Please refer to my former article for the buggy application source code.
Basic idea
Setting some memory regions to read-only is a practical method to aid debugging. But it does waste a huge mount of memory; the new method also use LD_PRELOAD environment variable to preload a shared library, which overrides the definitions of malloc/calloc/realloc/free functions; but instead of calling mprotect system call, it prints a single line of message to standard output for (almost) every invocation of the four functions. Each line of message will contain the memory address allocated or freed, its size and the return address in the caller function. After the application crashes, we will use a Lua 5.3 script to process the application heap, in order to find the problematic pointer. Here is the source code of new preloaded shared library:
/*
* Created by [email protected]
* Simple malloc/free hook for debugging
* 2020/09/19
*/
#include The above source code avoids using fprintf/snprintf because the function might need to allocated memory, thus causing a recursive problem.
Happy debugging
The above code has been compiled into a shared library, named mymalloc2.so; preloading the shared library will not produce more messages to standard output, because the contents of mallocOffsets are all zeros. Immediately upon the execution of main function, we set the offsets to non-zero values; The values are calculated from the disassembly of mymalloc2.so, for example, malloc_offset should be set to 0x14 in order to fetch the return address of malloc:

We now do not know the corrupted memory chunk is allocated by malloc/calloc/realloc, so we need to debug all the three functions, besides function free:
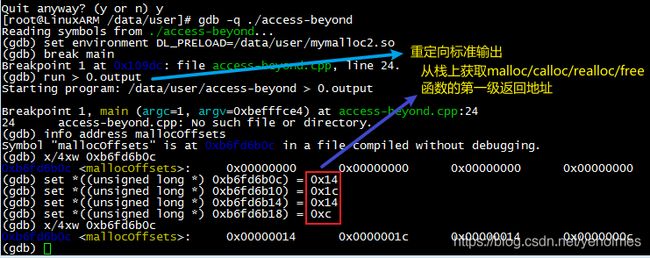
Please note that the standard output from application has been redirected to file 0.output. After the application crashes, we need to dump the heap to a file named 0.heap, and execute Lua script heap-dump.lua to determine the invalid pointer:
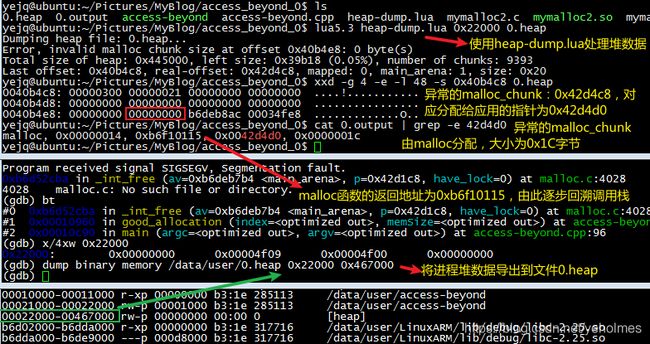 We can infer from the above picture that the invalid pointer is 0x42d4d0, which has a size of 28 bytes, and is allocated by function
We can infer from the above picture that the invalid pointer is 0x42d4d0, which has a size of 28 bytes, and is allocated by function malloc. The 4 zero bytes in the red rectangle is where an invalid write has occurred. Another piece of important information is that the return address of malloc is at address 0xb6f10115:
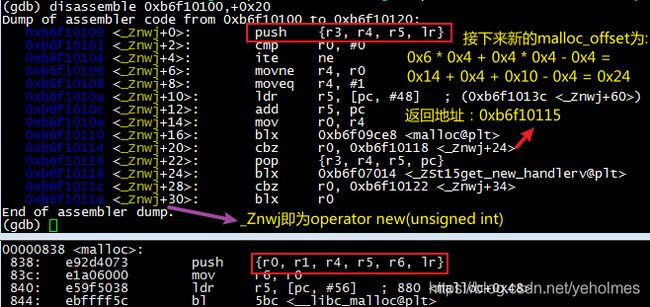
Now we know that the caller of malloc is _Znwj, which corresponds to operator new in C++. After calculating the malloc_offset, we need to debug again:
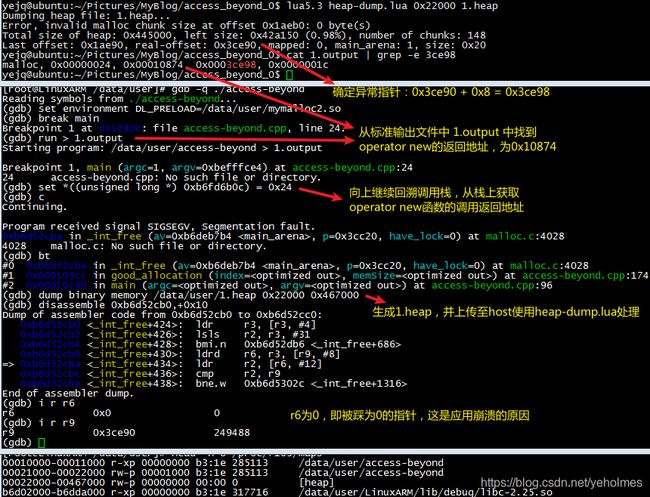
By repeating the process, we get a new return address, 0x10874 which in fact is an address from access-beyond, our beloved little application: Now we’ve manually back-traced to the buggy application, we know where the problematic pointer has been allocated, it is at line 193:
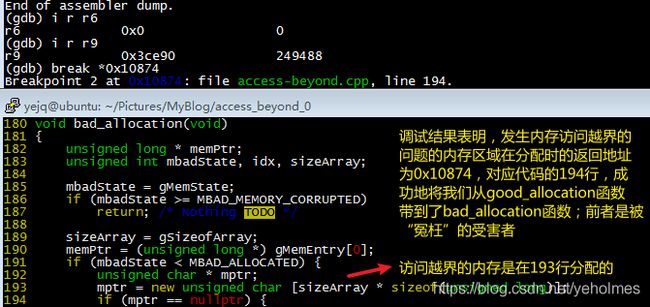
Knowing where the buggy pointer is allocated, we’ve now solved 90% of the problem. Then we need to debug the application again, use a watchpoint the monitor the end of memory pointed by memPtr. After more than half an hour’s impatient waiting, we finally find the bug:
 The bug is at line 210. Using watchpoints is sometimes not recommended, because it can significantly slow down your application. You can follow the pointer in the source code, if you are lucky, you can spot the bug very soon.
The bug is at line 210. Using watchpoints is sometimes not recommended, because it can significantly slow down your application. You can follow the pointer in the source code, if you are lucky, you can spot the bug very soon.
Conclusion
The method presented here finally solved my problem, after much effort indeed. I like it because it avoids wasting too much memory and calling mprotect, and does not fail us for the most occasions. Here is the complete listing of the Lua script, heap-dump.lua (it needs support from a specific version of luaposix):
#!/usr/bin/env lua5.3
-- Glibc ptmalloc heap memory dumper
-- 2020/09/19
-- load Lua modules
local posix = require 'posix'
-- script global variables
local heapDumper = {
} -- parent heap dumper class
local heap32Bit = true -- choose between 32-bit or 64-bit
local HEAP_MAX_SIZE = 0x20000000 -- maximum size of heap file, 512MB
local MCHUNK_MIN_SIZE = heap32Bit and 0x08 or 0x10 -- minimum size for malloc chunk
-- string format used to unpack `struct malloc_chunk:
local MCHUNK_FMT = heap32Bit and " or "
-- sizeof(struct malloc_chunk), please refer to malloc/malloc.c in glibc source code:
local MCHUNK_SIZE = string.packsize(MCHUNK_FMT)
-- size used to determine if a malloc chunk is in_smallbin_range
local MIN_LARGE_SIZE = heap32Bit and 512 or 1024
-- constants from malloc/malloc.c:
local PREV_INUSE = 0x1
local IS_MMAPPED = 0x2
local NON_MAIN_ARENA = 0x4
-- function to ruminate the parsed heap
function heapDumper:ruminate()
local nchk = self.numchunk
if nchk == 0 then
io.stderr:write("Warning, no malloc chunk found in heap file\n")
return false
end
local left = self.totalSize - self.curOffset
print(string.format("Total size of heap: %#x, left size: %#x (%.02f%%), number of chunks: %d",
self.totalSize, left, left / self.totalSize, nchk))
nchk = 2
local prevChunk, nextChunk = self.chunks[1], self.chunks[2]
while nextChunk do
local previnuse = (nextChunk.mc_size & PREV_INUSE) > 0
prevChunk.ck_inuse = previnuse
if previnuse then nextChunk.mc_prev_size = prevChunk.ck_size end
if prevChunk.ck_size ~= nextChunk.mc_prev_size then
io.stderr:write(string.format("Error, malloc chunk size mismatch: %#x, %#x\n",
prevChunk.ck_size, nextChunk.mc_prev_size))
end
nchk = nchk + 1
prevChunk = nextChunk
nextChunk = self.chunks[nchk]
end
return true
end
local function mcDumper(mc)
local typn = type(mc)
if typn ~= "table" then
io.stderr:write(string.format("Invalid type of malloc chunk: %s\n", typn))
return false
end
io.stdout:write(string.format("offset: %#x, real-offset: %#x, mapped: %d, main_arena: %d, size: %#x",
mc.ck_offset, mc.ck_real_offset, mc.ck_mapped and 1 or 0, mc.ck_main_arena and 1 or 0, mc.ck_size))
if mc.ck_inuse then
io.stdout:write("\n")
else
if mc.ck_small_bin then
io.stdout:write(string.format(", forward: %#x, backward: %#x\n", mc.mc_fd, mc.mc_bk))
else
io.stdout:write(string.format(", forward: %#x, backward: %#x\n", mc.mc_fd_nextsize, mc.mc_bk_nextsize))
end
end
return true
end
-- function to dump the malloc chunks parsed from heap file
function heapDumper:dumpChunks(onlyLast)
local nchk = self.numchunk
if nchk == 0 then
io.stderr:write("Warning, the malloc chunk list is empty!\n")
return false
end
if onlyLast then
io.stdout:write("Last ")
return mcDumper(self.chunks[nchk])
end
for idx = 1, nchk do mcDumper(self.chunks[idx]) end
return true
end
-- function to destroy heap dumper
function heapDumper:destroy()
local rfd = self.readFile
self.readFile = -1
posix.close(rfd); rfd = 0x1
while rfd <= self.numchunk do
local chunk = self.chunks[rfd]
self.chunks[rfd] = nil
chunk.ck_size = nil
chunk.ck_offset = nil
chunk.ck_real_offset = nil
chunk.ck_inuse = nil
chunk.ck_mapped = nil
chunk.ck_main_arena = nil
chunk.ck_small_bin = nil
chunk.mc_prev_size = nil
chunk.mc_size = nil
chunk.mc_fd = nil
chunk.mc_bk = nil
chunk.mc_fd_nextsize = nil
chunk.mc_bk_nextsize = nil
rfd = rfd + 1
end
self.devOffset = nil
self.readFile = nil
self.totalSize = nil
self.curOffset = nil
self.numchunk = nil
self.chunks = nil
setmetatable(self, nil)
return true
end
-- function to parse binary heap file
function heapDumper:parseNext()
local typn = type(self)
if typn ~= "table" then
io.stderr:write(string.format("Error, invalid hidden reference type: %s\n", typn))
return false
end
local offSet = self.curOffset
if offSet >= self.totalSize then return false end
-- set the file pointer to the beginning of next chunk
if offSet ~= posix.lseek(self.readFile, offSet, posix.SEEK_SET) then
io.stderr:write(string.format("Error, lseek(%d, %#x, SEEK_SET) has failed.\n",
self.readFile, offSet))
return false
end
-- read the heap file via system call
local mChunk = posix.read(self.readFile, MCHUNK_SIZE)
typn = type(mChunk)
if typn ~= "string" or #mChunk ~= MCHUNK_SIZE then
io.stderr:write(string.format("Error, cannot read heap file any further: %d\n",
typn == "string" and #mChunk or -1))
return false
end
-- unpack structure, `struct malloc_chunk
local mchunk_prev_size, mchunk_size, m_fd, m_bk, fd_nextsize, bk_nextsize = string.unpack(
MCHUNK_FMT, mChunk)
-- check the size of new chunk
local newSize = mchunk_size & 0xfffffffffffffff8 -- we are using Lua5.3, hahaha...
if newSize < MCHUNK_MIN_SIZE or newSize > (self.totalSize - offSet) then
io.stderr:write(string.format("Error, invalid malloc chunk size at offset %#x: %#x byte(s)\n",
offSet, mchunk_size))
return false
end
-- create a new chunk
local newChunk = {
}
newChunk.ck_size = newSize
newChunk.ck_offset = offSet
newChunk.ck_real_offset = offSet + self.devOffset
newChunk.ck_inuse = true -- deem as non-free memory
newChunk.ck_mapped = (mchunk_size & IS_MMAPPED) > 0
newChunk.ck_main_arena = (mchunk_size & NON_MAIN_ARENA) == 0
-- refer to macro in_smallbin_range() from malloc/malloc.c:
newChunk.ck_small_bin = newSize < MIN_LARGE_SIZE
newChunk.mc_prev_size = mchunk_prev_size
newChunk.mc_size = mchunk_size
newChunk.mc_fd = m_fd
newChunk.mc_bk = m_bk
newChunk.mc_fd_nextsize = fd_nextsize
newChunk.mc_bk_nextsize = bk_nextsize
self.numchunk = self.numchunk + 1
self.chunks[self.numchunk] = newChunk
self.curOffset = offSet + newSize
return true
end
-- function to create a heap-dumper
local function dumpInit(offSet, heapFile)
local typn = type(offSet)
if typn ~= "number" then offSet = tonumber(offSet) end
if not offSet then
io.stderr:write(string.format("Error, invalid offset given: %s\n", typn))
return nil
end
local fileHdl, fileStat = nil, nil
fileStat = posix.stat(heapFile)
if not fileStat then return nil end -- cannot access heap file
if fileStat["type"] ~= "regular" then
io.stderr:write(string.format("Error, not a regular file: %s\n", heapFile))
return nil
end
fileStat = fileStat["size"] -- get the file size
if fileStat < 0x10 or fileStat > HEAP_MAX_SIZE then
io.stderr:write(string.format("Error, invalid heap file size, %s: %d\n",
heapFile, fileStat))
return nil
end
fileHdl = posix.open(heapFile, posix.O_RDONLY)
if not fileHdl then
io.stderr:write(string.format("Error, cannot open file: %s\n", heapFile))
return nil
end
local dumper = {
}
dumper.devOffset = offSet -- heap memory offset when running
dumper.readFile = fileHdl -- file descriptor for reading
dumper.totalSize = fileStat -- heap file total size in bytes
dumper.curOffset = 0 -- processing offset in bytes
dumper.numchunk = 0 -- number of malloc chunk found
dumper.chunks = {
} -- list of malloc chunks
setmetatable(dumper, {
__index = heapDumper })
return dumper
end
-- function to inform user how to use the script
local function dumpHelp(argName)
if not argName then argName = "heap-dump" end
io.stderr:write(string.format("Usage: %s heap-offset path-to-heap-file\n", argName))
os.exit(1)
end
-- check the script command-line arguments
if #arg ~= 0x2 then dumpHelp(arg[0]) end
local dumper = dumpInit(arg[1], arg[2])
if not dumper then dumpHelp(arg[0]) end
print(string.format("Dumping heap file: %s...", arg[2]))
while true do
if not dumper:parseNext() then break end
end
dumper:ruminate(); dumper:dumpChunks(true); dumper:destroy(); os.exit(0)