根据txt文件提供的内容,在图片上面画框
import cv2
import os
filePath = 'D:\study\WongKinYiu\\test\images'#图片所在文件夹路劲
names = os.listdir(filePath)
print(names)
for name in names:
image = cv2.imread("D:\study\WongKinYiu\\test\\images\\"+ str(name))
print(name[0:5])
GrayImage = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
with open("D:\study\WongKinYiu\\test\\txt\\"+str(name[0:5])+".txt", 'r') as f:#每个txt文件所在文件夹
lines = f.readlines()
# if(len(lines!=1)):
for line in lines:
line_split = line.split(';')
draw_1 = cv2.rectangle(image, (int(line_split[1]), int(line_split[2])), (int(line_split[3]), int(line_split[4])), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imwrite("D:\study\WongKinYiu\\test\\rectangle_image\\"+str(name), draw_1)
# cv2.namedWindow("draw_0", 2)
# cv2.imshow("draw_0", draw_1) # 显示画过矩形框的图片
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyWindow("draw_0")
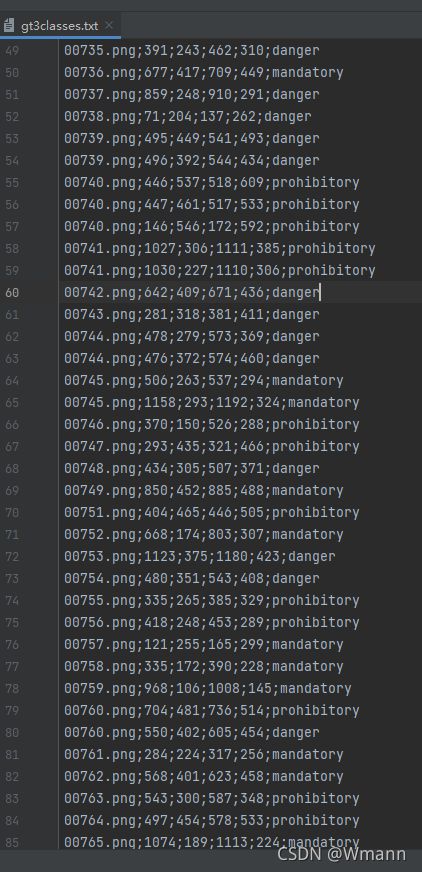
从一个txt文件生成多个txt文件
# 将一个txt文件里面的内容写入多个txt文件,可循环写入
import xlwt # 写入文件
import xlrd # 打开excel文件
fopen = open('D:\study\WongKinYiu\\test\\annotations\gt3classes.txt', 'r')
lines = fopen.readlines()
def delt(st):
if '\n' in st:
p = st.replace('\n', '')
return p
else:
return st
i = 0
txt_name_pre = 0
for line in lines:
line = line.strip('\n') # 去掉换行符
txt_name = int(line[0:5])
# 针对一个txt存有多个目标信息
if txt_name == txt_name_pre:
# http://www.cppcns.com/jiaoben/python/324611.html
line_split = line.split(';') # ['00700.png', '854', '431', '881', '458', '13']
# print(line)
# print(line_split)
# print(line_split[1])
pline = 'txt/%s.txt' % line[0:5]
txt_name_pre = int(line[0:5])
gg = open(pline, 'a') # 在上一个txt文件中追加内容,不会覆盖掉
gg.write("\n"+str(line_split[-1]) + ";" + str(line_split[1]) + ";" + str(line_split[2]) + ";" + str(line_split[3]) + ";" + str(line_split[4]))
gg.close()
else:
# print(txt_name)
# print(line[0:9])
# print(line)
# http://www.cppcns.com/jiaoben/python/324611.html
line_split = line.split(';') # ['00700.png', '854', '431', '881', '458', '13']
# print(line)
# print(line_split)
# print(line_split[1])
pline = 'txt/%s.txt' % line[0:5]
txt_name_pre = int(line[0:5])
gg = open(pline, 'w')
gg.write(str(line_split[-1]) + ";" + str(line_split[1]) + ";" + str(line_split[2]) + ";" + str(
line_split[3]) + ";" + str(line_split[4]))
gg.close()
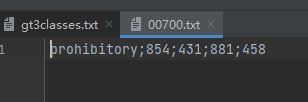
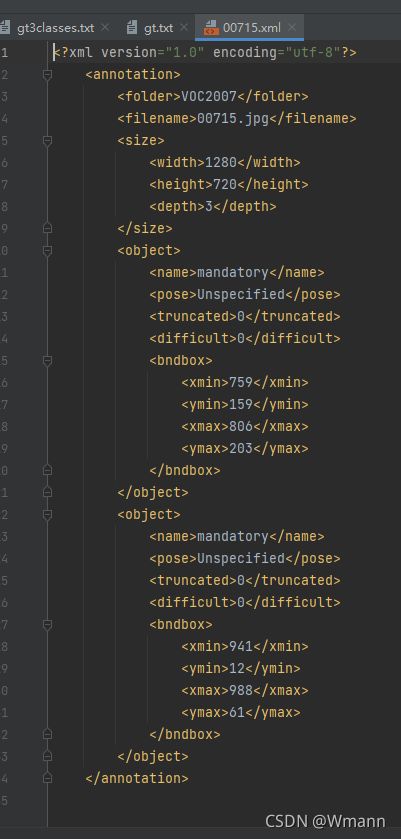
根据txt文件生成xml文件,一个xml文件可循环写入
# coding=utf-8
# makexml("txt所在文件夹","xml保存地址","图片所在地址")
from xml.dom.minidom import Document
import os
import cv2
def makexml(txtPath, xmlPath, picPath): # 读取txt路径,xml保存路径,数据集图片所在路径
dict = {'prohibitory': "prohibitory", # 字典对类型进行转换
'danger': "danger",
'mandatory': "mandatory",
}
files = os.listdir(txtPath)
for i, name in enumerate(files):
xmlBuilder = Document()
annotation = xmlBuilder.createElement("annotation") # 创建annotation标签
xmlBuilder.appendChild(annotation)
txtFile = open(txtPath + name, 'r', encoding='iso8859-1')
txtList = txtFile.readlines()
img = cv2.imread(picPath + name[0:-4] + ".png")
print(picPath + name[0:-4] + ".png")
Pheight, Pwidth, Pdepth = img.shape
# for i in txtList:
# oneline = i.strip().split(" ")
folder = xmlBuilder.createElement("folder") # folder标签
folderContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("VOC2007")
folder.appendChild(folderContent)
annotation.appendChild(folder)
filename = xmlBuilder.createElement("filename") # filename标签
filenameContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(name[0:-4] + ".jpg")
filename.appendChild(filenameContent)
annotation.appendChild(filename)
size = xmlBuilder.createElement("size") # size标签
width = xmlBuilder.createElement("width") # size子标签width
widthContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pwidth))
width.appendChild(widthContent)
size.appendChild(width)
height = xmlBuilder.createElement("height") # size子标签height
heightContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pheight))
height.appendChild(heightContent)
size.appendChild(height)
depth = xmlBuilder.createElement("depth") # size子标签depth
depthContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pdepth))
depth.appendChild(depthContent)
size.appendChild(depth)
annotation.appendChild(size)
for i in txtList:
# oneline = i.strip().split(" ")
oneline = i.split(";")
print(oneline)
object = xmlBuilder.createElement("object")
picname = xmlBuilder.createElement("name")
# if oneline[0] >= '4':
# continue
nameContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(dict[oneline[0]])
picname.appendChild(nameContent)
object.appendChild(picname)
pose = xmlBuilder.createElement("pose")
poseContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("Unspecified")
pose.appendChild(poseContent)
object.appendChild(pose)
truncated = xmlBuilder.createElement("truncated")
truncatedContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
truncated.appendChild(truncatedContent)
object.appendChild(truncated)
difficult = xmlBuilder.createElement("difficult")
difficultContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
difficult.appendChild(difficultContent)
object.appendChild(difficult)
bndbox = xmlBuilder.createElement("bndbox")
xmin = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmin")
# mathData = int(((float(oneline[1])) * Pwidth + 1) - (float(oneline[3])) * 0.5 * Pwidth)
mathData =int(oneline[1])
xminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
# if xminContent < 0:
# xminContent = 0
xmin.appendChild(xminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmin)
ymin = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymin")
# mathData = int(((float(oneline[2])) * Pheight + 1) - (float(oneline[4])) * 0.5 * Pheight)
mathData = int(oneline[2])
yminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
# if yminContent < 0:
# yminContent = 0
ymin.appendChild(yminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymin)
xmax = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmax")
# mathData = int(((float(oneline[1])) * Pwidth + 1) + (float(oneline[3])) * 0.5 * Pwidth)
mathData = int(oneline[3])
xmaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
# if xmaxContent > Pwidth:
# xmaxContent = Pwidth
xmax.appendChild(xmaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmax)
ymax = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymax")
# mathData = int(((float(oneline[2])) * Pheight + 1) + (float(oneline[4])) * 0.5 * Pheight)
mathData = int(oneline[4])
ymaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
# if ymaxContent > Pheight:
# ymaxContent = Pheight
ymax.appendChild(ymaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymax)
object.appendChild(bndbox)
annotation.appendChild(object)
f = open(xmlPath + name[0:-4] + ".xml", 'w')
xmlBuilder.writexml(f, indent='\t', newl='\n', addindent='\t', encoding='utf-8')
f.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
txt_path = 'D:\study\WongKinYiu\\test\\txt\\'
xml_path = 'D:\study\WongKinYiu\\test\\Annotations\\'
image_path = 'D:\study\WongKinYiu\\test\images\\'
makexml(txt_path, xml_path, image_path)
删除多余的image,根据txt的数量来删除,最终是为了使image和txt相互对应
import os
import numpy as np
def readname():
filePath = 'D:\HZQ\jtrafficsigns\yolov3-point\data\测试\Annotations\\'
name = os.listdir(filePath)
return name
def get_filename(path, filetype):
name = []
final_name = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for i in files:
if filetype in i:
name.append(i.replace(filetype, '')) # 生成不带‘.csv’后缀的文件名组成的列表
final_name = [item for item in name] # 生成‘.csv’后缀的文件名组成的列表
return final_name # 输出由有‘.csv’后缀的文件名组成的列表
def numpy_to_int(num):
name = []
for i in num:
i = int(i)
name.append(i)
return name
if __name__ == "__main__":
path1 = 'D:\HZQ\jtrafficsigns\yolov3-point\data\Annotations\\' # 指定文件所在路径
filetype1 = '.xml' # 指定文件类型
path2 = 'D:\HZQ\jtrafficsigns\yolov3-point\data\JPEGImages\\'
filetype2 = '.jpg'
name1 = get_filename(path1, filetype1) # xml删
name2 = get_filename(path2, filetype2) # jpg
result_name1 = numpy_to_int(name1)
# print("1",result_name1)
result_name2 = numpy_to_int(name2)
# print("2",result_name2)
result_name1 = np.sort(result_name1)
result_name2 = np.sort(result_name2)
# [2,4,6,7,8,10,33,67]
# [2,7,10,33,67]
# print(result_name1)
# print(result_name1.shape)
# print(result_name2)
# print(result_name2.shape)
length = len(result_name2)
# print(length)
i = 0
j = 0
while i < length:
if result_name1[j] == result_name2[i]:
i += 1
j += 1
else:
join1 = os.path.join('D:\HZQ\jtrafficsigns\yolov3-point\data\Annotations\\', str(result_name1[j]) + '.xml')
print(join1)
os.remove(join1)
j+=1



