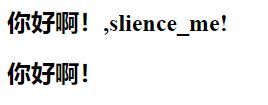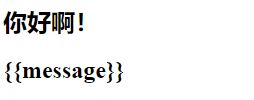Vue基础语法 ->(个人学习记录笔记)
文章目录
- Vue
-
- 1. 指令
-
- 1.1 mustache
- 1.2 v-once
- 1.3 v-html
- 1.4 v-text
- 1.5 v-pre
- 1.6 v-cloak
- 1.7 v-bind
-
- 1.7.1 基本使用
- 1.7.2 动态绑定class
-
- 对象语法
- 数组语法
- 案例
- 1.7.3 动态绑定style
-
- 对象绑定
- 数组绑定
- 1.8 v-on
-
- 1.8.1 基本使用
- 1.8.2 参数问题
- 1.8.3 修饰符
- 1.9 v-if & v-else
-
-
- 条件渲染案例
-
- 1.10 v-show
- 1.11 v-for
-
-
- 遍历数组
- 遍历对象
-
- 1.12 v-model
-
-
- 原理
- 基本使用
- v-model:radio
- v-model:checkbox
- v-model:select
- 修饰符
-
- -------------------------------
-
- 2.计算属性
-
- 2.1 基本使用
- 2.2 复杂操作
- 2.3 setter和getter
- 2.4 缓存
- 3. ES6补充
-
- 3.1 let/var
- 3.2 const的使用
- 4. 购物车案例
-
- index.html
- main.js
- style.css
- 效果图
- 5. JavaScript高阶函数
-
- filter()
- map()
- reduce()
- 综合
- 简化
Vue
1. 指令
1.1 mustache
- mustache
- { {}}
<div id="app">
<h2>{
{message}}h2>
<h2>{
{message}},李银河!h2>
<h2>{
{firstName + lastName}}h2>
<h2>{
{firstName + ' ' +lastName}}h2>
<h2>{
{firstName}} {
{lastName}}h2>
<h2>{
{counter * 2}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
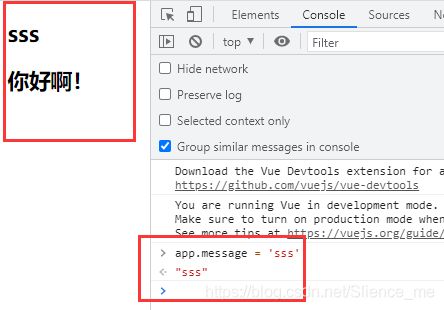
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
firstName: 'kobe',
lastName: 'bryant',
counter:100,
}
})
script>
1.2 v-once
v-once:- 该指令后边不需要跟任何表达式
- 该指令表示元素和组件只渲染一次,不会随着数据的改变而改变
<div id="app">
<h2>{
{message}}h2>
<h2 v-once>{
{message}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!'
}
})
script>
1.3 v-html
v-html:- 该指令后边往往会跟上一个string类型
- 会将string的html解析出来并且渲染
<div id="app">
<h2>{
{url}}h2>
<h2 v-html="url">h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
url: '百度一下'
}
})
script>
1.4 v-text
v-text:- 该指令和Mustache比较相似:都是用于将数据显示在界面中
- 该指令通常情况下,接受一个string类型
- 相对不灵活,不容易拼接内容,一般不用
<div id="app">
<h2>{
{message}},slience_me!h2>
<h2 v-text="message">,slience_me!h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!'
}
})
script>
1.5 v-pre
v-pre:- 该指令用于跳过这个元素和它的子元素的编译过程,用于显示原本的
Mustache语法 - 原封不动的显示出来
- 该指令用于跳过这个元素和它的子元素的编译过程,用于显示原本的
<div id="app">
<h2>{
{message}}h2>
<h2 v-pre>{
{message}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!'
}
})
script>
1.6 v-cloak
cloak:斗篷
v-cloak:- 该指令防止不友好的{ {message}}被看到
- 不会看到{ {}}内容
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
<style>
[v-cloak] {
display: none;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app" v-cloak>
<h2>{
{message}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
//在vue解析之前,div有一个属性v-cloak
//在vue解析之后,div中没有一个属性v-cloak
setTimeout(function () {
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!'
}
})
}, 1000)
script>
body>
html>
1.7 v-bind
1.7.1 基本使用
v-bind:- 作用:动态绑定属性
- 缩写:
: - 预期:any(with argument) | Object (without argument)
- 参数:attrOrProp(optional)
- 例子:
<div id="app">
<img v-bind:src="imgURL" alt="">
<a v-bind:href="aHref">百度一下a>
<br>
<img :src="imgURL" alt="">
<a :href="aHref">百度一下a>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
imgURL:'https://cn.vuejs.org/images/logo.svg',
aHref: 'https://www.baidu.com'
}
})
script>
1.7.2 动态绑定class
对象语法
<div id="app">
<h2 class="title" :class="getClasses()">{
{message}}h2>
<button v-on:click="btnClick">按钮button>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
isActive: true,
isLine: true
},
methods:{
btnClick:function (){
this.isActive = !this.isActive
},
getClasses:function () {
return {
active: this.isActive,line: this.isLine}
}
}
})
script>
数组语法
<div id="app">
<h2 class="title" :class="['active', 'line']">{
{message}}h2>
<h2 class="title" :class="[active, line]">{
{message}}h2>
<h2 class="title" :class="getClasses()">{
{message}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
active: 'aaaa',
line: 'bbbbbb'
},
methods: {
getClasses: function () {
return [this.active, this.line]
}
}
})
script>
案例
- 点击哪个那个变红
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
<style>
.active{
color: red;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="(m, index) in movies"
@click="liClick(index)"
:class="{active:currentIndex===index}"> {
{index}}-{
{m}}li>
ul>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
movies:['海王','海尔兄弟','火影忍者','进击的巨人'],
currentIndex: 0
},
methods:{
liClick(index){
this.currentIndex = index;
}
}
})
script>
body>
html>
1.7.3 动态绑定style
对象绑定
:style="{fontSize:finalSize + 'px',color:finalColor}"style后边跟的是一个对象类型- 对象的
key是CSS属性名称 - 对象的
value是具体赋的值,值可以来自于data中的属性
- 对象的
<div id="app">
<h2 :style="{fontSize:finalSize}">{
{message}}h2>
<h2 :style="{fontSize:finalSize + 'px',color:finalColor}">{
{message}}h2>
<h2 :style="getStyles()">{
{message}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
// finalSize: '100px'
finalSize: 100,
finalColor: 'red'
},
methods:{
getStyles:function () {
return {
fontSize:this.fontSize + 'px',backgroundColor: this.finalColor}
}
}
})
script>
数组绑定
style后边跟的是一个数组类型- 多个值以逗号
,分割即可
- 多个值以逗号
<div id="app">
<h2 :style="[baseStyle,baseStyle1]">{
{message}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
baseStyle:{
backgroundColor:'red'},
baseStyle1:{
fontSize:'100px'},
}
})
script>
1.8 v-on
- 作用:绑定事件监听器
- 缩写:
@ - 预期:Function|Inline Statement |Object
- 参数: event
1.8.1 基本使用
<div id="app">
<h2>{
{counter}}h2>
<button @click="increment()">+button>
<button @click="decrement()">-button>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
counter: 0
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.counter++;
},
decrement() {
this.counter--;
}
}
})
script>
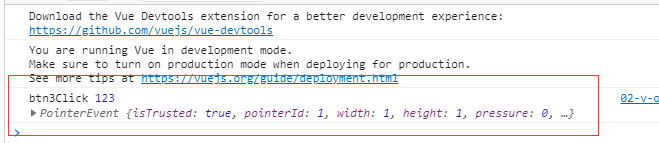
1.8.2 参数问题
- 情况一:如果该方法不需要额外参数,那么方法后的()可以不添加
- 但是注意:如果方法本身中有一个参数,那么会默认将原生事件event参数传递进去
- 情况二:如果需要同时传入某个参数,同时需要event时,可以通过$event传入事件
<div id="app">
<button @click="btn1Click()">按钮1button>
<button @click="btn1Click">按钮1button>
<button @click="btn2Click">按钮2button>
<button @click="btn3Click(abc,$event)">按钮3button>
<button>按钮4button>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
abc: 123
},
methods:{
btn1Click(){
console.log('btn1Click');
},
btn2Click(event){
console.log('btn2Click',event);
},
btn3Click(abc,event){
console.log('btn3Click',abc,event);
},
}
})
script>
1.8.3 修饰符
- Vue提供了修饰符来帮助我们方便的处理一些事件:
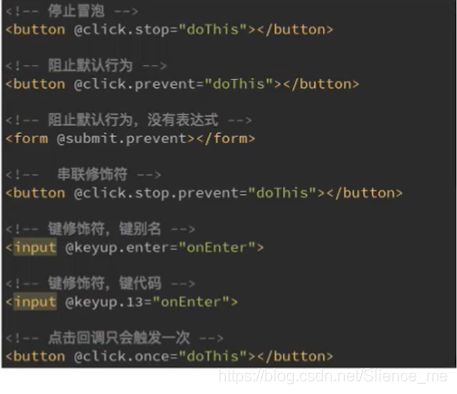
.stop调用event.stopPropagation()避免事件冒泡.prevent调用event.preventDefault()阻止默认事件.{keyCode|keyAlias}只是事件从特定键触发时才触发回调 监听键盘的某个键帽的点击.native监听组件根元素的原生事件.once只触发一次回调
1.9 v-if & v-else
<div id="app">
<h2 v-if="score>=90">优秀h2>
<h2 v-else-if="score>=80">良好h2>
<h2 v-else-if="score>=60">及格h2>
<h2 v-else>不及格h2>
------------------------------------
<h2>{
{result}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
score: 88
},
computed:{
result(){
let showMessage = ''
if (this.score>=90){
showMessage = '优秀';
}else if(this.score>=80){
showMessage = '良好';
}else if(this.score>=60){
showMessage='及格';
}else{
showMessage='不及格';
}
return showMessage;
}
}
})
script>
条件渲染案例
<div id="app">
<span v-if="isUser">
<label for="username">用户账号label>
<input type="text" id="username" placeholder="用户账号" key="username">
span>
<span v-else>
<label for="email">用户邮箱label>
<input type="text" id="email" placeholder="用户邮箱" key="email">
span>
<button @click="isUser = !isUser">切换类型button>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isUser: true
}
})
script>
1.10 v-show
v-if和v-show都可以决定一个元素是否渲染,区别是:v-if当条件为false时,压根不会有对应的元素在DOM中v-show当条件为false时,仅仅是将元素的display属性设置为none而已
- 开发中需要在显示与隐藏之间切片很频繁时建议选择
v-show - 只有一次切换时,建议使用
v-if
<div id="app">
<h2 v-if="isShow" id="aaa">{
{message}}h2>
<h2 v-show="isShow" id="bbb">{
{message}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
isShow:true
}
})
script>
1.11 v-for
v-for的语法类似于javaScript中的for循环- 格式如下:
item in items的形式
- 如果便利的过程不需要索引值
v-for="movie in movies"- 依次从
movies中取出movie,并且在元素中,我们可以使用Mustache语法,来使用movie
- 如果在遍历的过程中,我们需要拿到元素在数组中的索引值
- 语法格式:
v-for=(item, index) in items - 其中的
index就代表了去除的item在原数组的索引值
- 语法格式:
- 官方推荐我们在使用v-for时,给对应的元素或组件添加上一个
:key属性 - key的主要作用是为了高效的更新虚拟DOM
遍历数组
- 响应式的相关方法
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in names">{
{item}}li>
ul>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in names">{
{index+1}}. {
{item}}li>
ul>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
names:['why','kobe','james','curry']
}
})
script>
遍历对象
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in info">{
{item}}li>
ul>
<ul>
<li v-for="(value,key,index) in info">{
{value}}-{
{key}}-{
{index}}li>
ul>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
info:{
name:'why',
age:18,
height:1.88
}
}
})
script>
- 绑定唯一key
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in letters" :key="item">{
{item}}li>
ul>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
letters:['A','B','C','D','E']
}
})
script>
1.12 v-model
原理
<div id="app">
<input type="text" :value="message" @input="message = $event.target.value">
{
{message}}
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!'
},
methods:{
valueChange(event){
console.log('-----');
console.log(event);
this.message = event.target.value;
}
}
})
script>
基本使用
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="message">
{
{message}}
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!'
}
})
script>
v-model:radio
<div id="app">
<label for="male">
<input type="radio" id="male" value="男" v-model="sex">男
label>
<label for="female">
<input type="radio" id="female" value="女" v-model="sex">女
label>
<h2>您选择的性别是: {
{sex}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
sex:'男',
}
})
script>
v-model:checkbox
<div id="app">
<label for="agreement">
<input type="checkbox" id="agreement" v-model="isAgree">同意协议
label>
<h2>您选择的是:{
{isAgree}}h2>
<button :disabled="!isAgree">下一步button>
<br>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="篮球">篮球
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="足球">足球
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="乒乓球">乒乓球
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="羽毛球">羽毛球
label>
<h2>您的爱好是:{
{hobbies}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
isAgree:false,
hobbies:[]
},
})
script>
v-model:select
<div id="app">
<select name="abc" v-model="fruit">
<option value="苹果">苹果option>
<option value="香蕉">香蕉option>
<option value="西瓜">西瓜option>
<option value="菠萝">菠萝option>
select>
<h2>您选择是:{
{fruit}}h2>
<br>
<select name="abc" v-model="fruits" multiple>
<option value="苹果">苹果option>
<option value="香蕉">香蕉option>
<option value="西瓜">西瓜option>
<option value="菠萝">菠萝option>
select>
<h2>您选择是:{
{fruits}}h2>
<label v-for="item in originFruits" :for="item">
<input type="checkbox" :value="item" :id="item" v-model="balls">{
{item}}
label>
<h2>您选择是:{
{balls}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!',
fruit: '香蕉', //单选框
fruits:[], //多选框
originFruits:['篮球','足球','乒乓球','羽毛球','台球','高尔夫球'],
balls:[],
}
})
script>
修饰符
lazy修饰符:- 默认情况下,v-model默认是在input事件中同步输入框的数据的
- 一旦有数据发生改变对应的data中的数据就会自动发生改变
- lazy修饰符可以让数据失去焦点或者回车时才更新
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model.lazy="message">
<h2>{
{message}}h2>
<input type="number" v-model.number="age">
<h2>{
{typeof age}}h2>
<input type="text" v-model.trim="name">
<h2>{
{name}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '你好啊!'
}
})
script>
-
number修饰符:- 默认情况下,在输入框中无论输入字母还是数字,都被认为字符串处理
- 如果希望是数字类型,最好直接将内容数字处理
- number修饰符可以让输入框中的内容转成数字类型
-
trim修饰符:- trim修饰符可以去除两侧空格
-------------------------------
2.计算属性
2.1 基本使用
<div id="app">
<h2>{
{firstName + ' ' + lastName}}h2>
<h2>{
{firstName}} {
{lastName}}h2>
<h2>{
{getFullName()}}h2>
<h2 >{
{fullName}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: 'Lebron',
lastName: 'James'
},
computed:{
fullName: function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
}
},
methods: {
getFullName() {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
}
}
})
script>
2.2 复杂操作
<div id="app">
<h2>总价格:{
{totalPrice}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
books: [
{
id: 110, name: 'Unix编程艺术', price: 119},
{
id: 111, name: '代码大全', price: 105},
{
id: 112, name: '深入理解计算机原理', price: 98},
{
id: 113, name: '现代操作系统', price: 87},
]
},
computed: {
totalPrice: function () {
let result = 0
for (let i=0; i<this.books.length;i++){
result += this.books[i].price
}
return result
// for (let i in this.books) {
// result += this.books[i].price
// }
//
// for (let book of this.books) {
//
// }
}
}
})
script>
2.3 setter和getter
- 很好理解的
setter和getter - 一般只是用
getter来读取,而setter不常用
<div id="app">
<h2>{
{fullName}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: 'kobe',
lastName: 'Bryant'
},
computed:{
// fullName:function (){
// return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
// },
// name: 'coderwhy',
//计算属性一般是没有set方法,只读属性
fullName:{
set:function (newValue) {
console.log("---------"+ newValue);
const names = newValue.split(' ');
this.firstName = names[0];
this.lastName = names[1];
},
get:function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
}
},
// fullName:function () {
// return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
// }
}
})
script>
2.4 缓存
methods和computed都可以实现功能- 计算属性会进行缓存,如果多次使用时,计算属性只调用一次
computed效率高
<div id="app">
<h2>{
{firstName}} {
{lastName}}h2>
<h2>{
{getFullName()}}h2>
<h2>{
{getFullName()}}h2>
<h2>{
{getFullName()}}h2>
<h2>{
{getFullName()}}h2>
<h2>{
{getFullName()}}h2>
<h2>{
{fullName}}h2>
<h2>{
{fullName}}h2>
<h2>{
{fullName}}h2>
<h2>{
{fullName}}h2>
<h2>{
{fullName}}h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: 'kobe',
lastName: 'Bryant'
},
methods: {
getFullName() {
console.log('getFullName');
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
}
},
computed: {
fullName: function () {
console.log('fullName');
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
}
}
})
script>
3. ES6补充
3.1 let/var
-
事实上var的设计可以看成JavaScript语言设计上的错误,但是这种错误多半不能修复和移除,以为需要向后兼容
- 大概十年前,Brendan Eich 就决定修复这个问题,于是他添加了一个新的关键词:
let
- 大概十年前,Brendan Eich 就决定修复这个问题,于是他添加了一个新的关键词:
-
块级作用域
- JS中使用var来声明一个变量时,变量的作用域主要是和函数的定义有关
- 针对于其他块定义来说是没有作用域的,比如if/for等,这在我们开发中往往会引起一些问题
-
ES5之前因为if和for都没有块级作用域的概念,所以在很多时候,我们都必须借助于function的作用域来解决应用外面变量的问题
<script>
// 1.变量作用域:变量在什么范围内是可用的
// {
// var name = 'why'
// console.log(name);
// }
// console.log(name);
//2.没有块级作用域引起的问题 if 的块级
// var func;
// if (true){
// var name = 'why';
// func = function () {
// console.log(name);
// }
// func()
// }
// console.log(name);
//2.没有块级作用域引起的问题 for 的块级
var btns = document.getElementsByTagName('button');
for (var i = 0; i < btns.length; i++) {
(function (i) {
btns[i].addEventListener('click', function () {
console.log('第' + (i + 1) + '个按钮被点击');
})
})(i)
}
const btns = document.getElementsByTagName('button');
for (let i = 0; i < btns.length; i++) {
btns[i].addEventListener('click', function () {
console.log('第' + (i + 1) + '个按钮被点击');
})
}
script>
3.2 const的使用
- const关键字
- 将某个变量变为常量
- 在js中,使用其标识后,不可再次赋值
- 不可修改
- 定义必须赋值
4. 购物车案例
index.html
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="books.length">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>th>
<th>书籍名称th>
<th>出版日期th>
<th>价格th>
<th>购买数量th>
<th>操作th>
tr>
thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(item,index) in books">
<td>{
{item.id}}td>
<td>{
{item.name}}td>
<td>{
{item.date}}td>
<td>{
{item.price | showPrice}}td>
<td>
<button @click="decrement(index)" :disabled="item.count <= 1">-button>
{
{item.count}}
<button @click="increment(index)">+button>
td>
<td>
<button @click="removeHandle(index)">移除button>
td>
tr>
tbody>
table>
<h2>总价格:{
{totalPrice}}h2>
div>
<h2 v-else>购物车为空h2>
div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">script>
<script src="main.js">script>
body>
html>
main.js
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
books: [
{
id: 1,
name: '《算法导论》',
date: '2006-9',
price: 85.00,
count: 1
},
{
id: 2,
name: '《UNIX编程艺术》',
date: '2006-2',
price: 59.00,
count: 1
},
{
id: 3,
name: '《编程珠玑》',
date: '2006-10',
price: 39.00,
count: 1
},
{
id: 4,
name: '《代码大全》',
date: '2006-3',
price: 128.00,
count: 1
}
]
},
computed: {
totalPrice() {
// 1.普通for循环
let totalPrice = 0;
// for (let i = 0; i < this.books.length; i++) {
// totalPrice += this.books[i].count * this.books[i].price;
// }
// return totalPrice;
//2. for(let i in this.books)
// for (let i in this.books) {
// totalPrice += this.books[i].count * this.books[i].price;
// }
// return totalPrice;
// for(let i in/of this.books)
for(let item of this.books){
console.log(i);
totalPrice += item.count * item.price;
}
return totalPrice;
},
},
methods: {
// getFinalPrice(price){
// return '¥'+ price.toFixed(2);
// }
increment(index) {
this.books[index].count++;
},
decrement(index) {
this.books[index].count--;
},
removeHandle(index) {
this.books.splice(index, 1)
}
},
filters: {
showPrice(price) {
return '¥' + price.toFixed(2);
}
}
})
style.css
table{
border: 1px solid #e9e9e9;
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
}
th,td{
padding: 8px 16px;
border: 1px solid #e9e9e9;
text-align: left;
}
th{
background-color: #f7f7f7;
color: #5c6b77;
font-weight: 600;
}
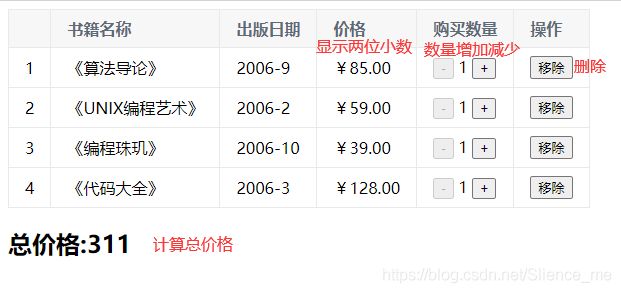
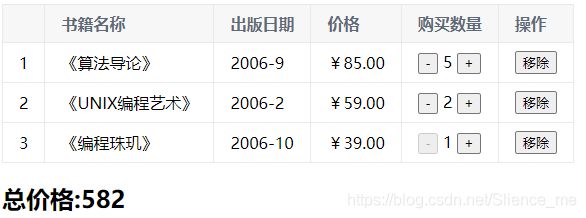
效果图
5. JavaScript高阶函数
filter()
const nums=[10,20,30,40,50,222,50,15]
let newNums = nums.filter(function (n) {
return n>=100;
})
//newNums = [10, 20, 40, 50]
map()
const newNums = [10, 20, 40, 50]
let new2Nums = newNums.map(function (n) {
return n*2;
})
//new2Nums= [20, 40, 80, 100]
reduce()
new2Nums= [20, 40, 80, 100]
let total = new2Nums.reduce(function (preValue,n) {
return preValue + n;
}, 0)
//240
综合
const nums=[10,20,111,222,444,40,50]
let total = nums.filter(function (n) {
return n < 100;
}).map(function (n) {
return n*2;
}).reduce(function (preValue,n) {
return preValue + n;
}, 0)
console.log(total);
简化
const nums=[10,20,111,222,444,40,50]
let total = nums.filter(n => n<100).map(n => n * 2).reduce((pre, n) => pre + n);
console.log(total);