神经网络学习小记录60——Pytorch GhostNet模型的复现详解
神经网络学习小记录60——Pytorch GhostNet模型的复现详解
- 学习前言
- 什么是GhostNet模型
- 源码下载
- GhostNet模型的实现思路
-
- 1、Ghost Module
- 2、Ghost Bottlenecks
- 3、Ghostnet的构建
- GhostNet的代码构建
-
- 1、模型代码的构建
- 2、Yolov4上的应用
学习前言
GhostNet是华为诺亚方舟实验室提出来的一个非常有趣的网络,我们一起来学习一下。
![]()
什么是GhostNet模型
2020年,华为新出了一个轻量级网络,命名为GhostNet。
在优秀CNN模型中,特征图存在冗余是非常重要的。如图所示,这个是对ResNet-50第一个残差块特征图进行可视化的结果,当我们给一个神经网络输入一张图片时,我们可以获得特别多的特征图。

利用小扳手连接起来的两幅特征图,它们的相似性就特别高,这个就是神经网络中存在的特征图冗杂的情况。
作者将相似的特征图认为是彼此的Ghost,所以这个网络就叫做GhostNet(误)。
在GhostNet这篇论文里面,作者认为可以使用一些计算量更低(Cheap Operations)的操作去生成这些冗余的特征图,这样就可以在保证良好检测效果的情况下,减少模型的参数量与提高模型的执行速度。
源码下载
https://github.com/bubbliiiing/mobilenet-yolov4-lite-pytorch
GhostNet模型的实现思路
1、Ghost Module
通过上述的介绍,我们了解到了,GhostNet的核心思想就是使用一些计算量更低(Cheap Operations)的操作去生成这些冗余的特征图。
在论文中,作者设计了一个名为Ghost Module的模块,他的功能是代替普通卷积。
Ghost Module将普通卷积分为两部分,首先进行一个普通的1x1卷积,这是一个少量卷积,比如正常使用32通道的卷积,这里就用16通道的卷积,这个1x1卷积的作用类似于特征整合,生成输入特征层的特征浓缩。
然后我们再进行深度可分离卷积,这个深度可分离卷积是逐层卷积,它也就是我们上面提到的Cheap Operations。它利用上一步获得的特征浓缩生成Ghost特征图。
因此,如果我们从整体上去看这个Ghost Module,它其实就是两步简单思想的汇总:
1、利用1x1卷积获得输入特征的必要特征浓缩。
2、利用深度可分离卷积获得特征浓缩的相似特征图(Ghost)。

Ghost Module的实现代码如下:
class GhostModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, kernel_size=1, ratio=2, dw_size=3, stride=1, relu=True):
super(GhostModule, self).__init__()
self.oup = oup
init_channels = math.ceil(oup / ratio)
new_channels = init_channels*(ratio-1)
self.primary_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, init_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(init_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
self.cheap_operation = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(init_channels, new_channels, dw_size, 1, dw_size//2, groups=init_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(new_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.primary_conv(x)
x2 = self.cheap_operation(x1)
out = torch.cat([x1,x2], dim=1)
return out[:,:self.oup,:,:]
2、Ghost Bottlenecks
Ghost Bottlenecks是由Ghost Module组成的瓶颈结构,就像这样。
其实本质上就是用Ghost Module,来代替瓶颈结构里面的普通卷积。
Ghost Bottlenecks可以分为两个部分,分别是主干部分和残差边部分,包含Ghost Module的,我们称它为主干部分。
Ghost Bottlenecks有两个种类,如下图所示,当我们需要对特征层的宽高进行压缩的时候,我们会设置这个Ghost Bottlenecks的Stride=2,即步长为2。此时我们会Bottlenecks里面多添加一些卷积层,在主干部分里,我们会在两个Ghost Module中添加一个步长为2x2的深度可分离卷积进行特征层的宽高压缩。在残差边部分,我们也会添加上一个步长为2x2的深度可分离卷积和1x1的普通卷积。
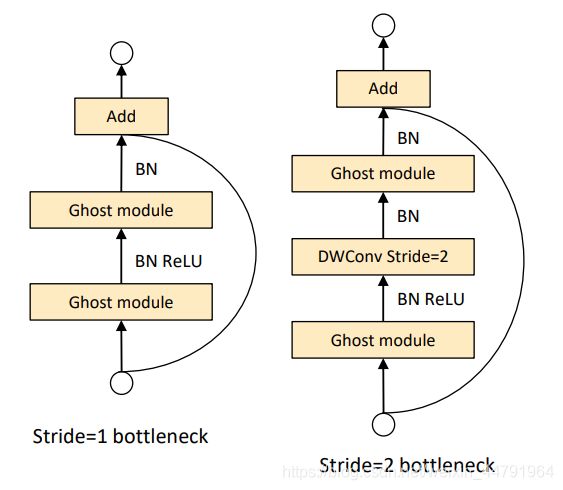
Ghost Bottlenecks的实现代码如下:
class GhostBottleneck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_chs, mid_chs, out_chs, dw_kernel_size=3, stride=1, act_layer=nn.ReLU, se_ratio=0.):
super(GhostBottleneck, self).__init__()
has_se = se_ratio is not None and se_ratio > 0.
self.stride = stride
self.ghost1 = GhostModule(in_chs, mid_chs, relu=True)
if self.stride > 1:
self.conv_dw = nn.Conv2d(mid_chs, mid_chs, dw_kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=(dw_kernel_size-1)//2,
groups=mid_chs, bias=False)
self.bn_dw = nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_chs)
if has_se:
self.se = SqueezeExcite(mid_chs, se_ratio=se_ratio)
else:
self.se = None
self.ghost2 = GhostModule(mid_chs, out_chs, relu=False)
if (in_chs == out_chs and self.stride == 1):
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
else:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_chs, in_chs, dw_kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=(dw_kernel_size-1)//2, groups=in_chs, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_chs),
nn.Conv2d(in_chs, out_chs, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chs),
)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
x = self.ghost1(x)
if self.stride > 1:
x = self.conv_dw(x)
x = self.bn_dw(x)
if self.se is not None:
x = self.se(x)
x = self.ghost2(x)
x += self.shortcut(residual)
return x
3、Ghostnet的构建
整个Ghostnet的构建方式如列表所示:
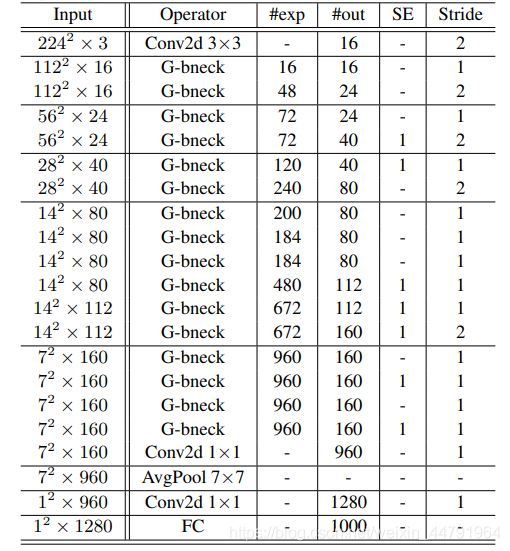
可以看到,整个Ghostnet都是由Ghost Bottlenecks进行组成的。
当一张图片输入到Ghostnet当中时,我们首先进行一个16通道的普通1x1卷积块(卷积+标准化+激活函数)。
之后我们就开始Ghost Bottlenecks的堆叠了,利用Ghost Bottlenecks,我们最终获得了一个7x7x160的特征层(当输入是224x224x3的时候)。
然后我们会利用一个1x1的卷积块进行通道数的调整,此时我们可以获得一个7x7x960的特征层。
之后我们进行一次全局平均池化,然后再利用一个1x1的卷积块进行通道数的调整,获得一个1x1x1280的特征层。
然后平铺后进行全连接就可以进行分类了。
GhostNet的代码构建
1、模型代码的构建
GhostNet的实现代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math
__all__ = ['ghost_net']
def _make_divisible(v, divisor, min_value=None):
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor
new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
if new_v < 0.9 * v:
new_v += divisor
return new_v
def hard_sigmoid(x, inplace: bool = False):
if inplace:
return x.add_(3.).clamp_(0., 6.).div_(6.)
else:
return F.relu6(x + 3.) / 6.
class SqueezeExcite(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_chs, se_ratio=0.25, reduced_base_chs=None,
act_layer=nn.ReLU, gate_fn=hard_sigmoid, divisor=4, **_):
super(SqueezeExcite, self).__init__()
self.gate_fn = gate_fn
reduced_chs = _make_divisible((reduced_base_chs or in_chs) * se_ratio, divisor)
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.conv_reduce = nn.Conv2d(in_chs, reduced_chs, 1, bias=True)
self.act1 = act_layer(inplace=True)
self.conv_expand = nn.Conv2d(reduced_chs, in_chs, 1, bias=True)
def forward(self, x):
x_se = self.avg_pool(x)
x_se = self.conv_reduce(x_se)
x_se = self.act1(x_se)
x_se = self.conv_expand(x_se)
x = x * self.gate_fn(x_se)
return x
class ConvBnAct(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_chs, out_chs, kernel_size,
stride=1, act_layer=nn.ReLU):
super(ConvBnAct, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_chs, out_chs, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chs)
self.act1 = act_layer(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
return x
class GhostModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, kernel_size=1, ratio=2, dw_size=3, stride=1, relu=True):
super(GhostModule, self).__init__()
self.oup = oup
init_channels = math.ceil(oup / ratio)
new_channels = init_channels*(ratio-1)
self.primary_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, init_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(init_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
self.cheap_operation = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(init_channels, new_channels, dw_size, 1, dw_size//2, groups=init_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(new_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.primary_conv(x)
x2 = self.cheap_operation(x1)
out = torch.cat([x1,x2], dim=1)
return out[:,:self.oup,:,:]
class GhostBottleneck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_chs, mid_chs, out_chs, dw_kernel_size=3, stride=1, act_layer=nn.ReLU, se_ratio=0.):
super(GhostBottleneck, self).__init__()
has_se = se_ratio is not None and se_ratio > 0.
self.stride = stride
self.ghost1 = GhostModule(in_chs, mid_chs, relu=True)
if self.stride > 1:
self.conv_dw = nn.Conv2d(mid_chs, mid_chs, dw_kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=(dw_kernel_size-1)//2,
groups=mid_chs, bias=False)
self.bn_dw = nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_chs)
if has_se:
self.se = SqueezeExcite(mid_chs, se_ratio=se_ratio)
else:
self.se = None
self.ghost2 = GhostModule(mid_chs, out_chs, relu=False)
if (in_chs == out_chs and self.stride == 1):
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
else:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_chs, in_chs, dw_kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=(dw_kernel_size-1)//2, groups=in_chs, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_chs),
nn.Conv2d(in_chs, out_chs, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chs),
)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
x = self.ghost1(x)
if self.stride > 1:
x = self.conv_dw(x)
x = self.bn_dw(x)
if self.se is not None:
x = self.se(x)
x = self.ghost2(x)
x += self.shortcut(residual)
return x
class GhostNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfgs, num_classes=1000, width=1.0, dropout=0.2):
super(GhostNet, self).__init__()
# setting of inverted residual blocks
self.cfgs = cfgs
self.dropout = dropout
# building first layer
output_channel = _make_divisible(16 * width, 4)
self.conv_stem = nn.Conv2d(3, output_channel, 3, 2, 1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channel)
self.act1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
input_channel = output_channel
# building inverted residual blocks
stages = []
block = GhostBottleneck
for cfg in self.cfgs:
layers = []
for k, exp_size, c, se_ratio, s in cfg:
output_channel = _make_divisible(c * width, 4)
hidden_channel = _make_divisible(exp_size * width, 4)
layers.append(block(input_channel, hidden_channel, output_channel, k, s,
se_ratio=se_ratio))
input_channel = output_channel
stages.append(nn.Sequential(*layers))
output_channel = _make_divisible(exp_size * width, 4)
stages.append(nn.Sequential(ConvBnAct(input_channel, output_channel, 1)))
input_channel = output_channel
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*stages)
# building last several layers
output_channel = 1280
self.global_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.conv_head = nn.Conv2d(input_channel, output_channel, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
self.act2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(output_channel, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv_stem(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
x = self.blocks(x)
x = self.global_pool(x)
x = self.conv_head(x)
x = self.act2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
if self.dropout > 0.:
x = F.dropout(x, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def ghostnet(**kwargs):
"""
Constructs a GhostNet model
"""
cfgs = [
# k, t, c, SE, s
# stage1
[[3, 16, 16, 0, 1]],
# stage2
[[3, 48, 24, 0, 2]],
[[3, 72, 24, 0, 1]],
# stage3
[[5, 72, 40, 0.25, 2]],
[[5, 120, 40, 0.25, 1]],
# stage4
[[3, 240, 80, 0, 2]],
[[3, 200, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 184, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 184, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 480, 112, 0.25, 1],
[3, 672, 112, 0.25, 1]
],
# stage5
[[5, 672, 160, 0.25, 2]],
[[5, 960, 160, 0, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 0.25, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 0, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 0.25, 1]
]
]
return GhostNet(cfgs, **kwargs)
if __name__ == "__main__":
from torchsummary import summary
# 需要使用device来指定网络在GPU还是CPU运行
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = ghostnet().to(device)
summary(model, input_size=(3,224,224))
2、Yolov4上的应用
作为一个轻量级网络,我把Ghostnet和Mobilenet放在一起,作为Yolov4的主干网络进行特征提取。
![]()
对于yolov4来讲,我们需要利用主干特征提取网络获得的三个有效特征进行加强特征金字塔的构建。
我们通过如下代码取出三个有效特征层:
class GhostNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, pretrained=True):
super(GhostNet, self).__init__()
model = ghostnet()
if pretrained:
state_dict = torch.load("model_data/ghostnet_weights.pth")
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
del model.global_pool
del model.conv_head
del model.act2
del model.classifier
del model.blocks[9]
self.model = model
self.layers_out_filters = [16, 24, 40, 112, 160]
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model.conv_stem(x)
x = self.model.bn1(x)
x = self.model.act1(x)
feature_maps = []
for idx, block in enumerate(self.model.blocks):
x = block(x)
if idx in [2,4,6,8]:
feature_maps.append(x)
return feature_maps[1:]
我们可以利用这三个有效特征层替换原来yolov4主干网络CSPdarknet53的有效特征层。
为了进一步减少参数量,我们可以使用深度可分离卷积代替yoloV3中用到的普通卷积。
最终Ghostnet-Yolov4的构建代码如下:
class GhostNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, pretrained=True):
super(GhostNet, self).__init__()
model = ghostnet()
if pretrained:
state_dict = torch.load("model_data/ghostnet_weights.pth")
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
del model.global_pool
del model.conv_head
del model.act2
del model.classifier
del model.blocks[9]
self.model = model
self.layers_out_filters = [16, 24, 40, 112, 160]
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model.conv_stem(x)
x = self.model.bn1(x)
x = self.model.act1(x)
feature_maps = []
for idx, block in enumerate(self.model.blocks):
x = block(x)
if idx in [2,4,6,8]:
feature_maps.append(x)
return feature_maps[1:]
def conv2d(filter_in, filter_out, kernel_size, groups=1, stride=1):
pad = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 if kernel_size else 0
return nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("conv", nn.Conv2d(filter_in, filter_out, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=pad, groups=groups, bias=False)),
("bn", nn.BatchNorm2d(filter_out)),
("relu", nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)),
]))
def conv_dw(filter_in, filter_out, stride = 1):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(filter_in, filter_in, 3, stride, 1, groups=filter_in, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(filter_in),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(filter_in, filter_out, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(filter_out),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True),
)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# SPP结构,利用不同大小的池化核进行池化
# 池化后堆叠
#---------------------------------------------------#
class SpatialPyramidPooling(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, pool_sizes=[5, 9, 13]):
super(SpatialPyramidPooling, self).__init__()
self.maxpools = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(pool_size, 1, pool_size//2) for pool_size in pool_sizes])
def forward(self, x):
features = [maxpool(x) for maxpool in self.maxpools[::-1]]
features = torch.cat(features + [x], dim=1)
return features
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 卷积 + 上采样
#---------------------------------------------------#
class Upsample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(Upsample, self).__init__()
self.upsample = nn.Sequential(
conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
)
def forward(self, x,):
x = self.upsample(x)
return x
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 三次卷积块
#---------------------------------------------------#
def make_three_conv(filters_list, in_filters):
m = nn.Sequential(
conv2d(in_filters, filters_list[0], 1),
conv_dw(filters_list[0], filters_list[1]),
conv2d(filters_list[1], filters_list[0], 1),
)
return m
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 五次卷积块
#---------------------------------------------------#
def make_five_conv(filters_list, in_filters):
m = nn.Sequential(
conv2d(in_filters, filters_list[0], 1),
conv_dw(filters_list[0], filters_list[1]),
conv2d(filters_list[1], filters_list[0], 1),
conv_dw(filters_list[0], filters_list[1]),
conv2d(filters_list[1], filters_list[0], 1),
)
return m
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 最后获得yolov4的输出
#---------------------------------------------------#
def yolo_head(filters_list, in_filters):
m = nn.Sequential(
conv_dw(in_filters, filters_list[0]),
nn.Conv2d(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 1),
)
return m
#---------------------------------------------------#
# yolo_body
#---------------------------------------------------#
class YoloBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors_mask, num_classes, backbone="mobilenetv2", pretrained=False):
super(YoloBody, self).__init__()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 生成mobilnet的主干模型,获得三个有效特征层。
#---------------------------------------------------#
if backbone == "mobilenetv1":
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 52,52,256;26,26,512;13,13,1024
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.backbone = MobileNetV1(pretrained=pretrained)
in_filters = [256,512,1024]
elif backbone == "mobilenetv2":
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 52,52,32;26,26,92;13,13,320
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.backbone = MobileNetV2(pretrained=pretrained)
in_filters = [32,96,320]
elif backbone == "mobilenetv3":
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 52,52,40;26,26,112;13,13,160
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.backbone = MobileNetV3(pretrained=pretrained)
in_filters = [40,112,160]
elif backbone == "ghostnet":
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 52,52,40;26,26,112;13,13,160
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.backbone = GhostNet(pretrained=pretrained)
in_filters = [40,112,160]
else:
raise ValueError('Unsupported backbone - `{}`, Use mobilenetv1, mobilenetv2, mobilenetv3, ghostnet.'.format(backbone))
self.conv1 = make_three_conv([512, 1024], in_filters[2])
self.SPP = SpatialPyramidPooling()
self.conv2 = make_three_conv([512, 1024], 2048)
self.upsample1 = Upsample(512, 256)
self.conv_for_P4 = conv2d(in_filters[1], 256,1)
self.make_five_conv1 = make_five_conv([256, 512], 512)
self.upsample2 = Upsample(256, 128)
self.conv_for_P3 = conv2d(in_filters[0], 128,1)
self.make_five_conv2 = make_five_conv([128, 256], 256)
# 3*(5+num_classes) = 3*(5+20) = 3*(4+1+20)=75
self.yolo_head3 = yolo_head([256, len(anchors_mask[0]) * (5 + num_classes)], 128)
self.down_sample1 = conv_dw(128, 256, stride = 2)
self.make_five_conv3 = make_five_conv([256, 512], 512)
# 3*(5+num_classes) = 3*(5+20) = 3*(4+1+20)=75
self.yolo_head2 = yolo_head([512, len(anchors_mask[1]) * (5 + num_classes)], 256)
self.down_sample2 = conv_dw(256, 512, stride = 2)
self.make_five_conv4 = make_five_conv([512, 1024], 1024)
# 3*(5+num_classes)=3*(5+20)=3*(4+1+20)=75
self.yolo_head1 = yolo_head([1024, len(anchors_mask[2]) * (5 + num_classes)], 512)
def forward(self, x):
# backbone
x2, x1, x0 = self.backbone(x)
# 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512 -> 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512 -> 13,13,2048
P5 = self.conv1(x0)
P5 = self.SPP(P5)
# 13,13,2048 -> 13,13,512 -> 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512
P5 = self.conv2(P5)
# 13,13,512 -> 13,13,256 -> 26,26,256
P5_upsample = self.upsample1(P5)
# 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256
P4 = self.conv_for_P4(x1)
# 26,26,256 + 26,26,256 -> 26,26,512
P4 = torch.cat([P4,P5_upsample],axis=1)
# 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256 -> 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256 -> 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256
P4 = self.make_five_conv1(P4)
# 26,26,256 -> 26,26,128 -> 52,52,128
P4_upsample = self.upsample2(P4)
# 52,52,256 -> 52,52,128
P3 = self.conv_for_P3(x2)
# 52,52,128 + 52,52,128 -> 52,52,256
P3 = torch.cat([P3,P4_upsample],axis=1)
# 52,52,256 -> 52,52,128 -> 52,52,256 -> 52,52,128 -> 52,52,256 -> 52,52,128
P3 = self.make_five_conv2(P3)
# 52,52,128 -> 26,26,256
P3_downsample = self.down_sample1(P3)
# 26,26,256 + 26,26,256 -> 26,26,512
P4 = torch.cat([P3_downsample,P4],axis=1)
# 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256 -> 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256 -> 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256
P4 = self.make_five_conv3(P4)
# 26,26,256 -> 13,13,512
P4_downsample = self.down_sample2(P4)
# 13,13,512 + 13,13,512 -> 13,13,1024
P5 = torch.cat([P4_downsample,P5],axis=1)
# 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512 -> 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512 -> 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512
P5 = self.make_five_conv4(P5)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 第三个特征层
# y3=(batch_size,75,52,52)
#---------------------------------------------------#
out2 = self.yolo_head3(P3)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 第二个特征层
# y2=(batch_size,75,26,26)
#---------------------------------------------------#
out1 = self.yolo_head2(P4)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 第一个特征层
# y1=(batch_size,75,13,13)
#---------------------------------------------------#
out0 = self.yolo_head1(P5)
return out0, out1, out2