01
Map提供了三个集合视图:
键集
值集
键-值 映射集
public String getWeek(int num){
if(num<0 || num>7){
throw new NoWeekException(num+"没有对应的星期");
String[] weeks = {"","星期一"...."星期日"};
return weeks[num];
}
}
Sunday(星期天)、Monday(星期一)、Tuesday(星期二)、Wednesday(星期三)、Thursday(星期四)、Friday(星期五)、Saturday(星期六)
java.util
接口 Map
参数:
K为此映射的键
V为此映射的值
知道的子接口:
Bindings,ConcurrentMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap
LogicalMessageContext,MessageContext,
NavigableMap
知道的实现类:
AbstractMap,Attributes,
AuthProvider,ConcurrentHashMap,
ConcurrentSkipListMap,
EnumMap,HashMap,Hashtable,
IdentityHashMap,LinkedHashMap,
PrinterStateReasons,Properties,
Provider,RenderingHints,
SimpleBindings,TabularDataSupport,
TreeMap,UIDefaults,WeakHashMap
实现的接口:
public interface Map
在映射中不能有重激java培训复的键,每个键只能映射在一个值上
在Map集合中的特点:
内部存储的模式是以键-值对的形式
Map中的键要具有唯一性
嵌套类(内部的):
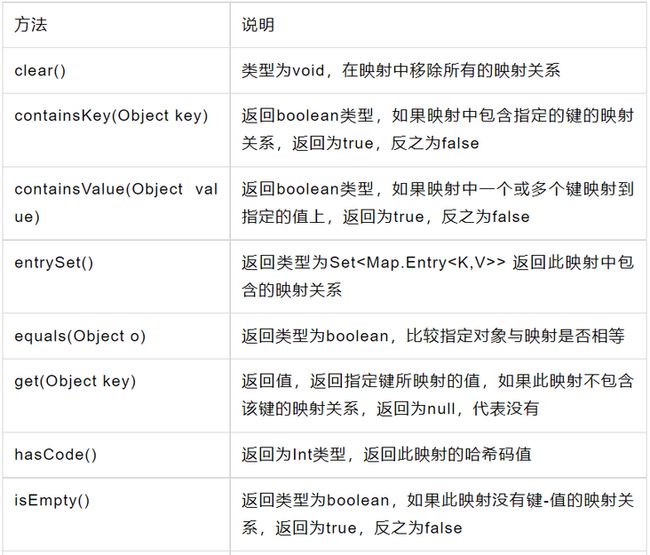
Map方法:
V put (E key, V value)
将对应的键与值,建立映射关系,添加映射关系的方法,如果之前就有这个映射关系,就会将指定的值替换掉旧的值。
参数:
key - 为指定的关联的键
value - 为指定的关联的值
会抛出的错误:
UnsupportedOperationException:不支持put操作
ClassCastException:不允许用映射关系
NullPointerException:将指定的键或者值为null,而此映射却不允许存储
IllegalArgumentException:指定的键或者值不允许存储到映射中
一般用的实现类:
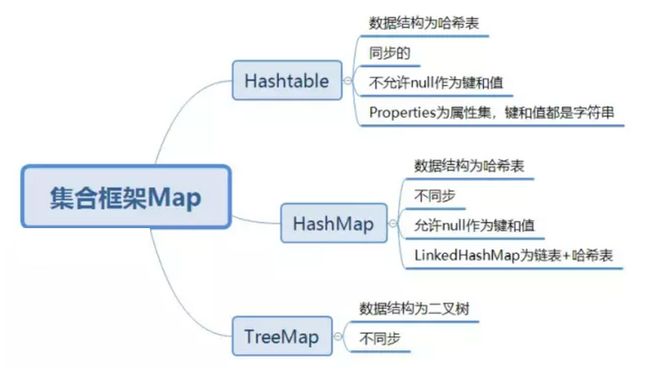
HashMap
java.util类
HashMap
java.lang.Object
-> java.util.AbstractMap
-> java.util.HashMap
参数:
K-为所对应的键
V-为所对应的值
已实现的接口:
Serializable,Cloneable,Map
已知的子类:
LinkedHashMap,PrinterStateReasons
所以:
public class HashMap
extends AbstractMap
implements Map
02
Map例子:
import java.util.HashMap;public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
// 建立map
Map
// 添加元素
map.put("星期一", "Monday");
mpa.put( ...// 自行添加 );
map.put("星期日", "Sunday");
// 添加元素时,如果键相同,值会覆盖
map.put("星期日", "SundayDemo");
// 值被覆盖
// 获取值
String value = map.get("星期日");
// 键存在,返回值,反之返回null,为空
// 删除元素
String s = map.remove("星期日");
// 删除对应的键值对关系,这样在Map集合中就少了这一对键值对
}
}
如何获取所有的键
Map
map.put("星期一", "Monday");
map.put("星期日", "Sunday");
使用keySet
Set
for(Iterator
String key = it.next();
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
可以使用foreach循环
for(String key : keySet){
System.out.println(key + " = " + map.get(key));
}
entrySet
Set
作用为返回此映射中包含的映射关系Set的视图,将map集合中映射关系存储到set集合中。
映射关系:指键和值对应的关系,数据类型Map.Entry(内部的)关系的类型
Set
Iterator< Map.Entry
while(it.hasNext(K,V)){
Map.Entry
// 获取键
String key = m.getKey();
// 获取值
String value = m.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
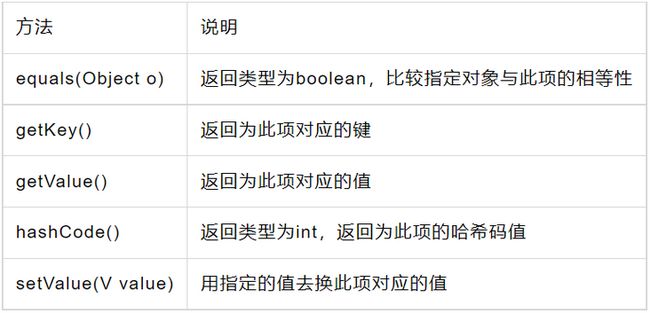
Map.Entry
java.util接口
Map.Entry
接口实现类:
AbstractMap.SimpleEntry , AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry
接口:
public static interface Map.Entry
// 为映射项 - 键-值 对
Map.Entry
方法:
for(Map.Entry
String key = m.getKey();
String value = m.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
interface Map{
public static interface Entry();
}
values()
返回类型为Collection
Collection
for(String value : values){
System.out.println("value:"+value);
}
总结:Map -> entrySet() getKey() getValue() -> keySet() get(key) -> values()
03
Hashmap
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
Map
// 添加元素
map.put(new Student("da",12), "1");
map.put(new Student("shu",13), "2");
map.put(new Student("dashu",14), "3");
// 取出数据
// Set
// for(Student key : keySet){}
for(Student key : map.keySet() ){
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key.toString() + " : " + value);
}
}
}
public class Student implements Comparable
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(){
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age){
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name = " + name +",age = " + age + "]";
}
@Override
public int hasCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime + result + age;
result = prime + result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(this == obj)
return true;
if(obj == null)
return false;
if(getClass() != obj.getClass() )
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if(age != other.age)
return false;
if(name == null){
if(other.name != null)
return false;
}else if(!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;}
@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o){
int temp = this.age - o.age; return temp == 0? this.name.compareTo(o.name) : temp;
}
}
TreeMap
public class TreeMapDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Map
// 添加元素
map.put(new Student("da",12), "1");
map.put(new Student("shu",13), "2");
map.put(new Student("dashu",14), "3");
// 取出数据
for(Map.Entry
Student key = m.getKey();
String value = m.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
}
}
public class ComparatorByName implements Comparator
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2){
int temp = o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
return temp == 0 ? o1.getAge() - o2.getAge() : temp;
}
}
04
实例:
public class CollectionsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map m = new HashMap();
m.put("da", "8");
m.put("shu", "9");
m.put("dashu", "10");
m.put("dashucoding", "12");
System.out.println(m);
}
}
Java Map 集合类
最常用的集合类就是List和Map,List的实现类包括ArrayList和Vector,可以变大小的列表,适合构建,存储,和操作任何类型对象元素的列表。
Map是比较通用的,Map集合类是用于存储元素对的,为键-值对,每个键映射到一个值,从理解上可以将List看作数值键的Map,但两者没有什么关系。
所有键值对 — entrySet()
所有键 — keySet()
值 — values()
Iterator keyValues = map.entrySet().iterator();
Iterator keys = map.keySet().iterator();
Iterator values = map.values().iterator();
entrySet():返回 Map 中所包含 映射 的 Set 视图。
keySet():返回 Map 中所包含 键 的 Set 视图。
values():返回 Map 中所包含 值 的 Collection 视图。