MyBatis最强笔记
MyBatis 沉。 Date:2020-10-26
环境:
- JDK1.8
- Mysql 5.7
- maven 3.6.1
- IDEA
回顾:
- JDBC
- Mysql
- Java基础
- Maven
- Junit
SSM框架:配置文件,最好的方式看官网文档
一、简介
1.1、什么是Mybaties
-
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架
-
它支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。
-
MyBatis避免了除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集
-
MyBatis可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口和 Java POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录。
-
MyBatis 本是**apache的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年这个项目由apache software foundation 迁移到了google code**,并且改名为MyBatis 。2013年11月迁移到Github。
1.2、如何获得Mybatis?
-
maven仓库:
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatisgroupId> <artifactId>mybatisartifactId> <version>3.5.2version> dependency> -
github:https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3
-
中文文档:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/
1.3、持久化
数据持久化
- 持久化就是讲程序的数据在持久状态和瞬时状态转化的过程
- 内存:断电即失
- 数据库(JDBC),IO文件持久化。
- 生活:冷藏、罐头
为什么需要持久化?
- 有一些对象,不能让他丢掉。
- 内存太贵了
1.4、持久层
Dao层,Serbvice层,Controller层…
- 完成持久化工作的代码块
- 层是界限十分明显的。
1.5、为什么需要Mybaties?
- 帮助程序猿将数据存入到数据库中
- 方便
- 传统的JDBC代码太复杂了、想要简化,所以出现了框架
- 不用Mybaties也可以。但是使用更容易上手。
- 优点
- 简单易学:本身就很小且简单。没有任何第三方依赖,最简单安装只要两个jar文件+配置几个sql映射文件易于学习,易于使用,通过文档和源代码,可以比较完全的掌握它的设计思路和实现。
- 灵活:mybatis不会对应用程序或者数据库的现有设计强加任何影响。 sql写在xml里,便于统一管理和优化。通过sql语句可以满足操作数据库的所有需求。
- 解除sql与程序代码的耦合:通过提供DAO层,将业务逻辑和数据访问逻辑分离,使系统的设计更清晰,更易维护,更易单元测试。sql和代码的分离,提高了可维护性。
- 提供映射标签,支持对象与数据库的orm字段关系映射
- 提供对象关系映射标签,支持对象关系组建维护
- 提供xml标签,支持编写动态sql。
最重要的一点:使用的人多!
Spring,SpringMVC,SpringBoot
二、第一个Mybaties程序
思路:搭建环境–>导入Mybatis–>编写代码–>测试
2.1、搭建环境
搭建数据库
CREATE DATABASE `mybatis`;
USE `mybatis`;
CREATE TABLE `user`(
`id` INT(20) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
`pwd` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `user`(`id`,`name`,`pwd`) VALUES
(1,'小王子','123456'),
(2,'小玫瑰','156312'),
(3,'张三','123456')
新建项目
-
新建一个普通的maven项目
-
删除src目录
-
导入maven依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>mysqlgroupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId> <version>5.1.47version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatisgroupId> <artifactId>mybatisartifactId> <version>3.5.2version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junitgroupId> <artifactId>junitartifactId> <version>4.12version> dependency> dependencies> <build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/resourcesdirectory> <includes> <include>**/*.propertiesinclude> <include>**/*.xmlinclude> includes> <filtering>truefiltering> resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/javadirectory> <includes> <include>**/*.propertiesinclude> <include>**/*.xmlinclude> includes> <filtering>truefiltering> resource> resources> build>
2.2、创建一个模块
-
IDEA数据库连接URL:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=UTC
-
编写mybatis的核心配置文件
<configuration> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="chen19990217...+"/> dataSource> environment> environments> <mappers> <mapper resource="com/chen/dao/userMapper.xml"/> mappers> configuration> -
编写mybatis的工具类
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; //sqlSessionFactory --> sqlSession public class MybatisUtils { private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; static { try { //1.使用Mybatis获取sqlSessionFactory对象 String resource = "org/mybatis/example/mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /* 既然有了 SqlSessionFactory,顾名思义,我们可以从中获得 SqlSession 的实例。SqlSession 提供了在数据库执行 SQL 命令所需的所有方法。 你可以通过 SqlSession 实例来直接执行已映射的 SQL 语句。 */ public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){ return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); } }
2.3、编写代码
-
实体类
package com.chen.util; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; //sqlSessionFactory --> sqlSession public class MybatisUtils { private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; static { try { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //获取SqlSession连接 public static SqlSession getSession(){ return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); } /* 既然有了 SqlSessionFactory,顾名思义,我们可以从中获得 SqlSession 的实例。SqlSession 提供了在数据库执行 SQL 命令所需的所有方法。 你可以通过 SqlSession 实例来直接执行已映射的 SQL 语句。 */ } -
Dao接口
public interface UserDao { List<User> getUserList(); } -
接口实现类由原来的UserDaoImpl转变为一个Mapper配置文件
<mapper namespace="com.chen.dao.UserDao"> <select id="getUserList" resultType="com.chen.pojo.User"> select * from user select> mapper>
2.4、测试
-
Junit测试
-
MapperRegister是什么
核心配置文件中注册mappers
-
可能会遇到的问题:
-
配置文件没有注册
-
绑定接口错误
-
方法名不对
-
返回类型不对
-
Maven静态资源过滤问题
<build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/resourcesdirectory> <includes> <include>**/*.propertiesinclude> <include>**/*.xmlinclude> includes> <filtering>truefiltering> resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/javadirectory> <includes> <include>**/*.propertiesinclude> <include>**/*.xmlinclude> includes> <filtering>truefiltering> resource> resources> build> -
测试类代码
package com.chen.dao; import com.chen.pojo.User; import com.chen.util.MybatisUtils; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.List; public class UserDaoTest { @Test public void test(){ SqlSession session = MybatisUtils.getSession(); //方式一:不推荐使用 // ListuserList1 = sqlSession.selectList("com.chen.dao.UserDao.getUserList"); // for (User user : userList1) { // System.out.println(user); // } //方法二: UserDao mapper = session.getMapper(UserDao.class); List<User> users = mapper.getUserList(); for (User user: users){ System.out.println(user); } session.close(); } }
-
三、CRUD
3.1、nameSpace
namespace的包名要和Dao/mappper接口的包名一致
3.2、select
选择,查询语句;
-
id:就是对应的namespace中的方法名
-
resultType:Sql语句执行的返回值!
-
parameterType:参数类型
-
编写接口
//根据id查询用户 User getUserById(int id); -
编写对应的mapper中的sql
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.chen.pojo.User"> select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id} select>
-
-
测试:
@Test
public void getUserById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = mapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}
3.3、Insert
3.4、Update
3.5、delete
//insert 一个用户
int addUser(User user);
//修改一个用户
int updateUser(User user);
//删除一个用户
int deleteUser(int id);
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.chen.pojo.User">
insert into mybatis.user(id, name, pwd) values (#{
id},#{
name},#{
pwd});
</insert>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.chen.pojo.User">
update mybatis.user set name = #{
name},pwd=#{
pwd} where id=#{
id} ;
</update>
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int">
delete from mybatis.user where id = #{
id};
</delete>
//增删改需要提交事务
@Test
public void addUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
int res = mapper.addUser(new User(4, "死猪", "123"));
if (res > 0){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
//提交事务!!!
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void updateUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.updateUser(new User(4,"呵呵","123123"));
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void deleteUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.deleteUser(4);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
注意:增删改需要提交事务
3.6、错误分析
- 标签必须要匹配
- resource绑定mapper,需要使用路径
- 程序配置文件必须符合规范
- NullPointerException,没有注册到资源!
- 输出的XML文件中存在中文乱码问题
- maven资源没有导出问题!
3.7、万能Map
假设我们的实体类,或者额数据库中的表,字段或者参数过多,我们应当考虑使用Map!
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="map">
insert into mybatis.user(id, name, pwd) values (#{userId},#{userName},#{passWord});
insert>
@Test
public void addUser2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("userId",5);
map.put("userName","小灰灰");
map.put("passWord","2222222");
mapper.addUser2(map);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
Map传递参数,直接在sql中取出key即可【parameterType=“map”】
对象传递参数,直接在sql中取对象的属性即可【parameterType=“Object”】
只有一个基本类型参数的情况下,可以直接在sql中取到!
多个参数用Map,或者注解!
3.8、思考题
模糊查询怎么写?
-
Java代码执行的时候,传递通配符%%
<select id="getUserLike" resultType="com.chen.pojo.User"> select * from mybatis.user where name like #{ value}; </select> @Test public void getUserLike(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); List<User> list = mapper.getUserLike("%小%"); for (User user : list) { System.out.println(user); } sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); } -
在sql拼接中使用通配符
select * from mybatis.user where name like "%"{value}"%"
四、配置解析
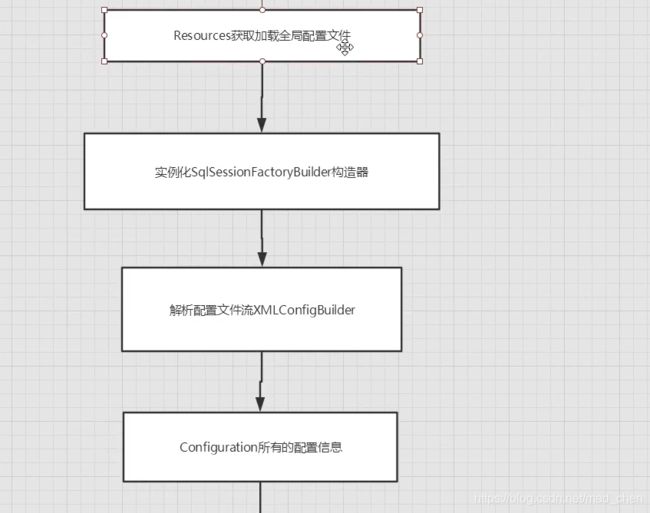
4.1、核心配置文件
-
mybatis-config.xml
-
mybatis的配置文件包含了会深深影响mybatis行为的设置和属性信息
MyBatis 的配置文件包含了会深深影响 MyBatis 行为的设置和属性信息。 配置文档的顶层结构如下: configuration(配置) properties(属性) settings(设置) typeAliases(类型别名) typeHandlers(类型处理器) objectFactory(对象工厂) plugins(插件) environments(环境配置) environment(环境变量) transactionManager(事务管理器) dataSource(数据源) databaseIdProvider(数据库厂商标识) mappers(映射器)
4.2、环境配置(environment)
MyBatis 可以配置成适应多种环境
不过要记住:尽管可以配置多个环境,但每个 SqlSessionFactory 实例只能选择一种环境
学会使用多种enviroment配置方案
Mybatis默认的事务管理器就是JDBC,连接池:POOLED
4.3、属性(properties)
我们可以通过properties属性来实现引用配置文件
这些属性可以在外部进行配置,并可以进行动态替换。你既可以在典型的 Java 属性文件中配置这些属性,也可以在 properties 元素的子元素中设置。
编写一个配置文件
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username=root
password=chen19990217...+
在核心配置文件中引用
//引入外部配置文件
<properties resource="db.properties"/>
- 可以直接引入外部文件
- 可以在其中增加一些属性配置
- 如果两个文件有同一个字段,优先使用外部配置文件的
4.4、类型别名(typeAliases)
类型别名可为 Java 类型设置一个缩写名字。
它仅用于 XML 配置,意在降低冗余的全限定类名书写。
//可以给实体类起别名
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.chen.pojo.User" alias="User"/>
typeAliases>
也可以指定一个包名,MyBatis 会在包名下面搜索需要的 Java Bean
扫描实体类的包,它的默认别名就为这个类的类名首字母小写
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.chen.pojo.User" alias="User"/>
<package name="com.chen.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
在实体类比较少的时候,使用第一种方式。
如果实体类十分多,建议使用第二种
第一种可以DIY别名,第二种则不行,如果非要改,需要在实体类上添加注解
@Alias("hello")
下面是一些为常见的 Java 类型内建的类型别名。它们都是不区分大小写的,注意,为了应对原始类型的命名重复,采取了特殊的命名风格。
| 别名 | 映射的类型 |
|---|---|
| _byte | byte |
| _long | long |
| _short | short |
| _int | int |
| _integer | int |
| _double | double |
| _float | float |
| _boolean | boolean |
| string | String |
| byte | Byte |
| long | Long |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| integer | Integer |
| double | Double |
| float | Float |
| boolean | Boolean |
| date | Date |
| decimal | BigDecimal |
| bigdecimal | BigDecimal |
| object | Object |
| map | Map |
| hashmap | HashMap |
| list | List |
| arraylist | ArrayList |
| collection | Collection |
| iterator | Iterator |
4.5、设置(settings)
这是 MyBatis 中极为重要的调整设置,它们会改变 MyBatis 的运行时行为。
4.6、其他配置
-
typeHandlers(类型处理器)
-
objectFactory(对象工厂)
-
plugins(插件)
- mybatis-generator-core
- mybatis-plus
- 通用mapper
4.7、映射器(mappers)
MapperRegistry:注册绑定我们的Mapper文件
方式一:使用相对于类路径的资源引用
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/chen/dao/userMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
方式二:使用class文件绑定
<mapper class="com.chen.dao.UserMapper" />
注意点:
- 接口和它的Mapper配置文件必须同名!
- 接口和他的Mapper配置文件必须在同一个包下!
方式三:使用扫描包进行注入绑定
<package name="com.chen.dao"/>
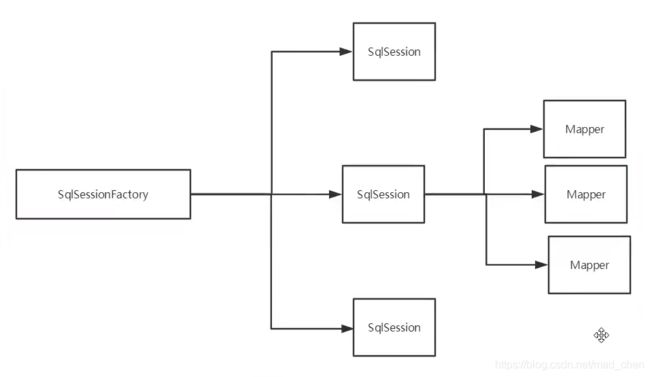
4.8、生命周期和作用域
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-enLPfy8L-1604189785588)(MyBatis.assets/image-20201027080848942.png)]
生命周期,和作用域是至关重要的,因为错误的使用会导致并发运行的错误
-
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
- 一旦创建了 SqlSessionFactory,就不再需要它了。
- 局部变量
-
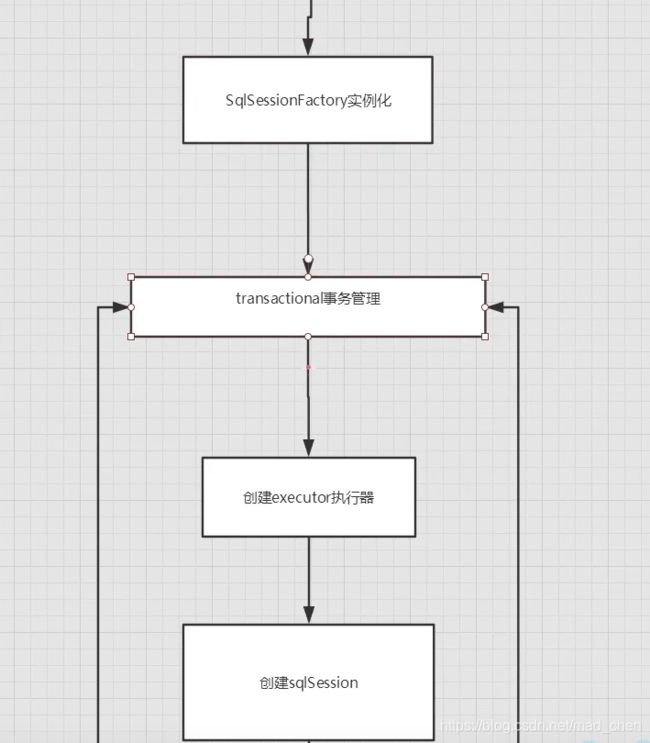
SqlSessionFactory
- 说白了就是可以想象为:数据库连接池
- SqlSessionFactory 一旦被创建就应该在应用的运行期间一直存在,没有任何理由丢弃它或重新创建另一个实例。
- 因此SqlSessionFactory 的最佳作用域是应用作用域。
- 最简单的就是使用单例模式或者静态单例模式。
-
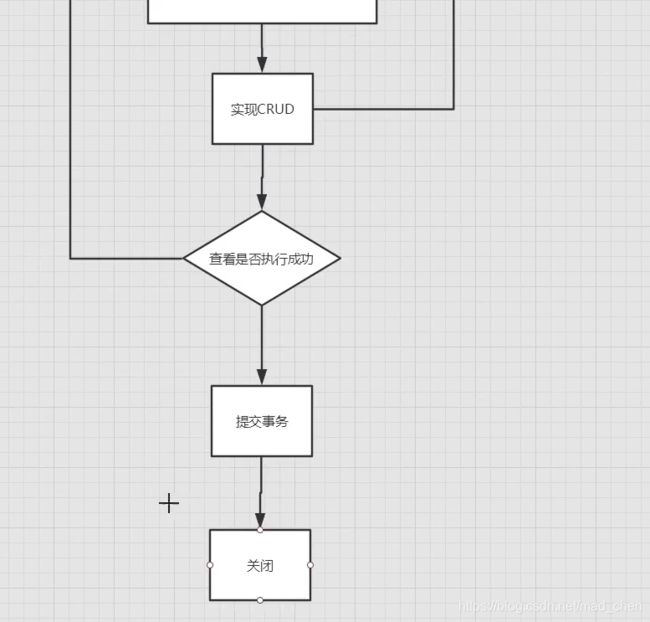
SqlSession
- 连接到连接池的一个请求
- SqlSession的实例不是线程安全的,因此是不能被共享的,所以它的最佳的作用域是请求或方法作用域。
- 用完之后需要关闭,否则资源被占用
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-POpt0wCT-1604189785589)(MyBatis.assets/image-20201027081617555.png)]
这里面的每一个Mapper,代表一个具体的业务
五、解决属性名和字段名不一致的问题ResultMap
5.1、新建一个项目,拷贝之前的项目进行测试
修改实体类的属性名为不一致
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;}
测试出现问题:password为空
//select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id};
//类型处理器
//select id,name,pwd from mybatis.user where id = #{id};
解决方案:
-
起别名
select id,name,pwd as password from mybatis.user where id = #{id};
5.2、resultMap
结果集映射
id name pwd
id name password
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<result column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="pwd" property="password"/>
resultMap>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="UserMap">
select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id};
select>
- ResultMap 元素是 MyBatis 中最重要最强大的元素。
- ResultMap 的设计思想是,对简单的语句做到零配置,对于复杂一点的语句,只需要描述语句之间的关系就行了。
- ResultMap 最优秀的地方在于,虽然你已经对它相当的了解了,但是根本就不需要显式的用到他们。
- 如果世界总是这么简单就好了
六、日志
6.1、日志工厂
如果一个数据粗操作,出现了异常,我们需要拍错,日志就是最好的助手
曾经:sout、debug
- SLF4J
- LOG4J【掌握】
- LOG4J2
- JDK_LOGGING
- COMMONS_LOGGING
- STDOUT_LOGGING【掌握】
- NO_LOGGING
在Mybatis中具体使用哪一个日志实现,在设置中设置
STDOUT_LOGGING标准日志输入
在Mybatis核心配置文件中,配置我们的日志!
//标志的日志工厂实现
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
settings>
6.2、LOG4J日志
什么是LOG4J?
- Log4j是Apache的一个开源项目,通过使用Log4j,我们可以控制日志信息输送的目的地是控制台、文件、GUI组件
- 我们也可以控制每一条日志的输出格式
- 通过定义每一条日志信息的级别,我们能够更加细致地控制日志的生成过程
- 这些可以通过一个配置文件来灵活地进行配置,而不需要修改应用的代码。
- 先导入log4j的包
<dependency>
<groupId>log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4jartifactId>
<version>1.2.17version>
dependency>
- log4j.properties
#将等级为DEBUG的日志信息输出到console和file这两个目的地,console和file的定义在下面的代码
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,console,file
#控制台输出的相关设置
log4j.appender.console = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.Target = System.out
log4j.appender.console.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.console.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=[%c]-%m%n
#文件输出的相关设置
log4j.appender.file = org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.file.File=./log/chen.log
log4j.appender.file.MaxFileSize=10mb
log4j.appender.file.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=[%p][%d{yy-MM-dd}][%c]%m%n
#日志输出级别
log4j.logger.org.mybatis=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG
- 配置为log4j为日志的实现
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/>
settings>
- log4j的使用,直接测试运行
D:\java\jdk-8\bin\java.exe -ea -Didea.test.cyclic.buffer.size=1048576 "-javaagent:D:\idea\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.1\lib\idea_rt.jar=55179:D:\idea\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.1\bin" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath "D:\idea\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.1\lib\idea_rt.jar;D:\idea\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.1\plugins\junit\lib\junit-rt.jar;D:\idea\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.1\plugins\junit\lib\junit5-rt.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\charsets.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\deploy.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\access-bridge-64.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\cldrdata.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\dnsns.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\jaccess.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\jfxrt.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\localedata.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\nashorn.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\sunec.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\sunjce_provider.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\sunmscapi.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\sunpkcs11.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\ext\zipfs.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\javaws.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\jce.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\jfr.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\jfxswt.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\jsse.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\management-agent.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\plugin.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\resources.jar;D:\java\jdk-8\jre\lib\rt.jar;F:\JavaWebProjects\mybatis\October-Mybatis\mybatis-04\target\test-classes;F:\JavaWebProjects\mybatis\October-Mybatis\mybatis-04\target\classes;F:\maven\jarpool\maven_repository\log4j\log4j\1.2.17\log4j-1.2.17.jar;F:\maven\jarpool\maven_repository\mysql\mysql-connector-java\5.1.47\mysql-connector-java-5.1.47.jar;F:\maven\jarpool\maven_repository\org\mybatis\mybatis\3.5.2\mybatis-3.5.2.jar;F:\maven\jarpool\maven_repository\junit\junit\4.12\junit-4.12.jar;F:\maven\jarpool\maven_repository\org\hamcrest\hamcrest-core\1.3\hamcrest-core-1.3.jar" com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.JUnitStarter -ideVersion5 -junit4 com.chen.dao.UserMapperTest,test
[org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory]-Logging initialized using 'class org.apache.ibatis.logging.log4j.Log4jImpl' adapter.
[org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory]-Logging initialized using 'class org.apache.ibatis.logging.log4j.Log4jImpl' adapter.
[org.apache.ibatis.io.VFS]-Class not found: org.jboss.vfs.VFS
[org.apache.ibatis.io.JBoss6VFS]-JBoss 6 VFS API is not available in this environment.
[org.apache.ibatis.io.VFS]-Class not found: org.jboss.vfs.VirtualFile
[org.apache.ibatis.io.VFS]-VFS implementation org.apache.ibatis.io.JBoss6VFS is not valid in this environment.
[org.apache.ibatis.io.VFS]-Using VFS adapter org.apache.ibatis.io.DefaultVFS
[org.apache.ibatis.io.DefaultVFS]-Find JAR URL: file:/F:/JavaWebProjects/mybatis/October-Mybatis/mybatis-04/target/classes/com/chen/pojo
[org.apache.ibatis.io.DefaultVFS]-Not a JAR: file:/F:/JavaWebProjects/mybatis/October-Mybatis/mybatis-04/target/classes/com/chen/pojo
[org.apache.ibatis.io.DefaultVFS]-Reader entry: User.class
[org.apache.ibatis.io.DefaultVFS]-Listing file:/F:/JavaWebProjects/mybatis/October-Mybatis/mybatis-04/target/classes/com/chen/pojo
[org.apache.ibatis.io.DefaultVFS]-Find JAR URL: file:/F:/JavaWebProjects/mybatis/October-Mybatis/mybatis-04/target/classes/com/chen/pojo/User.class
[org.apache.ibatis.io.DefaultVFS]-Not a JAR: file:/F:/JavaWebProjects/mybatis/October-Mybatis/mybatis-04/target/classes/com/chen/pojo/User.class
[org.apache.ibatis.io.DefaultVFS]-Reader entry: ���� 1 @
[org.apache.ibatis.io.ResolverUtil]-Checking to see if class com.chen.pojo.User matches criteria [is assignable to Object]
[org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource]-PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections.
[org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource]-PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections.
[org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource]-PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections.
[org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource]-PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections.
[org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransaction]-Opening JDBC Connection
[org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource]-Created connection 500179317.
[org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransaction]-Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@1dd02175]
[com.chen.dao.UserMapper.getUserById]-==> Preparing: select * from mybatis.user where id = ?;
[com.chen.dao.UserMapper.getUserById]-==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
[com.chen.dao.UserMapper.getUserById]-<== Total: 1
User{id=1, name='小王子', pwd='123456'}
[org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransaction]-Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@1dd02175]
[org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransaction]-Closing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@1dd02175]
[org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource]-Returned connection 500179317 to pool.
Process finished with exit code 0
简单使用
-
在要使用Log4j的类中,导入包import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
-
日志对象,参数为当前类的class
Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(UserMapperTest.class); -
日志级别
@Test public void testLog4j(){ logger.info("info:进入了testLog4j方法"); logger.debug("debug:进入了testLog4j"); logger.error("error:进入了testLog4j"); }
七、分页
思考:为什么要分页?
- 减少数据的处理量
7.1、使用Limit分页
语法:select * from user limit startIndex,pageSize
使用Mybatis实现分页,核心就是SQL
-
接口
//分页 List<User> getUserByLimit(Map<String,Integer> map); -
Mapper.XML
<select id="getUserByLimit" parameterType="map" resultType="user"> select * from mybatis.user limit #{startIndex},#{pageSize}; select> -
测试
@Test public void getUserByLimit(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); map.put("startIndex",0); map.put("pageSize",2); List<User> userByLimit = mapper.getUserByLimit(map); for (User user : userByLimit) { System.out.println(user); } }
7.2、RowBounds分页(了解)
不再使用SQL实现分页
-
接口
//分页2 List<User> getUserByRowBounds(); -
mapper.xml
<select id="getUserByRowBounds" resultType="user"> select * from mybatis.user ; select> -
测试
@Test public void getUserByRowBounds(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); //RowBounds实现 RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(1, 2); //通过java代码层面实现分页 List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.chen.dao.UserMapper.getUserByRowBounds",null,rowBounds); for (User user : list) { System.out.println(user); } sqlSession.close(); }7.3、分页插件
了解即可,以后有用再拿出来
八、使用注解开发
8.1、面向接口编程
- 大家之前都学过面向对象编程,也学习过接口,但在真正的开发中,很多时候我们会选择面向接口编程
- 根本原因 : 解耦 , 可拓展 , 提高复用 , 分层开发中 , 上层不用管具体的实现 , 大家都遵守共同的标准 , 使得开发变得容易 , 规范性更好
- 在一个面向对象的系统中,系统的各种功能是由许许多多的不同对象协作完成的。在这种情况下,各个对象内部是如何实现自己的,对系统设计人员来讲就不那么重要了;
- 而各个对象之间的协作关系则成为系统设计的关键。小到不同类之间的通信,大到各模块之间的交互,在系统设计之初都是要着重考虑的,这也是系统设计的主要工作内容。面向接口编程就是指按照这种思想来编程。
关于接口的理解
- 接口从更深层次的理解,应是定义(规范,约束)与实现(名实分离的原则)的分离。
- 接口的本身反映了系统设计人员对系统的抽象理解。
- 接口应有两类:
-
- 第一类是对一个个体的抽象,它可对应为一个抽象体(abstract class);
- 第二类是对一个个体某一方面的抽象,即形成一个抽象面(interface);
- 一个体有可能有多个抽象面。抽象体与抽象面是有区别的。
三个面向区别
- 面向对象是指,我们考虑问题时,以对象为单位,考虑它的属性及方法 .
- 面向过程是指,我们考虑问题时,以一个具体的流程(事务过程)为单位,考虑它的实现 .
- 接口设计与非接口设计是针对复用技术而言的,与面向对象(过程)不是一个问题.更多的体现就是对系统整体的架构
8.2、使用注解开发
-
注解在接口上实现
@Select("select * from user") List<User> getUsers(); -
在核心配置文件绑定接口
<mappers> <mapper class="com.chen.dao.UserMapper" /> mappers> -
测试
@Test public void test(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); //核心:底层主要使用反射 UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); List<User> users = mapper.getUsers(); for (User user : users) { System.out.println(user); } sqlSession.close(); }
本质:反写机制实现
底层:动态代理!
8.3、CRUD
我们可以在工具类创建的时候实现自动提交事务
//获取SqlSession连接
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
}
编写接口增加注解
//方法存在多个参数,所有的参数前面必须加上@Param("id")注解
@Select("select * from user where id = #{id}")
User getUserById(@Param("id") int id);
@Insert("insert into user(id,name,pwd) values(#{id},#{name},#{pwd})")
int addUser(User user);
@Update("update user set name=#{name},pwd=#{pwd} where id=#{id}")
int updateUser(User user);
@Delete("delete from user where id = #{uid}")
int deleteUser(@Param("uid") int id);
测试类
@Test
public void test1(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//核心:底层主要使用反射
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User userById = mapper.getUserById(2);
System.out.println(userById);
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void test2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//核心:底层主要使用反射
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.addUser(new User(5,"啧啧啧","1111111"));
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void test3(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//核心:底层主要使用反射
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.updateUser(new User(5,"to","21313"));
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void test4(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//核心:底层主要使用反射
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.deleteUser(5);
sqlSession.close();
}
【注意:我们必须要将接口注册绑定到我们的核心配置中】
关于@Param注解
- 基本类型的参数或者String类型,需要加上
- 引用类型不需要加
- 如果只有一个基本类型的话,可以忽略,但是建议加上
- 我们再SQL中引用的就是我们这里的**@Param中设置的属性名**
- #{} 代表PrepareStatement;${}就是代表Statement
九、Lombok
通过注解生成getter和setter等方法
使用步骤:
1. 在IDEA中安装LOmbok插件
2. 在项目中导入lombok的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.12version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
- 在实体类上加注解即可
lombok中的注解:
@NonNull
@Getter and @Setter
@Accessors
@AllArgsConstructor
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString和@EqualsAndHashCode
@Data
@Value
@Builder和@Singular
@Singular
@Builder
@Cleanup
@ExtensionMethod : 可以扩展已有的类(不建议使用)
@FieldDefaults (官方待转正)
@Delegate (不建议使用)
@Wither(不推荐)
说明:
@Data :无参构造,get,set,toString,hashCode,equals
十、多对一处理
- 多个学生,对应一个老师
- 对于学会说呢过这边而言,关联…多个学生关联一个老师
- 对于老师而言,一对多的关系,集合
10.1、SQL:
CREATE TABLE teacher (
`id` INT(10) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`)
)ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
INSERT INTO teacher(`id`,`name`) VALUES (1,'王老师');
CREATE TABLE student (
`id` INT(10) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
`tid` INT(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`),
KEY `fktid` (`tid`),
CONSTRAINT `fktid` FOREIGN KEY (`tid`) REFERENCES `teacher` (`id`)
)ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO student (`id` , `name` , `tid`) VALUES(1,'小明',1);
INSERT INTO student (`id` , `name` , `tid`) VALUES(2,'小张',1);
INSERT INTO student (`id` , `name` , `tid`) VALUES(3,'小宏',1);
INSERT INTO student (`id` , `name` , `tid`) VALUES(4,'小李',1);
INSERT INTO student (`id` , `name` , `tid`) VALUES(5,'小龙',1);
SELECT * FROM student;
SELECT * FROM teacher;
10.2、测试环境搭建
- 导入lombok
- 新建实体类Teacher,Student
- 建立Mapper接口
- 建立Mapper.XML文件
- 在核心配置文件汇总绑定注册我们的Mapper接口或者文件!【方式很多,随机选】
- 测试查询是否成功
10.3、按照查询嵌套处理
<mapper namespace="com.chen.dao.StudentMapper">
<select id="getStudent" resultMap="StudentTeacher">
select * from student
select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<association property="teacher" column="tid" javaType="Teacher" select="getTeacher"/>
resultMap>
<select id="getTeacher" resultType="Teacher">
select * from teacher where id = #{id}
select>
mapper>
10.4、按照结果嵌套处理
<select id="getStudent2" resultMap="StudentTeacher2">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname
from student s,teacher t
where s.tid = t.id;
select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher2" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher">
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
association>
resultMap>
回顾Mysql多对一查询方式:
- 子查询
- 连表查询
十一、一对多的处理
11.1、环境搭建
和之前方法一样
实体类有所改变
@Data
public class Teacher {
private int id;
private String name;
//一个老师又有多个学生
private int tid;
}
@Data
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int tid;
}
11.2、按照结果嵌套处理
<select id="getTeacher" resultMap="TeacherStudent">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname,t.id tid
from student s,teacher t
where s.tid = t.id and t.id=#{tid}
select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent" type="Teacher" >
<result property="id" column="tid"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<collection property="students" ofType="Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="tid" column="tid"/>
collection>
resultMap>
11.3、按照查询嵌套处理
<select id="getTeacher2" resultMap="TeacherStudent2">
select * from mybatis.teacher where id = #{tid}
select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent2" type="Teacher">
<collection property="students" javaType="ArrayList" ofType="Student" select="getStudentByTeacherID" column="id"/>
resultMap>
<select id="getStudentByTeacherID" resultType="Student" >
select * from student where tid=#{tid}
select>
11.4、小结
- 关联 - association 【多对一】
- 集合 - collection【一对多】
- javaType & ofType
- javaType 用来指定实体类中属性的类型
- ofType用来指定映射到List或者集合中的pojo类型,泛型中的约束类型
注意点:
- 保证SQL的可读性,尽量保证通俗易懂
- 注意一对多和多对一中,属性名和字段的问题
- 如果问题不好排查错误,可以使用日志,建议使用LOG4J
面试高频
- Mysql引擎
- InnoDb底层原理
- 索引
- 索引优化!
十二、动态SQL
12.1、什么是动态SQL?
动态SQL就是指根据不同的条件生成不同的SQL语句
动态 SQL 元素和JSTL标签或基于XML的文本处理器类似。在 MyBatis 之前的版本中,需要花时间了解大量的元素。借助功能强大的基于 OGNL 的表达式,MyBatis 3 替换了之前的大部分元素,大大精简了元素种类,现在要学习的元素种类比原来的一半还要少。
if
choose (when, otherwise)
trim (where, set)
foreach
12.2、搭建环境
SQL:
create table `blog`(
`id` varchar(50) not null comment '博客id',
`title` varchar(100) not null comment '博客标题',
`author` varchar(30) not null comment '博客作者',
`create_time` datetime not null comment '创建时间',
`views` int(30) not null comment '浏览量',
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
创建一个基础工程:
-
导包
-
编写配置文件
-
编写实体类
@Data public class Blog { private int id; private String title; private String author; private Date createTime; private int views; } -
表写实体类对应Mapper接口和Mapper.XML文件
<mapper namespace="com.chen.dao.BlogMapper"> <insert id="addBlog" parameterType="blog"> insert into blog (id, title, author,create_time, views) values (#{id},#{title},#{author},#{createTime},#{views}); insert> -
测试类
@Test public void addInitBlog(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); Blog blog = new Blog(); blog.setId(IDUtils.getId()); blog.setTitle("Mybatis如此简单"); blog.setAuthor("小王子"); blog.setCreateTime(new Date()); blog.setViews(9999); mapper.addBlog(blog); blog.setId(IDUtils.getId()); blog.setTitle("Java如此简单"); mapper.addBlog(blog); blog.setId(IDUtils.getId()); blog.setTitle("Spring如此简单"); mapper.addBlog(blog); blog.setId(IDUtils.getId()); blog.setTitle("微服务如此简单"); mapper.addBlog(blog); sqlSession.close(); }
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
mapUnderscoreToCamelCase 是否开启驼峰命名自动映射,即从经典数据库列名 A_COLUMN 映射到经典 Java 属性名 aColumn。
12.3、IF
<select id="queryBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog where 1=1
<if test="title != null">
and title = #{title}
if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
if>
select>
12.4、choose(when,otherwise)
<select id="queryBlogChoose" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
title = #{title}
when>
<when test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
when>
<otherwise >
and views = #{views}
otherwise>
choose>
where>
select>
12.4、trim(where,set)
<select id="queryBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title}
if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
if>
where>
select>
<update id="updateBlog" parameterType="map" >
update blog
<set>
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title},
if>
<if test="author != null">
author = #{author},
if>
set>
where id = #{id}
update>
所谓的动态SQL,本质还是SQL语句,只是我们可以在SQL层面取执行一些逻辑代码
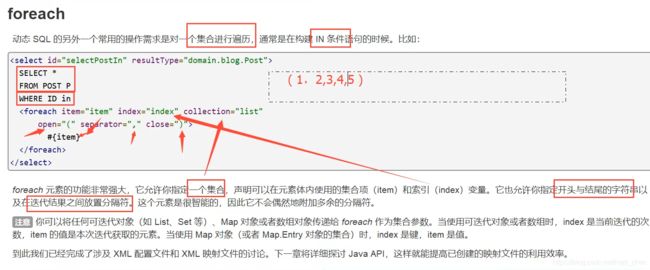
12.5、ForEach
<select id="queryBlogForeach" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="and (" close=")" separator="or">
id = #{id}
foreach>
where>
select>
测试类
@Test
public void queryBlogForeach(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
ArrayList<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<Integer>();
map.put("ids",ids);
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.queryBlogForeach(map);
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
System.out.println(blog);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
12.6、SQL片段
有的时候,我们可能会将一些公共的部分抽取出来作为一个SQL片段,方便复用
- 使用SQL标签抽取公共部分
<sql id="if-title-author">
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title}
if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
if>
sql>
- 在需要使用的地方使用include标签引用
<select id="queryBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<include refid="if-title-author">include>
where>
select>
注意事项:
- 最好基于单表来定义SQL片段!
- 不要存在where标签
建议:
- 先在Mysql中写出完整的SQL,再对应的去修改成为我们的动态SQL实现通用即可
十三、缓存
13.1、简介
查询 : ;连接数据库,好资源
一次查询的结果,给他暂存在一个可以直接取到的地方-->内存:缓存
我们再次查询相同数据的时候,直接走缓存,就不用了走数据库了
1、什么是缓存 [ Cache ]?
- 存在内存中的临时数据。
- 将用户经常查询的数据放在缓存(内存)中,用户去查询数据就不用从磁盘上(关系型数据库数据文件)查询,从缓存中查询,从而提高查询效率,解决了高并发系统的性能问题。
2、为什么使用缓存?
- 减少和数据库的交互次数,减少系统开销,提高系统效率。
3、什么样的数据能使用缓存?
- 经常查询并且不经常改变的数据。
13.2、Mybatis缓存
-
MyBatis包含一个非常强大的查询缓存特性,它可以非常方便地定制和配置缓存。缓存可以极大的提升查询效率。
-
MyBatis系统中默认定义了两级缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存
- 默认情况下,只有一级缓存开启。(SqlSession级别的缓存,也称为本地缓存)
- 二级缓存需要手动开启和配置,他是基于namespace级别的缓存。
- 为了提高扩展性,MyBatis定义了缓存接口Cache。我们可以通过实现Cache接口来自定义二级缓存
13.3、一级缓存
一级缓存也叫本地缓存:
- 与数据库同一次会话期间查询到的数据会放在本地缓存中。
- 以后如果需要获取相同的数据,直接从缓存中拿,没必须再去查询数据库;
测试步骤:
-
开启日志
-
测试在一个Session中查询两次相同的记录
-
查看日志输出发现值进行了一次查询:
缓存失效的情况:
-
查询不同的东西
-
增删改操作,可能会改变原来的数据,所以必定会刷新缓存
-
查询不同的Mapper.xml
-
手动清除缓存!
//手动清理缓存 sqlSession.clearCache();
**小结:**一级缓存默认是开启的,只在一次SqlSession中有效,也就是拿到连接到关闭连接的这个区间段!
一级缓存就相当一个Map
13.4、二级缓存
-
二级缓存也叫全局缓存,一级缓存作用域太低了,所以诞生了二级缓存
-
基于namespace级别的缓存,一个名称空间,对应一个二级缓存;
-
工作机制
- 一个会话查询一条数据,这个数据就会被放在当前会话的一级缓存中;
- 如果当前会话关闭了,这个会话对应的一级缓存就没了;但是我们想要的是,会话关闭了,一级缓存中的数据被保存到二级缓存中;
- 新的会话查询信息,就可以从二级缓存中获取内容;
- 不同的mapper查出的数据会放在自己对应的缓存(map)中;
步骤:
-
开启全局缓存
设置名 描述 有效值 默认值 cacheEnabled 全局性地开启或关闭所有映射器配置文件中已配置的任何缓存。 true | false true //显示的开启全局缓存 <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>也可以自定义参数
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
-
测试
-
问题:我们需要将实体类序列化!否则报错
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class User implements Serializable { private int id; private String name; private String pwd; } -
测试类代码
@Test public void test1(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user1 = mapper.queryUserById(1); System.out.println(user1); sqlSession.close(); UserMapper mapper1 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user2 = mapper1.queryUserById(1); System.out.println(user2); System.out.println(user1 == user2); sqlSession2.close(); } -
小结
- 只要开启了二级缓存没在同一个Mapper下就有效
- 所有的数据都会先放在以及缓存中
- 只有当会话提交过着关闭的时候,才会提价殴打哦二级缓存中
-
13.5、缓存原理
13.6、自定义缓存
Ehcache是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存。主要面向通用缓存
要在程序中使用ehcache,先要导包!
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.cachesgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcacheartifactId>
<version>1.1.0version>
dependency>
在Mapper.xml中指定我们的ehcache缓存实现
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
ehcache.xml
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
updateCheck="false">
<diskStore path="./tmpdir/Tmp_EhCache"/>
<defaultCache
eternal="false"
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="1800"
timeToLiveSeconds="259200"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<cache
name="cloud_user"
eternal="false"
maxElementsInMemory="5000"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="1800"
timeToLiveSeconds="1800"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
ehcache>
目前最多的用Redis数据库来做缓存