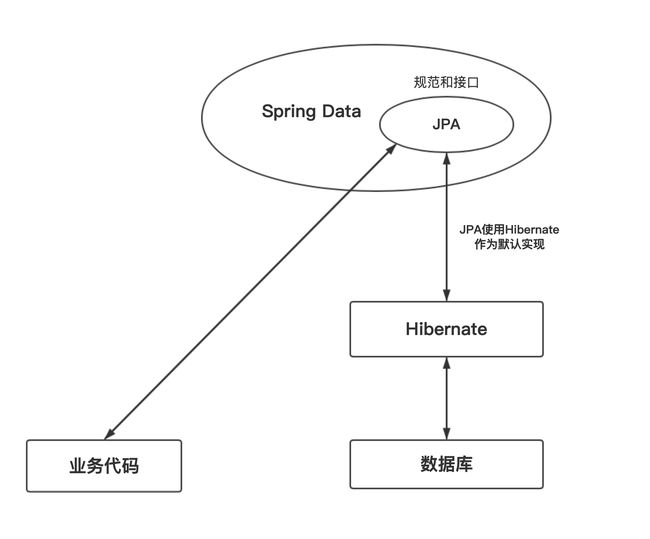
1、认识JPA
JPA(Java Persistence API)是Java的持久化API,用于对象的持久化。它是一个非常强大的ORM持久化的解决方案,免去了使用JDBCTemplate 开发的编写脚本工作。JPA通过简单约定好接口方法的规则自动生成相应的 JPQL 语句,然后映射成 POJO 对象。
JPA是一个规范化接口,封装了 Hibernate 的操作作为默认实现,让用户不通过任何配置即可完成数据库的操作。JPA、SpringData 和 Hibernate的关系如图所示。
2、使用JPA
2.1、Maven依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.4.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
mysql
mysql-connector-java
2.2、配置
spring:
application:
name: jpa-basic
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://148.70.153.63:3306/ttms?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false
username: root
password: password
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jpa:
show-sql: true
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
database: MYSQL
properties:
hibernate:
format_sql: true
主要说明一下 spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto这个属性:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| create | 每次应用启动的时候会重新根据实体建立表,之前的表和数据都会被删除。 |
| create-drop | 和上面的功能一样,但是多了一样,就是在应用关闭的时候,也就是sessionFactory一关闭,会把表删除。 |
| update | 最常用的,第一次启动根据实体建立表结构,之后启动会根据实体的改变更新表结构,之前的数据都在。 |
| validate | 会验证创建数据库表结构,只会和数据库中的表进行比较,不会创建新表,但是会插入新值。 运行程序会校验实体字段与数据库已有的表的字段类型是否相同,不同会报错。 |
2.3、事务的支持
由于SpringBoot2.x版本后,创建 mysql 表默认用的是 myisam 引擎,是不支持事务的。为了支持事务,我们创建表时需要使用 innodb 引擎。很多网上教程使用的是增加如下配置:
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
虽然也能达到效果,但是查看 MySQL5InnoDBDialect 类的源码可以知道,此类已经被 @Deprecated 了,建议使用如下方式:
在 resources 目录下创建 hibernate.properties 文件
# hibernate建表时指定innodb作为存储引擎
hibernate.dialect.storage_engine=innodb
或者在启动时设置为JVM参数,如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("hibernate.dialect.storage_engine", "innodb");
SpringApplication.run(JpaBasicApplication.class, args);
}
2.4、定义实体类
@Entity
@Table(name = "actor")
@Data
public class Actor {
/**
* 采用序列sequence作为主键
* initialValue:初始值
* allocationSize:步进,每次递增的大小
*/
// @Id
// @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE, generator = "actor_sequence")
// @SequenceGenerator(name = "actor_sequence", initialValue = 100, allocationSize = 20, sequenceName = "actor_seq")
// private Long id;
/**
* 主键生成采用数据库自增方式,比如MySQL的AUTO_INCREMENT
*/
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(name = "actor_name", nullable = false, length = 128, unique = true)
private String actorName;
@Column(name = "actor_age", nullable = false)
private int actorAge;
@Column(name = "actor_email", length = 64, unique = true)
private String actorEmail;
@Column(name = "create_time", nullable = false, length = 32)
private String createTime = DateUtil.format(new Date(), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS");
}
注意以上注解使用的是 javax.persistence 包中的。
常用注解解释:
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Entity | 声明类为实体 |
| @Table | 声明表名,一般和@Entity一块使用,如果表名和实体类名相同,那么@Table可以省略 |
| @Id | 指定主键字段 |
| @GeneratedValue | 指定主键的生成策略,主要有TABLE、SEQUENCE、IDENTITY、AUTO这几种 |
| @Transient | 指定忽略的字段,不做持久化,一般用于排除非表中的字段 |
| @Column | 指定属性对应的表中字段名和约束条件 |
| @SequenceGenerator | 一般和@GeneratedValue一块使用。 如果主键生成策略是SEQUENCE,那么可以用这个注解来定义如何创建序列 |
| @Basic | 指定实体属性的加载方式,比如@Basic(fetch = FetchType.LAZY) |
2.5、自动建表
启动项目,查看控制台,发现会有建表语句输出:
Hibernate:
create table actor (
id bigint not null auto_increment,
actor_age integer not null,
actor_email varchar(64),
actor_name varchar(128) not null,
create_time varchar(32) not null,
primary key (id)
) engine=InnoDB
查看数据库,可以看到表已经建立好了。当然在一些情况下,我们并不希望使用JPA自动为我们创建的表,我们可以先提前建好表,最后再根据表结构定义实体类。
3、新增和删除
3.1、创建Repository
public interface ActorSaveAndDeleteRepository extends JpaRepository {
}
需要继承 JpaRepository,并指定表对应的实体类和主键类型。这里不需要写任何具体的实现方法或sql就能完成我们需要的操作。
3.2、Service
@Service
@Transactional
public class ActorSaveAndDeleteServiceImpl implements ActorSaveAndDeleteService {
@Autowired
private ActorSaveAndDeleteRepository actorSaveAndDeleteRepository;
/**
* 新增1条数据
*
* @param actorName
* @param actorAge
* @param actorEmail
* @return
*/
@Override
public Actor save(String actorName, int actorAge, String actorEmail) {
Actor actor = new Actor();
actor.setActorName(actorName);
actor.setActorAge(actorAge);
actor.setActorEmail(actorEmail);
Actor storeObj = actorSaveAndDeleteRepository.save(actor);
return storeObj;
}
/**
* 批量新增
*/
@Override
public void batchSave() {
List actors = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
Actor actor = new Actor();
actor.setActorName("name:" + RandomUtil.randomString(5));
actor.setActorAge(RandomUtil.randomInt(1, 100));
actor.setActorEmail("email:" + RandomUtil.randomString(5));
actors.add(actor);
}
actorSaveAndDeleteRepository.saveAll(actors);
}
/**
* 删除指定id的一条数据
*
* @param id
*/
@Override
public void delete(Long id) {
actorSaveAndDeleteRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
@Transactional注解用于开启事务。
3.3、测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class ActorSaveAndDeleteTest {
@Autowired
private ActorSaveAndDeleteService actorSaveAndDeleteService;
@Test
public void testSave() {
Actor actor = actorSaveAndDeleteService.save("高庸涵", 28, "[email protected]");
log.info(JSONUtil.toJsonPrettyStr(actor));
}
@Test
public void testBatchSave() {
actorSaveAndDeleteService.batchSave();
}
@Test
public void testDelete() {
actorSaveAndDeleteService.delete(10L);
}
}
3.4、结果查看
可以看到控制台会有如下sql输出,最后查看数据库确实已经有数据插入。
Hibernate:
insert
into
actor
(actor_age, actor_email, actor_name, create_time)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
{
"actorAge": 28,
"createTime": "2020-11-21 22:37:32 541",
"actorEmail": "[email protected]",
"actorName": "高庸涵",
"id": 1
}
这里我们完全不需要写sql就可以达到操作数据库的效果,原因在于JPA已经把常用的方法已经封装好了,我们只需要去继承就可以获得这些方法,最后在执行时会自动把这些方法转换成相应的sql去执行。
4、更新数据库
4.1、创建Repository
public interface ActorUpdateRepository extends JpaRepository {
/**
* JPQL更新数据
*
* @param email
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Modifying
@Query("update Actor a set a.actorEmail = ?1 where a.id = ?2")
int updateActorEmailById(String email, Long id);
/**
* 使用原生sql批量更新
*
* @return
*/
@Modifying
@Query(value = "update actor a set a.create_time = ?1 where a.id >= ?2", nativeQuery = true)
int updateCreateTimeById(String createTime, Long id);
}
第1种是使用 JPQL 方式,表名需要用实体类名来表示,字段也需要用实体类中的属性来表示,参数序号需要一一对应。@Modifying 注解表示这是一个更新数据的操作。JPA会把 JPQL 翻译成sql去执行。
第2种是使用原生sql的方式,用nativeQuery = true这个属性来表示是否为原生sql。
4.2、Service
@Service
@Transactional
public class ActorUpdateServiceImpl implements ActorUpdateService {
@Autowired
private ActorUpdateRepository actorUpdateRepository;
/**
* 使用JPQL语句更新数据
*
* @param email
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Override
public int updateActorEmailById(String email, Long id) {
return actorUpdateRepository.updateActorEmailById(email, id);
}
/**
* 使用原生sql批量更新数据
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Override
public int updateCreateTimeById(Long id) {
String createTime = DateUtil.format(new Date(), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS");
return actorUpdateRepository.updateCreateTimeById(createTime, id);
}
}
4.3、测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class ActorUpdateTest {
@Autowired
private ActorUpdateService actorUpdateService;
@Test
public void testUpdateActorEmailById() {
int row = actorUpdateService.updateActorEmailById("[email protected]", 1L);
log.info("更新数量:{}", row);
}
@Test
public void testUpdateCreateTimeById() {
int row = actorUpdateService.updateCreateTimeById(2L);
log.info("更新数量:{}", row);
}
}
Hibernate:
update
actor
set
actor_email=?
where
id=?
更新数量:1
Hibernate:
update
actor a
set
a.create_time = ?
where
a.id >= ?
更新数量:99
5、查询数据库
5.1、使用约定方法名查询
约定方法名一定要根据命名规范来写,JPA会根据前缀、中间连接词(Or、And、Like、NotNull等类似SQL中的关键字)、内部拼接SQL代理生成方法的实现。约定方法名的方法如下表:
| SQL | 方法例子 | JPQL语句 |
|---|---|---|
| and | findByNameAndAge | where x.name = ?1 and x.age = ?2 |
| or | findByNameOrAge | where x.name = ?1 or x.age = ?2 |
| = | findByName | where x.name = ?1 |
| between xxx and xxx | findByStartDateBetween | where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
| < | findByAgeLessThan | where x.age < ?1 |
| <= | findByAgeLessThanEqual | where x.age <= ?1 |
| > | findByAgeGreaterThan | where x.age > ?1 |
| >= | findByAgeGreaterThanEqual | where x.age >= ?1 |
| > | findByStartDateAfter | where x.startDate > ?1 |
| < | findByStartDateBefore | where x.startDate < ?1 |
| is null | findByAgeIsNull | where x.age is null |
| is not null | findByAgeNotNull | where x.age not null |
| like | findByNameLike | where x.name like ?1 |
| not like | findByNameNotLike | where x.name not like ?1 |
| like 'xxx%' | findByNameStartingWith | where x.name like ?1 参数后需要带有 % 号 |
| like '%xxx' | findByNameEndingWith | where x.name like ?1 参数前需要带有 % 号 |
| like '%xxx%' | findByNameContaining | where x.name like ?1 参数需要被 % 号包装 |
| order by | findByNameOrderByAgeDesc | where x.name = ?1 order by age desc |
| <> | findByAgeNot | where x.age <> ?1 |
| int() | findByAgeIn(Collection |
where x.age in ?1 |
| not int() | findByAgeNotIn(Collection |
where x.age not in ?1 |
约定方法名还支持以下几种用法:
PagequeryFirst100ByName(String name, Pageable pageable) ListfindTop100ByName(String name, Pageable pageable)
5.1.1、测试使用方法名映射成sql查询单条数据
public interface ActorFindRepository extends JpaRepository {
/**
* 使用方法名映射成sql查询单条数据,如果查询到多条数据则会报错
* 等价于 where actor_name = ? and actor_email = ?
*
* @param name
* @param email
* @return
*/
Actor findByActorNameAndActorEmail(String name, String email);
}
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class ActorFindTest {
@Autowired
private ActorFindRepository actorFindRepository;
/**
* 测试使用方法名映射成sql查询单条数据
*/
@Test
public void testFindByActorNameAndActorEmail() {
Actor actor = actorFindRepository.findByActorNameAndActorEmail("高庸涵", "[email protected]");
log.info(JSONUtil.toJsonPrettyStr(actor));
}
}
5.1.2、测试使用方法名映射成sql查询多条数据并排序
/**
* 使用方法名映射成sql查询多条数据并排序
* 等价于 where actor_name like 'xxx%' and id >= ? order by actor_age
*
* @param name
* @param id
* @return
*/
List findByActorNameStartingWithAndIdGreaterThanEqualOrderByActorAge(String name, Long id);
/**
* 测试使用方法名映射成sql查询多条数据并排序
*/
@Test
public void testFindByLikeActorName() {
List actorList = actorFindRepository.findByActorNameStartingWithAndIdGreaterThanEqualOrderByActorAge("name", 50L);
log.info(JSONUtil.toJsonPrettyStr(actorList));
}
5.1.3、测试带条件查询并排序
/**
* 使用方法名映射成sql,带条件查询并排序
*
* @param id
* @param sort
* @return
*/
List findByIdGreaterThanEqual(Long id, Sort sort);
/**
* 测试带条件查询并排序
*/
@Test
public void testFindBySort() {
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "actorAge");
List actorList = actorFindRepository.findByIdGreaterThanEqual(90L, sort);
log.info(JSONUtil.toJsonPrettyStr(actorList));
}
注意排序字段是实体类中的属性字段而不是表中的字段名。如果对于多个字段排序方式不同,可以用如下方式构建 Sort 排序对象:
List orders = new ArrayList<>();
orders.add(new Sort.Order((Sort.Direction.DESC), "id"));
orders.add(new Sort.Order((Sort.Direction.ASC), "actorAge"));
Sort sort = Sort.by(orders);
5.1.4、测试带条件分页查询并排序
/**
* 使用方法名映射成sql,带条件查询分页并排序
*
* @param id
* @param pageable
* @return
*/
Page findByIdGreaterThanEqual(Long id, Pageable pageable);
/**
* 带条件分页查询并排序
*/
@Test
public void testFindByPagination() {
// 指定排序,等价于 order by actor_age,create_time
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "actorAge", "createTime");
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(0, 10, sort);
// Page actorPage = actorRepository.findAll(pageRequest); // 不带条件分页查询
Page actorPage = actorFindRepository.findByIdGreaterThanEqual(1L, pageRequest); // 带条件分页查询
log.info("共有:[{}]数据,共有:[{}]页", actorPage.getTotalElements(), actorPage.getTotalPages());
List actorListByPagination = actorPage.getContent();
log.info(JSONUtil.toJsonPrettyStr(actorListByPagination));
}
5.2、使用JPQL分页查询并排序
/**
* 使用JPQL分页查询
*
* @param id
* @param pageable
* @return
*/
@Query("from Actor a where a.id >= ?1")
Page findByPaginationWithJPQL(Long id, Pageable pageable);
/**
* 测试带条件分页查询并排序,用JPQL方式
*/
@Test
public void testFindByPaginationWithJPQL() {
// 指定的字段需要和实体类中属性相同,而非表中字段
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "actorAge", "createTime");
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(0, 10, sort);
Page actorPage = actorFindRepository.findByPaginationWithJPQL(1L, pageRequest);
log.info("共有:[{}]数据,共有:[{}]页", actorPage.getTotalElements(), actorPage.getTotalPages());
List actorListByPagination = actorPage.getContent();
log.info(JSONUtil.toJsonPrettyStr(actorListByPagination));
}
5.3、使用原生sql分页查询
/**
* 使用原生sql分页查询
*
* @param id
* @param pageable
* @return
*/
@Query(value = "select * from actor where id >= ?1", nativeQuery = true)
Page findByPaginationWithSql(Long id, Pageable pageable);
/**
* 测试带条件分页查询并排序,用原生sql方式
*/
@Test
public void testFindByPaginationWithSql() {
// 如果使用原生sql,指定的字段就需要和表中字段相同
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "actor_age", "create_time");
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(0, 10, sort);
Page actorPage = actorFindRepository.findByPaginationWithSql(1L, pageRequest);
log.info("共有:[{}]数据,共有:[{}]页", actorPage.getTotalElements(), actorPage.getTotalPages());
List actorListByPagination = actorPage.getContent();
log.info(JSONUtil.toJsonPrettyStr(actorListByPagination));
}
注意如果使用原生sql方式,排序指定的字段须为表中字段。
代码地址
- github:https://github.com/senlinmu1008/jpa-action/tree/master/jpa-basic
- gitee:https://gitee.com/ppbin/jpa-action/tree/master/jpa-basic