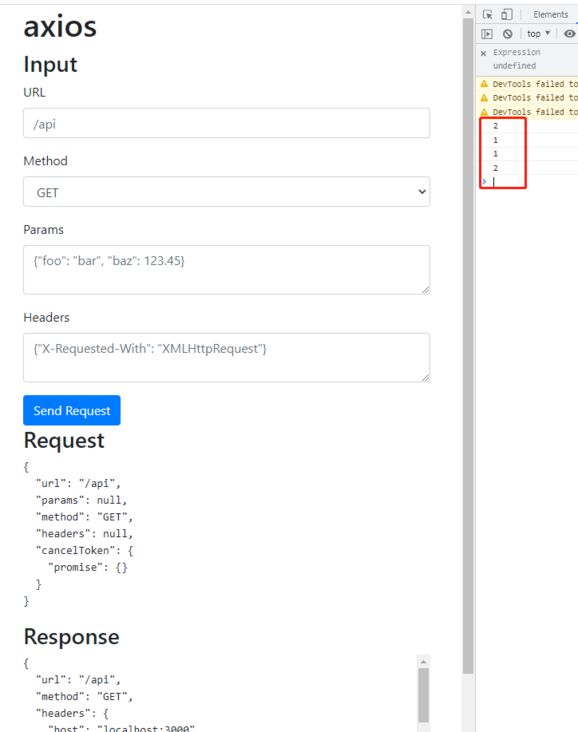
1. 拦截器使用方法
// 请求拦截器1
axios.interceptors.request.use(options => {
console.log('1')
return options
})
// 请求拦截器2
axios.interceptors.request.use(options => {
console.log('2')
return options
})相应拦截器
// 相应拦截器1
axios.interceptors.response.use(options => {
console.log('2')
return options
})
// 响应拦截器2
axios.interceptors.response.use(options => {
console.log('1')
return options
})发送请求
axios(options).then(function (res) {}).catch(function (res) {});注意点:请求拦截器先加入的后执行,响应拦截器先加入的先执行
2. 拦截器对应源码实现
axios.interceptors.response.use调用的对应函数\lib\core\InterceptorManager.js
InterceptorManager.prototype.use = function use(fulfilled, rejected, options) {
this.handlers.push({
fulfilled: fulfilled,
rejected: rejected,
synchronous: options ? options.synchronous : false,
runWhen: options ? options.runWhen : null
});
return this.handlers.length - 1;
};接收拦截器执行成功回调,失败回调和配置参数,上方示例只添加了拦截器执行成功回调,相当于rejected是undefined, return this.handlers.length - 1 返回当前拦截器的id,方便后续取消拦截器
顺便看下拦截器的取消
InterceptorManager.prototype.eject = function eject(id) {
if (this.handlers[id]) {
this.handlers[id] = null;
}
};将对应id的拦截器置为空,想取消拦截器即可调用axios.interceptors.request.eject(1),这里取消了索引为1,即第二个请求拦截器
拦截器与真正请求的组合调用方式
axios(options).then(function (res) {}).catch(function (res) {});发送请求时,执行了Axios.prototype.request
Axios.prototype.request = function request(config) {
// filter out skipped interceptors
var requestInterceptorChain = [];
var synchronousRequestInterceptors = true;
this.interceptors.request.forEach(function unshiftRequestInterceptors(interceptor) {
// options ? options.synchronous : false,
synchronousRequestInterceptors = synchronousRequestInterceptors && interceptor.synchronous;
// 向数组开头添加(多个参数表示多个元素)
// 为什么直接访问了interceptor.fulfilled而不是interceptor.handlers.fulfilled,
requestInterceptorChain.unshift(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected);
});
var responseInterceptorChain = [];
this.interceptors.response.forEach(function pushResponseInterceptors(interceptor) {
responseInterceptorChain.push(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected);
});
var promise;
if (!synchronousRequestInterceptors) {
var chain = [dispatchRequest, undefined];
// unshift() 方法可向数组的开头添加一个或更多元素,并返回新的长度。
Array.prototype.unshift.apply(chain, requestInterceptorChain);
chain.concat(responseInterceptorChain);
/* 将现有对象转为 Promise 对象
Promise.resolve('foo')
// 等价于
new Promise(resolve => resolve('foo')) */
promise = Promise.resolve(config);
while (chain.length) {
// 调用拦截器,请求连
promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift());
}
return promise;
}
var newConfig = config;
while (requestInterceptorChain.length) {
// 删除第一个元素并返回第一个元素
var onFulfilled = requestInterceptorChain.shift();
var onRejected = requestInterceptorChain.shift();
try {
newConfig = onFulfilled(newConfig);
} catch (error) {
onRejected(error);
break;
}
}
try {
promise = dispatchRequest(newConfig);
} catch (error) {
return Promise.reject(error);
}
while (responseInterceptorChain.length) {
promise = promise.then(responseInterceptorChain.shift(), responseInterceptorChain.shift());
}
return promise;
};上方源码只粘贴了主要代码
分别遍历请求拦截器个响应拦截器,像请求拦截器数组前方和响应拦截器后方依次添加拦截器成功回调和失败回调,定义一个真正发起请求时执行的函数数组var chain = [dispatchRequest, undefined];分别在前方加入请求拦截器,后方加入返回拦截器,最后chain形如
[请求拦截器成功回调函数, 请求拦截器失败回调函数,dispatchRequest,undefined,响应拦截器成功回调函数,响应拦截器失败回调函数]遍历chain 依次用promise链去执行:如:
while (chain.length) {
// 调用拦截器,请求连
promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift());
}测试执行过程
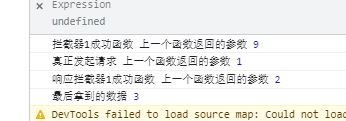
let fun1 = function (e) {
console.log('拦截器1成功函数', '上一个函数返回的参数', e)
return 1
}
let fun2 = function (e) {
console.log('真正发起请求', '上一个函数返回的参数', e)
return 2
}
let fun3 = function (e) {
console.log('响应拦截器1成功函数', '上一个函数返回的参数', e)
return 3
}
let arr = [fun1, undefined, fun2, undefined, fun3, undefined]
let promise = Promise.resolve(9);
while (arr.length) {
promise = promise.then(arr.shift(), arr.shift());
}
promise.then(res => {
console.log('最后拿到的数据', res)
})更多关于axios的详细解析:若川大佬的源码解析系列