本系列是 我TM人傻了 系列第五期[捂脸],往期精彩回顾:
本篇文章涉及底层设计以及原理,以及问题定位和可能的问题点,非常深入,篇幅较长,所以拆分成上中下三篇:
- 上:问题简单描述以及 Spring Cloud Gateway 基本结构和流程以及底层原理
- 中:Spring Cloud Sleuth 如何在 Spring Cloud Gateway 加入的链路追踪以及为何会出现这个问题
- 下:现有 Spring Cloud Sleuth 的非侵入设计带来的性能问题,其他可能的问题点,以及如何解决
我们的网关使用的是 Spring Cloud Gateway,并且加入了 spring-cloud-sleuth 的依赖,用于链路追踪。并且通过 log4j2 的配置,将链路信息输出到日志中,相关的占位符是:
%X{traceId},%X{spanId}但是最近发现,日志中链路信息出现丢失的情况,这是怎么回事呢?
Spring Cloud Gateway 的基本流程与实现
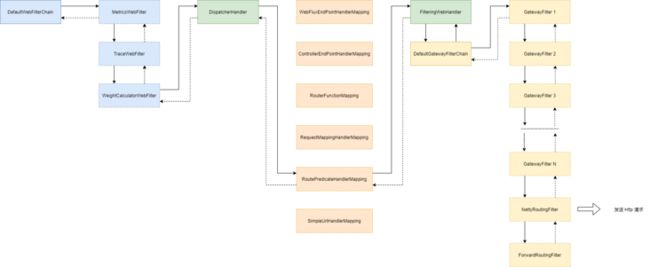
首先简单介绍一下 Spring Cloud Gateway 的基本结构,以及 Spring Cloud Sleuth 是如何在其中嵌入链路追踪相关代码的。加入 Spring Cloud Sleuth 以及 Prometheus 相关依赖之后, Spring Cloud Gateway 的处理流程如下所示:
Spring Cloud Gateway 是基于 Spring WebFlux 开发的异步响应式网关,异步响应式代码比较难以理解和阅读,我这里给大家分享一种方法去理解,通过这个流程来理解 Spring Cloud Gateway 的工作流程以及底层原理。其实可以理解为,上图这个流程,就是拼出来一个完整的 Mono(或者 Flux)流,最后 subscribe 执行。
当收到一个请求的时候,会经过 org.springframework.web.server.handler.DefaultWebFilterChain,这是 WebFilter 的调用链,这个链路包括三个 WebFilter:
org.springframework.boot.actuate.metrics.web.reactive.server.MetricsWebFilter:添加 Prometheus 相关依赖之后,会有这个 MetricsWebFilter,用于记录请求处理耗时,采集相关指标。org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.instrument.web.TraceWebFilter:添加 Spring Cloud Sleuth 相关依赖之后,会有这个 TraceWebFilter。org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.WeightCalculatorWebFilter:Spring Cloud Gateway 路由权重相关配置功能相关实现类,这个我们这里不关心。
在这个 DefaultWebFilterChain 会形成这样一个 Mono,我们依次将他们标记出来,首先是入口代码 org.springframework.web.server.handler.DefaultWebFilterChain#filter:
public Mono filter(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return Mono.defer(() ->
// this.currentFilter != null 代表 WebFilter 链还没有结束
// this.chain != null 代表 WebFilter 链不为空
this.currentFilter != null && this.chain != null ?
//在 WebFilter 链没有结束的情况下,调用 WebFilter
invokeFilter(this.currentFilter, this.chain, exchange) :
//在 WebFilter 结束的情况下,调用 handler
this.handler.handle(exchange));
} 对于我们这里的 WebFilter 链的第一个 MetricsWebFilter,假设启用了对应的采集统计的话,这时候生成的 Mono 就是:
return Mono.defer(() ->
chain.filter(exchange).transformDeferred((call) -> {
long start = System.nanoTime();
return call
//成功时,记录响应时间
.doOnSuccess((done) -> MetricsWebFilter.this.onSuccess(exchange, start))
//失败时,记录响应时间和异常
.doOnError((cause) -> MetricsWebFilter.this.onError(exchange, start, cause));
});
);这里为了方便,我们对代码做了简化,由于我们要将整个链路的所有 Mono 和 Flux 拼接在一起行程完整链路,所以原本是 MetricsWebFilter中的 onSuccess(exchange, start)方法,被改成了 MetricsWebFilter.this.onSuccess(exchange, start) 这种伪代码。
接着,根据DefaultWebFilterChain 的源码分析,chain.filter(exchange) 会继续 WebFilter 链路,到达下一个 WebFilter,即 TraceWebFilter。经过 TraceWebFilter,Mono 就会变成:
return Mono.defer(() ->
new MonoWebFilterTrace(source, chain.filter(exchange), TraceWebFilter.this.isTracePresent(), TraceWebFilter.this, TraceWebFilter.this.spanFromContextRetriever()).transformDeferred((call) -> {
//MetricsWebFilter 相关的处理,在前面的代码中给出了,这里省略
});
);可以看出,在 TraceWebFilter 中,整个内部 Mono (chain.filter(exchange) 后续的结果)都被封装成了一个 MonoWebFilterTrace,这也是保持链路追踪信息的关键实现。
继续 WebFilter 链路,经过最后一个 WebFilter WeightCalculatorWebFilter; 这个 WebFilter 我们不关心,里面对路由权重做了一些计算操作,我们这里直接忽略即可。这样我们就走完了所有 WebFilter 链路,来到了最后的调用 DefaultWebFilterChain.this.handler,这个 handler 就是 org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler。在 DispatcherHandler 中,我们会计算出路由并发送请求到符合条件的 GatewayFilter。经过 DispatcherHandler,Mono 会变成:
return Mono.defer(() ->
new MonoWebFilterTrace(source,
Flux.fromIterable(DispatcherHandler.this.handlerMappings) //读取所有的 handlerMappings
.concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange)) //按顺序调用所有的 handlerMappings 的 getHandler 方法,如果有对应的 Handler 会返回,否则返回 Mono.empty();
.next() //找到第一个返回不是 Mono.empty() 的 Handler
.switchIfEmpty(DispatcherHandler.this.createNotFoundError()) //如果没有返回不为 Mono.empty() 的 handlerMapping,则直接返回 404
.flatMap(handler -> DispatcherHandler.this.invokeHandler(exchange, handler)) //调用对应的 Handler
.flatMap(result -> DispatcherHandler.this.handleResult(exchange, result)), //处理结果
TraceWebFilter.this.isTracePresent(), TraceWebFilter.this, TraceWebFilter.this.spanFromContextRetriever()).transformDeferred((call) -> {
//MetricsWebFilter 相关的处理,在前面的代码中给出了,这里省略
});
);
handlerMappings 包括:
org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.web.reactive.WebFluxEndPointHandlerMapping:由于我们项目中添加了 Actuator 相关依赖,所以这里有这个 HandlerMapping。Actuator 相关路径映射,不是我们这里关心的。但是可以看出,Actuator 相关路径优先于 Spring Cloud Gateway 配置路由org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.web.reactive.ControllerEndpointHandlerMapping:由于我们项目中添加了 Actuator 相关依赖,所以这里有这个 HandlerMapping。使用 @ControllerEndpoint 或者 @RestControllerEndpoint 注解标注的 Actuator 相关路径映射,不是我们这里关心的。org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.support.RouterFunctionMapping:在 Spring-WebFlux 中,你可以定义很多不同的 RouterFunction 来控制路径路由,但这也不是我们这里关心的。但是可以看出,自定义的 RouterFunction 会优先于 Spring Cloud Gateway 配置路由org.springframework.web.reactive.result.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping:针对 @RequestMapping 注解的路径的 HandlerMapping,不是我们这里关心的。但是可以看出,如果你在 Spring Cloud Gateway 中指定 RequestMapping 路径,会优先于 Spring Cloud Gateway 配置路由。org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.RoutePredicateHandlerMapping:这个是 Spring Cloud Gateway 的 HandlerMapping,会读取 Spring Cloud Gateway 配置并生成路由。这个是我们这里要详细分析的。
其实这些 handlerMappings,我们这里肯定走的是 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 的相关逻辑,所以我们的 Mono 又可以简化成:
return Mono.defer(() ->
new MonoWebFilterTrace(source,
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.getHandler(exchange)
.switchIfEmpty(DispatcherHandler.this.createNotFoundError()) //如果没有返回不为 Mono.empty() 的 handlerMapping,则直接返回 404
.flatMap(handler -> DispatcherHandler.this.invokeHandler(exchange, handler)) //调用对应的 Handler
.flatMap(result -> DispatcherHandler.this.handleResult(exchange, result)), //处理结果
TraceWebFilter.this.isTracePresent(), TraceWebFilter.this, TraceWebFilter.this.spanFromContextRetriever()).transformDeferred((call) -> {
//MetricsWebFilter 相关的处理,在前面的代码中给出了,这里省略
});
);我们来看 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping,首先这些 handlerMapping 都是继承了抽象类 org.springframework.web.reactive.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping, 前面我们拼接的 Mono 里面的 getHandler 的实现其实就在这个抽象类中:
public Mono可以看出,其实核心就是每个实现类的 getHandlerInternal(exchange) 方法,所以在我们拼接的 Mono 中,我们会忽略抽象类中的针对 handler 之后的 map 处理。
return Mono.defer(() ->
new MonoWebFilterTrace(source,
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.getHandlerInternal(exchange)
.switchIfEmpty(DispatcherHandler.this.createNotFoundError()) //如果没有返回不为 Mono.empty() 的 handlerMapping,则直接返回 404
.flatMap(handler -> DispatcherHandler.this.invokeHandler(exchange, handler)) //调用对应的 Handler
.flatMap(result -> DispatcherHandler.this.handleResult(exchange, result)), //处理结果
TraceWebFilter.this.isTracePresent(), TraceWebFilter.this, TraceWebFilter.this.spanFromContextRetriever()).transformDeferred((call) -> {
//MetricsWebFilter 相关的处理,在前面的代码中给出了,这里省略
});
);接下来经过 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 的 getHandlerInternal(exchange) 方法,我们的 Mono 变成了:
return Mono.defer(() ->
new MonoWebFilterTrace(source,
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.lookupRoute(exchange) //根据请求寻找路由
.flatMap((Function>) r -> {
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR, r); //将路由放入 Attributes 中,后面我们还会用到
return Mono.just(RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.webHandler); //返回 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 的 FilteringWebHandler
}).switchIfEmpty( //如果为 Mono.empty(),也就是没找到路由
Mono.empty() //返回 Mono.empty()
.then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> { //返回 Mono.empty() 之后,记录日志
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No RouteDefinition found for [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "]");
}
})))
.switchIfEmpty(DispatcherHandler.this.createNotFoundError()) //如果没有返回不为 Mono.empty() 的 handlerMapping,则直接返回 404
.flatMap(handler -> DispatcherHandler.this.invokeHandler(exchange, handler)) //调用对应的 Handler
.flatMap(result -> DispatcherHandler.this.handleResult(exchange, result)), //处理结果
TraceWebFilter.this.isTracePresent(), TraceWebFilter.this, TraceWebFilter.this.spanFromContextRetriever()).transformDeferred((call) -> {
//MetricsWebFilter 相关的处理,在前面的代码中给出了,这里省略
});
); RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.lookupRoute(exchange) 根据请求寻找路由,这个我们就不详细展开了,其实就是根据你的 Spring Cloud Gateway 配置,找到合适的路由。接下来我们来看调用对应的 Handler,即 FilteringWebHandler。DispatcherHandler.this.invokeHandler(exchange, handler) 我们这里也不详细展开,我们知道其实就是调用 Handler 的 handle 方法,即 FilteringWebHandler 的 handle 方法,所以 我们的 Mono 变成了:
return Mono.defer(() ->
new MonoWebFilterTrace(source,
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.lookupRoute(exchange) //根据请求寻找路由
.flatMap((Function>) r -> {
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR, r); //将路由放入 Attributes 中,后面我们还会用到
return Mono.just(RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.webHandler); //返回 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 的 FilteringWebHandler
}).switchIfEmpty( //如果为 Mono.empty(),也就是没找到路由
Mono.empty()
.then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> { //返回 Mono.empty() 之后,记录日志
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No RouteDefinition found for [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "]");
}
})))
.switchIfEmpty(DispatcherHandler.this.createNotFoundError()) //如果没有返回不为 Mono.empty() 的 handlerMapping,则直接返回 404
.then(FilteringWebHandler.this.handle(exchange).then(Mono.empty())) //调用对应的 Handler
.flatMap(result -> DispatcherHandler.this.handleResult(exchange, result)), //处理结果
TraceWebFilter.this.isTracePresent(), TraceWebFilter.this, TraceWebFilter.this.spanFromContextRetriever()).transformDeferred((call) -> {
//MetricsWebFilter 相关的处理,在前面的代码中给出了,这里省略
});
); 由于调用对应的 Handler,最后返回的是 Mono.empty(),所以后面的 flatMap 其实不会执行了。所以我们可以将最后的处理结果这一步去掉。所以我们的 Mono 就变成了:
return Mono.defer(() ->
new MonoWebFilterTrace(source,
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.lookupRoute(exchange) //根据请求寻找路由
.flatMap((Function>) r -> {
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR, r); //将路由放入 Attributes 中,后面我们还会用到
return Mono.just(RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.webHandler); //返回 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 的 FilteringWebHandler
}).switchIfEmpty( //如果为 Mono.empty(),也就是没找到路由
Mono.empty()
.then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> { //返回 Mono.empty() 之后,记录日志
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No RouteDefinition found for [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "]");
}
})))
.switchIfEmpty(DispatcherHandler.this.createNotFoundError()) //如果没有返回不为 Mono.empty() 的 handlerMapping,则直接返回 404
.then(FilteringWebHandler.this.handle(exchange).then(Mono.empty()))), //调用对应的 Handler
TraceWebFilter.this.isTracePresent(), TraceWebFilter.this, TraceWebFilter.this.spanFromContextRetriever()).transformDeferred((call) -> {
//MetricsWebFilter 相关的处理,在前面的代码中给出了,这里省略
});
); FilteringWebHandler.this.handle(exchange) 其实就是从 Attributes 中取出路由,从路由中取出对应的 GatewayFilters,与全局 GatewayFilters 放到同一个 List 中,并按照这些 GatewayFilter 的顺序排序(可以通过实现 org.springframework.core.Ordered 接口来制定顺序),然后生成 DefaultGatewayFilterChain 即 GatewayFilter 链路。对应的源码是:
public Mono handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
//从 Attributes 中取出路由,从路由中取出对应的 GatewayFilters
Route route = exchange.getRequiredAttribute(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR);
List gatewayFilters = route.getFilters();
//与全局 GatewayFilters 放到同一个 List 中
List combined = new ArrayList<>(this.globalFilters);
combined.addAll(gatewayFilters);
//按照这些 GatewayFilter 的顺序排序(可以通过实现 `org.springframework.core.Ordered` 接口来制定顺序)
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(combined);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Sorted gatewayFilterFactories: " + combined);
}
//生成调用链
return new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(combined).filter(exchange);
} 这个 GatewayFilter 调用链和 WebFilter 调用链类似,参考 DefaultGatewayFilterChain 的源码:
public Mono filter(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return Mono.defer(() -> {
//如果链路没有结束,则继续链路
if (this.index < filters.size()) {
GatewayFilter filter = filters.get(this.index);
//这里将 index + 1,也就是调用链路中的下一个 GatewayFilter
DefaultGatewayFilterChain chain = new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(this, this.index + 1);
//每个 filter 中如果想要继续链路,则会调用 chain.filter(exchange),这也是我们开发 GatewayFilter 的时候的使用方式
return filter.filter(exchange, chain);
}
else {
//到达末尾,链路结束
return Mono.empty(); // complete
}
});
} 所以,经过 DefaultGatewayFilterChain 后,我们的 Mono 就会变成:
return Mono.defer(() ->
new MonoWebFilterTrace(source,
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.lookupRoute(exchange) //根据请求寻找路由
.flatMap((Function>) r -> {
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR, r); //将路由放入 Attributes 中,后面我们还会用到
return Mono.just(RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.webHandler); //返回 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 的 FilteringWebHandler
}).switchIfEmpty( //如果为 Mono.empty(),也就是没找到路由
Mono.empty()
.then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> { //返回 Mono.empty() 之后,记录日志
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No RouteDefinition found for [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "]");
}
})))
.switchIfEmpty(DispatcherHandler.this.createNotFoundError()) //如果没有返回不为 Mono.empty() 的 handlerMapping,则直接返回 404
.then(new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(combined).filter(exchange).then(Mono.empty()))), //调用对应的 Handler
TraceWebFilter.this.isTracePresent(), TraceWebFilter.this, TraceWebFilter.this.spanFromContextRetriever()).transformDeferred((call) -> {
//MetricsWebFilter 相关的处理,在前面的代码中给出了,这里省略
});
); 再继续展开 DefaultGatewayFilterChain 的链路调用,可以得到:
return Mono.defer(() ->
new MonoWebFilterTrace(source,
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.lookupRoute(exchange) //根据请求寻找路由
.flatMap((Function>) r -> {
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR, r); //将路由放入 Attributes 中,后面我们还会用到
return Mono.just(RoutePredicateHandlerMapping.this.webHandler); //返回 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 的 FilteringWebHandler
}).switchIfEmpty( //如果为 Mono.empty(),也就是没找到路由
Mono.empty()
.then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> { //返回 Mono.empty() 之后,记录日志
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No RouteDefinition found for [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "]");
}
})))
.switchIfEmpty(DispatcherHandler.this.createNotFoundError()) //如果没有返回不为 Mono.empty() 的 handlerMapping,则直接返回 404
.then(
Mono.defer(() -> {
//如果链路没有结束,则继续链路
if (DefaultGatewayFilterChain.this.index < DefaultGatewayFilterChain.this.filters.size()) {
GatewayFilter filter = DefaultGatewayFilterChain.this.filters.get(DefaultGatewayFilterChain.this.index);
//这里将 index + 1,也就是调用链路中的下一个 GatewayFilter
DefaultGatewayFilterChain chain = new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(DefaultGatewayFilterChain.this, DefaultGatewayFilterChain.this.index + 1);
//每个 filter 中如果想要继续链路,则会调用 chain.filter(exchange),这也是我们开发 GatewayFilter 的时候的使用方式
return filter.filter(exchange, chain);
}
else {
return Mono.empty(); //链路完成
}
})
.then(Mono.empty()))
), //调用对应的 Handler
TraceWebFilter.this.isTracePresent(), TraceWebFilter.this, TraceWebFilter.this.spanFromContextRetriever()).transformDeferred((call) -> {
//MetricsWebFilter 相关的处理,在前面的代码中给出了,这里省略
});
); 这样,就形成了 Spring Cloud Gateway 针对路由请求的完整 Mono 调用链。
微信搜索“我的编程喵”关注公众号,每日一刷,轻松提升技术,斩获各种offer:
![]()