1、遍历方式
1.1 迭代器 EntrySet
/**
* 1. 迭代器 EntrySet
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
Iterator> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}
1.2 迭代器 KeySet
/**
* 2. 迭代器 KeySet
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
Iterator iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer key = iterator.next();
System.out.println(key + ":" + map.get(key));
}
}
1.3 ForEach EntrySet
/**
* 3. ForEach EntrySet
*/
@Test
public void test3() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}
1.4 ForEach KeySet
/**
* 4. ForEach KeySet
*/
@Test
public void test4() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + ":" + map.get(key));
}
}
1.5 Lambda 表达式
/**
* 5. Lambda 表达式
*/
@Test
public void test5() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + ":" + value);
});
}
1.6 Stream API 单线程
/**
* 6. Stream API 单线程
*/
@Test
public void test6() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
map.entrySet().stream().forEach((entry) -> {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
});
}
1.7 Stream API 多线程
/**
* 7. Stream API 多线程
*/
@Test
public void test7() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
map.entrySet().parallelStream().forEach((entry) -> {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
});
}
1.8 代码汇总
/**
* HashMap 的 7 种遍历方式
* @ClassName HashMapTraverse
* @Author YH
* @Date 2021/11/12
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class HashMapTraverseTest {
/**
* 1. 迭代器 EntrySet
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
Iterator> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}
/**
* 2. 迭代器 KeySet
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
Iterator iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer key = iterator.next();
System.out.println(key + ":" + map.get(key));
}
}
/**
* 3. ForEach EntrySet
*/
@Test
public void test3() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}
/**
* 4. ForEach KeySet
*/
@Test
public void test4() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + ":" + map.get(key));
}
}
/**
* 5. Lambda 表达式
*/
@Test
public void test5() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + ":" + value);
});
}
/**
* 6. Stream API 单线程
*/
@Test
public void test6() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
map.entrySet().stream().forEach((entry) -> {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
});
}
/**
* 7. Stream API 多线程
*/
@Test
public void test7() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "JavaSE");
map.put(3, "JavaEE");
map.put(4, "Spring");
map.put(5, "SpringMVC");
map.put(6, "MyBatis");
map.entrySet().parallelStream().forEach((entry) -> {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
});
}
}
2、性能分析
使用 Oracle 官方提供的性能测试工具 JMH(Java Microbenchmark Harness,JAVA 微基准测试套件)来测试一下这 7 种循环的性能。
使用 JMH 进行性能基准测试
2.1 引入依赖
org.openjdk.jmh jmh-core 1.23 org.openjdk.jmh jmh-generator-annprocess 1.23 provided
2.2 编写测试类
直接复制粘贴即可!
/**
* @ClassName HashMapCycleTest
* @Author YH
* @Date 2021/11/12
* @Version 1.0
*/
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime) // 测试完成时间
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)
@Warmup(iterations = 2, time = 1, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 预热 2 轮,每次 1s
@Measurement(iterations = 5, time = 1, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 测试 5 轮,每次 1s
@Fork(1) // fork 1 个线程
@State(Scope.Thread) // 每个测试线程一个实例
public class HashMapCycleTest {
/**
* 类加载时赋值
*/
static Map map = new HashMap() {{
// 添加数据
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
put(i, "val:" + i);
}
}};
public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException {
// 启动基准测试
Options opt = new OptionsBuilder()
// 要导入的测试类
.include(HashMapCycleTest.class.getSimpleName())
// 输出测试结果的文件
.output("D:/JAVA/面试/workplace/interview/jmh-hashMap.log")
.build();
// 执行测试
new Runner(opt).run();
}
/**
* 迭代器 EntrySet
*/
@Benchmark
public void entrySet() {
// 遍历
Iterator> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = iterator.next();
Integer k = entry.getKey();
String v = entry.getValue();
}
}
/**
* ForEach EntrySet
*/
@Benchmark
public void forEachEntrySet() {
// 遍历
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer k = entry.getKey();
String v = entry.getValue();
}
}
/**
* 迭代器 KeySet
*/
@Benchmark
public void keySet() {
// 遍历
Iterator iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer k = iterator.next();
String v = map.get(k);
}
}
/**
* ForEach KeySet
*/
@Benchmark
public void forEachKeySet() {
// 遍历
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
Integer k = key;
String v = map.get(k);
}
}
/**
* Lambda 表达式
*/
@Benchmark
public void lambda() {
// 遍历
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
Integer k = key;
String v = value;
});
}
/**
* Stream API 单线程
*/
@Benchmark
public void streamApi() {
// 单线程遍历
map.entrySet().stream().forEach((entry) -> {
Integer k = entry.getKey();
String v = entry.getValue();
});
}
/**
* Stream API 多线程
* 这个不用测,可以肯定性能是最好的。
* 如果把这个加入进测试了,理论上来说性能应该是最差的(已经测试过)
* 为啥这么说?因为你本来就开了好几个线程来测试其他方法了,
* 你这个方法还想再多搞几个线程来提升性能已经不可能了,线程都分配完了。
* 线程上下文切换的时间会更长!!!所以不能一起测试!!!
*/
public void parallelStreamApi() {
// 多线程遍历
map.entrySet().parallelStream().forEach((entry) -> {
Integer k = entry.getKey();
String v = entry.getValue();
});
}
}
2.3 测试结果
运行程序,查看输出日志!
(1)第一次
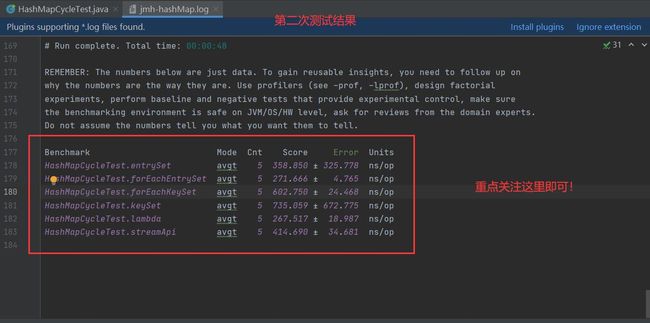
(2)第二次
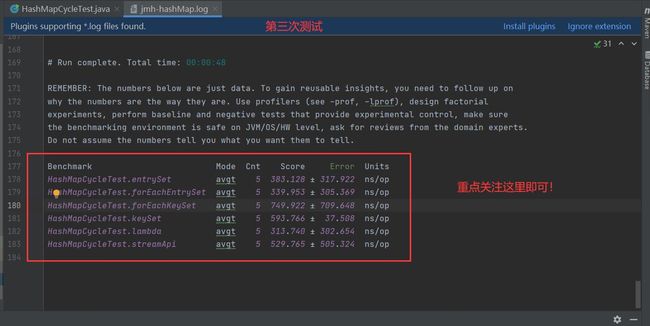
(3)第三次
2.4 分析
上图解释:测试结论{测试的方法(Benchmark)、测试类型(Mode)、测试总次数(Cnt)、测试结果(Score)、误差(Error)、单位(Units)}
其中 Units 为 ns/op 意思是执行完成时间(单位为纳秒),而 Score 列为平均执行时间, ± 符号表示误差。
从以上结果可以看出,Lambda 和两个 EntrySet 的性能相近,接下来是 Stream API 单线程,然后是 KeySet,性能最差。
2.5 总结
从以上结果可以看出 entrySet 的性能比 keySet 的性能高出了一倍之多,因此我们应该尽量使用 entrySet 来实现 Map 集合的遍历,当然,如果熟练 Lambda 用 Lambda 更好咯,毕竟代码简洁。
如果想深入了解为啥性能会差别这么大,建议查看字节码文件进行分析。或者是使用 javap -c 类名.class 进行反编译,查看底层的实现。
到此这篇关于java中HashMap的7种遍历方式与性能分析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java HashMap遍历 内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!