React 路由组件 详解
文章目录
-
- 路由组件
-
- 1、HashRouter和BrowserRouter
- 2、Route
- 3、Router
- 4、Link和NavLink
- 5、Redirect
- 6、Switch
- 7、withRouter
- 嵌套路由
- 向路由组件传递参数
- 路由跳转的两种模式
- 编程式路由导航
- Router Hooks
路由组件
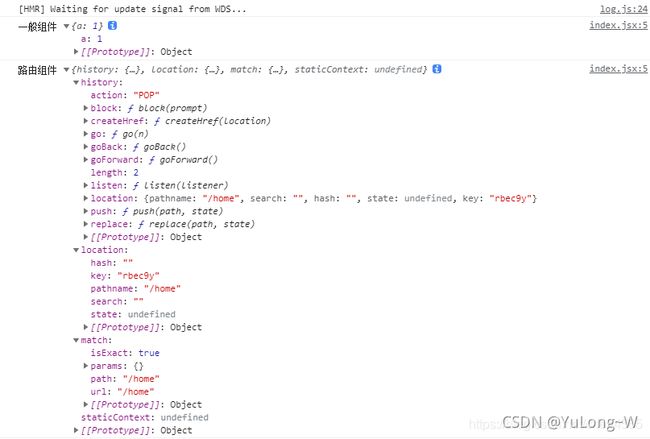
1、写法不同:
- 一般组件:
- 路由组件:
2、存放位置不同:
- 一般组件:components目录
- 路由组件:pages目录
3、接收到的props不同:
- 一般组件:写组件标签时传递了什么,就能收到什么
- 路由组件:接收到三个固定的 属性
- history:
- go: ƒ go(n)
- goBack: ƒ goBack()
- goForward: ƒ goForward()
- push: ƒ push(path, state)
- replace: ƒ replace(path, state)
- location:
- pathname: “/about”
- search: “”
- state: undefined
- match:
- params: {}
- path: “/about”
- url: “/about”
- history:
1、HashRouter和BrowserRouter
其实就是路由的hash和history两种模式,并且这两个组件是路由的容器,必须在最外层
// hash模式
ReactDOM.render(
<HashRouter>
<Route path="/" component={
Home}/>
</HashRouter>
)
// history模式
ReactDOM.render(
<BrowserRouter>
<Route path="/" component={
Home} />
</BrowserRouter>
)
区别:
- 底层原理不一样
- BrowserRouter使用的是H5的history API,不兼容IE9及以下版本
- HashRouter使用的是URL的哈希值
- path表现形式不一样
- BrowserRouter的路径中没有#,例如:localhost:3000/demo/test
- HashRouter的路径包含#,例如:localhost:3000/#/demo/test
- 刷新后对路由state参数的影响
- BrowserRouter没有任何影响,因为state 保存在history对象中
- HashRouter刷新后会导致路由state 参数的丢失!
- 备注:HashRouter可以用于解决一些路径错误相关的问题。
2、Route
路由的一个原材料,它是控制路径对应显示的组件
Route的参数:
- path:跳转的路径
- component: 对应路径显示的组件
- render:可以自己写render函数返回具体的dom,而不需要去设置component
- location: 传递route对象,和当前的route对象对比,如果匹配则跳转
- exact: 匹配规则,true的时候则精确匹配
3、Router
低级路由,适用于任何路由组件,主要和redux深度集成,使用必须配合history对象,使用Router路由的目的是和状态管理库如redux中的history同步对接
<Router history={
history}>
...
</Router>
4、Link和NavLink
两者都是跳转路由,NavLink的参数更多些
Link:
- to: 有两种写法,表示跳转到哪个路由
- 字符串写法:
- 对象写法:
- replace:就是将push改成replace
- innerRef:访问Link标签的dom
NavLink:
-
Link的所有参数
-
activeClassName: 路由激活的时候设置的类名 实现路由链接的高亮
-
activeStyle :路由激活设置的样式
-
exact: 参考Route,符合这个条件才会激活active类
-
strict: 参考Route,符合这个条件才会激活active类
-
isActive: 接收一个回调函数,active状态变化的时候回触发,返回false则中断跳转
const oddEvent = (match, location) => { console.log(match,location) if (!match) { return false } console.log(match.id) return true } <NavLink isActive={ oddEvent} to="/a/123">组件一</NavLink> -
location: 接收一个location对象,当url满足这个对象的条件才会跳转
<NavLink to="/a/123" location={ { key:"mb5wu3", pathname:"/a/123" }}/>
NavLink的使用:
在之前的效果展示中,Link组件不会进行高亮显示,因此改成NavLink用法

App.js文件修改的代码:
{
/* 在React中靠路由链接实现切换组件 */}
<NavLink activeClassName="add" className="list-group-item" to="/home">Home</NavLink>
<NavLink activeClassName="add" className="list-group-item" to="/about">About</NavLink>
//这里用 activeClassName="add" 来控制按钮高亮的颜色显示
index.html 文件修改后的代码:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/bootstrap.css">
<style>
.add{
background-color: rgb(209,137,4) !important; // 因为 bootstrap 的权重比较高,所以要用!important
color:white !important;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="root">div>
body>
html>
NavLink的封装:
因为在 App.js 文件中写 NavLink 太长了, 所以在这里把 NavLink 单独提出来写 MyNavLink 一个组件, 使用时调用它,可以使代码更加简洁
MyNavLink组件代码:
import React, {
Component } from 'react'
import {
NavLink} from 'react-router-dom'
export default class MyNavLink extends Component {
render() {
return (
<NavLink activeClassName="add" className="list-group-item" {
...this.props} />
)
}
}
App.js修改后的代码:
{
/* 在React中靠路由链接实现切换组件 */}
<MyNavLink to="/home">Home</MyNavLink>
<MyNavLink to="/about">About</MyNavLink>
进行封装的知识点:
- 标签体内容是一个特殊的标签属性children
- 通过this.props.children可以获取标签体内容
问题:
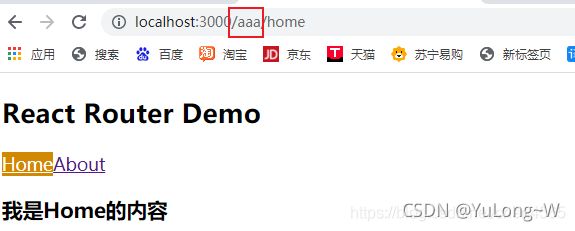
1、解决多级路径刷新页面样式丢失
如果匹配的路径不对, 就会引发css样式的丢失问题
默认执行index.html文件
App.js代码修改:
{
/* 在React中靠路由链接实现切换组件 */}
<MyNavLink to="/aaa/home">Home</MyNavLink>
<MyNavLink to="/aaa/about">About</MyNavLink>
{
/* 注册路由 路由组件写法 */}
<Switch>
<Route path="/aaa/home" component={
Home}/>
<Route path="/aaa/about" component={
About}/>
</Switch>
- public/index.html 中 引入样式时不写 ./ 写 / (常用)
- public/index.html 中 引入样式时不写 ./ 写 %PUBLIC_URL% (常用)
- 使用HashRouter
2、路由的严格匹配与模糊匹配
- 1.默认使用的是模糊匹配(简单记:【输入的路径】必须包含要【匹配的路径】,且顺序要一致)
- 2.开启严格匹配:
- 3.严格匹配不要随便开启,需要再开,有些时候开启会导致无法继续匹配二级路由
App.js代码修改:
{
/* 在React中靠路由链接实现切换组件 */}
<MyNavLink to="/home">Home</MyNavLink>
<MyNavLink to="/aaa/about">About</MyNavLink>
{
/* 注册路由 路由组件写法 */}
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/home" component={
Home}/>
<Route exact path="/about" component={
About}/>
</Switch>
5、Redirect
页面重定向:一般写在所有路由注册的最下方,当所有路由都无法匹配时,跳转到Redirect指定的路由
<Switch>
<Route path="/about" component={
About}/>
<Route path="/home" component={
Home}/>
<Redirect to="/about"/>
</Switch>
用法:
// 基本的重定向
<Redirect to="/somewhere/else" />
// 对象形式
<Redirect
to={
{
pathname: "/login",
search: "?utm=your+face",
state: {
referrer: currentLocation }
}}
/>
// 采用push生成新的记录
<Redirect push to="/somewhere/else" />
// 配合Switch组件使用,form表示重定向之前的路径,如果匹配则重定向,不匹配则不重定向
<Switch>
<Redirect from='/old-path' to='/new-path'/>
<Route path='/new-path' component={
Place}/>
</Switch>
6、Switch
路由切换,只会匹配第一个路由,可以想象成tab栏。Switch内部只能包含Route、Redirect和Router。
通常情况下,path和component是一一对应的关系。Switch可以提高路由匹配效率(单一匹配)。
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={
Home}/>
<Route path="/about" component={
About}/>
<Route path="/:user" component={
User}/>
<Route component={
NoMatch}/>
</Switch>
7、withRouter
当一个非路由组件也想访问到当前路由的match、location、history对象,那么withRouter将是一个非常好的选择,可以理解为将一个组件包裹成路由组件
- withRouter可以加工一般组件, 让一般组件具备路由组件所特有的API
- withRouter的返回值是一个新组件
import {
withRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
const MyComponent = (props) => {
const {
match, location, history } = this.props
return (
<div>{
props.location.pathname}</div>
)
}
const FirstTest = withRouter(MyComponent);
示例:
Header 组件代码:
import React, {
Component } from 'react'
import {
withRouter} from 'react-router-dom'
class Header extends Component {
// 回退
back = () => {
this.props.history.goBack()
}
// 前进
forward = () => {
this.props.history.goForward()
}
/// go
go = () => {
this.props.history.go(2)
}
render() {
// console.log('一般组件',this.props)
return (
<div className="page-header">
<h2>React Router Demo</h2>
<button onClick={
this.back}>回退</button>
<button onClick={
this.forward}>前进</button>
<button onClick={
this.go}>go</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default withRouter(Header)
嵌套路由
1.注册子路由时要写上父路由的path值
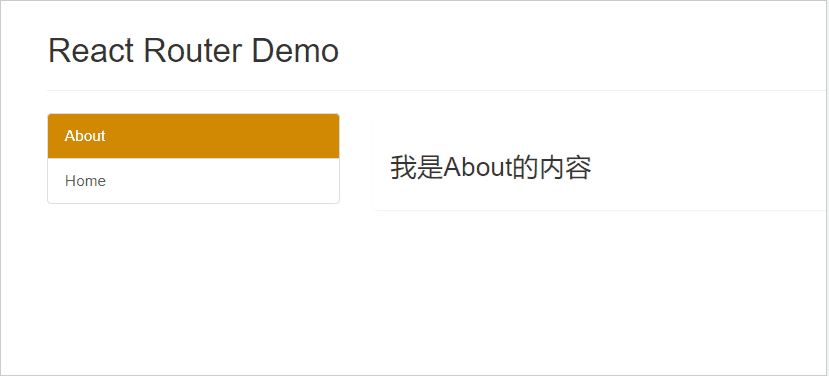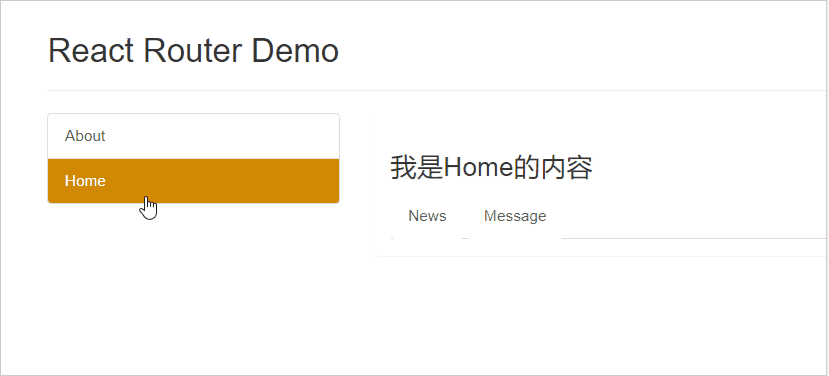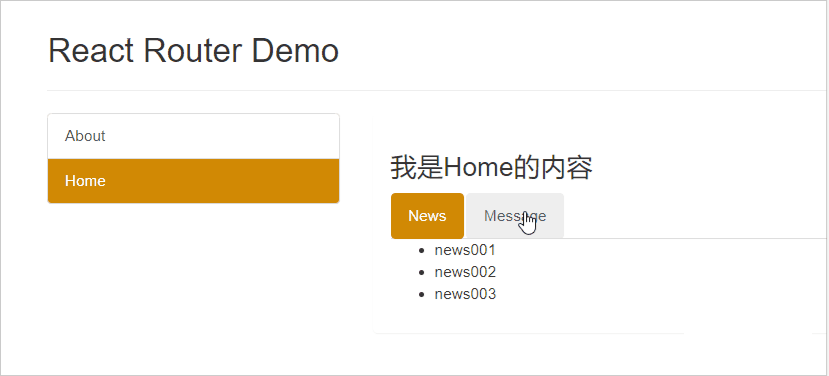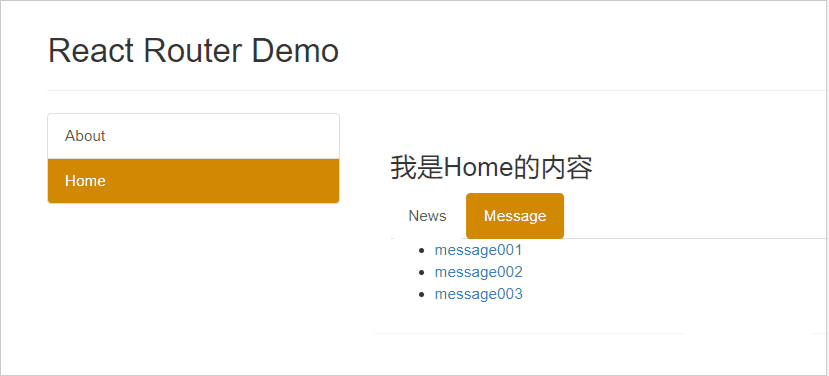
News 组件代码:
import React, {
Component } from 'react'
export default class News extends Component {
render() {
return (
<ul>
<li>news001</li>
<li>news002</li>
<li>news003</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
Message 组件代码:
import React, {
Component } from 'react'
export default class Message extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="/message1">message001</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="/message2">message002</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="/message/3">message003</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
)
}
}
Home组件代码:
import React, {
Component } from 'react'
import MyNavLink from '../../components/MyNavLink'
import {
Route,Switch } from 'react-router-dom'
import News from './News'
import Message from './Message'
export default class Home extends Component {
render() {
console.log('路由组件', this.props)
return (
<div>
<h3>我是Home的内容</h3>
<div>
<ul class="nav nav-tabs">
<li>
{
/* 注册子路由时要写上父路由的path值 */}
<MyNavLink to="/home/news">News</MyNavLink>
</li>
<li>
<MyNavLink to="/home/message">Message</MyNavLink>
</li>
</ul>
{
/* 注册路由 */}
<Switch>
{
/* 注册子路由时要写上父路由的path值 */}
<Route path="/home/news" component={
News}/>
<Route path="/home/message" component={
Message}/>
</Switch>
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
向路由组件传递参数
- params参数
- 路由链接(携带参数):
详情 - 注册路由(声明接收):
- 接收参数:this.props.match.params
- 路由链接(携带参数):
- search参数
- 路由链接(携带参数):
详情 - 注册路由(无需声明,正常注册即可):
- 接收参数:this.props.location.search
- 备注:获取到的search是urlencoded编码字符串,需要借助querystring解析
- 路由链接(携带参数):
- state参数
- 路由链接(携带参数):
详情 - 注册路由(无需声明,正常注册即可):
- 接收参数:this.props.location.state
- 备注:刷新也可以保留住参数
- 路由链接(携带参数):
Message 组件代码:
import React, {
Component } from 'react'
import {
Link, Route} from 'react-router-dom'
import Detail from './Detail'
export default class Message extends Component {
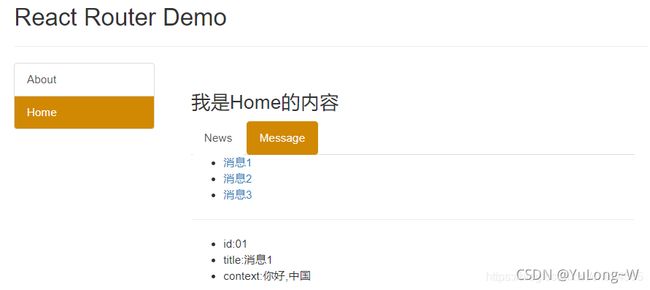
state = {
messageArr:[
{
id:'01',title:'消息1'},
{
id:'02',title:'消息2'},
{
id:'03',title:'消息3'},
]
}
render() {
const {
messageArr } = this.state;
return (
<div>
<ul>
{
messageArr.map((msgObj)=>{
return (
<li key={
msgObj.id}>
{
/* 1、向路由组件传递params参数 */}
{
/*
{msgObj.title}
*/}
{
/* 2、向路由组件传递search参数 */}
{
/*
{msgObj.title}
*/}
{
/* 3、向路由组件传递state参数 */}
<Link
to={
{
pathname:"/home/message/detail",state:{
id:msgObj.id,title:msgObj.title}>{
msgObj.title}
</Link>
</li>
)
})
}
</ul>
<hr />
{
/* 1、声明接收params参数 */}
{
/* */ }
{
/* 2、params参数无需声明接收, 正常注册即可 */}
{
/* */ }
{
/* 3、state参数无需声明接收, 正常注册即可 */}
<Route path="/home/message/detail" component={
Detail}/>
</div>
)
}
}
Detail 组件代码:
import React, {
Component } from 'react'
// import qs from 'querystring'
const DetailData = [
{
id:'01',content:'你好,中国'},
{
id:'02',content:'你好,世界'},
{
id:'03',content:'你好,我'}
]
export default class Detail extends Component {
render() {
// 1、接收params参数
// const {id,title} = this.props.match.params
// 2、接收search参数
// const {search} = this.props.location
// const {id,title} = qs.parse(search.slice(1))
// 3、接收state参数
const {
id,title} = this.props.location.state
const findResult = DetailData.find((datailObj)=>{
return datailObj.id === id
})
return (
<ul>
<li>id:{
id}</li>
<li>title:{
title}</li>
<li>context:{
findResult.content}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
路由跳转的两种模式
push与replace
默认为push,要使用replace时,在标签上加replace就行
<Link
replace
to={
{
pathname:"/home/message/detail",state:{
id:msgObj.id,title:msgObj.title}>{
msgObj.title}
</Link>
编程式路由导航
借助this.prosp.history对象上的API对操作路由跳转、前进、后退
- this.prosp.history.push()
- this.prosp.history.replace()
- this.prosp.history.goBack()
- this.prosp.history.goForward()
- this.prosp.history.go()
import React, {
Component } from 'react'
import {
Link, Route, repalce} from 'react-router-dom'
import Detail from './Detail'
export default class Message extends Component {
state = {
messageArr:[
{
id:'01',title:'消息1'},
{
id:'02',title:'消息2'},
{
id:'03',title:'消息3'},
]
}
// push查看
pushShow = (id,title) => {
//push跳转+携带params参数
// this.props.history.push(`/home/message/detail/${id}/${title}`)
// push 跳转+携带search参数
// this.props.history.push(`/home/message/detail?id=${id}&title=${title}`)
// push 跳转+携带state参数
this.props.history.push(`/home/message/detail`,{
id,title})
}
// replace 查看
replaceShow = (id,title) => {
// replace跳转+携带params参数
// this.props.history.replace(`/home/message/detail/${id}/${title}`)
// replace跳转+携带search参数
// this.props.history.replace(`/home/message/detail?id=${id}&title=${title}`)
// push 跳转+携带state参数
this.props.history.replace(`/home/message/detail`,{
id,title})
}
back = () => {
this.props.history.goBack()
}
forward = () => {
this.props.history.goForward()
}
go = () => {
this.props.history.go(2)
}
render() {
const {
messageArr } = this.state;
return (
<div>
<ul>
{
messageArr.map((msgObj)=>{
return (
<li key={
msgObj.id}>
{
/* 向路由组件传递params参数 */}
{
/*
{msgObj.title}
*/}
{
/* 向路由组件传递search参数 */}
{
/*
{msgObj.title}
*/}
{
/* 向路由组件传递state参数 */}
<Link
to={
{
pathname:"/home/message/detail",state:{
id:msgObj.id,title:msgObj.title}>{
msgObj.title}
</Link>
</li>
<button onClick={
()=> this.pushShow(msgObj.id,msgObj.title)}>push查看</button>
<button onClick={
()=> this.replaceShow(msgObj.id,msgObj.title)}>repalce查看</button>
)
})
}
</ul>
<hr />
{
/* 声明接收params参数 */}
{
/* */ }
{
/* params参数无需声明接收, 正常注册即可 */}
{
/* */ }
{
/* state参数无需声明接收, 正常注册即可 */}
<Route path="/home/message/detail" component={
Detail}/>
<button onClick={
this.back}>回退</button>
<button onClick={
this.forward}>前进</button>
<button onClick={
this.go}>go</button>
</div>
)
}
}
Router Hooks
在Router5.x中新增加了Router Hooks用于在函数组件中获取路由信息。使用规则和React的其他Hooks一致
(1)useHistory:返回history对象
(2)useLocation:返回location对象
(3)useRouteMatch:返回match对象
(4)useParams:返回match对象中的params,也就是path传递的参数
import React from 'react';
import {
useHistory } from 'react-router-dom';
function backBtn(props) {
let history = useHistory;
return <button onClick={
()=> {
history.goBack();
}>返回上一页</button>
}