Spring Security如何来实践
本文来说下Spring Security如何来实践。在使用这个框架的时候,有种不知道从何处开始的感觉,本文来说下security的实践思路。
文章目录
- 概述
- Security初体验
- Security定制登录退出行为
- Security定制自定义用户认证
- Security定制自定义授权策略
- 本文小结
概述
我们都知道Security主要做两件事,一件是认证,一件是授权。这个也是security的核心。
Spring Security实践思路
- 首先导入security的maven依赖,编写一个配置类(SecurityConfig)来重写WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
- 在配置类SecurityConfig中重写configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth),这个方法是将数据库和security关联起来
- 在AuthenticationManagerBuilder 里面需要添加UserDetailsService的实现类(UserDetailsServiceImpl),UserDetailsServiceImpl需要实现loadUserByUsername(String username)方法,这个方法到数据库中去查询查询数据,返回一个UserDetails对象,
- UserDetails对象会被security框架封装成一个Authentication对象,存放在SecurityContextHolder上下文中,需要使用的时候只要到AuthenticationManager中去拿。
Security初体验
Spring Security如何使用,先在你的项目pom.xml文件中声明依赖。
maven导入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId>
dependency>
然后创建一个类并继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter这个方法
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth){
super.configure(auth);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http){
super.configure(http);
}
@Override
protected void configure(WebSecurity web){
super.configure(web);
}
}
接下来我们先看看protected void configure(HttpSecurity http)这个方法提供了一个默认的配置。
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.httpBasic();
}
http.authorizeRequests()其中这里的意思是指通过authorizeRequests()方法来开始请求权限配置。
而接着的.anyRequest().authenticated()是对http所有的请求必须通过授权认证才可以访问。
HttpSecurity如何来过滤请求
过滤请求的方法直观描述
方法描述
在实际开发中,使用ant风格的形式来匹配url请求
configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity)样例代码
/**
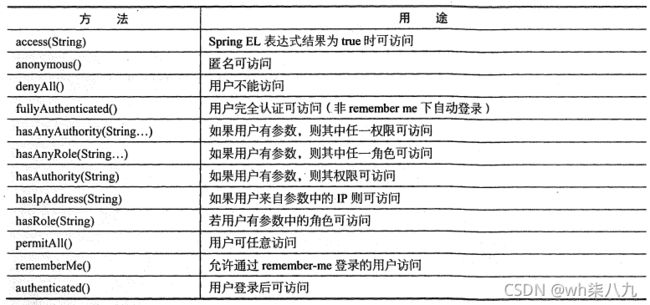
* anyRequest | 匹配所有请求路径
* access | SpringEl表达式结果为true时可以访问
* anonymous | 匿名可以访问
* denyAll | 用户不能访问
* fullyAuthenticated | 用户完全认证可以访问(非remember-me下自动登录)
* hasAnyAuthority | 如果有参数,参数表示权限,则其中任何一个权限可以访问
* hasAnyRole | 如果有参数,参数表示角色,则其中任何一个角色可以访问
* hasAuthority | 如果有参数,参数表示权限,则其权限可以访问
* hasIpAddress | 如果有参数,参数表示IP地址,如果用户IP和参数匹配,则可以访问
* hasRole | 如果有参数,参数表示角色,则其角色可以访问
* permitAll | 用户可以任意访问
* rememberMe | 允许通过remember-me登录的用户访问
* authenticated | 用户登录后可访问
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
httpSecurity
// CSRF禁用,因为不使用session
.csrf().disable()
// 认证失败处理类
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(unauthorizedHandler).and()
// 基于token,所以不需要session
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS).and()
// 过滤请求
.authorizeRequests()
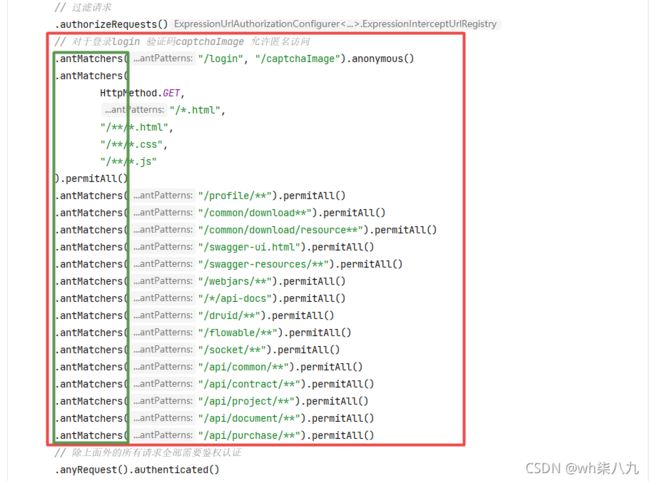
// 对于登录login 验证码captchaImage 允许匿名访问
.antMatchers("/login", "/captchaImage").anonymous()
.antMatchers(
HttpMethod.GET,
"/*.html",
"/**/*.html",
"/**/*.css",
"/**/*.js"
).permitAll()
.antMatchers("/profile/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/common/download**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/common/download/resource**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/swagger-ui.html").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/swagger-resources/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/webjars/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/*/api-docs").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/druid/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/flowable/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/socket/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/common/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/contract/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/project/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/document/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/purchase/**").permitAll()
// 除上面外的所有请求全部需要鉴权认证
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.headers().frameOptions().disable();
httpSecurity.logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler);
// 添加JWT filter
httpSecurity.addFilterBefore(authenticationTokenFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
// 添加CORS filter
httpSecurity.addFilterBefore(corsFilter, JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter.class);
httpSecurity.addFilterBefore(corsFilter, LogoutFilter.class);
}
Ant通配符说明
ANT通配符有三种:
| 通配符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ? | 匹配任何单字符 |
| * | 匹配0或者任意数量的字符 |
| ** | 匹配0或者更多的目录 |
例子:
URL路径 说明
/app/*.x 匹配(Matches)所有在app路径下的.x文件
/app/p?ttern 匹配(Matches) /app/pattern 和 /app/pXttern,但是不包括/app/pttern
/**/example 匹配(Matches) /app/example, /app/foo/example, 和 /example
/app/**/dir/file. 匹配(Matches) /app/dir/file.jsp, /app/foo/dir/file.html,/app/foo/bar/dir/file.pdf, 和 /app/dir/file.java
/**/*.jsp 匹配(Matches)任何的.jsp 文件
属性:
最长匹配原则(has more characters)
说明,URL请求/app/dir/file.jsp,现在存在两个路径匹配模式/**/*.jsp和/app/dir/*.jsp,那么会根据模式/app/dir/*.jsp来匹配
而and()是返回一个securityBuilder对象,formLogin()和httpBasic()是授权的两种方式。
httpBasic()授权认证
formLogin()授权认证
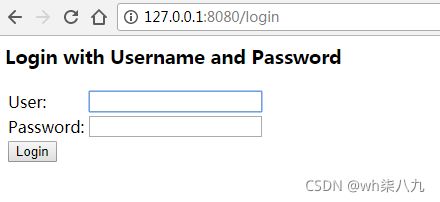
当然这些界面都是spring security原生的界面,我们也可以自定义我们的formLogin页面!
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
//指定登录页的路径
.loginPage("/login")
//必须允许所有用户访问我们的登录页(例如未验证的用户,否则验证流程就会进入死循环)
//这个formLogin().permitAll()方法允许所有用户基于表单登录访问/login这个page。
.permitAll();
}
提示一下,这个自定义表单登录的自定义页面中的登录名参数必须被命名为username,密码参数必须被命名为password。而接下来当我们需要对某些开放的url,给与任何人访问的时候,我们应该如何设置呢?答案很简单我们先看着代码慢慢深入!
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
//http.authorizeRequests()方法有多个子节点,每个macher按照他们的声明顺序执行
.authorizeRequests()
//我们指定任何用户都可以访问多个URL的模式。
//任何用户都可以访问以"/resources/","/signup", 或者 "/about"开头的URL。
.antMatchers("/resources/**", "/signup", "/about").permitAll()
//以 "/admin/" 开头的URL只能让拥有 "ROLE_ADMIN"角色的用户访问。
//请注意我们使用 hasRole 方法,没有使用 "ROLE_" 前缀。
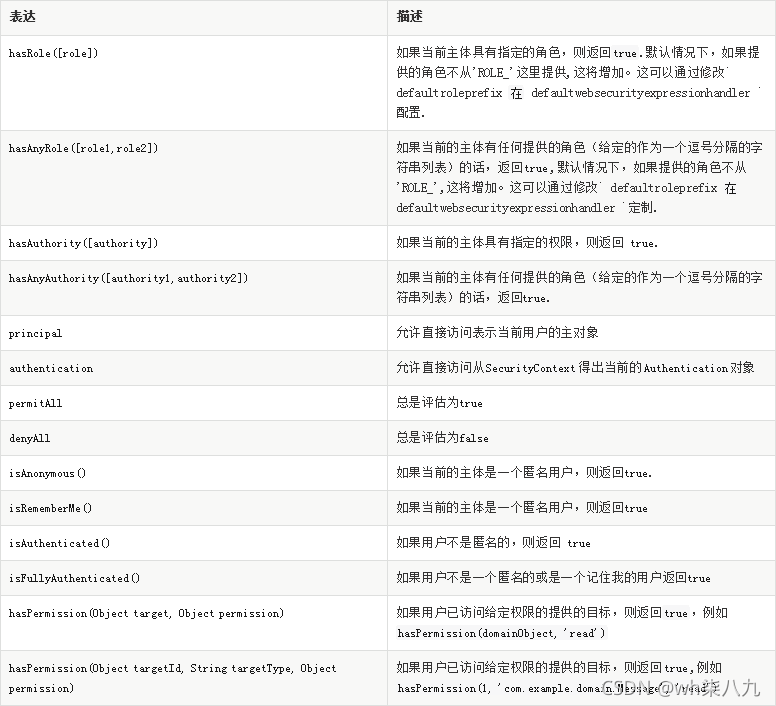
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
//任何以"/db/" 开头的URL需要同时具有 "ROLE_ADMIN" 和 "ROLE_DBA"权限的用户才可以访问。
//和上面一样我们的 hasRole 方法也没有使用 "ROLE_" 前缀。
.antMatchers("/db/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")
//任何以"/db/" 开头的URL只需要拥有 "ROLE_ADMIN" 和 "ROLE_DBA"其中一个权限的用户才可以访问。
//和上面一样我们的 hasRole 方法也没有使用 "ROLE_" 前缀。
.antMatchers("/db/**").hasAnyRole("ADMIN", "DBA")
//尚未匹配的任何URL都要求用户进行身份验证
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
// ...
.formLogin();
}
我们可以在authorizeRequests() 后定义多个antMatchers()配置器来控制不同的url接受不同权限的用户访问,而其中permitAll() 方法是运行所有权限用户包含匿名用户访问。
而hasRole(“权限”)则是允许这个url给与参数中相等的权限访问。access(“hasRole(‘权限’) and hasRole(‘权限’)”) 是指允许访问这个url必须同时拥有参数中多个身份权限才可以访问。hasAnyRole(“ADMIN”, “DBA”)是指允许访问这个url必须同时拥有参数中多个身份权限中的一个就可以访问该url。
Security定制登录退出行为
我们接下来就简单的定制一下登录登出行为
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
//通过formlogin方法登录,并设置登录url为/api/user/login
.formLogin().loginPage("/api/user/login")
//指定登录成功后跳转到/index页面
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index")
//指定登录失败后跳转到/login?error页面
.failureUrl("/login?error")
.permitAll()
.and()
//开启cookie储存用户信息,并设置有效期为14天,指定cookie中的密钥
.rememberMe().tokenValiditySeconds(1209600).key("mykey")
.and()
.logout()
//指定登出的url
.logoutUrl("/api/user/logout")
//指定登场成功之后跳转的url
.logoutSuccessUrl("/index")
.permitAll();
}
Security定制自定义用户认证
用户认证流程
定制自定义用户认证
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
//重写了configure参数为AuthenticationManagerBuilder的方法
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth){
//并根据传入的AuthenticationManagerBuilder中的userDetailsService方法来接收我们自定义的认证方法。
//且该方法必须要实现UserDetailsService这个接口。
auth.userDetailsService(new myUserDetailsService())
//密码使用BCryptPasswordEncoder()方法验证,因为这里使用了BCryptPasswordEncoder()方法验证。
// 所以在注册用户的时候在接收前台明文密码之后也需要使用BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode(明文密码)方法加密密码。
.passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder());;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http){
super.configure(http);
}
@Override
protected void configure(WebSecurity web){
super.configure(web);
}
}
新建myUserDetailsService方法并实现UserDetailsService这个接口
@Component
public class myUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
//由于是演示这里就不再创建service层了,直接注入UserRepository。
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String userName) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//查询账号是否存在,是就返回一个UserDetails的对象,否就抛出异常!
User user = userRepository.findByName(userName);
if (user == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("UserName " + userName + " not found");
}
return new SecurityUser(user);
}
}
基本的认证逻辑就到这里了,对于有另外的业务需求都可以在自定义的myUserDetailsService中处理完成!
Security定制自定义授权策略
Spring Security定制自定义授权策略
@EnableGlobalAuthentication
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin").permitAll()
//使用自定义授权策略
.anyRequest().access("@mySecurity.check(authentication,request)");
}
}
新建MySecurity类
@Component("mySecurity")
public class MySecurity(){
//这里应该注入用户和该用户所拥有的权限(权限在登录成功的时候已经缓存起来,当需要访问该用户的权限是,直接从缓存取出!),然后验证该请求是否有权限,有就返回true,否则则返回false不允许访问该Url。
//而且这里还传入了request,我也可以使用request获取该次请求的类型。
//根据restful风格我们可以使用它来控制我们的权限,例如当这个请求是post请求,证明该请求是向服务器发送一个新建资源请求,我们可以使用request.getMethod()来获取该请求的方式,然后在配合角色所允许的权限路径进行判断和授权操作!
public boolean check(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request){
//如果能获取到Principal对象不为空证明,授权已经通过
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
if(principal != null && principal instanceof UserDetails){
//获取请求登录的url
System.out.println(((UserDetails)principal).getAuthorities()) ;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
本文小结
本文介绍了Security的基础知识,以及Security如何来定制退出登录,如何来自定义用户认证,如何来自定授权策略等security的基础知识。