前端必看js数据结构与算法(队列,链表,集合,字典,树,图,堆)
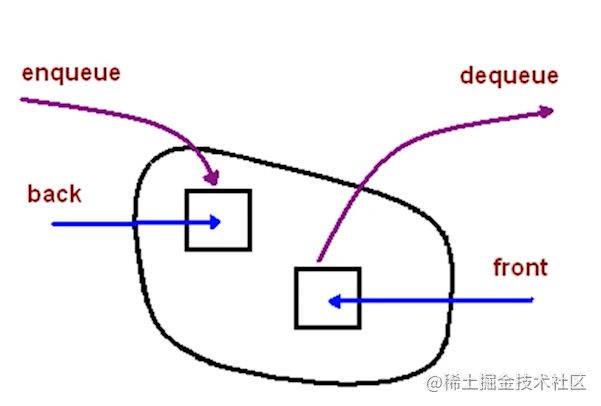
队列
队列简介
- 一个先进先出的数据结构
- js中没有队列,但是可以用Array实现对队列的所有功能
const queue = []
// 进队列
queue.push(1)
queue.push(2)
// 出队列
const itme1 = queue.shift()
const itme2 = queue.shift()
什么时候用
- 食堂排队打饭
- 所有先进先出的场景
- js 异步中的任务队列
一个leetcode题 第933题
链表
链表是什么
- 多个元素组成的列表
- 匀速存储不连续, 用next指针连在一起
数组 vs 链表
- 数组:增删非收尾元素是往往需要移动元素
- 链表:增删非收尾元素,不需要移动元素,只需要更改next指针即可
js中的链表
- js没有链表的数据结构
- 可以用Object模拟链表
const a = {
val: 'a' }
const b = {
val: 'b' }
const c = {
val: 'c' }
const d = {
val: 'd' }
a.next = b
b.next = c
c.next = d
// 遍历
let point = a
while (point) {
console.log(point.val)
point = point.next
}
// 插入
(c-d)中插入d
const e = {
val:'e'}
c.next = e
e.next = d
// 删除 (删除e)
c.next = d
leetcode练习:第83题-删除链表重复元素
var deleteDuplicates = function(head) {
// 定义链表的一个头部的指针
let p = head
while(p && p.next) {
if(p.val === p.next.val) {
// 删除链表的一项
p.next = p.next.next
}else {
// 不相同的时候再移动指针
p = p.next
}
}
return head
};
- 前端原型链的链表 JavaScript 一文搞定理解原型与原型链
手写一个instanceof
function myInstanceof (A, B) {
// 遍历链表
let p = A
while (p) {
p = p.__proto__
// B的 prototype 属性是否出现在A实例对象的原型链上
if (p === B.prototype) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
function Foo () {
}
var f = new Foo()
console.log(myInstanceof(f, Foo)); // true
console.log(myInstanceof(f, Object)); // true
集合
集合简介
- 一种无序且唯一的数据结构
- ES6中有集合, 名为Set
- 集合常用操作: 去重,判断某元素是否在集合中,求交集
// 去重
const arr = [1,1,2,3,4,3]
const arr2 = [...new Set(arr)]
// 判断元素是否在集合中
let set = new Set(arr)
// add 方法
set.add(1)
set.add('text')
set.add({
a:1,b:2})
// has方法
const has =set.has(3)
// delete方法
set.delete(1)
// 获取size 方法
console.log(set.size)
// 求交集
const set2 = new Set([2,3])
const set3 new Set([...set]).filter(item => set2.has(item))
// 求差集
const set2 = new Set([2,3])
const set4 = new Set([...set]).filter(item => !set2.has(item))
// 数组转为set
set2 = new Set([1,2,3])
// 迭代方法 fot ..of
for (let item of set) console.log(item)
for (let item of set.keys())) console.log(item)
for (let item of set.values()) console.log(item)
for (let item of set.entrise()) console.log(item)
补充说明迭代
内置迭代器:
可迭代的对象,都内置以下3种迭代器
entries(): 返回一个迭代器,值为键值对
values(): 返回一个迭代器, 值为集合的值
keys(): 返回一个迭代器,值为集合中的所有键
let userList = [ 'ghostwu', '悟空', '八戒' ];
for ( let name of userList.entries() ) {
console.log( name );
}
let set = new Set( [ 10, 20, 30 ] );
for ( let num of set.entries() ){
console.log( num );
}
let map = new Map( [ [ 'name', 'ghostwu' ], [ 'age', 22 ] ] );
for ( let detail of map.entries() ){
console.log( detail );
}
字典
字典简介
- 与集合相似, 字典也是一种存储为一值的数据结构, 但他是以键值对的形式存储
- ES6中有字典–>Map(映射)
- 常见操作 增(
set) 删(delete) 改(set) 查(get)
const m = new Map()
//增
m.set('a','aaa')
// 删
m.delete('a')
m.clear()
// 改
m.set('a','aaaaa')
// 查
m.get('a')
使用Map取两个数组的交集
var intersection = function(nums1, nums2) {
// new Set(nums1) 去重
return [...new Set(nums1)].filter(item => nums2.includes(item))
};
树
树简介
- 一种分层数据的抽象模型
- 前端工作中常见的树包括:DOM树,级联选择,树形控件…
- js中没有树,但是可以用Array 和Object构建树
- 树的常用操作: 深度/广度优先遍历 , 先中后序遍历
树的深度/广度优先遍历
const tree = {
val: 'a',
children: [
{
val: 'b',
children: [
{
val: 'd',
children: [
]
},
{
val: 'e',
children: [
]
}
]
},
{
val: 'c',
children: [
{
val: 'f',
children: [
]
},
{
val: 'g',
children: [
]
}
]
}
]
}
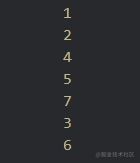
const dfs =(root) => {
console.log(root.val)
root.children.forEach(dfs)
}
dfs(tree)
打印结果
- 广度优先遍历:先访问离根节点最近的节点
- 新建一个队列, 把根节点入队
- 把对头出队并访问
- 把对头的children挨个入队
- 重复第二,第三,直到队列为空
const bfc = (root) => {
const q = [root]
while (q.length > 0) {
const n = q.shift()
console.log(n.val)
n.children.forEach(child => {
q.push(child)
})
}
}
打印结果:
二叉树的先中后序遍历
二叉树是什么?
-
树中每个节点最多只能有两个子节点
-
在js中通常用Object来模拟二叉树
const binaryTree = {
val: 1,
left: {
val:2,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val:3,
left: null,
right: null
}
}
先序遍历算法
- 访问
根节点 - 对根节点的
左子树进行先序遍历 - 对根节点的
右子树进行先序遍历
定义一棵树
const binaryTree = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: {
val: 7,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: null,
},
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: null,
right: {
val: 6,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
};
递归版:
const preorder = root => {
if (!root) return;
console.log(root.val);
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
};
preorder(binaryTree);
非递归(栈特性):
const preorder = root => {
if (!root) return;
const stack = [root];
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
n.right && stack.push(n.right);
n.left && stack.push(n.left);
}
};
preorder(binaryTree);
打印结果:
中序遍历算法
- 对根节点的
左子树进行中序遍历 - 访问
根接节点 - 对根节点的
右子树进行中序遍历
还是使用binaryTree这个树
递归版实现:
const inorder = root => {
if(!root) return
inorder(root.left)
console.log(root.val)
inorder(root.right)
}
inorder(binaryTree)
非递归版实现:
const inorder = root => {
if (!root) return;
const stack = [];
let p = root;
while (stack.length || p) {
while (p) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
const n = stack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
p = n.right;
}
}
inorder(binaryTree)
打印结果:
后序遍历算法
- 对根节点的
左子树进行中序遍历 - 对根节点的
右子树进行中序遍历 - 访问
根接节点
还是使用binaryTree这个树
递归版实现:
const postorder = (root) => {
if (!root) return;
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
console.log(root.val);
};
postorder(binaryTree);
非递归版实现:
const inorder = root => {
if (!root) return;
const outputStack = [];
const stack = [root];
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop();
outputStack.push(n);
if (n.left) stack.push(n.left);
if (n.right) stack.push(n.right);
}
while (outputStack.length) {
const n = outputStack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
}
}
inorder(binaryTree)
打印结果:
前端与树
遍历JSON的所有节点值
使用深度优先遍历
const json = {
a: {
b: {
c: 1 } },
d: [1, 2],
};
// 深度优先遍历
const dfs = (n, path) => {
console.log(n, path);
Object.keys(n).forEach((k) => {
dfs(n[k], path.concat(k));
});
};
dfs(json, []);
打印结果
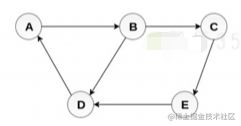
图
图是什么
- 图是网络结构的抽象模型, 是一组由边连接的节点
- 图可以表示任何二元关系, 比如路,航班
- js没有图, 可以用Array Object模拟
图的表示法
邻接矩阵
邻接表
图的遍历
- 深度优先遍历: 尽可能深的搜索图的分支
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的
没访问过得相邻节点挨个进行深度优先遍历
const graph = {
0:[1,2],
1:[2],
2:[0,3],
3:[3]
}
使用深度优先遍历
const visited = new Set()
const dfs = n => {
console.log(n)
visited.add(n)
graph[n].forEach(c => {
if(!visited.has(c)) {
dfs(c)
}
})
}
dfs(2)
打印结果
- 广度优先遍历: 先访问离根节点最近的节点
- 新建一个队列, 把根节点入队
- 把队头出队并访问
- 把队头的
没访问过得相邻节点入队 - 重复第二 三步, 直到队列为空
const bfs = node => {
const visited = new Set()
visited.add(node)
const q = [node]
while (q.length) {
const n = q.shift()
console.log(n)
graph[n].forEach(c => {
if(!visited.has(c)) {
q.push(c)
visited.add(c)
}
})
}
}
bfs(2)
打印结果:
堆
堆是什么
-
所有的节点都大于等于(最大堆)或小于等于(最小堆)他的节点
-
js中通常用数组表述堆
-
左侧子节点的位置是
2 * index + 1 -
右侧子节点的位置是
2 * index + 2 -
父节点的位置是
(index - 1) / 2
堆的应用
- 对能高效快速地找出最大值和最小值, 时间复杂度:O(1)
- 找出第K个最大(小)元素
第K个最大元素
- 构建一个最小堆, 并将元素依次插入堆中
- 当堆的容量超过K, 就是删除堆顶
- 插入结束后, 堆顶就是第K个最大元素
js实现最小堆类
- 构建一个类
- 在类里, 声明一个数组, 用来装元素
- 主要方法: 插入, 删除堆顶, 获取堆顶, 获取堆大小
- 插入
- 将值插入堆的底部,即数组的尾部
- 然后上移: 将这个值和它的防父节点进行交换, 直到父节点小于等于这个插入的值
- 大小为k的堆中插入元素的时间复杂度为O(logk)
- 删除堆顶
- 用数组尾部元素替换堆顶(直接删除堆顶会破坏堆结构)
- 然后下移: 将新堆顶和它的子节点进行交换, 直到子节点大于等于这个新堆顶
- 大小为k的堆中删除堆顶得时间复杂度为O(logk)