《剑指offer》专题—算法训练 day04
文章目录
- 《剑指offer》专题—算法训练day04
- 一、反转链表
-
- 思路一
- 思路二
- 二、合并有序链表
-
- 思路一
- 思路二
- 递归思路
- 三、树的子结构
-
- 思路
- 四、镜像二叉树
-
- 思路
- 未完待续...
《剑指offer》专题—算法训练day04
一、反转链表
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/75e878df47f24fdc9dc3e400ec6058ca?
思路一
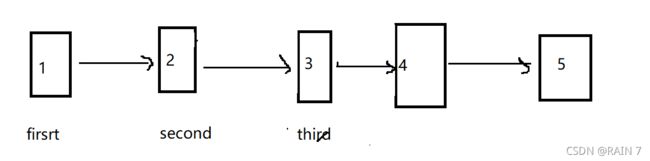
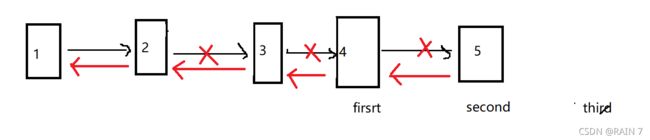
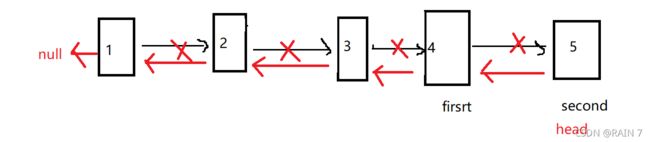
定义三个指针,进行迭代,整体右移,边移动,边翻转,保证不会断链
原链表
第一次循环结束
相关代码
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
// 设置三个引用指向连续的三个节点
// 如果这个链表中 只有一个节点或者 没有节点时 ,直接返回 head
if(head== null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
// 不带头节点,至少还有2个节点
ListNode left = head; // 指向第一个节点
ListNode mid = left.next;// 指向第二个节点
ListNode right = mid.next; // 指向第三个节点 ,可能为null
while(right != null){
// 翻转操作
mid.next = left;
// 将中间节点的next 置为 前一个节点
// 平移这三个节点
left = mid;
mid = right;
right = right.next;
}
// 当上面这个循环走完时,最后一个节点 mid 还未反转,或者 这个链表中就只有两个节点
mid.next = left;
// 反转完毕后,头节点的next 置为 null
head.next = null;
// 反转后的开始节点置为头节点
head = mid;
return head;
}
}
思路二
可以采取头插法的思想进行翻转,可以每次把链表的第一个节点拿下来,头插进一个新的链表当中
相关代码
头插法进行反转链表
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
// 头插法进行反转链表
ListNode new_head = null;
while(head!=null){
// 把原链表的第一个节点拿下来
ListNode p = head;
// 第一个节点继续指
head = head.next;
// 然后这个节点头插进入新的链表当中
p.next = new_head;
new_head = p;
}
return new_head;
}
}
二、合并有序链表
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d8b6b4358f774294a89de2a6ac4d9337?
思路一
有傀儡节点
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1 ==null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
// 建立一个傀儡节点
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tmp = newHead;
while(list1!=null && list2 !=null){
if(list1.val <list2.val){
tmp.next = list1;
tmp = tmp.next;
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
tmp.next = list2;
tmp = tmp.next;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if(list1 == null){
tmp.next = list2;
}
if(list2 ==null){
tmp.next = list1;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}
思路二
设立一个新的链表,同时定义头尾指针,
1.找到我们需要插入的节点
2.在原来表中删去该节点
3.将该节点尾插到新的链表当中
相关代码
无傀儡节点
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 ==null){
return list1;
}
ListNode new_head = null;// 新链表的头指针
ListNode new_end = null; // 新链表的尾指针
while(list1!=null && list2!=null){
//1.找到我们要删除的节点
ListNode p = list1.val<list2.val?list1:list2;
// 2.在原链表中删除节点
if(p == list1){
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
list2 = list2.next;
}
//3.放入新链表中
//3.1第一次插入节点|| 其他的情况
if(new_head == null){
new_head = p;
new_end = p;
}else{
//3.2 如果不是第一次插入,那么我们就将这个节点进行尾插
new_end.next = p;
new_end = p;
}
}
// 如果两个链表的长度不一样,那么就会出现
// list1 == null || list2 == null
if(list1 == null){
new_end.next = list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
new_end.next = list1;
}
return new_head;
}
}
递归思路
重复的过程用递归来进行表示,缩小问题的规模
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 ==null){
return list1;
}
ListNode head = null;// 新链表的头指针
if(list1.val <list2.val){
head = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
head = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
head.next = Merge(list1,list2);
return head ;
}
}
三、树的子结构
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6e196c44c7004d15b1610b9afca8bd88?
思路
二叉树都是递归定义的,所以递归操作是比较常见的做法
首先明白:子结构怎么理解,可以理解成子结构是原树的子树(或者一部分)
也就是说,B要是A的子结构,B的根节点+左子树+右子树,都在A中存在且构成树形结构
比较的过程要分为两步
1.先确定起始位置
2.在确定从该位置开始,后续的左右子树的内容是否一致
相关代码
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean isSameChild(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2){
// 这个函数用来判断左右子树是否相等
if(root2 ==null){
// 原子树全部遍历完,说明左右子树相等
return true;
}
if(root1 == null){
// 目标子树全部遍历完,说明左右子树不相等
return false;
}
if(root1.val != root2.val){
return false;
}
return isSameChild(root1.left,root2.left ) && isSameChild(root1.right,root2.right);
}
public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null || root2== null){
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
// 1.先找对应的起始位置
if(root1.val == root2.val){
// 此时判断左右子树是否相等
result = isSameChild(root1,root2);
}
// 如果resule 为 false ,那么没找到起始位置,继续从左子树找
if(result != true){
result = HasSubtree(root1.left,root2);
}
// 如果result 为 false ,那么没找到 起始位置,继续从右子树找
if(result !=true){
result = HasSubtree(root1.right,root2);
}
return result;
}
}
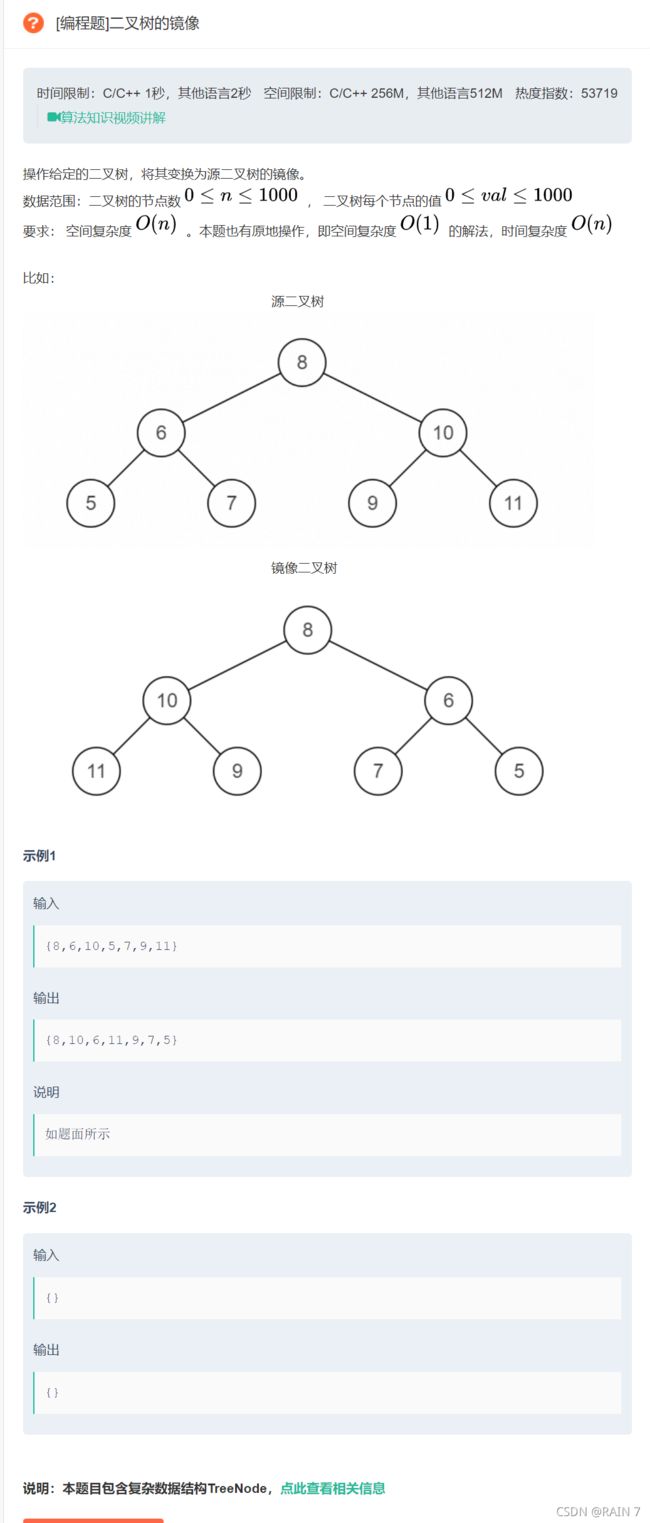
四、镜像二叉树
https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/a9d0ecbacef9410ca97463e4a5c83be7
思路
二叉树的常规操作是递归思路,缩小问题的规模
这道题镜像二叉树,我们可以看到整颗树的左右子树都交换位置,我们缩小问题的规模,变成每颗子树的问题,每颗子树我们都需要进行交换左右子树的位置,进行递归操作.
相关代码
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pRoot TreeNode类
* @return TreeNode类
*/
public TreeNode Mirror (TreeNode pRoot) {
// write code here
if(pRoot == null){
return null;
}
TreeNode temp = pRoot.right;
pRoot.right = pRoot.left;
pRoot.left = temp;
Mirror(pRoot.left);
Mirror(pRoot.right);
return pRoot;
}
}
好了,今天的内容就结束了,希望大家多多练习~~
谢谢欣赏!!!
《剑指offer》 算法训练day5 敬请期待…