title: 设计模式—创建型模式
categories: 设计模式
tags: 设计模式
1.什么是创建型模式?
创建型模式提供了一种在创建对象的同时隐藏创建逻辑的方式,而不是使用new直接去实例化对象,这使得程序在创建对象时更加灵活和有针对性
主要包括 单例模式,工厂模式,抽象工厂模式,建造者模式等
2.单例模式
单例(Singleton)模式的定义:指一个类只有一个实例,且该类能自行创建这个实例的一种模式
单例模式有 3 个特点:
- 单例类只有一个实例对象;
- 该单例对象必须由单例类自行创建;
- 单例类对外提供一个访问该单例的全局访问点。
public class Singleton {
}
//懒汉式
class LazySingleton {
private static volatile LazySingleton instance ;
private LazySingleton() {}
public static synchronized LazySingleton getInstance() {
if(instance == null) {
instance = new LazySingleton();
}
return instance;
}
}
//饿汉式
class HungrySingleton {
private static HungrySingleton instance = new HungrySingleton();
private HungrySingleton () {}
public static HungrySingleton getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
//双重校验锁
class DoubleSingleton {
private static volatile DoubleSingleton instance;
private DoubleSingleton (){}
public static DoubleSingleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (DoubleSingleton.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new DoubleSingleton();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
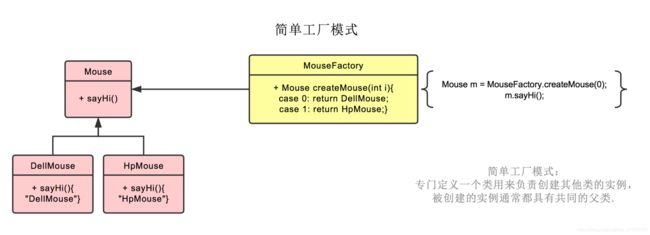
3.简单工厂模式
- 我们把被创建的对象称为“产品”,把创建产品的对象称为“工厂”。如果要创建的产品不多,只要一个工厂类就可以完成,这种模式叫“简单工厂模式”。
- 在简单工厂模式中创建实例的方法通常为静态(static)方法,因此简单工厂模式(Simple Factory Pattern)又叫作静态工厂方法模式(Static Factory Method Pattern)。
- 简单来说,简单工厂模式有一个具体的工厂类,可以生成多个不同的产品,属于创建型设计模式。简单工厂模式不在 GoF 23 种设计模式之列。
- 简单工厂模式每增加一个产品就要增加一个具体产品类和一个对应的具体工厂类,这增加了系统的复杂度,违背了“开闭原则”。
- “工厂方法模式”是对简单工厂模式的进一步抽象化,其好处是可以使系统在不修改原来代码的情况下引进新的产品,即满足开闭原则。
public interface Computer {
void start();
}
public class AsusComputer implements Computer {
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("华硕电脑启动");
}
}
public class HpComputer implements Computer {
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("惠普电脑启动");
}
}
public class LenovoComputer implements Computer{
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("联想电脑启动");
}
}
public class SimpleFactory {
public static Computer createComputer (String type) {
Computer computer = null;
switch (type) {
case "lenovo" :
computer = new LenovoComputer();
break;
case "hp":
computer = new HpComputer();
break;
case "asus":
computer = new AsusComputer();
break;
}
return computer;
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleFactory.createComputer("hp").start();
}
}
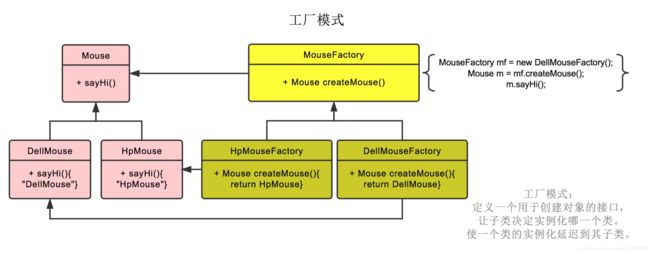
4.工厂方法模式
工厂方法模式(Factory Method Pattern):又称为工厂模式或者多态工厂模式。在 *工厂方法模式中,工厂父类负责定义创建产品对象的公共接口,而工厂子类则负责生成具 * 体的产品对象,这样做的目的是将产品的实例化操作延迟到工厂子类中完成,即通过工厂 * 子类来确定究竟应该实例化哪一个具体产品类。
public interface MachineApi {
void process (String material);
}
public class BoodleMachine implements MachineApi{
@Override
public void process(String material) {
System.out.println("我把" + material + "加工成了面条");
}
}
public class SteamedBunMachine implements MachineApi{
@Override
public void process(String material) {
System.out.println("我把" + material + "加工成了馒头");
}
}
public abstract class Factory {
public abstract MachineApi newMachine();
public void process (String material) {
MachineApi machine = newMachine();
machine.process(material);
}
}
public class NoodleFactory extends Factory {
@Override
public MachineApi newMachine() {
return new BoodleMachine();
}
}
public class SteamedBunFactory extends Factory {
@Override
public MachineApi newMachine() {
return new SteamedBunMachine();
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Factory factory1 = new SteamedBunFactory ();
factory1.process("面粉");//我把面粉加工成了馒头
Factory factory2 = new NoodleFactory ();
factory2.process("米粉");//我把面粉加工成了馒头
}
}
5.抽象工厂模式
抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory Pattern)是围绕一个超级工厂创建其他工厂。该超级工厂又称为其他工厂的工厂。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
在抽象工厂模式中,接口是负责创建一个相关对象的工厂,不需要显式指定它们的类。每个生成的工厂都能按照工厂模式提供对象。
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
public class Rectangle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle::draw() method.");
}
}
public class Square implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method.");
}
}
public class Circle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Circle::draw() method.");
}
}
public interface Color {
void fill();
}
public class Red implements Color {
@Override
public void fill() {
System.out.println("Inside Red::fill() method.");
}
}
public class Green implements Color {
@Override
public void fill() {
System.out.println("Inside Green::fill() method.");
}
}
public class Blue implements Color {
@Override
public void fill() {
System.out.println("Inside Blue::fill() method.");
}
}
public abstract class AbstractFactory {
public abstract Color getColor(String color);
public abstract Shape getShape(String shape) ;
}
public class ShapeFactory extends AbstractFactory {
@Override
public Shape getShape(String shapeType){
if(shapeType == null){
return null;
}
if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("CIRCLE")){
return new Circle();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("RECTANGLE")){
return new Rectangle();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("SQUARE")){
return new Square();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Color getColor(String color) {
return null;
}
}
public class ColorFactory extends AbstractFactory {
@Override
public Shape getShape(String shapeType){
return null;
}
@Override
public Color getColor(String color) {
if(color == null){
return null;
}
if(color.equalsIgnoreCase("RED")){
return new Red();
} else if(color.equalsIgnoreCase("GREEN")){
return new Green();
} else if(color.equalsIgnoreCase("BLUE")){
return new Blue();
}
return null;
}
}
public class FactoryProducer {
public static AbstractFactory getFactory(String choice){
if(choice.equalsIgnoreCase("SHAPE")){
return new ShapeFactory();
} else if(choice.equalsIgnoreCase("COLOR")){
return new ColorFactory();
}
return null;
}
}
public class AbstractFactoryPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取形状工厂
AbstractFactory shapeFactory = FactoryProducer.getFactory("SHAPE");
//获取形状为 Circle 的对象
Shape shape1 = shapeFactory.getShape("CIRCLE");
//调用 Circle 的 draw 方法
shape1.draw();
//获取形状为 Rectangle 的对象
Shape shape2 = shapeFactory.getShape("RECTANGLE");
//调用 Rectangle 的 draw 方法
shape2.draw();
//获取形状为 Square 的对象
Shape shape3 = shapeFactory.getShape("SQUARE");
//调用 Square 的 draw 方法
shape3.draw();
//获取颜色工厂
AbstractFactory colorFactory = FactoryProducer.getFactory("COLOR");
//获取颜色为 Red 的对象
Color color1 = colorFactory.getColor("RED");
//调用 Red 的 fill 方法
color1.fill();
//获取颜色为 Green 的对象
Color color2 = colorFactory.getColor("Green");
//调用 Green 的 fill 方法
color2.fill();
//获取颜色为 Blue 的对象
Color color3 = colorFactory.getColor("BLUE");
//调用 Blue 的 fill 方法
color3.fill();
}
}
三大工厂模式的区别可见:
www.zhihu.com/question/20367734/answer/807965357
在这里插入图片描述
6.建造者模式
建造者模式(Builder Pattern)使用多个简单的对象一步一步构建成一个复杂的对象。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
参考:https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern