在了解了Spring IOC和AOP之后,继续了解Spring MVC 的实现。 Spring MVV 是Spring的一个重要模块,很多Web应用是由Spring来支撑的。
在没有Spring Boot之前,我们开发Spring 的Web的应用,都是从以下web.xml配置开始的。
dispatcher
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
2
dispatcher
/*
contextConfigLocation
/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
在上面的配置文件中,首先定义了一个DispatcherServlet的servlet对象,同时定义了这个DispatcherServlet的参数,context-param参数的用来制定Spring IOC容器读区Bean定义的XML文件的路径,最后定义了一个ContextLoaderListener的监听器。
上述定义的servlet和listener就是Spring MVC在Web容器中的入口,这些接口通过与Web容器耦合,Web容器的ServletContext为Spring IOC 容器提供了一个宿主环境,这个宿主环境中,Spring 通过上述的servlet和listener建立了一个IOC的容器体系。这个IOC容器体系是通过ContextLoaderListener的初始化来建立的,在IOC容器体系建立之后,把DispatcherServlet作为Spring MVC处理Web请求的转发器初始化,从而完成响应HTTP请求的准备。
所以整个Spring MVC的初始化可以概括为以下两步:
- ContextLoaderListener监听Web容器的启动初始化一个根上下文。
- 初始化DispatcherServlet,同时初始化一个用来保存控制器需要的MVC对象的上下文,并将第一步的上下文作为根上下文。
Spring MVC 拥有两个上下文,其中一个为另一个的根上下文。
在分析Spring MVC的实现之前,先了解一下Web容器下的上下文,即IOC容器,看看Web环境下的上下文与普通的IOC容器的有哪些特别之处。为了方便在Web环境中使用IOC容器,Spring 为Web应用提供了上下文的扩展接口WebApplicationContext来满足启动过程的需要,Spring 提供了WebApplicationContext的多个实现,我们以XmlWebApplicationContext入手来了解其实现。
XmlWebApplicationContext的继承关系如上所示。
我们主要关注以下几个接口:
- ApplicationContext
- WebApplicationContext
- ConfigurableApplicationContext
- ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
- AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext
ApplicationContext
从上述的类图中可以看到ApplicationContext继承自BeanFactory,除了BeanFactory, ApplicationContext集成了众多接口,比简单的IOC容器拥有了更多特性。
ApplicationContext接口定义了以下方法。
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
@Nullable
String getId();
String getApplicationName();
String getDisplayName();
long getStartupDate();
@Nullable
ApplicationContext getParent();
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext在ApplicationContext的基础上,定义了若干Spring MVC需要使用的常量,其中一个常量用于存取根上下文的key。
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";同时定义了getServletContext()方法,通过这个方法获取Web容器的ServletContext。
ConfigurableApplicationContext
ConfigurableApplicationContext 提供了对大部分ApplicationContext进行配置的方法。其中的refresh()用于初始化一个ApplicationContext。
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 继承自ConfigurableApplicationContext和WebApplicationContext,在ConfigurableApplicationContext的基础上提供了更多对ApplicationContext进行配置的方法。
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext抽象类提供了对ApplicationContext配置文件进行配置的方法,同时定义了子类实现的loadBeanDefintion方法,通过loadBeanDefintion()以及配置文件的路径加载BeanDefinition.
XmlWebApplicationContext
XmlWebApplicationContext继承自AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext,并实现了loadBeanDefintion方法。同时定义了对XmlWebApplicationContext而言,默认的配置文件为WEB-INF下的applicationContext.xml.
可以看到XmlWebApplicationContext定义了Web应用中默认的配置文件,同时提供了对Ioc容器的配置方法,但是殊途同归,整个ApplicationContext的初始化依旧是先加载BeanDefiniton,然后根据BeanDefiniton实例化IOC容器中的Bean。
在了解了XmlWebApplicationContext之后,下面我们从以下三方面来分析Srping MVC的实现。
- ContextLoaderListener的初始化。
- DispatcherServlet的初始化。
- HTTP请求分发。
ContextLoaderListener的初始化
在ContextLoaderListener中,是实现了ServletContextListener的接口,ServletContextListener定义了两个在Web容器启动和销毁时会回调方法,Spring MVC两个上下文中的根上下文就是在Web容器启动时的回调方法contextInitialized()中初始化的。
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}ContextLoaderListener继承自ContextLoader, ContextLoaderListener通过ContextLoader中的initWebApplicationContext()初始化根上下文:
/**
* Initialize Spring's web application context for the given servlet context,
* using the application context provided at construction time, or creating a new one
* according to the "{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}" and
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}" context-params.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}根据上述的代码,整个根上下文的初始化的过程如下:
- 通过createWebApplicationContext()创建根上下文。
- 如果有parent上下文,则设置parent, 对于根上下文而言,其parent为null。
- 通过configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()对根上下文进行配置,即设置servletContext,contextConfigLocation(前面的web.xml配置文件有配置)到根上下文中,以及通过customizeContext对上下文进行设置,最后通过refresh()方法初始化根上下文。
- 将根上下文。保存到servletContext中。
createWebApplicationContext()的实现如下:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}protected Class determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}这里通过首先通过determineContextClass确定使用哪个Ioc容器,可以通过Context_class_param参数设置,如果没有设置,则使用默认的Ioc容器,即XmlWebApplicationContext。
到这里根上下文的初始化就完成了,即通过ServletContext初始化根上下文,同时对根上下文进行配置,然后保存到ServletContext中去,使得在全局中都可以获取到该上下文。
DispatcherServlet的初始化
可以看到DispatcherServlet继承自FrameworkServlet, FrameworkServlet继承自HttpServletBean, HttpServletBean继承自HttpServlet, HttpServlet继承自GenericServlet, GenericServlet继承自Servlet。
DispatcherServlet的初始化是通过HttpServletBean的init()方法。
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}可以看到HttpServletBean的init()方法中首先设置通过BeanWrapper设置在web.xml中设置的一些参数,然后便调用了FrameworkServlet的initServletBean()方法,我们继续看initServletBean()的实现。
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}initServletBean()中只有两个方法调用,分别是通过initWebApplicationContext()初始化前面提到的第二个上下文,以及initFrameworkServlet(),initFrameworkServlet()在FrameworkServlet是一个空实现。继续看initFrameworkServlet()。
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}首先判断上下文是否存在,如果存在就设置parent和通过configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()进行配置,如果不存在,则通过findWebApplicationContext()尝试寻找一个已经存在的上下文,如果依旧没有找到,则通过createWebApplicationContext()创建一个上下文。最后也会将这个上下文保存到ServletContext中。创建上下文的过程如下:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}
可以看到这里的上下文的创建过程与根上下文的创建类似,但是又有些不同,区别在于这里设置了Environment,同时configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext中设置了一个ContextRefreshListener类型的ApplicationListener,ContextRefreshListener对ApplicationEvent进行监听,如果是ContextRefreshedEvent,则调用onRefresh()方法。如果this.refreshEventReceived = false,也会调用onRefresh()方法,防止没有对ContextRefreshedEvent进行监听或者不支持ContextRefreshedEvent监听,也可以调用onRefresh()方法。接下来继续看onRefresh()方法。
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}可以看到onRefresh()方法中调用了iniStrategies()方法。iniStrategies()方法中初始化化了MultipartResolver, LocalResolver, ThemeResolver, HandlerMappings, HanderAdapters, HanderExceptionResolvers, RequestToViewNameTranslator, ViewResolver, FlashMapManager()等。
下面以初始化HandlerMappings为例,看看其具体的实现。
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
if (mapping.usesPathPatterns()) {
this.parseRequestPath = true;
break;
}
}
} HandlerMappings的初始化的过程如下:
- 判断是否检测所有的HandelrMappings, 如果需要则通过beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors获取所有的HandelrMapping, 并按照Order排序。
- 如果不需要检测所有的HandlerMapping, 则通过默认的beanName从IOC容器中取得。
- 如果没有拿到HandelrMappping, 则初始化默认的HandlerMappings(BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RouterFunctionMapping)
- 设置parseRequestPath。
前面Spring MVC的初始化已经完成了,在初始化完成时,在上下文环境中已定义好的所有的HandlerMapping都已经加载完成了,这些handlerMapping保存在一个List中并被排序,存储中HTTP请求的对应的映射数据,每一个HandlerMapping都可以持有一些列从URL到Controller的映射,而Spring MVC 提供了一系列HandlerMapping的实现,如下所示
以SimpleUrlHandlerMapping为例继续分析HandlerMapping的设计与实现。
首先看一下HandlerMapping接口,HandlerMapping中只定义的了一个方法。
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;入参是HttpServletRequest, 返回的是HandlerExecutionChain。HandlerExecutionChain的实现如下:
public class HandlerExecutionChain {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(HandlerExecutionChain.class);
private final Object handler;
private final List interceptorList = new ArrayList<>();
private int interceptorIndex = -1;
...
} 可以看到HandlerExecutionChain保存了一个interceptors链和一个handler对象,这个handler对象实际上就是HTTP请求对应的Controller, 在持有这个handler对象的同时,通过这个interceptor链为handler对象提供功能的增强。HandlerExecutionChain中的interceptors链和handler对象需要在初始化HandlerMapping的时候设置好。对于SimpleUrlHandlerMapping而言,则是通过Bean的postProcessor来完成了的,因为SimpleUrlHandlerMapping是ApplicationContextAware的子类,在setApplicationContext的时候回调WebApplicationObjectSupport的initApplicationContext方法,继而回调到SimpleUrlHandlerMapping的initApplicationContext方法。
public void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
super.initApplicationContext();
registerHandlers(this.urlMap);
}
protected void registerHandlers(Map urlMap) throws BeansException {
if (urlMap.isEmpty()) {
logger.trace("No patterns in " + formatMappingName());
}
else {
urlMap.forEach((url, handler) -> {
// Prepend with slash if not already present.
if (!url.startsWith("/")) {
url = "/" + url;
}
// Remove whitespace from handler bean name.
if (handler instanceof String) {
handler = ((String) handler).trim();
}
registerHandler(url, handler);
});
logMappings();
}
} 对于SimpleUrlHandlerMapping而言,则需要在初始化SimpleUrlHandlerMapping时指定urlMap, 对于BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping而言,则会扫描IOC容器中的bean,并建立url到handler的映射。同时真正的注册过程是通过父类AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的registerHandler完成的。
protected void registerHandler(String[] urlPaths, String beanName) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPaths, "URL path array must not be null");
for (String urlPath : urlPaths) {
registerHandler(urlPath, beanName);
}
}
protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null");
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
// Eagerly resolve handler if referencing singleton via name.
if (!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext();
if (applicationContext.isSingleton(handlerName)) {
resolvedHandler = applicationContext.getBean(handlerName);
}
}
Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (mappedHandler != null) {
if (mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot map " + getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath +
"]: There is already " + getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped.");
}
}
else {
if (urlPath.equals("/")) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Root mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setRootHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else if (urlPath.equals("/*")) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Default mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else {
this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
if (getPatternParser() != null) {
this.pathPatternHandlerMap.put(getPatternParser().parse(urlPath), resolvedHandler);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped [" + urlPath + "] onto " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
}
}
}最终url到handler之间的映射关系保存在AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的handlerMap中,同时设置了rootHandelr, defaultHandelr, 以及pathPatternHandlerMap。
经过上述的初始化过程,handlerMappings变量就已经在获取了在BeanDefiniton中配置好的映射关系,其他的初始化过程与handlerMapping比较类似,都是直接从IOC容器中读入配置,所以这里的MVC的初始化过程是建立在IOC容器已经初始化完成的基础上的。
HTTP请求分发
在前面的Spring MVC 初始化的过程了初始化了Spring MVC 需要的各个组件,最重要的是建立了HTTP请求到Handler的映射关系,下面来看看具体的请求过程。
从Servlet开始分析,前面我们提到了DispatcherServlet继承自FrameworkServlet,而FrameworkServlet继承自HttpServletBean, HttpServletBean继承自HttpServlet。
而HttpServletBean重写了HttpServlet的doGet, doPost, doPut等一系列方法,我们以doGet()方法为例进行分析,其他的与doGet类似。
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
可以看到,首先做了一些准备工作,包括获取和设置localeContext, requestAttributes,注册interceptor的回调等,然后调用子类的doService()方法,继续看doService()方法。
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath) request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
}
} DispatcherServlet中的doService()同样是先设置若干的属性,然后调用doDispatch()。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}doDispatch()方法中可以是DispatcherServlet的主要方法,这个方法中可以看到MVC模式的核心实现,包括准备ModelAndView, 调用getHandler来响应Http请求,然后执行Handle得到返回的ModelAndView,最后将这个ModelAndView对象交给相应的视图对象去呈现。在这里完成了模型,视图,控制器的紧密结合。整个过程如下:
- getHandelr根据HTTP请求拿到对应的HandlerExecutionChain.
- 通过getHandlerAdapter得到HandlerExecutionChain对应的HandlerAdapter。
- 通过applyPreHandle对handler进行前置增强。
- 通过HandlerAdapter的handler方法对HTTP请求进行响应,对于不同的HandlerAdapter有不同的处理。
- 通过applyPostHandle对handler进行后置增强。
- 通过processDispatchResult将这个ModelAndView对象交给相应的视图对象去呈现。
下面看一下getHandelr(), getHandlerAdapter()和processDispatchResult()方法。
getHandler()的实现如下:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}在所有的handlerMapping中找到到一个与当前request匹配的handler, 找到就返回。
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// Ensure presence of cached lookupPath for interceptors and others
if (!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasCachedPath(request)) {
initLookupPath(request);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !DispatcherType.ASYNC.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (getCorsConfigurationSource() != null) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = getCorsConfigurationSource().getCorsConfiguration(request);
config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(config) : config);
}
if (config != null) {
config.validateAllowCredentials();
}
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}取得handler的具体过程在getHandlerInternal() 方法中,这个方法接受HTTP请求作为参数。得到handler之后封装成HandlerExecutionChain返回。
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
Object handler;
if (usesPathPatterns()) {
RequestPath path = ServletRequestPathUtils.getParsedRequestPath(request);
handler = lookupHandler(path, lookupPath, request);
}
else {
handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
}
if (handler == null) {
// We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to
// expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well.
Object rawHandler = null;
if (StringUtils.matchesCharacter(lookupPath, '/')) {
rawHandler = getRootHandler();
}
if (rawHandler == null) {
rawHandler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (rawHandler != null) {
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (rawHandler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) rawHandler;
rawHandler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(rawHandler, request);
handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null);
}
}
return handler;
}在getHandlerInternal中可以看到具体的url的匹配过程,即首先判断是否有设置模式解析器,如果有,则对url的模式进行匹配,如果没有则直接查找,如果前面没有找到合适的handler,则依次尝试rootHandelr ,defaultHandler是否匹配,如果找到则返回对应的handler,否则返回null。
接下来看getHandlerAdapter()。
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}getHandlerAdapter()通过supports()方法找到一个合适的HandlerAdapter。
对HandlerAdapter的handler方法则有不同实现,因为这个Handler可能是一个独立的Bean,也可能使Bean中的某个方法,HandlerAdapter就是不同的Handler的实现做一个适配,具体可以到具体的HandlerAdapter实现。
继续看一下processDispatchResult()。
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled..
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}得到ModelAndView之后就可以通过不同的视图对象去呈现视图,processDispatchResult()先取得ModelAndView, 然后通过调用视图对象的render()方法完成特定视图的呈现工作。
视图呈现
前面得到ModelAndView对象之后交给具体的视图对象去完成相应的视图呈现。
在看render()方法之前先看一下Spring中的视图对象。
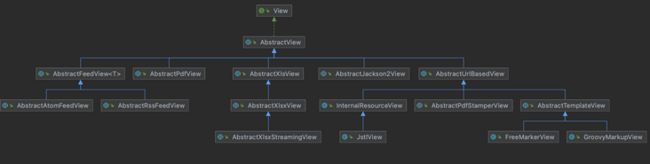
可以看到,在View接口下,实现了一系列具体的View对象,而这些View对象,又根据其不同的特性归类到不同的抽象类中,比如AbstractView类细分为AbstractFeedView, AbstractPdfView, AbstractXlsView, AbstractJackson2View, AbtractUrlBaseView。通过对不同的视图类实现方式进行归类,便于应用的使用和扩展,同时View接口的设计也很简单,只需要实现render()。
继续看前面提到render()方法。
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale =
(this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
if (viewName != null) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view [" + view + "] ");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "]", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}从上面可以看到,首先在ModelAndView对象中得到View对象,如果ModelAndView对象中已经有了最终完成的视图呈现的对象,就直接调用视图对象的render()方法,如果没有就看是否设置了视图对象的名称,并通过视图对象的名称进行解析,从而得到需要使用的视图对象。
看一下视图对象的render()方法。这里以常用的JSP页面对应的JstlView对象为例来分析视图的呈现。JstlView没有实现render()方法,使用的render()方法是它的基类AbstractView中的实现的。
public void render(@Nullable Map model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("View " + formatViewName() +
", model " + (model != null ? model : Collections.emptyMap()) +
(this.staticAttributes.isEmpty() ? "" : ", static attributes " + this.staticAttributes));
}
Map mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
} 这个render方法主要完成一些数据准备工作,createMergedOutputModel()将所有的数据属性整合到一个mergedModel里面。prepareResponse()则设置响应头的属性,renderMergedOutputModel()的实现在InternalResourceView中。
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Expose the model object as request attributes.
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request);
// Expose helpers as request attributes, if any.
exposeHelpers(request);
// Determine the path for the request dispatcher.
String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(request, response);
// Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP).
RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(request, dispatcherPath);
if (rd == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() +
"]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!");
}
// If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward.
if (useInclude(request, response)) {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Including [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
rd.include(request, response);
}
else {
// Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
rd.forward(request, response);
}
} renderMergedOutputModel()主要完成的工作如下:
- exposeModelAsRequestAttributes()将模型对象存放到HttpServletRequest里面。
- exposeHelpers()设置LocalizationContext。
- getRequestDispatcher()获取RequestDispatcher。
- 通过RequestDispatcher转发请求到对应的视图资源上,完成JSP页面的呈现。
总结
整个Spring MVC的原理以DispatcherServlet为核心,总的来说,Spring MVC的实现大致由以下几个部分组成。
- 建立HTTP请求到Controller的映射。
- HTTP请求到达之后,通过getHandler得到handlerExecutionChain对请求进行响应。
- 得到相应的ModelAndView,由视图对象的render()方法对视图进行呈现。