深度学习 — yolov5迁移学习,自定义数据集训练
文章目录
- 深度学习 — yolov5迁移学习,自定义数据集训练
-
- 一、简介
- 二、自定义数据集训练
-
- (一) VOC格式数据集
-
- 1. 准备数据集
- 2. 划分数据集
- 3. 处理标注结果
- 4. 构建数据集配置文件
- 5. 自定义模型配置文件
- 6. 修改训练参数
- 7. 开始训练
- 8. 性能评估
- (二) coco数据集
- 三、训练结果解析
- 参考资料
- 转载请备注原文出处,谢谢:https://blog.csdn.net/pentiumCM/article/details/110426036
深度学习 — yolov5迁移学习,自定义数据集训练
一、简介
本文介绍如何在自己的数据集上训练YOLO5目标检测模型,包括VOC格式的数据集和coco格式的数据集。
二、自定义数据集训练
yolov5训练时候代码中默认识别 images 和 labels 两个文件夹,将 images 作为输入的图像文件夹,labels作为标注文件夹,所以我们不管采用何种数据集格式,只要最终能够生成这两个文件夹即可。
(一) VOC格式数据集
1. 准备数据集
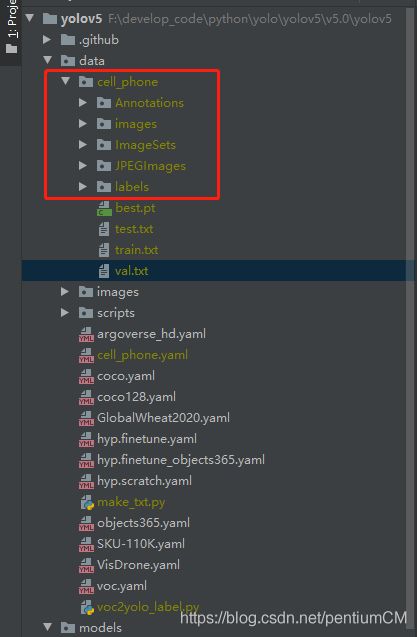
数据集目录如下,cell_phone为我自定义数据集文件夹名称:
└─cell_phone: 自定义数据集
├─Annotations 存放的是数据集标签文件,xml格式
├─images yolov5将此文件夹当作训练图片的输入,直接将 JPEGImages 中的内容放进去
├─ImageSets 数据集的划分文件
│ └─Main
├─JPEGImages 存放的是数据集图片
└─labels yolov5将此文件夹当作训练的标注文件夹
与默认的VOC数据格式不同的是,我们在这一步新建了 images 和 labels 文件夹,images 直接将 JPEGImages 中的图片复制进去即可。labels 作为后续保存标注文件的文件夹。建好的目录如下图所示:
2. 划分数据集
生成 ImageSets/Main/ 下的划分文件,train.txt、val.txt、trainval.txt、test.txt。
划分数据集的代码如下,直接执行下面代码,便可在 ImageSets / Main下生成 train.txt、val.txt、trainval.txt、test.txt四个文件
#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
'''
@Author : pentiumCM
@Email : [email protected]
@Software: PyCharm
@File : make_txt.py
@Time : 2020/11/25 16:51
@desc : 划分数据集 ——
生成:trainval.txt,train.txt,val.txt,test.txt
为ImageSets文件夹下面Main子文件夹中的训练集+验证集、训练集、验证集、测试集的划分
'''
import os
import random
def ds_partition(annotation_filepath, ds_divide_save__path):
"""
数据集划分:训练集,验证集,测试集,在ImageSets/Main/生成 train.txt,val.txt,trainval.txt,test.txt
:param annotation_filepath: 标注文件的路径 Annotations
:param ds_divide_save__path: 数据集划分保存的路径 ImageSets/Main/
:return:
"""
if not os.path.exists(ds_divide_save__path):
os.mkdir(ds_divide_save__path)
# train_percent:训练集占(训练集+验证集)的比例
train_percent = 0.8
# trainval_percent:(训练集+验证集)占总数据集的比例。测试集所占比例为:1-trainval_percent
trainval_percent = 1
temp_xml = os.listdir(annotation_filepath)
total_xml = []
for xml in temp_xml:
if xml.endswith(".xml"):
total_xml.append(xml)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
print("train and val size", tv)
print("traub suze", tr)
ftrainval = open(os.path.join(ds_divide_save__path, 'trainval.txt'), 'w')
ftest = open(os.path.join(ds_divide_save__path, 'test.txt'), 'w')
ftrain = open(os.path.join(ds_divide_save__path, 'train.txt'), 'w')
fval = open(os.path.join(ds_divide_save__path, 'val.txt'), 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftrain.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftest.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 自定义数据集文件夹的名称
dataset_name = r'./cell_phone/'
annotation_filepath = dataset_name + 'Annotations/'
divide_save_path = dataset_name + 'ImageSets/Main/'
ds_partition(annotation_filepath, divide_save_path)
3. 处理标注结果
VOC 的标注转为 yolo 标注结果
VOC的标注采用 xml 文件存放,其中 VOC 对应一个标注框的规则为:xmin ymin xmax ymax
yolo的标注采用 txt 文件存放,其中 yolo 对应一个标注框的规则为:class center_x center_y width height
转化代码如下,执行完代码之后会生成 lables 文件夹与 test.txt、train.txt、val.txt 文件:
- labels里面存放 VOC 解析成yolo的标注结果
- 另外三个txt文件为划分的对应数据集中图片的绝对路径
#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
'''
@Author : pentiumCM
@Email : [email protected]
@Software: PyCharm
@File : voc2yolo_label.py
@Time : 2020/11/25 16:54
@desc : 类别文件格式转换 ——
把数据集标注格式转换成yolo_txt格式,即将每个xml标注提取bbox信息为txt格式
'''
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
sets = ['train', 'test', 'val']
# 改成自己训练所需要的类
classes = ['cell phone']
def convert(size, box):
"""
将 VOC 的标注转为 yolo的标注,即 xyxy -> xywh
:param size: 图片尺寸
:param box: 标注框(xyxy)
:return:
"""
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
# 中心点坐标
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
# 宽高
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
# 归一化
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(annotation_filepath, label_dir, image_id):
"""
VOC 标注的结果转为 yolo 数据集的标注结果
:param annotation_filepath: VOC标注文件夹路径
:param label_dir: 解析成 yolo 标注文件夹的路径
:param image_id: 文件名
:return:
"""
in_file = open(annotation_filepath + '%s.xml' % (image_id))
out_file = open(label_dir + '%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 当前文件的绝对路径
abs_path = os.getcwd() + '/'
# 自定义数据集文件夹的名称
dataset_name = 'cell_phone'
# VOC数据集标注文件
annotation_filepath = dataset_name + '/Annotations/'
# 数据集划分文件
txtfile_dir = dataset_name + '/ImageSets/Main/'
# coco训练图像输入的文件夹
image_dir = dataset_name + '/images/'
# 标注文件解析之后的文件夹路径
label_dir = dataset_name + '/labels/'
if not os.path.exists(label_dir):
os.makedirs(label_dir)
for image_set in sets:
txtfile = txtfile_dir + '%s.txt' % (image_set)
image_ids = open(txtfile).read().strip().split()
list_file = open(dataset_name + '/%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write((abs_path + image_dir + '%s.jpg\n' % (image_id)).replace('\\', '/'))
convert_annotation(annotation_filepath, label_dir, image_id)
list_file.close()
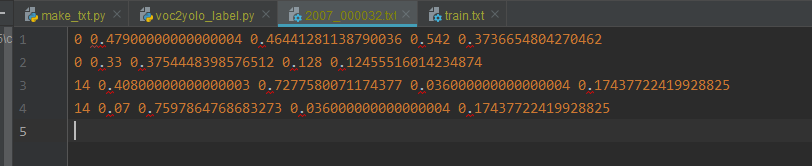
解析之后的labels文件夹中的标签文件内容如下图所示,每一行对应一个标注框,一行字第一个值对应类别号,后面四个值分别对应中心点坐标和标注框的宽高(归一化到0~1之间)。
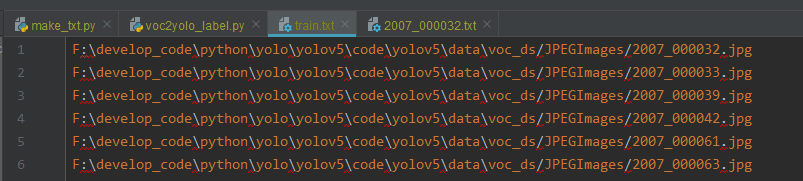
test.txt、train.txt、val.txt文件内容如下图所示,为每一中数据集中图片的路径:
4. 构建数据集配置文件
我们需要新建对应于我们自定义 VOC 数据集的yaml配置文件,如 vocds.yaml,内容主要为:
- train,val 为第 3 步中生成的 txt 文件路径
- nc:类别数(不需要 +1)
- names:类别名称
yaml文件内容如下:
# train2017 and val2017 data as 1) directory: path/images/, 2) file: path/images.txt, or 3) list: [path1/images/, path2/images/]
#train2017: ../VOC/images/train2017/ # 16551 images
#val2017: ../VOC/images/val2017/ # 4952 images
train: F:/develop_code/python/yolo/yolov5/v5.0/yolov5/data/cell_phone/train.txt
val: F:/develop_code/python/yolo/yolov5/v5.0/yolov5/data/cell_phone/val.txt
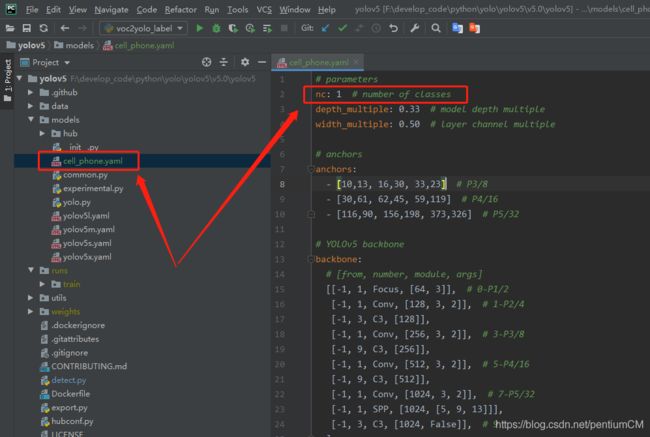
# number of classes:数据集的类别数
nc: 1
# class names
names: ['cell phone']
5. 自定义模型配置文件
想要训练哪一种模型,就修改对应的 model.yaml。
如,我们采用的预训练模型为 yolov5s ,我们就需要修改对应的配置文件,我是直接复制对应的配置文件,修改模型预测的类别数,类别数为我们自定义数据集的类被数,其他地方没有修改
6. 修改训练参数
修改train.py的训练参数:
–data:对应于 ‘data/cell_phone.yaml’
–cfg:对应于预训练的模型配置文件,‘models/cell_phone.yaml’
–weights:预训练模型权重文件,如 yolov5s.pt
–epochs,–batch-size:视自己电脑显卡配置而定,太大了会报显存不够
7. 开始训练
-
一般直接执行:python train.py ,即可。
但是如果是使用终端连接服务器训练,最好使用:nohup python train.py > train_nub.log 2>&1 &,好处是当我们与服务器断开时,训练也会继续在后台执行,不会终端。 -
.cache:训练的过程中会生成缓存文件,这是为了训练的过程中断,下次继续训练。(同样如果我们要重写训练,则需要清理该文件,以防止上次训练结果的干扰)
-
模型训练的结果在根目录的 runs 文件夹中
-
训练过程截图:
8. 性能评估
模型性能评估:
# 模型测试:
python test.py --data ./data/vocds.yaml --weights runs/train/exp5/weights/best.pt --augment
(二) coco数据集
-
准备数据集
准备数据集文件夹coco,数据集和 yolov5 的代码同级,目录结构如下:├─coco: 数据集根目录 │ ├─images: 数据集图片 │ │ ├─train2017: 训练集 │ │ └─val2017: 验证集 │ └─labels: 数据集标签 │ ├─train2017 │ └─val2017 └─yolov5: yolov5源代码,(数据集和源代码同级) -
新建数据集的配置文件 yaml
我们新建 coco_custom.yaml文件,文件内容如下:# train2017 and val2017 data as 1) directory: path/images/, 2) file: path/images.txt, or 3) list: [path1/images/, path2/images/] train: ../coco/images/train2017/ val: ../coco/images/val2017/ # number of classes nc: 2 # class names names: ['person_legal', 'person_illegal'] -
修改预训练模型的配置文件
-
修改train.py的训练参数
-
开始训练
-
模型性能评估
以上内容同 上一节的步骤,在此就不赘述了。
三、训练结果解析
yolov5 每次 train 完成都会在run目录下生成 expi 目录(i 代表生成结果次数,第一次训练完成生成 exp0,第二次生成 exp1…以此类推)
expi 目录下会保存可视化的训练结果:confusion_matrix.png(混淆矩阵)、F1_curve.png(F1曲线)、P_curve.png(P曲线)、R_curve.png(R曲线)、PR_curve.png(PR曲线)、result.png、results.txt 以及训练权重weights(last.pt和best.pt);下面简单解释一下参数:
- result.png:
参考资料
- https://www.freesion.com/article/77231070357/
- https://zhouchen.blog.csdn.net/article/details/108122600