剑指Offer---2021/7/19
目录
- 剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
- 剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符
- 剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度
- 剑指 Offer 57. 和为s的两个数字
- 剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
- 剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
- 剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序
- 剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
- 剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
- 剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
- 剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
- 剑指 Offer 65. 不用加减乘除做加法
- 剑指 Offer 61. 扑克牌中的顺子
- 剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树
- 剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字
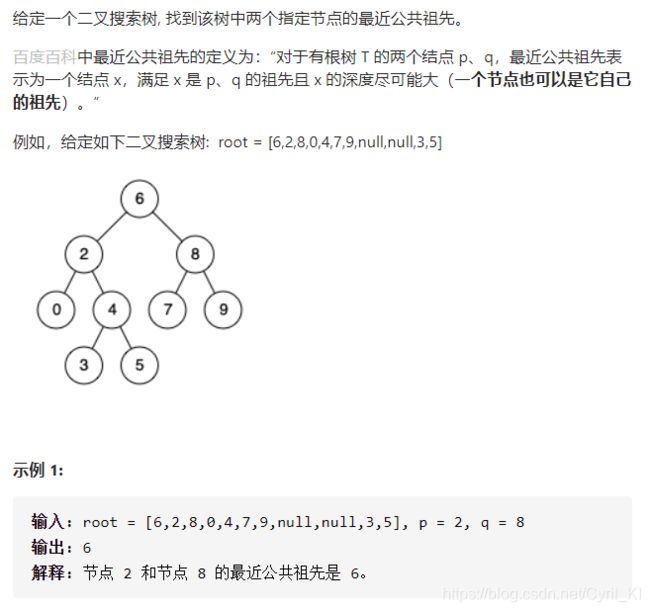
- 剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
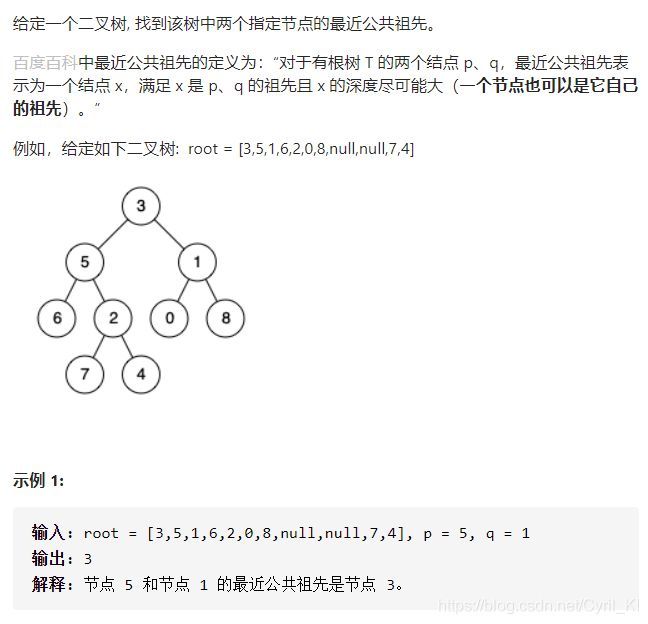
- 剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
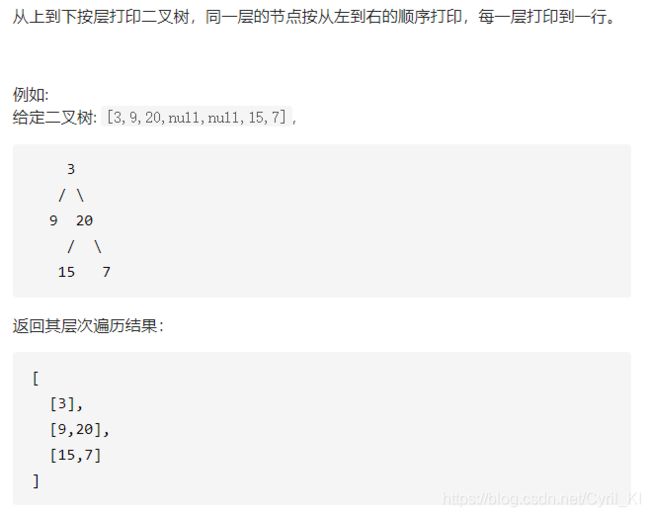
剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(!root) {
return res;
}
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
vector<int> temp;
int n = que.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
TreeNode* ft = que.front();
que.pop();
temp.push_back(ft->val);
if(ft->left) {
que.push(ft->left);
}
if(ft->right) {
que.push(ft->right);
}
}
res.push_back(temp);
}
return res;
}
};
剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符
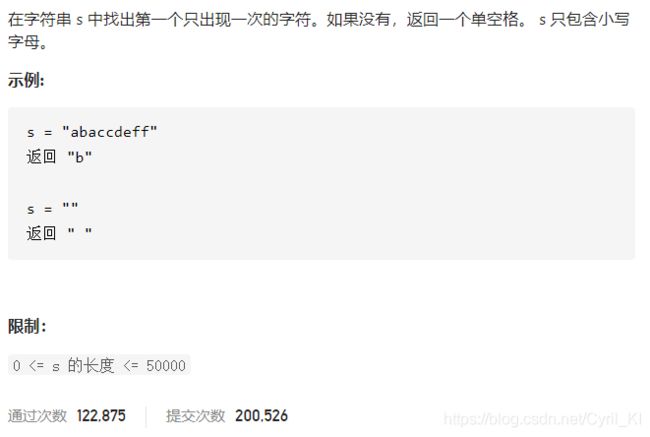
分析:
利用哈希表统计每个字符出现的个数,然后遍历哈希表返回满足条件的字符。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
char firstUniqChar(string s) {
if(s == "") {
return ' ';
}
int n = s.size();
map<char, int> mp;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
mp[s[i]]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(mp[s[i]] == 1) {
return s[i];
}
}
return ' ';
}
};
剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) {
return 0;
}
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
方法二:
bfs层序遍历,遍历一层层数加1,最后输出层数。
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) {
return 0;
}
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
int cnt = 0;
while(!que.empty()) {
int n = que.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
TreeNode* tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(tmp->left) {
que.push(tmp->left);
}
if(tmp->right) {
que.push(tmp->right);
}
}
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
};
剑指 Offer 57. 和为s的两个数字
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<int> res;
if(nums[0] > target) {
return res;
}
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left <= right) {
int x = nums[left] + nums[right];
if(x == target) {
res.push_back(nums[left]);
res.push_back(nums[right]);
return res;
}else if(x > target) {
right--;
}else {
left++;
}
}
return res;
}
};
剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findContinuousSequence(int target) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> temp;
int limit = (target - 1) / 2;
for(int i = 1; i <= limit; i++) {
int sum = 0, j = i;
for(; ; j++) {
sum += j;
if(sum > target) {
break;
}
if(sum == target) {
temp.clear();
for(int k = i; k <= j; k++) {
temp.push_back(k);
}
res.push_back(temp);
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public int[][] findContinuousSequence(int target) {
List<int[]> vec = new ArrayList<int[]>();
int sum = 0, limit = (target - 1) / 2; // (target - 1) / 2 等效于 target / 2 下取整
for (int x = 1; x <= limit; ++x) {
long delta = 1 - 4 * (x - (long) x * x - 2 * target);
if (delta < 0) {
continue;
}
int delta_sqrt = (int) Math.sqrt(delta + 0.5);
if ((long) delta_sqrt * delta_sqrt == delta && (delta_sqrt - 1) % 2 == 0) {
int y = (-1 + delta_sqrt) / 2; // 另一个解(-1-delta_sqrt)/2必然小于0,不用考虑
if (x < y) {
int[] res = new int[y - x + 1];
for (int i = x; i <= y; ++i) {
res[i - x] = i;
}
vec.add(res);
}
}
}
return vec.toArray(new int[vec.size()][]);
}
}
剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点

方法一:
首先遍历headA,将所有节点存入到集合中。接着遍历headB,返回第一个存在于集合中的节点指针。
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
unordered_set<ListNode *> visited;
ListNode *temp = headA;
while (temp != nullptr) {
visited.insert(temp);
temp = temp->next;
}
temp = headB;
while (temp != nullptr) {
if (visited.count(temp)) {
return temp;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if (headA == nullptr || headB == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
ListNode *pA = headA, *pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == nullptr ? headB : pA->next;
pB = pB == nullptr ? headA : pB->next;
}
return pA;
}
};
剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序
class Solution {
public:
string reverseWords(string s) {
if(s == "" || s == " ") {
return "";
}
int n = s.size();
vector<string> res;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(s[i] == ' ') {
continue;
}
string tmp = "";
while(i < n && s[i] != ' ') {
tmp += s[i];
i++;
}
res.push_back(tmp);
}
if(res.size() == 0) {
return "";
}
string t = res[res.size() - 1];
for(int i = res.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
t += (" " + res[i]);
}
return t;
}
};
剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
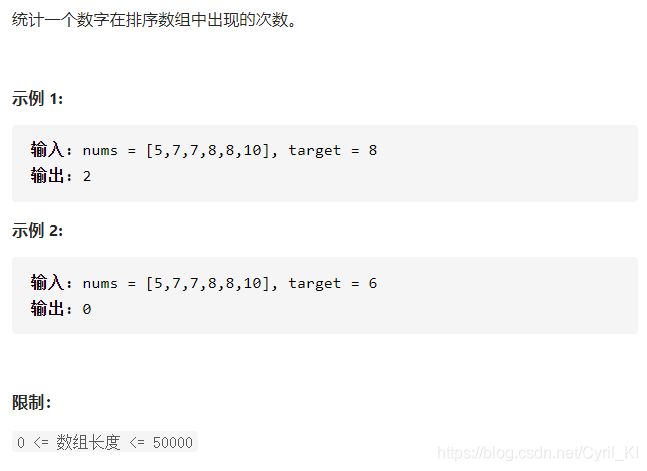
分析:
lower_bound()返回数组中第一个大于等于target的位置,upper_bound()返回数组中第一个大于target的位置,二者相减即为该数字在数组中出现的次数。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
/*int cnt = 0;
for(int x : nums) {
if(x == target) {
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;*/
int low = lower_bound(begin(nums), end(nums), target) - begin(nums);
int high = upper_bound(begin(nums), end(nums), target) - begin(nums);
return high - low;
}
};
剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string s, int n) {
int len = s.size();
string res = s.substr(n, len - n) + s.substr(0, n);
return res;
}
};
剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
for(int x : nums) {
if(x == ind) {
ind++;
continue;
}else {
return ind;
}
}
return ind;
}
};
方法二:
二分查找。每次判断mid位置的数是否为mid:如果等于表示不缺失,则缺失元素一定在mid右边,执行left = mid + 1;如果不等于则缺失元素在左边。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size();
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (mid != nums[mid]) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
};
剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> res;
public:
void inorder(TreeNode* T) {
if(!T) {
return;
}
inorder(T->left);
res.push_back(T->val);
inorder(T->right);
}
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
inorder(root);
return res[res.size() - k];
}
};
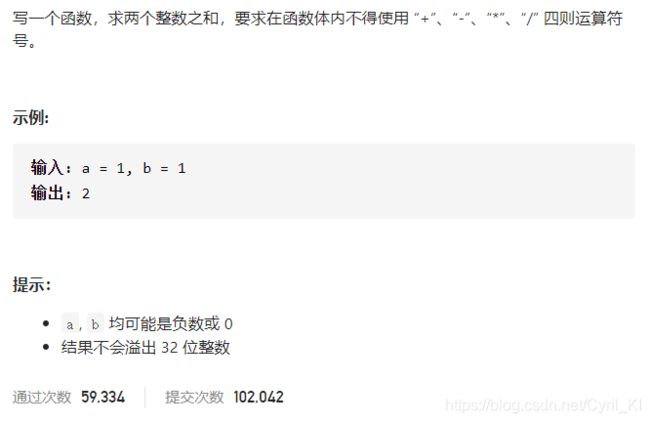
剑指 Offer 65. 不用加减乘除做加法
class Solution {
public:
int add(int a, int b) {
while(b!=0) {
int c=(unsigned int)(a&b)<<1;
a^=b;
b=c;
}
return a;
}
};
剑指 Offer 61. 扑克牌中的顺子
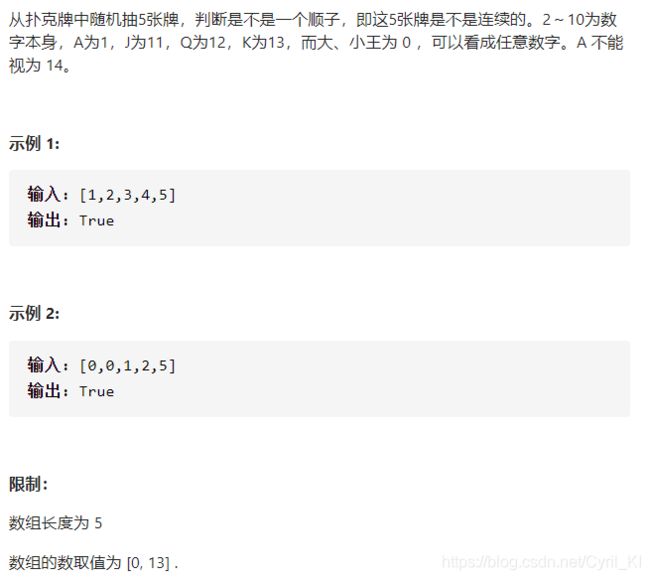
分析:
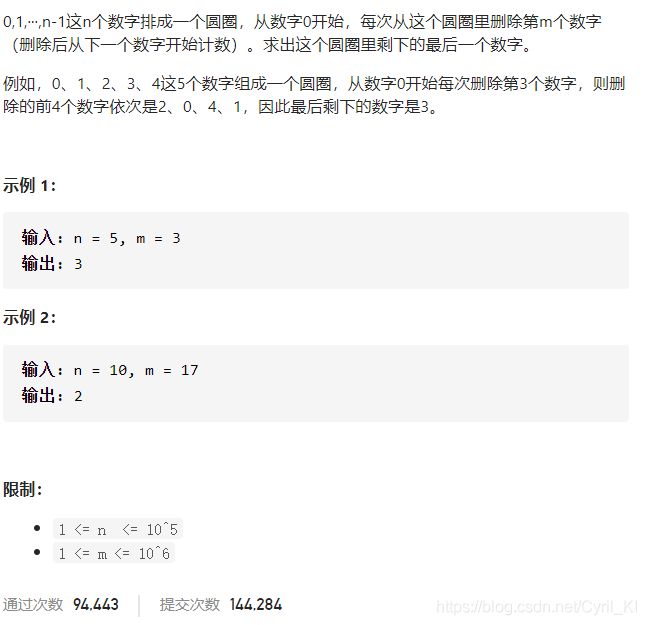
由于0可以替换为任意数,所以五张牌中,设除了大小王之外还有n张牌,如果n张牌中的最大值与最小值的差小于5,就能构成顺子。如果大于等于5,比如5,则即使有两张0也不能构成顺子,比如[00126],替换后只能为[12346];如果小于5,比如为[01235]或者[00234],都能构成顺子。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool isStraight(vector<int>& nums) {
set<int> temp;
int _min = 14, _max = 0;
for(int x : nums) {
if(x == 0) {
continue;
}
if(temp.count(x) != 0) {
return false;
}
temp.insert(x);
_min = min(_min, x);
_max = max(_max, x);
}
return _max - _min < 5;
}
};
剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int height(TreeNode* T) {
if(!T) {
return 0;
}else {
return max(height(T->left), height(T->right)) + 1;
}
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) {
return true;
}else {
return abs(height(root->left) - height(root->right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
}
}
};
剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字
class Solution {
public:
int lastRemaining(int n, int m) {
vector<int> res;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res.push_back(i);
}
int index = 0;
while(res.size() != 1) {
index = (index + m - 1) % res.size();
res.erase(res.begin() + index);
}
return res[0];
}
};
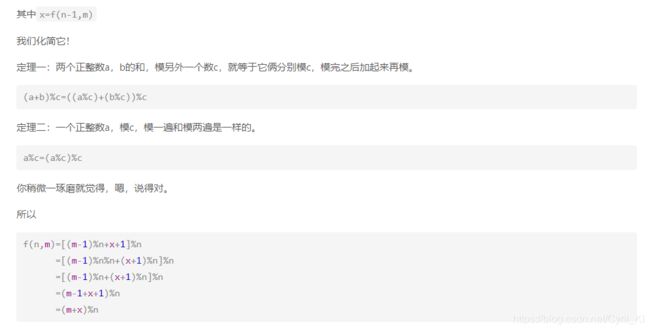
class Solution {
int f(int n, int m) {
if (n == 1) {
return 0;
}
int x = f(n - 1, m);
return (m + x) % n;
}
public:
int lastRemaining(int n, int m) {
return f(n, m);
}
};
剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
TreeNode* ancestor = root;
while (true) {
if (p->val < ancestor->val && q->val < ancestor->val) {
ancestor = ancestor->left;
}
else if (p->val > ancestor->val && q->val > ancestor->val) {
ancestor = ancestor->right;
}
else {
break;
}
}
return ancestor;
}
};
剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* ans;
bool dfs(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (root == nullptr) return false;
bool lson = dfs(root->left, p, q);
bool rson = dfs(root->right, p, q);
if ((lson && rson) || ((root->val == p->val || root->val == q->val) && (lson || rson))) {
ans = root;
}
return lson || rson || (root->val == p->val || root->val == q->val);
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
dfs(root, p, q);
return ans;
}
};