Spring Boot在内部启动了一个嵌入式Web容器。
Tomcat是组件化设计,所以就是启动这些组件。
Tomcat独立部署模式是通过startup脚本启动,Tomcat中的Bootstrap和Catalina会负责初始化类加载器,并解析server.xml和启动这些组件。
内嵌模式,Bootstrap和Catalina的工作由Spring Boot代劳,Spring Boot调用Tomcat API启动这些组件。
Spring Boot中Web容器相关接口
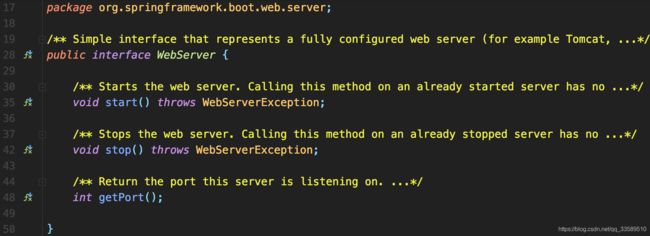
WebServer
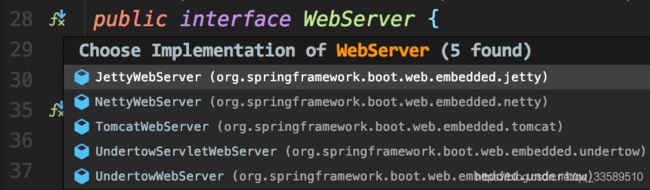
为支持各种Web容器,Spring Boot抽象出嵌入式Web容器,定义WebServer接口:
Web容器比如Tomcat、Jetty去实现该接口
ServletWebServerFactory
创建Web容器,返回的就是上面提到的WebServer。
public interface ServletWebServerFactory {
WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers);
}
ServletContextInitializer入参表示ServletContext的初始化器,用于ServletContext中的一些配置:
public interface ServletContextInitializer {
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException;
}
getWebServer会调用ServletContextInitializer#onStartup,即若想在Servlet容器启动时做一些事情,比如注册自己的Servlet,可以实现一个ServletContextInitializer,在Web容器启动时,Spring Boot会把所有实现ServletContextInitializer接口的类收集起来,统一调其onStartup。
WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor
一个BeanPostProcessor,为定制化嵌入式Web容器,在postProcessBeforeInitialization过程中去寻找Spring容器中WebServerFactoryCustomizer类型的Bean,并依次调用WebServerFactoryCustomizer接口的customize方法做一些定制化。
public interface WebServerFactoryCustomizer{ void customize(T factory); }
创建、启动嵌入式Web容器
Spring的ApplicationContext,其抽象实现类AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
用来新建或刷新一个ApplicationContext,在refresh中会调用onRefresh,AbstractApplicationContext的子类可以重写onRefresh实现Context刷新逻辑。
因此重写 ServletWebServerApplicationContext#onRefresh 创建嵌入式Web容器:
重写onRefresh方法,调用createWebServer创建和启动Tomcat。
createWebServer
private void createWebServer() {
// WebServer是Spring Boot抽象出来的接口,具体实现类就是不同Web容器
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
// 若Web容器尚未创建
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
// 通过Web容器工厂创建
ServletWebServerFactory factory = this.getWebServerFactory();
// 传入一个"SelfInitializer"
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(new ServletContextInitializer[]{this.getSelfInitializer()});
} else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
this.getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
} catch (ServletException var4) {
...
}
}
this.initPropertySources();
}
getWebServer
以Tomcat为例,主要调用Tomcat的API去创建各种组件:
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
// 1.实例化一个Tomcat【Server组件】
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
// 2. 创建一个临时目录
File baseDir = this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory : this.createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
// 3.初始化各种组件
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
this.customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
this.configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
// 4. 创建定制版的"Context"组件
this.prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return this.getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
prepareContext的Context指Tomcat的Context组件,为控制Context组件行为,Spring Boot自定义了TomcatEmbeddedContext类,继承Tomcat的StandardContext:
注册Servlet
有@RestController,为什么还要自己去注册Servlet给Tomcat?
可能有些场景需要注册你自己写的一个Servlet提供辅助功能,与主程序分开。
Sprong Boot 不注册Servlet 给Tomcat 直接用 @Controller 就能实现Servlet功能是为啥呢?
因为Sprong Boot默认给我们注册了DispatcherSetvlet。
Servlet注解
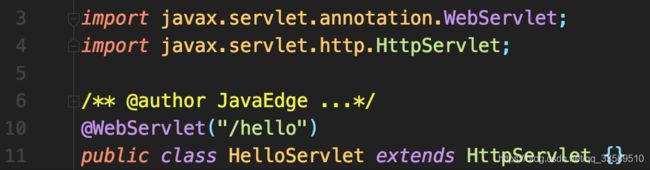
在Spring Boot启动类上加上 @ServletComponentScan 注解后,使用@WebServlet、@WebFilter、@WebListener标记的Servlet、Filter、Listener就可以自动注册到Servlet容器。
在Web应用的入口类上加上@ServletComponentScan,并且在Servlet类上加上@WebServlet,这样Spring Boot会负责将Servlet注册到内嵌的Tomcat中。
ServletRegistrationBean
Spring Boot提供了
- ServletRegistrationBean
- FilterRegistrationBean
- ServletListenerRegistrationBean
分别用来注册Servlet、Filter、Listener。
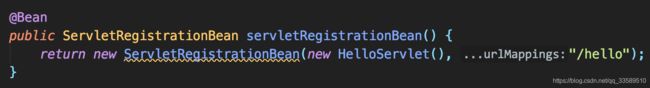
假如要注册一个Servlet:
返回一个ServletRegistrationBean,并将它当作Bean注册到Spring,因此你需要把这段代码放到Spring Boot自动扫描的目录中,或者放到**@Configuration**标识的类中。
Spring会把这种类型的Bean收集起来,根据Bean里的定义向Tomcat注册Servlet。
动态注册
可以创建一个类去实现ServletContextInitializer接口,并把它注册为一个Bean,Spring Boot会负责调用这个接口的onStartup。
实现ServletContextInitializer接口的类会被spring管理,而不是被Servlet容器管理。
@Component
public class MyServletRegister implements ServletContextInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) {
// Servlet 3.0规范新的API
ServletRegistration myServlet = servletContext
.addServlet("HelloServlet", HelloServlet.class);
myServlet.addMapping("/hello");
myServlet.setInitParameter("name", "Hello Servlet");
}
}
ServletRegistrationBean也是通过ServletContextInitializer实现的,它实现了ServletContextInitializer接口。
注意到onStartup方法的参数是我们熟悉的ServletContext,可以通过调用它的addServlet方法来动态注册新的Servlet,这是Servlet 3.0以后才有的功能。
通过 ServletContextInitializer 接口可以向 Web 容器注册 Servlet,实现 ServletContextInitializer 接口的Bean被speing管理,但是在什么时机触发其onStartup()方法的呢?
通过 Tomcat 中的 ServletContainerInitializer 接口实现者,如TomcatStarter,创建tomcat时设置了该类,在tomcat启动时会触发ServletContainerInitializer实现者的onStartup()方法,在这个方法中触发ServletContextInitializer接口的onStartup()方法,如注册DispatcherServlet。
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean实现了ServletContextInitializer接口,它的作用就是向Tomcat注册DispatcherServlet,那它是在什么时候、如何被使用的呢?
prepareContext方法调用了另一个私有方法configureContext,这个方法就包括了往Tomcat的Context添加ServletContainerInitializer对象:
context.addServletContainerInitializer(starter, NO_CLASSES);
其中有DispatcherServletRegistrationBean。
定制Web容器
如何在Spring Boot中定制Web容器。在Spring Boot 2.0中可通过如下方式:
ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory
通用的Web容器工厂,定制Web容器通用参数:
@Component public class MyGeneralCustomizer implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer{ public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) { factory.setPort(8081); factory.setContextPath("/hello"); } }
TomcatServletWebServerFactory
通过特定Web容器工厂进一步定制。
给Tomcat增加一个Valve,这个Valve的功能是向请求头里添加traceid,用于分布式追踪。
class TraceValve extends ValveBase {
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
request.getCoyoteRequest().getMimeHeaders().
addValue("traceid").setString("1234xxxxabcd");
Valve next = getNext();
if (null == next) {
return;
}
next.invoke(request, response);
}
}
跟方式一类似,再添加一个定制器:
@Component
public class MyTomcatCustomizer implements
WebServerFactoryCustomizer {
@Override
public void customize(TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory) {
factory.setPort(8081);
factory.setContextPath("/hello");
factory.addEngineValves(new TraceValve() );
}
}
到此这篇关于SpringBoot启动嵌入式Tomcat的实现步骤的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot启动嵌入式Tomcat内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!