学习Vue看这个就够了(下)
学习Vue看就够了(下)
Vue全家桶-Vuex
1.什么是Vuex
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理数据,以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化,vuex是Vue官方推荐的集中式状态管理机制
2.Vue中存的什么
- 多个组件共享状态,才存储在Vuex中
- 某个组件中的私有数据,依旧存储在Data中
例如:
- 登录的用户名需要在首页,个人中心、结算页面使用,用户名存在vuex中
- 文章详情的数据,只有在文章详情页查看,在自身data中声明
3.为什么要学vuex
程序页面多, 数据变量多
- 不同组件数据保持同步
- 数据的修改都是可追踪
4.vuex五个核心概念是?
| 配置项 | 含义 | 注意 |
|---|---|---|
| state | 单一状态树 | 类似data |
| mutations | 数据管家(同步) | 唯一修改state地方 |
| actions | 异步请求 | 要改state需要提交给mutations |
| getters | vuex计算属性 | 类似computed |
| modules | 模块拆分 |
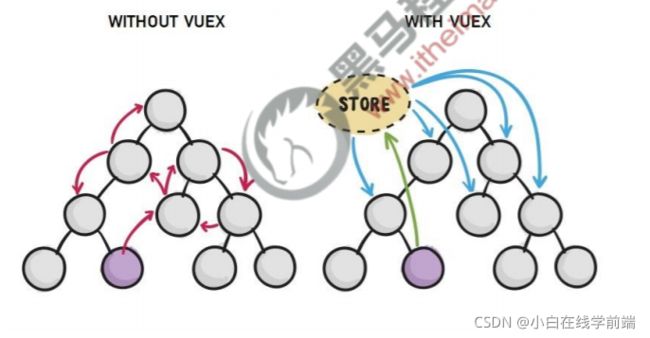
图示关系
单一定义store对象, 里面5个配置项, 在任意组件可以使用

5.vuex实例
初始化新的工程 vuex-demo
vue create vuex-demo
清空欢迎界面
并设置三个组件,目录如下:
|-components
|---AddItem.vue
|---SubItem.vue
|-App.vue
App.vue
复制标签和样式, 引入AddItem和SubItem2个子组件显示
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件h1>
<span>库存总数:span>
<input type="text">
<div style="border:1px solid black; width: 300px;">
<AddItem>AddItem>
div>
<hr>
<div style="border:1px solid black; width: 300px;">
<SubItem>SubItem>
div>
div>
template>
<script>
import AddItem from '@/components/AddItem'
import SubItem from '@/components/SubItem'
export default {
components: {
AddItem,
SubItem
}
}
script>
<style>
#app {
width: 300px;
margin: 20px auto;
border:1px solid #ccc;
padding:4px;
}
style>
AddItem.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>AddItem组件h3>
<p>已知库存数: 0p>
<button>库存+1button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
}
script>
SubItem.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>SubItem组件h3>
<p>已知库存数: 0p>
<button>库存-1button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
}
script>
创建store仓库
和路由模块router/index.js类似,维护项目目录的整洁,新建src/store/index.js文件
- 下载vuex
yarn add vuex
npm install vuex
- 在store/index.js 创建定义导出store
// 目标: 创建store仓库对象
// 1. 下载vuex: 终端命令(yarn add vuex)
// 2. 引入vuex
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 3. 注册
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 4. 实例化store对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
})
// 5. 导出store对象
export default store
- main.js - 导入注入到Vue中
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from '@/store' // 导入store对象
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
// 6. 注入到Vue实例中(确保组件this.$store使用)
store,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
6.vuex-state数据源
state是唯一的公共数据源,统一存储数据
定义state
在store/index.js定义state语法:
/*
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
变量名: 初始值
}
})
*/
具体代码:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 100 // 库存
}
})
使用state种方式
方式1: 组件内 - 直接使用:语法
this.$store.state.变量名
方式2: 组件内 - 映射使用 (推荐):语法
// 1. 拿到mapState辅助函数
import {
mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
// 2. 把state里变量映射到计算属性中
...mapState(['state里的变量名'])
}
}
AddItem直接用
<template>
<div>
<h3>AddItem组件h3>
<p>已知库存数: {
{ $store.state.count }}p>
<button>库存+1button>
div>
template>
App.vue直接用
计算属性count, 和输入框的v-model双向绑定
<input type="text" v-model="count">
<script>
export default {
computed: {
count: {
set(){
},
get(){
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
}
}
script>
SubItem映射用
<template>
<div>
<h3>SubItem组件h3>
<p>已知库存数: {
{ count }}p>
<button>库存-1button>
div>
template>
<script>
// 需求1: 映射state到计算属性
// 1. 拿到辅助函数 mapState
// 2. 在computed内, ...mapState(['state变量名'])
// 3. 当计算属性使用
import {
mapState } from 'vuex'
// let r = mapState(['count']) // 提取store里的state叫count的变量
// console.log(r); // 返回值: {count: 函数体(return state里count的值)}
export default {
computed: {
// 映射count, 得到对象展开, 合并到计算属性中
...mapState(['count'])
},
}
script>
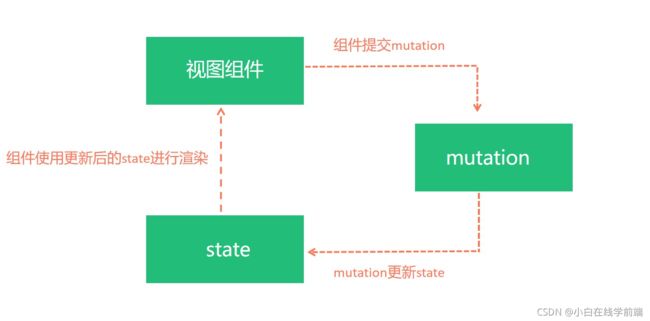
整个过程的示意图如下
注意:
state是响应式的, 只要state值变化, 页面上使用的地方会自动更新同步
7.vuex-mutations定义-同步修改
mutations类似数据管家, 操作state里的数据
在store/index.js定义mutations
语法:
/*
const store = new Vuex.Store({
mutations: {
函数名 (state, 可选值) {
// 同步修改state值代码
}
}
})
*/
具体代码
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 100 // 库存
},
mutations: {
addCount (state, value) {
// 负责增加库存的管家
state.count += value
},
subCount (state, value) {
// 负责减少库存的管家
state.count -= value
},
setCount (state, value) {
// 负责直接修改库存的管家
state.count = value;
}
}
})
注意
- mutations是唯一能修改state的地方, 确保调试工具可以追踪变化
- mutations函数内, 只能写同步代码, 调试工具可追踪变化过程
- 因为调试工具要立刻产生一次记录, 所以必须是同步的
使用mutations的2种方式
方式1: 组件内 - 直接使用
语法:
this.$store.commit("mutations里的函数名", 具体值)
方式2: 组件内 - 映射使用
语法:
// 1. 拿到mapMutations辅助函数
import {
mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
// 2. 把mutations里方法映射到原地
...mapMutations(['mutations里的函数名'])
}
}
直接使用
<button @click="addFn">库存+1button>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
addFn(){
this.$store.commit('addCount', 1)
}
}
}
script>
在App.vue直接用
- 触发计算属性的set方法
- 提交mutations传入值
<span>库存总数: span>
<input type="text" v-model="count">
<script>
export default {
computed: {
count: {
set(val){
this.$store.commit('setCount', val) // 把表单值提交给store下的mutations
},
get(){
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
}
}
script>
SubItem映射用
- 点击事件
- 映射mutations的方法
- 调用mutations方法传值
注意
mutations函数上, 只能接收一个参数值, 如果传对个, 请传一个对象
8.vuex-actions定义-异步修改
定义actions
在store/index.js定义actions
语法:
/*
const store = new Vuex.Store({
actions: {
函数名 (store, 可选值) {
// 异步代码, 把结果commit给mutations给state赋值
}
}
})
*/
具体代码:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...省略state和mutations此处
actions: {
asyncAddCount(store, num){
setTimeout(() => {
// 1秒后, 异步提交给add的mutations
store.commit('addCount', num)
}, 1000)
},
asyncSubCount(store, num) {
setTimeout(() => {
// 1秒后, 异步提交给sub的mutations
store.commit('subCount', num)
}, 1000)
}
}
})
使用actions的2种方式
方式1: 组件内 - 直接使用
语法:
this.$store.dispatch('actions函数名', 具体值)
方式2: 组件内 - 映射使用
语法:
// 1. 拿到mapActions辅助函数
import {
mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
// 2. 把actions里方法映射到原地
...mapActions(['actions里的函数名'])
}
}
AddItem直接用
- 点击事件
- dispatch触发action
<button @click="asyncAddFn">延迟1秒, 库存+5button>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
asyncAddFn(){
this.$store.dispatch('asyncAddCount', 5)
}
}
}
script>
SubItem映射用
- 点击事件
- 映射actions的方法
- 调用actions的方法传值
<button @click="asyncSubFn">延迟1秒, 库存-5</button>
<script>
// 需求3: 映射actions到方法里
// 1. 拿到辅助函数 mapActions
// 2. 在methods内, ...mapActions(['actions函数名'])
// 3. 当普通方法使用
import {
mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
...mapActions(['asyncSubCount']),
asyncSubFn(){
this.asyncSubCount(5)
}
}
}
</script>
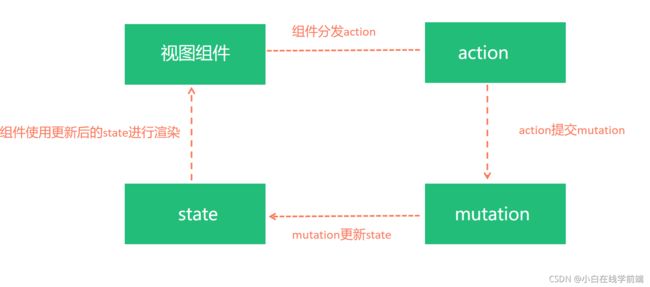
视图组件, state, mutations, actions的关系是?
9.vuex-getters定义-计算属性
概念:vuex身上的全局状态-属于全局计算属性, 类似于computed,getters 依赖于 state中原始数据的变化,并返回计算后的新数据
-
定义getters
-
在store/index.js定义getters
语法:
/* const store = new Vuex.Store({ getters: { 计算属性名 (state) { return 值给计算属性 } } }) */ -
-
具体的代码
const store = new Vuex.Store({ // ...省略其他 getters: { allCount(state) { return state.goodsList.reduce((sum, obj) => { if (obj.goods_state === true) { // 选中商品才累加数量 sum += obj.goods_count; } return sum; }, 0) }, allPrice(state) { return state.goodsList.reduce((sum, obj) => { if (obj.goods_state) { sum += obj.goods_count * obj.goods_price } return sum; }, 0) } } }) -
使用getters的2种方式
-
方式1: 组件内 - 直接使用
语法:
this.$store.getters.计算属性名-
方式2: 组件内 - 映射使用
语法:
// 1. 拿到mapGetters辅助函数 import { mapGetters } from 'vuex' export default { computed: { // 2. 把getters里属性映射到原地 ...mapGetters(['getters里的计算属性名']) } } -
在APP.vue里面使用
- 使用2种方式给计算属性值
<script>
import {
mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
allCount(){
return this.$store.getters.allCount;
},
...mapGetters(['allPrice'])
}
}
script>
10.vuex-modules定义
-
为何分模块
由于使用的是单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象,
当应用变的非常复杂的时候,store对象就有可能变得相当臃肿!!!,为了解决这个问题,Vuex允许我们**将store分割成模块**(module)。每个模块拥有自己的state,mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块 -
代码上的对比
- 创建modules模块对象
- 新建store/modules/user.js
- 新建store/modules/cart.js
- 语法,对象里面包含5个核心,只有state变成函数的形式
user.js - 用户模块对象
// 用户模块对象
const userModule = {
state(){
return {
name: "",
age: 0,
sex: ''
}
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
getters: {
}
}
export default userModule
cart.js - 购物车模块对象
// 购物车模块对象
import axios from 'axios'
const cartModule = {
state() {
return {
goodsList: []
}
},
mutations: {
setGoodsList(state, newList) {
state.goodsList = newList
}
},
actions: {
async asyncGetGoodsList(store) {
const url = `https://www.escook.cn/api/cart`
// 发送异步请求
const res = await axios({
url: url });
store.commit('setGoodsList', res.data.list) // 提交mutation修改state中的数据
}
},
getters: {
allCount(state) {
return state.goodsList.reduce((sum, obj) => {
if (obj.goods_state === true) {
// 选中商品才累加数量
sum += obj.goods_count;
}
return sum;
}, 0)
},
allPrice(state) {
return state.goodsList.reduce((sum, obj) => {
if (obj.goods_state) {
sum += obj.goods_count * obj.goods_price
}
return sum;
}, 0)
}
}
}
export default cartModule
定义模块(module)
在store/index.js中引入这两个组件,注册一下
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import cartModule from './modules/cart'
import userModule from './modules/user'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//注册
modules: {
user: userModule,
cart: cartModule
}
})
export default store
注意:只要使用了模块,state取值的方式会发生变化
state使用方式修改
方式1: 组件内 - 直接使用
原语法:
this.$store.state.变量名
分模块后的语法:
this.$store.state.模块名.变量名
方式2 组件内映射的方式使用
原语法:
...mapState(['state里变量名'])
...mapState({
'变量名': "state里变量名"})
分模块后语法:
...mapState({
'变量名': state => state.模块名.变量名
})
分模块-命名空间开启
命名空间开启是为了:防止多个模块之间,mutations/actions/getters的名字冲突
开启命名空间
在模块对象内设置namespaced: true
const moduleShopCar = {
//开启命名空间,防止多个模块之间,mutations/actions/getters的名字发生冲突
namespaced: true,
state () {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
getters: {
},
modules: {
}
}
state使用方式修改
- 直接使用无变化: this.$store.state.模块名.变量名
- 辅助函数需要遵守格式
...mapState("模块名", ['state变量名'])
mutations使用方式修改
方式1: 组件内 - 直接使用
- 原语法:
this.$store.commit("mutations里的函数名", 具体值)
- 开命名空间后语法:
this.$store.commit("模块名/mutations里的函数名", 具体值)
方式2: 组件内 - 映射使用
- 原语法:
...mapMutations(['mutations里方法名'])
- 开命名空间后语法:
...mapMutations("模块名", ['mutations里方法名'])
actions使用方式修改
-
方式1: 组件内 - 直接使用
-
原语法:
this.$store.dispatch("actions里的函数名", 具体值) -
开命名空间后语法:
this.$store.dispatch("模块名/actions里的函数名", 具体值)
-
-
方式2: 组件内 - 映射使用
-
原语法:
...mapActions(['actions里方法名']) -
开命名空间后语法:
...mapActions("模块名", ['actions里方法名'])
-
getters使用方式修改
-
方式1: 组件内 - 直接使用
-
原语法:
this.$store.getters.计算属性名 -
开命名空间后语法:
this.$store.getters['模块名/计算属性名']
-
-
方式2: 组件内 - 映射使用
-
原语法:
...mapGetters(['getters里计算属性名']) -
开命名空间后语法:
...mapGetters("模块名", ['getters里计算属性名'])
-