知识要点
. 前言
在一个完整的离线大数据处理系统中,除了hdfs+mapreduce+hive组成分析系统的核心之外,还需要数据采集、结果数据导出、任务调度等不可或缺的辅助系统,而这些辅助工具在hadoop生态体系中都有便捷的开源框架,如图所示:
2. Flume基本介绍
1. 概述
Flume是一个分布式、可靠、和高可用的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的系统。
Flume可以采集文件,socket数据包、文件、文件夹、kafka等各种形式源数据,又可以将采集到的数据(下沉sink)输出到HDFS、hbase、hive、kafka等众多外部存储系统中
一般的采集需求,通过对flume的简单配置即可实现
Flume针对特殊场景也具备良好的自定义扩展能力,因此,flume可以适用于大部分的日常数据采集场景
2. 运行机制
Flume分布式系统中最核心的角色是agent,flume采集系统就是由一个个agent所连接起来形成的
每一个agent相当于一个数据传递员,内部有三个组件:
Source:采集组件,用于跟数据源对接,以获取数据
Sink:下沉组件,用于往下一级agent传递数据或者往最终存储系统传递数据
Channel:传输通道组件,用于从source将数据传递到sink
3. Flume采集系统结构图
1. 简单结构
单个agent采集数据
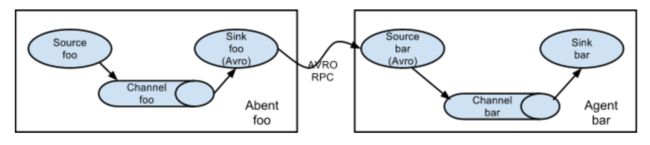
2. 复杂结构
两个agent之间串联
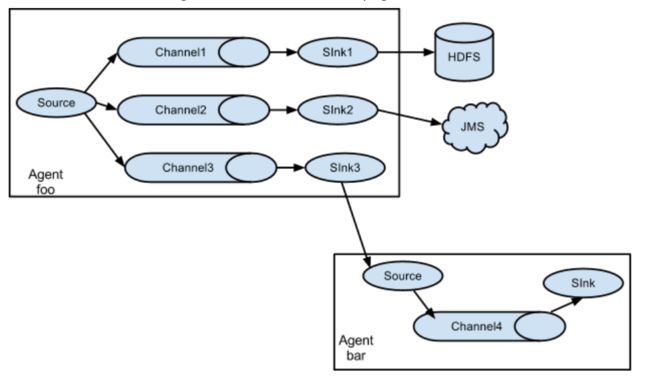
多级agent之间串联
多级channel
3. Flume安装部署
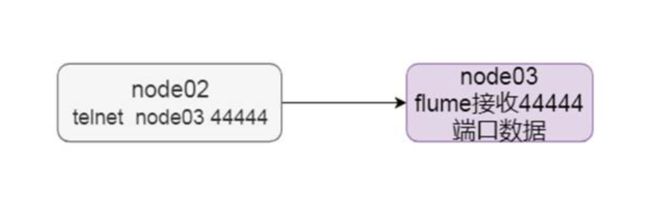
需求:收集网络端口的数据,并将数据打印到linux的控制台上面
第一步:下载解压修改配置文件
Flume的安装非常简单,只需要解压即可,当然,前提是已有hadoop环境
上传安装包到数据源所在节点上
这里我们在第三台机器node03来进行安装
cd /kkb/soft
tar -zxvf flume-ng-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2.tar.gz -C /kkb/install/
cd /kkb/install/apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin/conf
cp flume-env.sh.template flume-env.sh
vim flume-env.sh
修改如下内容
export JAVA_HOME=/kkb/install/jdk1.8.0_141
第二步:开发配置文件
根据数据采集的需求配置采集方案,描述在配置文件中(文件名可任意自定义)
配置我们的网络收集的配置文件(视需求而定)
在flume的conf目录下新建一个配置文件(采集方案)
vim /kkb/install/apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin/conf/netcat-logger.conf
内容如下
# 定义这个agent中各组件的名字
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# 描述和配置source组件:r1
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
# 当前节点的ip地址
a1.sources.r1.bind = node03
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# 描述和配置sink组件:k1
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# 描述和配置channel组件,此处使用是内存缓存的方式
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
# channel中存储的event的最大个数
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
# channel每次从source获得的event最多个数或一次发往sink的event最多个数
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# 描述和配置source channel sink之间的连接关系
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
第三步:启动配置文件
指定采集方案配置文件,在相应的节点上启动flume agent
先用一个最简单的例子来测试一下程序环境是否正常
启动agent去采集数据
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/netcat-logger.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
-c conf 指定flume自身的conf目录中的配置文件
-f conf/netcat-logger.con 指定我们所描述的采集方案
-n a1 指定我们这个agent的名字
-Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console 将info级别的日志打印到控制台
第四步:安装telent准备测试
在node02机器上面安装telnet客户端,用于模拟数据的发送
sudo yum -y install telnet
telnet node03 44444 # 使用telnet模拟数据发送
2. 更多采集案例
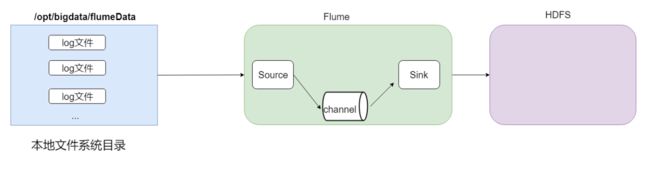
1. 采集目录到HDFS
需求分析
结构示意图:
采集需求:某服务器的某特定目录下,会不断产生新的文件,每当有新文件出现,就需要把文件采集到HDFS中去
根据需求,首先定义以下3大要素
数据源组件,即source ——监控文件目录 : spooldir
spooldir特性:
1、监视一个目录,只要目录中出现新文件,就会采集文件中的内容
2、采集完成的文件,会被agent自动添加一个后缀:COMPLETED
3、此source==可靠==,不会丢失数据;即使flume重启或被kill
要求:
所监视的目录中不允许有同名的文件;且分件被放入spooldir后,就不能修改
①如果文件放入spooldir后,又向文件写入数据,会打印错误及停止
②如果有同名的文件出现在spooldir,也会打印错误及停止
下沉组件,即sink——HDFS文件系统 : hdfs sink
通道组件,即channel——可用file channel 也可以用内存channel
flume配置文件开发
配置文件编写:
cd /kkb/install/apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin/conf
mkdir -p /kkb/install/dirfile
vim spooldir.conf
配置文件编写:
cd /kkb/install/apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin/conf
mkdir -p /kkb/install/dirfile
vim spooldir.conf
内容如下
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
# 注意:不能往监控目中重复丢同名文件
a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir
# 监控的路径
a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /kkb/install/dirfile
a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://node01:8020/spooldir/files/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/
# 指定在hdfs上生成的文件名前缀
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events-
# timestamp向下舍round down
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
# 按10分钟,为单位向下取整;如55分,舍成50;38 -> 30
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
# round的单位
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
# 每3秒滚动生成一个文件
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 3
# 每x字节,滚动生成一个文件
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 20
# 每x个event,滚动生成一个文件
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 5
# 每x个event,flush到hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 1
# 使用本地时间
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#生成的文件类型,默认是Sequencefile,可用DataStream,则为普通文本
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
# channel中存储的event的最大数目
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
# 每次传输数据,从source最多获得event的数目或向sink发送的event的最大的数目
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
Channel参数解释:
capacity:默认该通道中最大的可以存储的event数量
trasactionCapacity:每次最大可以从source中拿到或者送到sink中的event数量
keep-alive:event添加到通道中或者移出的允许时间
启动flume
bin/flume-ng agent -c ./conf -f ./conf/spooldir.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
上传文件到指定目录
将不同的文件上传到下面目录里面去,注意文件不能重名
cd /kkb/install/dirfile
mkdir /home/hadoop/datas
cd /home/hadoop/datas
vim a.txt
# 加入如下内容
ab cd ef
english math
hadoop alibaba
再执行;
cp a.txt /kkb/install/dirfile
然后观察flume的console动静、hdfs webui生成的文件
将同名文件再次放到/kkb/install/dirfile观察现象:
cp a.txt /kkb/install/dirfile
flume控制台报错
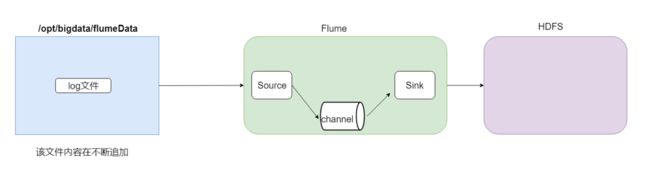
2. 采集文件到HDFS
需求分析:
采集需求:比如业务系统使用log4j生成的日志,日志内容不断增加,需要把==追加到日志文件中的数据实时采集到hdfs==
根据需求,首先定义以下3大要素
采集源,即source——监控文件内容更新 : exec ‘tail -F file’
下沉目标,即sink——HDFS文件系统 : hdfs sink
Source和sink之间的传递通道——channel,可用file channel 也可以用 内存channel
flume的配置文件开发
node03开发配置文件
cd /kkb/install/apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin/conf
vim tail-file.conf
配置文件内容
agent1.sources = source1
agent1.sinks = sink1
agent1.channels = channel1
# Describe/configure tail -F source1
agent1.sources.source1.type = exec
agent1.sources.source1.command = tail -F /kkb/install/taillogs/access_log
agent1.sources.source1.channels = channel1
#configure host for source
#agent1.sources.source1.interceptors = i1
#agent1.sources.source1.interceptors.i1.type = host
#agent1.sources.source1.interceptors.i1.hostHeader = hostname
# Describe sink1
agent1.sinks.sink1.type = hdfs
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.path = hdfs://node01:8020/weblog/flume-collection/%y-%m-%d/%H-%M
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.filePrefix = access_log
# 允许打开的文件数;如果超出5000,老文件会被关闭
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.maxOpenFiles = 5000
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.batchSize= 100
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.writeFormat =Text
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.rollSize = 102400
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.rollCount = 1000000
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.rollInterval = 60
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.round = true
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
agent1.channels.channel1.type = memory
# 向channel添加一个event或从channel移除一个event的超时时间
agent1.channels.channel1.keep-alive = 120
agent1.channels.channel1.capacity = 500000
agent1.channels.channel1.transactionCapacity = 600
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
agent1.sources.source1.channels = channel1
agent1.sinks.sink1.channel = channel1
启动flume
cd /kkb/install/apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/tail-file.conf -n agent1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
开发shell脚本定时追加文件内容
mkdir -p /kkb/install/shells/
cd /kkb/install/shells/
vim tail-file.sh
#!/bin/bash
while true
do
date >> /kkb/install/taillogs/access_log;
sleep 0.5;
done
创建文件夹
mkdir -p /kkb/install/taillogs
启动脚本
chmod u+x tail-file.sh
sh /kkb/install/shells/tail-file.sh
3. flume的tail-dir source实现断点续传功能
不管是上面的spoolDir还是exec Source dir都有一个缺陷就是没法实现==断点续传==的功能,为此在flume1.7当中特地新增加一个source叫做tail-dir source,专门用于解决断点续传的问题,tail-dirsource可以监控文件或者文件夹,允许我们使用正则表达式的方式来对我们的文件或者文件夹进行监听
apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin已增加此功能
需求分析:
采集需求,使用tail-dir source监听某个目录下的多个文件,并且实现文件的断点续传功能
flume配置文件开发
定义flume的配置文件
cd /kkb/install/apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin/conf
mkdir /kkb/install/dirfile
vim tail-dir.conf
内容如下
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
# 以json格式,记录读取的每个文件及读取的position
a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /kkb/install/apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin/taildir_position.json
# 每个filegroup代表一系列待tail的文件
a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1
# 指定filegroup的绝对路径
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /kkb/install/dirfile/.*log.*
# 此项用于控制从一个文件连续读取数据的批次;比如有A、B、C多个文件,如果向A文件写入的频率非常高,导致一直循环的从A中采集获取数据,而B、C的数据不被处理;可将此值调低;每个批次由属性batchSize控制,默认500行
a1.sources.r1.maxBatchCount = 1000
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://node01:8020/taildir/files/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events-
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 3
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 5000
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 50000
# 没x个event flush到hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 5000
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#生成的文件类型,默认是Sequencefile,可用DataStream,则为普通文本
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
启动flume
node03执行以下命令启动flume
cd /kkb/install/apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/tail-dir.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
可观察下taildir_position.json文件中记录的内容
cd /kkb/install/apache-flume-1.6.0-cdh5.14.2-bin
vim taildir_position.json
创建文件
node03执行以下命令创建文件到指定文件夹下
echo "testlog" >> /kkb/install/dirfile/file.log
echo "testlog2" >> /kkb/install/dirfile/file1.log
echo "testlog3" >> /kkb/install/dirfile/file2.log