问题描述:
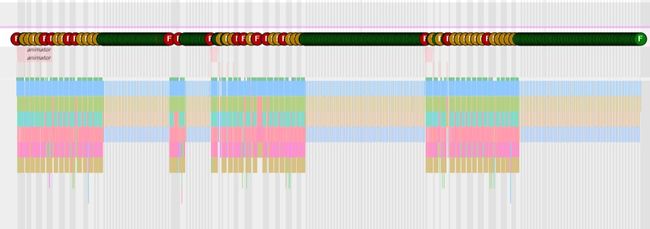
在开机向导界面滑动wifi列表界面时比较卡顿,概率为必现
抓一份systrace,红色帧有多处,总体上看有不少处发生掉帧
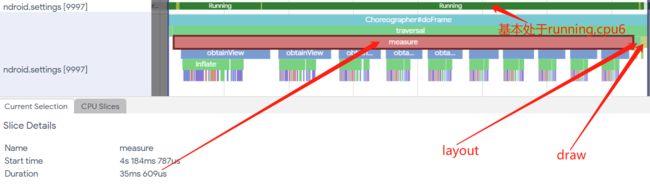
挑其中一处红色帧放大看下
耗时中的measure是大头,其中一次measure有数十次obtainview,对比其他绿色正常帧,发现正常的时候没有measure的过程
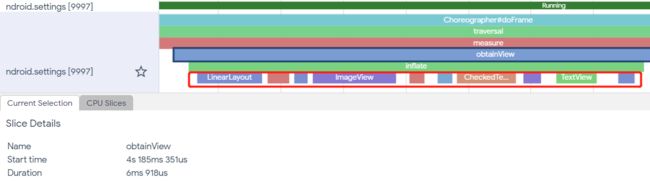
放大一次obtainview的过程,做的其实是inflate一项item的过程,红圈处对应了wifi一个item的布局
我们都知道,ViewRootImpl的
performTraversals方法会经过measure、layout和draw三个流程才能将一帧View需要显示的内容绘制到屏幕上
- performMeasure: 从根节点向下遍历View树,完成所有ViewGroup和View的测量工作,计算出所有ViewGroup和View显示出来需要的高度和宽度
- performLayout():从根节点向下遍历View树,完成所有ViewGroup和View的布局计算工作,根据测量出来的宽高及自身属性,计算出所有ViewGroup和View显示在屏幕上的区域;
- performDraw():从根节点向下遍历View树,完成所有ViewGroup和View的绘制工作,根据布局过程计算出的显示区域,将所有View的当前需显示的内容画到屏幕上
对应到我们这个问题,此时大概心里有数了,一帧的耗时并不是计算显示在哪个区域以及本身的内容绘制耗时,而是计算需要显示的高度或宽度耗时,注意这里是计算这个列表的高度或宽度耗时了,因为每次measure都对应了数十次的加载item的过程,很显然需要依据item的高度或宽度来最终确定列表的高度或宽度
故真相只有一个,就是列表很可能使用了自适应的高度或宽度
看下代码
果不其然,这里设置了自适应的高度,修改为match_parent后再次测试发现卡顿消失
抓取改后的systrace
基本上没有了红色帧,每一帧的绘制不再有measure的过程
其实这个问题不抓systrace,看traceview同样能够定位,只是没有systrace直观
到这里,还有一个疑问,当view设置了自适应高度后,它的高度由其子view的高度决定,故需要计算它的所有子view高度后才能确定自身的显示高度
这一点容易理解,但是具体到onMeasure的代码里是如何实现的呢?
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
//这里对应了systrace中measure tag
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
其中的mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);通过参数可以看到,view的显示宽高用到了其子view的宽高作为约束条件
listview必定会重写onMeasure,直接跟到其源码中
frameworks/base/core/java/android/widget/ListView.java
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// Sets up mListPadding
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//....
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
// TODO: after first layout we should maybe start at the first visible position, not 0
heightSize = measureHeightOfChildren(widthMeasureSpec, 0, NO_POSITION, heightSize, -1);
}
//...
}
我们都知道wrap_content对应的mode为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,这时候调用到measureHeightOfChildren开始计算其子view的宽高
这里看注释描述,如果指定了高度,则measure会停止
/**
* Measures the height of the given range of children (inclusive) and
* returns the height with this ListView's padding and divider heights
* included. If maxHeight is provided, the measuring will stop when the
* current height reaches maxHeight.
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec The width measure spec to be given to a child's
* {@link View#measure(int, int)}.
* @param startPosition The position of the first child to be shown.
* @param endPosition The (inclusive) position of the last child to be
* shown. Specify {@link #NO_POSITION} if the last child should be
* the last available child from the adapter.
* @param maxHeight The maximum height that will be returned (if all the
* children don't fit in this value, this value will be
* returned).
* @param disallowPartialChildPosition In general, whether the returned
* height should only contain entire children. This is more
* powerful--it is the first inclusive position at which partial
* children will not be allowed. Example: it looks nice to have
* at least 3 completely visible children, and in portrait this
* will most likely fit; but in landscape there could be times
* when even 2 children can not be completely shown, so a value
* of 2 (remember, inclusive) would be good (assuming
* startPosition is 0).
* @return The height of this ListView with the given children.
*/
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = Build.VERSION_CODES.P, trackingBug = 115609023)
final int measureHeightOfChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int startPosition, int endPosition,
int maxHeight, int disallowPartialChildPosition) {
final ListAdapter adapter = mAdapter;
if (adapter == null) {
return mListPadding.top + mListPadding.bottom;
}
// Include the padding of the list
int returnedHeight = mListPadding.top + mListPadding.bottom;
final int dividerHeight = mDividerHeight;
// The previous height value that was less than maxHeight and contained
// no partial children
int prevHeightWithoutPartialChild = 0;
int i;
View child;
// mItemCount - 1 since endPosition parameter is inclusive
endPosition = (endPosition == NO_POSITION) ? adapter.getCount() - 1 : endPosition;
final AbsListView.RecycleBin recycleBin = mRecycler;
final boolean recyle = recycleOnMeasure();
final boolean[] isScrap = mIsScrap;
for (i = startPosition; i <= endPosition; ++i) {
child = obtainView(i, isScrap);
measureScrapChild(child, i, widthMeasureSpec, maxHeight);
if (i > 0) {
// Count the divider for all but one child
returnedHeight += dividerHeight;
}
// Recycle the view before we possibly return from the method
if (recyle && recycleBin.shouldRecycleViewType(
((LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams()).viewType)) {
recycleBin.addScrapView(child, -1);
}
returnedHeight += child.getMeasuredHeight();
if (returnedHeight >= maxHeight) {
// We went over, figure out which height to return. If returnedHeight > maxHeight,
// then the i'th position did not fit completely.
return (disallowPartialChildPosition >= 0) // Disallowing is enabled (> -1)
&& (i > disallowPartialChildPosition) // We've past the min pos
&& (prevHeightWithoutPartialChild > 0) // We have a prev height
&& (returnedHeight != maxHeight) // i'th child did not fit completely
? prevHeightWithoutPartialChild
: maxHeight;
}
if ((disallowPartialChildPosition >= 0) && (i >= disallowPartialChildPosition)) {
prevHeightWithoutPartialChild = returnedHeight;
}
}
// At this point, we went through the range of children, and they each
// completely fit, so return the returnedHeight
return returnedHeight;
}
这里最关键的代码: child = obtainView(i, isScrap);
/**
* Gets a view and have it show the data associated with the specified
* position. This is called when we have already discovered that the view
* is not available for reuse in the recycle bin. The only choices left are
* converting an old view or making a new one.
*
* @param position the position to display
* @param outMetadata an array of at least 1 boolean where the first entry
* will be set {@code true} if the view is currently
* attached to the window, {@code false} otherwise (e.g.
* newly-inflated or remained scrap for multiple layout
* passes)
*
* @return A view displaying the data associated with the specified position
*/
View obtainView(int position, boolean[] outMetadata) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "obtainView");
//...
//obtainView方法里面核心的代码其实就两行,首先从复用缓存中取出一个可以复用的View,然后作为参传入getView中,
//也就是convertView。这里会走到obtainview,子View实例都是由obtainView方法返回的,然后再调用具体measureScrapChild
//来具体测量子View的高度.
//正常情况下这里for循环的次数就等于所有子项的个数,不过特殊的是已测量的子View高度之和大于maxHeight
//就直接return出循环了。这种做法其实很好理解,ListView能显示的最大高度就是屏幕的高度,如果有1000个子项
//前面10项已经占满了一屏幕了,那后面的990项就没必要继续测量高度了,这样可以大大提高性能
final View scrapView = mRecycler.getScrapView(position);
final View child = mAdapter.getView(position, scrapView, this);
if (scrapView != null) {
if (child != scrapView) {
// Failed to re-bind the data, return scrap to the heap.
mRecycler.addScrapView(scrapView, position);
} else if (child.isTemporarilyDetached()) {
outMetadata[0] = true;
// Finish the temporary detach started in addScrapView().
child.dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach();
}
}
//....
setItemViewLayoutParams(child, position);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
return child;
}
出现问题时正是触发了onMeasure,导致遍历可见范围内的数十个wifi item并计算他们的高度
一点小结
一个View最终显示到屏幕上一共分为三个阶段:Measure、Layout、Draw,而使用不当会造成其重复调用,尤其是Measure过程最为敏感。
因为当根布局做measure的时候,需要逐级measure子View和子布局,当所有子View或子布局measure完成的时候才能最终确定根部局的大小,
所以子布局的measure调用时机是由父布局来决定的。而像ListView这种在其onMeasure中直接调用getView的情况,
如果onMeasure被调用次数过多,将严重影响性能。
这里的listview还好外边没有裹着RelativeLayout,不然会导致子View的onMeasure重复调用,卡顿也会更加明显,假设RelativeLayout嵌套层数为n,子View的onMeasure次数为2^(n+1)
使用ListView的时候注意尽量使用layout_height=”match_parent”,如果无法避免,外边也不能裹着RelativeLayout
总而言之: 写代码三思而后行,谨慎再谨慎