❤️【python入门项目】在 Python 中创建条形图追赶动画(评论区送书)❤️
动画是使可视化更具吸引力和用户吸引力的好方法。它帮助我们以有意义的方式展示数据可视化。Python 帮助我们使用现有的强大 Python 库创建动画可视化。Matplotlib是一个非常流行的数据可视化库,通常用于数据的图形表示以及使用内置函数的动画。
直接跳到末尾 去评论区领书
在 Python 中创建条形图追赶动画(评论区送书)
-
- 方法一:使用 pause() 函数
- 方法二:使用 FuncAnimation() 函数
-
- 线性图动画:
- Python 中的条形图追赶动画
- Python 中的散点图动画:
- 条形图追赶的水平移动:
- 评论区抽粉丝送书啦
使用 Matplotlib 创建动画有两种方法:
- 使用 pause() 函数
- 使用 FuncAnimation() 函数
方法一:使用 pause() 函数
在暂停()的matplotlib库的pyplot模块在功能上用于暂停为参数提到间隔秒。考虑下面的示例,我们将使用 matplotlib 创建一个简单的线性图并在其中显示动画:
创建 2 个数组 X 和 Y,并存储从 1 到 100 的值。
使用 plot() 函数绘制 X 和 Y。
以合适的时间间隔添加 pause() 函数
运行程序,你会看到动画。
Python
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
x = []
y = []
for i in range(100):
x.append(i)
y.append(i)
# 提及 x 和 y 限制以定义其范围
plt.xlim(0, 100)
plt.ylim(0, 100)
# 绘制图形
plt.plot(x, y, color = 'green')
plt.pause(0.01)
plt.show()
输出 :
同样,你也可以使用 pause() 函数在各种绘图中创建动画。
方法二:使用 FuncAnimation() 函数
这个FuncAnimation() 函数不会自己创建动画,而是从我们传递的一系列图形中创建动画。
语法: FuncAnimation(figure, animation_function, frames=None, init_func=None, fargs=None, save_count=None, *, cache_frame_data=True,
**kwargs)
现在您可以使用 FuncAnimation 函数制作多种类型的动画:
线性图动画:
在这个例子中,我们将创建一个简单的线性图,它将显示一条线的动画。同样,使用 FuncAnimation,我们可以创建多种类型的动画视觉表示。我们只需要在一个函数中定义我们的动画,然后用合适的参数将它传递给FuncAnimation。
Python
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
import numpy as np
x = []
y = []
figure, ax = plt.subplots()
# 设置 x 和 y 轴的限制
ax.set_xlim(0, 100)
ax.set_ylim(0, 12)
# 绘制单个图形
line, = ax.plot(0, 0)
def animation_function(i):
x.append(i * 15)
y.append(i)
line.set_xdata(x)
line.set_ydata(y)
return line,
animation = FuncAnimation(figure,
func = animation_function,
frames = np.arange(0, 10, 0.1),
interval = 10)
plt.show()
输出:
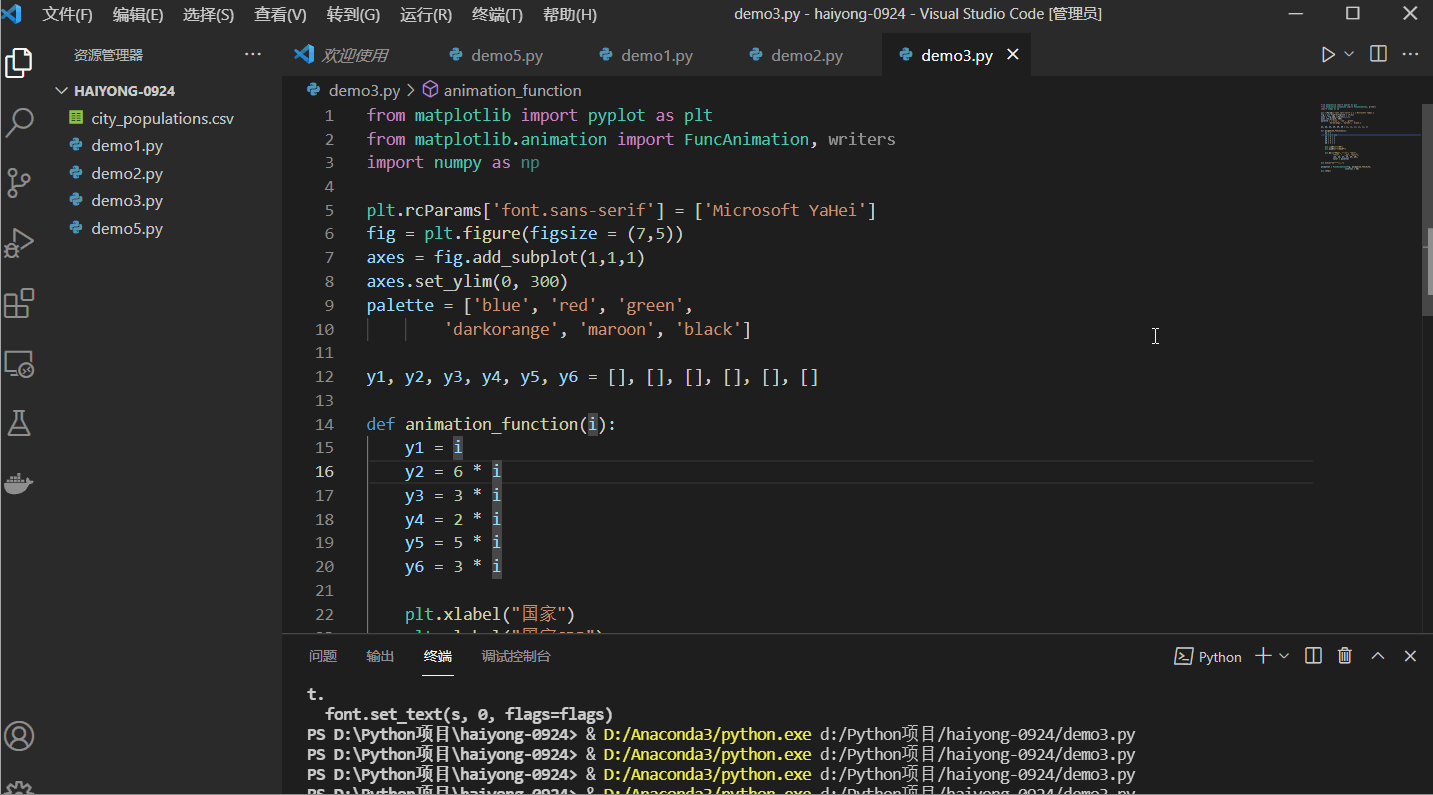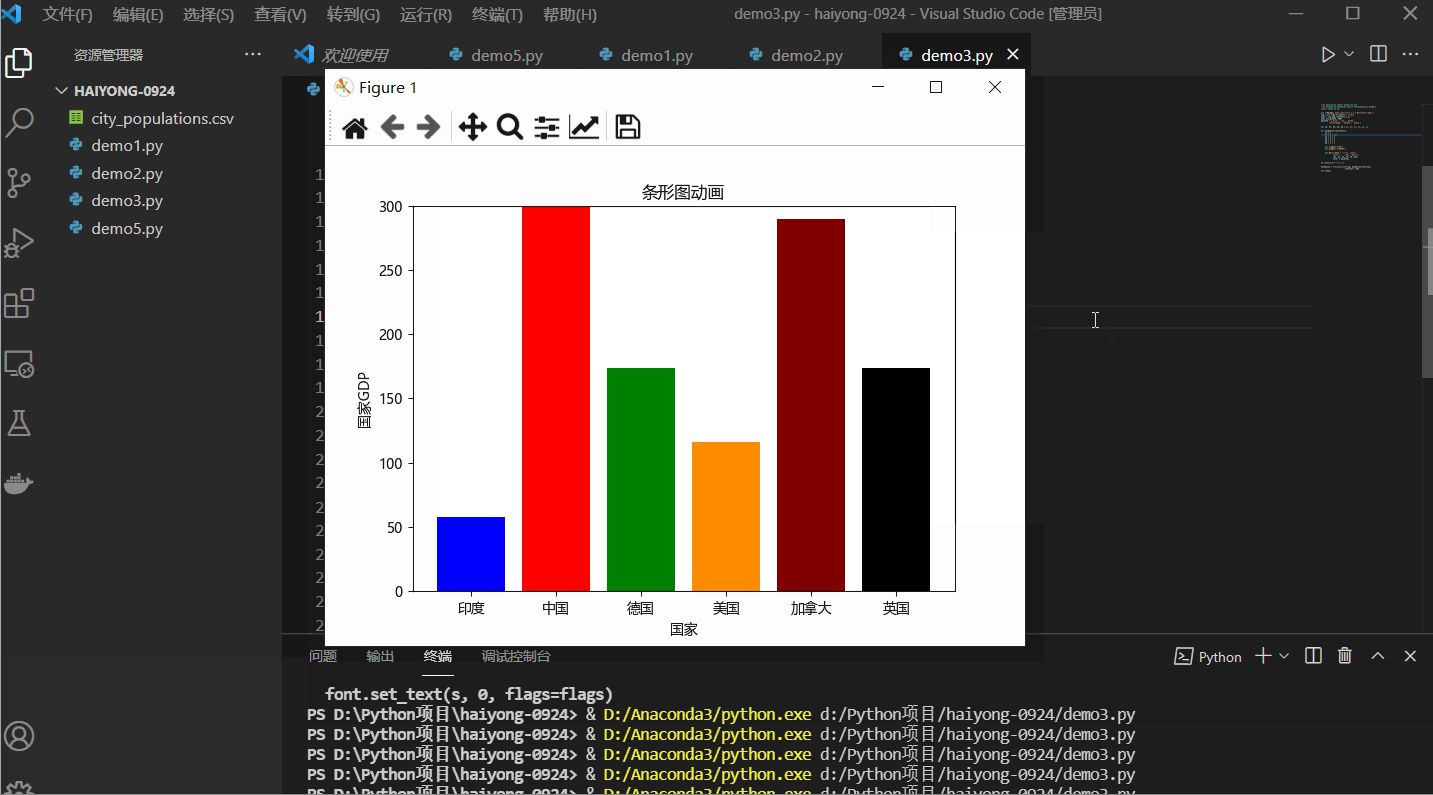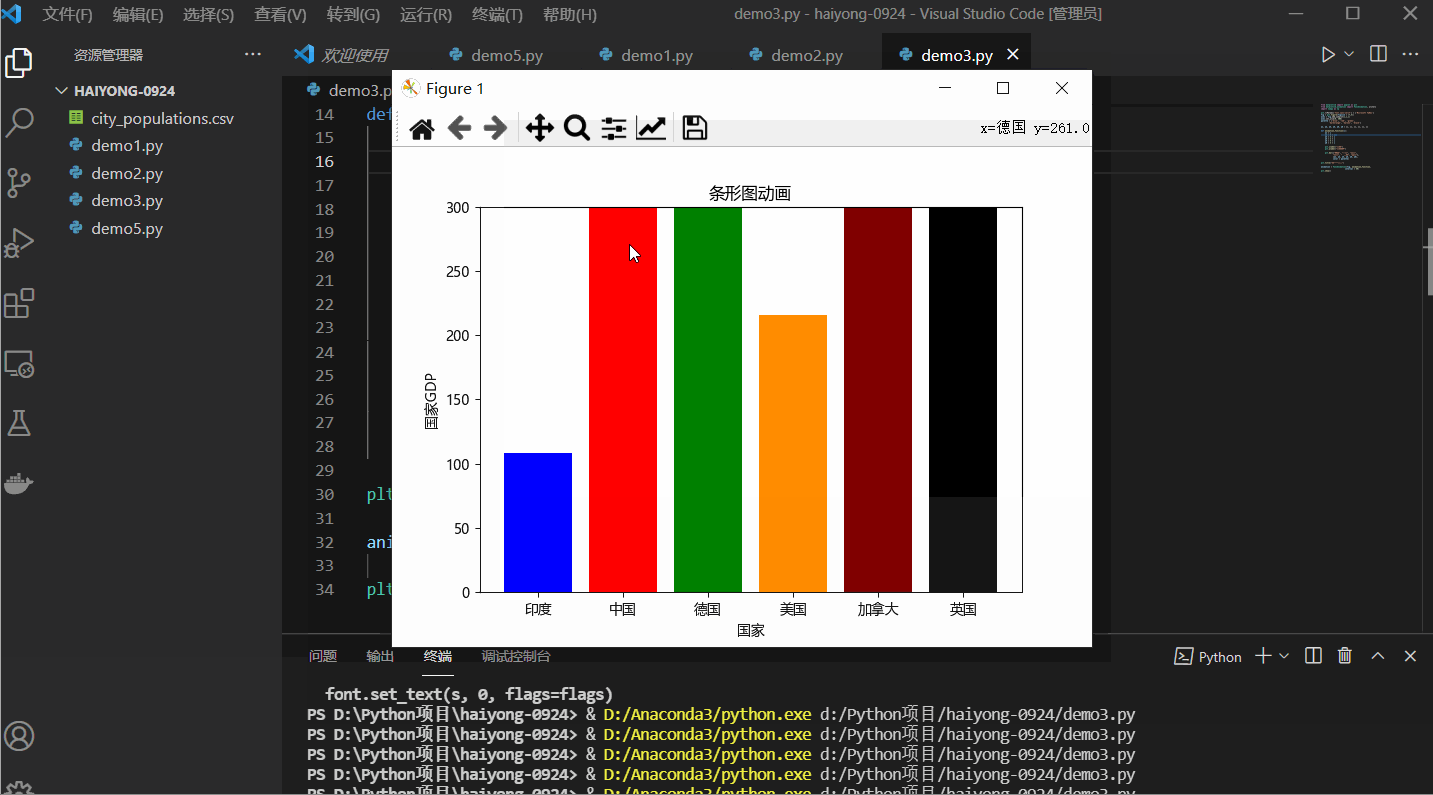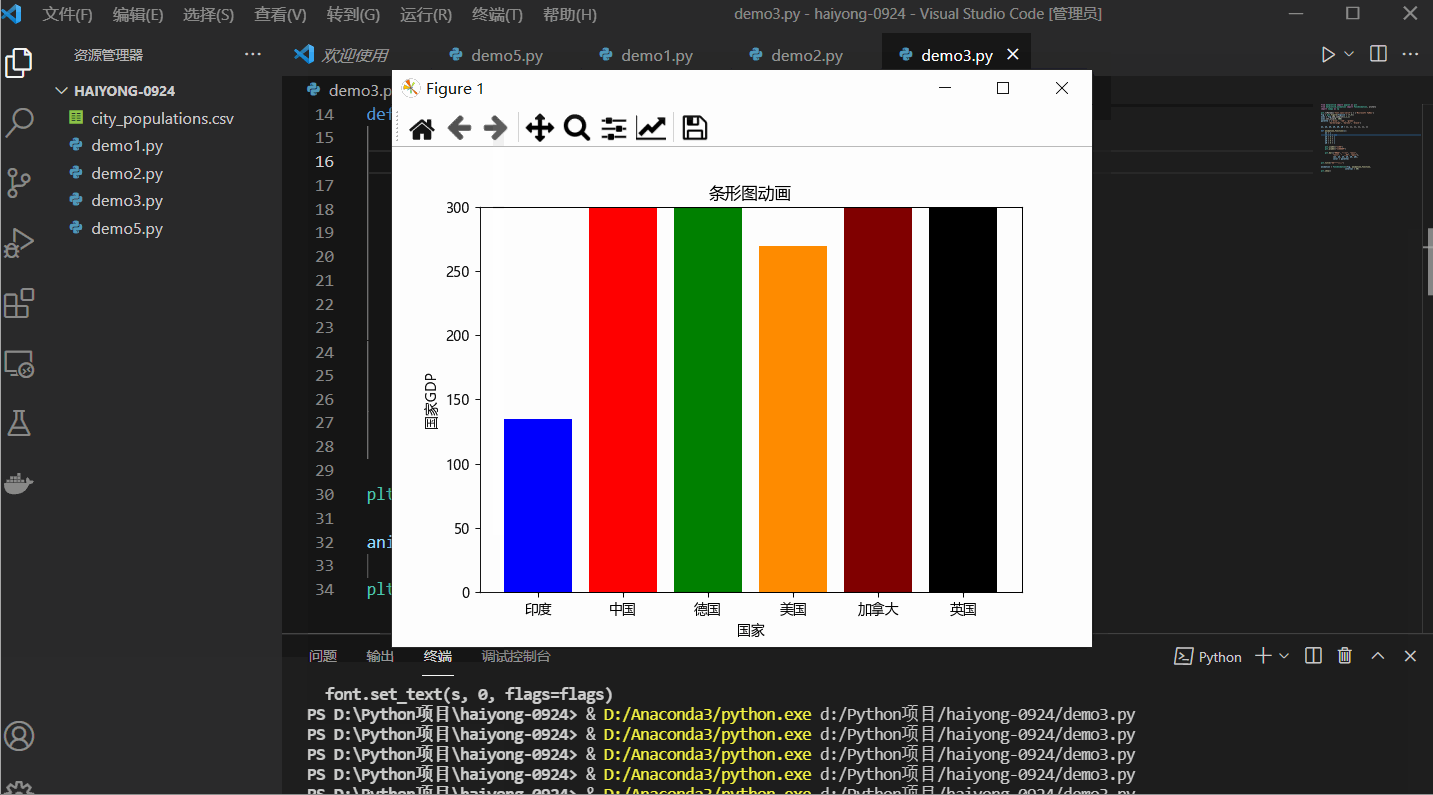
Python 中的条形图追赶动画
在此示例中,我们将创建一个简单的条形图动画,它将显示每个条形的动画。
Python
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation, writers
import numpy as np
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Microsoft YaHei']
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (7,5))
axes = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
axes.set_ylim(0, 300)
palette = ['blue', 'red', 'green',
'darkorange', 'maroon', 'black']
y1, y2, y3, y4, y5, y6 = [], [], [], [], [], []
def animation_function(i):
y1 = i
y2 = 6 * i
y3 = 3 * i
y4 = 2 * i
y5 = 5 * i
y6 = 3 * i
plt.xlabel("国家")
plt.ylabel("国家GDP")
plt.bar(["印度", "中国", "德国",
"美国", "加拿大", "英国"],
[y1, y2, y3, y4, y5, y6],
color = palette)
plt.title("条形图动画")
animation = FuncAnimation(fig, animation_function,
interval = 50)
plt.show()
输出:
Python 中的散点图动画:
在这个例子中,我们将使用随机函数在 python 中动画散点图。我们将遍历animation_func并在迭代时绘制 x 和 y 轴的随机值。
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
import random
import numpy as np
x = []
y = []
colors = []
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7,5))
def animation_func(i):
x.append(random.randint(0,100))
y.append(random.randint(0,100))
colors.append(np.random.rand(1))
area = random.randint(0,30) * random.randint(0,30)
plt.xlim(0,100)
plt.ylim(0,100)
plt.scatter(x, y, c = colors, s = area, alpha = 0.5)
animation = FuncAnimation(fig, animation_func,
interval = 100)
plt.show()
输出:
条形图追赶的水平移动:
在这里,我们将使用城市数据集中的最高人口绘制条形图竞赛。
不同的城市会有不同的条形图,条形图追赶将从 1990 年到 2018 年迭代。
我从人口最多的数据集中选择了最高城市的国家。
需要用到的数据集可以从这里下载:city_populations
Python
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Microsoft YaHei']
df = pd.read_csv('city_populations.csv',
usecols=['name', 'group', 'year', 'value'])
colors = dict(zip(['India','Europe','Asia',
'Latin America','Middle East',
'North America','Africa'],
['#adb0ff', '#ffb3ff', '#90d595',
'#e48381', '#aafbff', '#f7bb5f',
'#eafb50']))
group_lk = df.set_index('name')['group'].to_dict()
def draw_barchart(year):
dff = df[df['year'].eq(year)].sort_values(by='value',
ascending=True).tail(10)
ax.clear()
ax.barh(dff['name'], dff['value'],
color=[colors[group_lk[x]] for x in dff['name']])
dx = dff['value'].max() / 200
for i, (value, name) in enumerate(zip(dff['value'],
dff['name'])):
ax.text(value-dx, i, name,
size=14, weight=600,
ha='right', va='bottom')
ax.text(value-dx, i-.25, group_lk[name],
size=10, color='#444444',
ha='right', va='baseline')
ax.text(value+dx, i, f'{
value:,.0f}',
size=14, ha='left', va='center')
ax.text(1, 0.4, year, transform=ax.transAxes,
color='#777777', size=46, ha='right',
weight=800)
ax.text(0, 1.06, 'Population (thousands)',
transform=ax.transAxes, size=12,
color='#777777')
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.StrMethodFormatter('{x:,.0f}'))
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('top')
ax.tick_params(axis='x', colors='#777777', labelsize=12)
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.margins(0, 0.01)
ax.grid(which='major', axis='x', linestyle='-')
ax.set_axisbelow(True)
ax.text(0, 1.12, '从 1500 年到 2018 年世界上人口最多的城市',
transform=ax.transAxes, size=24, weight=600, ha='left')
ax.text(1, 0, 'by haiyong.site | 海拥',
transform=ax.transAxes, ha='right', color='#777777',
bbox=dict(facecolor='white', alpha=0.8, edgecolor='white'))
plt.box(False)
plt.show()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15, 8))
animator = FuncAnimation(fig, draw_barchart,
frames = range(1990, 2019))
plt.show()
输出:
评论区抽粉丝送书啦
欢迎大家在评论区提出意见和建议!(抽两位幸运儿送书,实物图如下)
《机器学习入门:基于数学原理的Python实战》
简介:理论性与实用性兼备,既可作为初学者的入门书籍,也可作为求职者的面试宝典,更可作为职场人士转岗的实用手册。本书适合需要全面学习机器学习算法的初学者、希望掌握机器学习算法数学理论的程序员、想转行从事机器学习算法的专业人员、对机器学习算法兴趣浓厚的人员、专业培训机构学员和希望提高 Python 编程水平的程序员。
优点:
1.与周志华编写的《机器学习》相比,本书多了对算法的数学原理详细严谨的推导。
2.与李锐翻译的《机器学习实战》相比,本书多了用面向对象思想将算法模块化,并且书中代码在Python 3 环境下运行。
3.为了照顾初学者,本书补充了全书涉及的高等数学、线性代数、概率论与数理统计、Jessen不等式等数学基础知识。
也有不想抽奖自己买的同学可以参考下面的链接
京东自营购买链接:
《机器学习入门:基于数学原理的Python实战》(戴璞微,潘斌)【摘要 书评 试读】- 京东图书
当当自营购买链接:
《机器学习入门:基于数学原理的Python实战》(戴璞微)【简介_书评_在线阅读】 - 当当图书
注意:
大家点赞关注,三天后也就是 9月28日 从评论区留言的同学中抽取两位送书
行业资料:精品PPT模板几千套,简历模板一千多套
面试题库:Java核心知识点大全和面试真题资料
学习资料:2300套PHP建站源码,微信小程序入门资料,Python全集(400集)
如果中奖了联系不上则视为放弃,可以从下方公众号里找到作者的联系方式,回复【资源】获取上面的资料