【值得收藏】针对Python初学者,整理的入门常见错误汇总+十份Python迷你小程序(附代码)
前言
不知道世界上最好的编程语言是什么?
但人生苦短,我用Python!
写代码,出错在所难免,关键是如何快速定位错误,解决bug。错误提示,有时候并不能提供有效
信息,尤其是编程新手,常常会犯一些低级错误,比如缩进不对,引号缺失,括号不全等,下面是
新手常犯的一些代码错误,希望对刚入门的同学有一点帮助哦~
免费源码领取:微信公众号——Python顾木子吖
除了汇总一下新手编程常见错误还会附一些简单的新手小项目供大家学习啦!
正文
新手编程常见错误有哪些?
1、新手常犯的基础错误
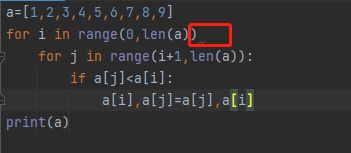
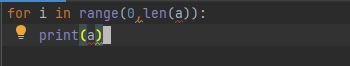
缺少冒号:
a=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
for i in range(0,len(a))
for j in range(i+1,len(a)):
if a[j]错误提示:#语法错误:无效语法
2、缩进不正确
对于类定义、函数定义、流程控制语句、异常处理语句等,行尾的冒号和下一行的缩进,表示下一
个代码块的开始,而缩进的结束则表示此代码块的结束。具有相同缩进的代码被视为代码块。
num = 2
if num < 5:
print(num)
错误提示:#缩进错误:需要缩进的块
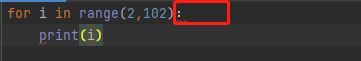
3、符号是中文
比如冒号、括号是中文符号等。
for i in range(2,102):
print(i)错误提示:
4、数据类型错误
常见的比如:不同类型的数据进行拼接等。
name = 'xiaoming'
age = 16
print(name+age)错误提示:
5、变量或者函数名拼写错误
6、使用关键字作为文件名、类名、函数名或者变量名。
类名、函数名或者变量名,不能使用Python语言关键字。文件名,不能与标准库冲突。
Python3的关键字有:
and, as, assert, break, class, continue, def, del, elif,else, except, False, finally, for, from, global, if, import, in, is, lambda,None, nonlocal, not, or, pass, raise, return, True, try, while, with, yield错误:
7、"="当做“==”使用
"="是赋值操作符,"==" 是等于比较运算,用作条件判断。
错误:
正确:
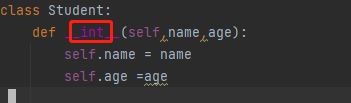
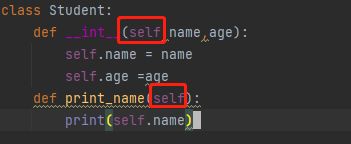
8、缺少参数参self
初始化函数,实例函数,实例变量需要默认参数self。
9、变量未定义
错误提示:
![]()
代码检查清单:
下面是一个简单的代码检查清单,希望对编程新手有一点帮助,仅做借鉴,你也可以总结自己的编程易错点。
附:新手入门小程序尝试写代码嘛?
这些例子都很简单实用,非常适合初学者用来练习。大家也可尝试根据项目的目的及提示,自己构
建解决方法,提高编程水平。
1、石头剪刀布游戏
目标:创建一个命令行游戏,游戏者可以在石头、剪刀和布之间进行选择,与计算机PK。如果游戏者赢了,得分就会
添加,直到结束游戏时,最终的分数会展示给游戏者。
提示:接收游戏者的选择,并且与计算机的选择进行比较。计算机的选择是从选择列表中随机选取的。如果游戏者获
胜,则增加1分。
import random
choices = ["Rock", "Paper", "Scissors"]
computer = random.choice(choices)
player = False
cpu_score = 0
player_score = 0
while True:
player = input("Rock, Paper or Scissors?").capitalize()
# 判断游戏者和电脑的选择
if player == computer:
print("Tie!")
elif player == "Rock":
if computer == "Paper":
print("You lose!", computer, "covers", player)
cpu_score+=1
else:
print("You win!", player, "smashes", computer)
player_score+=1
elif player == "Paper":
if computer == "Scissors":
print("You lose!", computer, "cut", player)
cpu_score+=1
else:
print("You win!", player, "covers", computer)
player_score+=1
elif player == "Scissors":
if computer == "Rock":
print("You lose...", computer, "smashes", player)
cpu_score+=1
else:
print("You win!", player, "cut", computer)
player_score+=1
elif player=='E':
print("Final Scores:")
print(f"CPU:{cpu_score}")
print(f"Plaer:{player_score}")
break
else:
print("That's not a valid play. Check your spelling!")
computer = random.choice(choices)
2、自动发送邮件
目的:编写一个Python脚本,可以使用这个脚本发送电子邮件。
提示:email库可用于发送电子邮件。
import smtplib
from email.message import EmailMessage
email = EmailMessage()
email['from'] = 'xyz name'
email['to'] = 'xyz id'
email['subject'] = 'xyz subject'
email.set_content("Xyz content of email")
with smtlib.SMTP(host='smtp.gmail.com',port=587)as smtp:
## sending request to server
smtp.ehlo()
smtp.starttls()
smtp.login("email_id","Password")
smtp.send_message(email)
print("email send") 3、Hangman小游戏
目的:创建一个简单的命令行hangman游戏。
提示:创建一个密码词的列表并随机选择一个单词。现在将每个单词用下划线“_”表示,给用户提供猜单词的机会,如果用户猜对了单词,则将“_”用单词替换。
import time
import random
name = input("What is your name? ")
print ("Hello, " + name, "Time to play hangman!")
time.sleep(1)
print ("Start guessing...\n")
time.sleep(0.5)
## A List Of Secret Words
words = ['python','programming','treasure','creative','medium','horror']
word = random.choice(words)
guesses = ''
turns = 5
while turns > 0:
failed = 0
for char in word:
if char in guesses:
print (char,end="")
else:
print ("_",end=""),
failed += 1
if failed == 0:
print ("\nYou won")
break
guess = input("\nguess a character:")
guesses += guess
if guess not in word:
turns -= 1
print("\nWrong")
print("\nYou have", + turns, 'more guesses')
if turns == 0:
print ("\nYou Lose") 4、闹钟
目的:编写一个创建闹钟的Python脚本。
提示:你可以使用date-time模块创建闹钟,以及playsound库播放声音。
from datetime import datetime
from playsound import playsound
alarm_time = input("Enter the time of alarm to be set:HH:MM:SS\n")
alarm_hour=alarm_time[0:2]
alarm_minute=alarm_time[3:5]
alarm_seconds=alarm_time[6:8]
alarm_period = alarm_time[9:11].upper()
print("Setting up alarm..")
while True:
now = datetime.now()
current_hour = now.strftime("%I")
current_minute = now.strftime("%M")
current_seconds = now.strftime("%S")
current_period = now.strftime("%p")
if(alarm_period==current_period):
if(alarm_hour==current_hour):
if(alarm_minute==current_minute):
if(alarm_seconds==current_seconds):
print("Wake Up!")
playsound('audio.mp3') ## download the alarm sound from link
break5、猜数字
目的:编写一个猜大小的Python小游戏。
提示:你可以使用random随机生成数字。
# 猜数游戏人机对战
import random
target=random.randint(1,100)
count=0
while True:
guess=eval(input('请输入一个猜测的整数(1至100)'))
count+=1
if guess>target:
print('猜大了')
elif guess6、数学加减法
目的:编写一个数学计算的Python小游戏。
提示:你可以使用random随机生成数字相互之间加减,答对了即可进入下一关。
from random import randint
level=0 #0级开始
while level<10: #当级别小于10级时
a=randint(0,100) #随机生成两位数整数
b=randint(0,100)
c=input(f"{a}+{b}=")
c=int(c)
if c==a+b: #计算结果正确
level+=1 #级别加1
print(f"答对啦!现在等级是{level}级,达到10级就胜利了!")
else: #计算结果错误
level-=1
print(f"答错啦!现在等级是{level},达到10级就胜利了!再接再厉!")
print(f"成功达到10级!挑战成功!棒棒哒!")
#减法闯关小游戏,对上面程序进行改造,需要注意进行减法前需对两个数字进行比较,以免出现负数。
from random import randint
level=0 #0级开始
while level<10: #当级别小于10级时
a=randint(0,100) #随机生成两位数整数
b=randint(0,100)
if a>=b:
c=input(f"{a}-{b}=")
c=int(c)
if c==a+b: #计算结果正确
level+=1 #级别加1
print(f"答对啦!现在等级是{level}级,达到10级就胜利了!")
else: #计算结果错误
level-=1
print(f"答错啦!现在等级是{level},达到10级就胜利了!再接再厉!")
print(f"成功达到10级!挑战成功!棒棒哒!")7、猜单词
目的:编写一个英语单词填填填的Python小游戏。
提示:你可以使用random随机生成一个英语单词,答对了即可!
import random
# 存放单词的列表(可以自己填写需要背诵的单词)
words = ["print", "int", "str", "len", "input", "format", "if","for","def"]
#初始化信息↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
def init():
# 声明三个全局变量
global word
global tips
global ranList
#随机获取单词列表里的一个单词
word = list(words[random.randint(0, len(words) - 1)])
#随机数列表,存放着与单词长度一致的随机数(不重复)
ranList = random.sample(range(0, len(word)), len(word))
#存放提示信息
tips = list()
#初始化提示信息
#存放跟单词长度一致的下划线
for i in range(len(word)):
tips.append("_")
#随机提示两个字母
tips[ranList[0]] = word[ranList[0]]
tips[ranList[1]] = word[ranList[1]]
#函数部分↓↓↓↓↓
#展示菜单
def showMenu():
print("需要提示请输入'?'")
print("结束游戏请输入'quit!'")
#显示提示信息
def showtips():
for i in tips:
print(i, end=" ")
print()
#需要提示
def needTips(tipsSize):
#至少有两个未知字母
if tipsSize <= len(word)-3:
tips[ranList[tipsSize]] = word[ranList[tipsSize]]
tipsSize += 1
return tipsSize
else:
print("已没有提示!")
#主要运行函数↓↓↓↓↓↓
def run():
print("------python关键字版本-------")
init()
tipsSize = 2
showMenu()
while True:
print("提示:",end="")
showtips()
guessWord = input("猜一下这个单词:")
# ''.join(word)>把word列表的内容转换成字符串
if guessWord == ''.join(word):
print("恭喜你,猜对了!就是%s!"%(''.join(word)))
print("再猜一次")
init()
elif guessWord == '?':
tipsSize = needTips(tipsSize)
elif guessWord == 'quit!':
break
else:
print("猜错了!")
continue
run()8、人脸检测
目的:编写一个Python脚本,可以检测图像中的人脸,并将所有的人脸保存在一个文件夹中。
提示:可以使用haar级联分类器对人脸进行检测。它返回的人脸坐标信息,可以保存在一个文件中。
import cv2
# Load the cascade
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
# Read the input image
img = cv2.imread('images/img0.jpg')
# Convert into grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Detect faces
faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 4)
# Draw rectangle around the faces
for (x, y, w, h) in faces:
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (255, 0, 0), 2)
crop_face = img[y:y + h, x:x + w]
cv2.imwrite(str(w) + str(h) + '_faces.jpg', crop_face)
# Display the output
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow("imgcropped",crop_face)
cv2.waitKey()9、键盘记录器
目的:编写一个Python脚本,将用户按下的所有键保存在一个文本文件中。
提示:pynput是Python中的一个库,用于控制键盘和鼠标的移动,它也可以用于制作键盘记录器。简单地读取用户按
下的键,并在一定数量的键后将它们保存在一个文本文件中。
from pynput.keyboard import Key, Controller,Listener
import time
keyboard = Controller()
keys=[]
def on_press(key):
global keys
#keys.append(str(key).replace("'",""))
string = str(key).replace("'","")
keys.append(string)
main_string = "".join(keys)
print(main_string)
if len(main_string)>15:
with open('keys.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(main_string)
keys= []
def on_release(key):
if key == Key.esc:
return False
with listener(on_press=on_press,on_release=on_release) as listener:
listener.join()10、短网址生成器
目的:编写一个Python脚本,使用API缩短给定的URL。
from __future__ import with_statement
import contextlib
try:
from urllib.parse import urlencode
except ImportError:
from urllib import urlencode
try:
from urllib.request import urlopen
except ImportError:
from urllib2 import urlopen
import sys
def make_tiny(url):
request_url = ('http://tinyurl.com/api-create.php?' +
urlencode({'url':url}))
with contextlib.closing(urlopen(request_url)) as response:
return response.read().decode('utf-8')
def main():
for tinyurl in map(make_tiny, sys.argv[1:]):
print(tinyurl)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
-----------------------------OUTPUT------------------------
python url_shortener.py https://www.wikipedia.org/
https://tinyurl.com/buf3qt3结尾
好啦!以上就是今天要给大家分享的内容,如果有需要可以收藏起来慢慢看哈~
边看的话也要试着自己敲代码啦!
快来跟我一起学习吧!关注小编,每天更新精彩内容哦~
源码基地:点击蓝色字体或私信小编06即可免费拿!往期源码也都在地哦~
想跟大家一起交流学习滴可以加入我的公众号关注下哈:Python顾木子吖!