第11章 图像金字塔 -- 下采样cv2.pyrDown() , 上采样cv2.pyrUp()
《OpenCV 轻松入门 面向Python》 学习笔记
图像金字塔
-
-
- 1. cv2.pyrDown()
- 2. cv2.pyrUp()
- 3. 采样可逆性研究
- 4. 拉普拉斯金字塔
-
1. cv2.pyrDown()
函数cv2.pyrDown() 用于实现高斯金字塔中的下采样。
函数原型:
dst_img = cv2.pyrDown(src_img, dstsize)
参数:
- dst_img:目标图像
- src_img:原始图像
- dstsize:目标图像大小。 默认行和列都会变成原始图像行和列的1/2, 整幅图像会变成原始图像的1/4。
cv2.pyrDown()函数首先对原始图像进行高斯变换,再通过抛弃偶数行和偶数列实现下采样。
举例:
import cv2
import numpy as np
image = cv2.imread("/Users/manmi/Desktop/lena.bmp", 0)
result_1 = cv2.pyrDown(image)
result_2 = cv2.pyrDown(result_1)
result_3 = cv2.pyrDown(result_2)
cv2.imshow('image', image)
cv2.imshow('result_1', result_1)
cv2.imshow('result_2', result_2)
cv2.imshow('result_3', result_3)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
输出为:
2. cv2.pyrUp()
函数cv2.pyrUp() 用于实现高斯金字塔中的上采样。
函数原型:
dst_img = cv2.pyrUp(src_img, dstsize)
参数:
- dst_img:目标图像
- src_img:原始图像
- dstsize:目标图像大小。 默认行和列都会变成原始图像行和列的2倍, 整幅图像会变成原始图像的4倍。
cv2.pyrUp() 函数首先在原始图像的每个像素的右侧和下侧分别插入零值列和零值行,得到一个偶数行,偶数列(新增的行和列)都是零值的新图,在进行高斯变换,得到上采样的结果图像。
举例:
import cv2
import numpy as np
image = cv2.imread("/Users/manmi/Desktop/result_3.bmp", 0)
result_1 = cv2.pyrUp(image)
result_2 = cv2.pyrUp(result_1)
result_3 = cv2.pyrUp(result_2)
print('image.shape =', image.shape)
print('result_1.shape =', result_1.shape)
print('result_2.shape =', result_2.shape)
print('result_3.shape =', result_3.shape)
cv2.imshow('image', image)
cv2.imshow('result_1', result_1)
cv2.imshow('result_2', result_2)
cv2.imshow('result_3', result_3)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 输出:
# image.shape = (64, 64)
# result_1.shape = (128, 128)
# result_2.shape = (256, 256)
# result_3.shape = (512, 512)
输出为:
3. 采样可逆性研究
原始图像先下采样再上采样,得到的结果图像和原始图像尺寸一样,但是二者像素值并不是一致的。
原始图像先上采样再下采样,得到的结果图像和原始图像尺寸一样,但是二者像素值并也不是一致的。
所以,结论是,上采样和下采样不是互逆的。(上采样并不是下采样的逆运算)
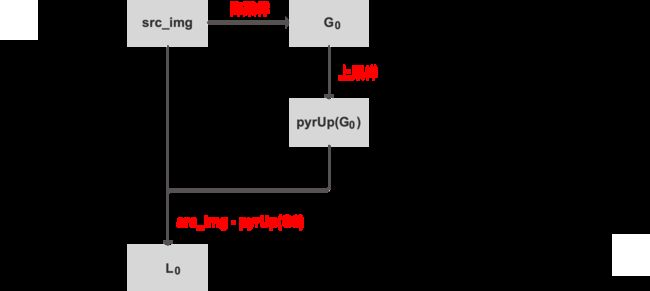
4. 拉普拉斯金字塔
构造拉普拉斯金字塔的目的就是为了恢复高分辨率的图像。