Spark-Core ——上篇
文章目录
- 一、Spark简介
-
- 1.简介
- 2.DAG
- 3. MR
-
- 3.1 什么是MR?
- 3.2 Hadoop和Spark的区别
- 二、常见Api
-
- 1.SparkConf
-
- 1.1作用
- 1.2 创建
- 1.3 常见方法
- 2.SparkContext(帮忙提交driver)
-
- 2.1 作用
- 2.2 创建
- 2.3 常见方法
- 2.4 WordCount:
-
- 2.4.1 Hadoop与Spark的写法区别
- 2.4.2 代码
- 2.4.3 SparkContext的解释作用
- 2.5 编程模型及其获取
- 三、安装Spark
-
- 3.1 本地模式
-
- 3.1.1 linux的本地模式
- 3.2 独立模式 =>(standalone是spark提供的一个独立集群)
-
- 3.2.1 介绍
- 3.2.2 安装
- 3.2.3 常见的端口号
- 3.2.4 测试
- 3.2.5 --deploy-mode(很重要)
- 3.3 配置历史服务
-
- 3.3.1 作用
- 3.3.2 原理
- 3.3.3 过程
- 3.4 spark on yarn
-
- 3.4.1 配置
- 3.4.2 测试
- 3.4.3 修改队列中的AM个数
- 四、提交流程
-
- 4.1 SparkOnYarn Client模式提交流程:
- 4.2 SparkOnYarn Cluster模式提交流程:
- 4.3 Job提交运行的大致流程:
- 五、核心概念
-
- 5.1 partition
- 5.2 术语
- 六、核心编程------RDD
-
- 6.1 RDD的介绍
-
- 6.1.1 什么是RDD?
- 6.1.2 RDD的特点:
- 6.2 RDD的核心特征
-
- RDD源码解释
- 6.3 创建RDD
-
- 6.3.1 从集合中创建RDD(makeRDD)
-
- 6.3.1.1 分区数
- 6.3.1.2 分区策略
- 6.3.2 **从外部存储(文件)创建RDD( textfile)**
-
- 6.3.2.1 分区数
- 6.3.2.2 分区策略
-
- HadoopRDD中的getPartitions方法
- HadoopRDD中的getSplits方法:
- 6.4 转换算子 (见中篇)
- 6.5 行动算子 (见下篇)
1、存储:hdfs、hbase、kafka
2、传输:flume、sqoop
3、数据清洗(也包含传输):ETL
4、调度:azikaban
5、可视化:让人更好的理解数据
6、计算
(1)计算平台:yarn、k8s
(2)计算引擎:hive、spark
一、Spark简介
1.简介
Spark: 快速统一的分析引擎!
--统一性作何解?
统一: a) 涵盖了所有的数据分析场景(离线,实时,sql,图计算,ML)
b) 可以对接多种数据源( orc,parquet,mysql,hbase,es,hdfs)
2.DAG
DAG: 有向无环图!
Hadoop 中计算的引擎 MR :不支持DAG!
分析一个复杂的任务:
Job1(Mapper------Reducer) <-- Job2(Mapper------Reducer)
Hive :
select
*
from
(select
*
from t1 join t2 on xxx
group by xxx
order by xxx) t3 join t4
group by xxx
order by xxx
翻译为N个Job 运算! 根本原因在于Hadoop的MR不支持DAG!
Spark:
Spark支持DAG运算,可以将复杂的任务,通过划分stage(阶段)的方式,整合到一个Job中!
select
*
from
(select
*
from t1 join t2 on xxx
group by xxx
order by xxx) t3 join t4
group by xxx
order by xxx
使用spark执行,只需要启动一个Job!
将支持DAG的运算引擎,称为第二代大数据计算引擎: Spark ,Tez
结论:
--Spark比hadoop快的原因
a) 基于内存运算,减少落盘的IO操作。 需要更强大的硬件支持!
b) 支持DAG,只需要一个Job就可以完成复杂的运算
DAG是Spark区分Hadoop MR的根本特征!
3. MR
3.1 什么是MR?
MR(分治)是一种数据处理的思想,将数据通过Map,进行映射处理 !
之后再通过reduce合并之前Map处理的结果
Map:转换,映射 !
原数据: 猴子
猴子 ------>Map ------> 动物
Reduce:合并,归并 !
将Map阶段的结果,进行合并 !
OOP------> Java,Python,C++
3.2 Hadoop和Spark的区别
Hadoop提供了MapReduce(计算模块)基于MR这种思想来处理数据
实现MAp:Mapper.map()
实现Reduce:Reducer.rduce()
Spark 也是一个MR计算引擎! 改进了Hadoop中MR的实现方式,支持DAG!
实现Map: map(scala集合有map)算子
实现Reduce: reduce(fold)算子
Spark诞生于伯克利大学的AMPLab实验室
二、常见Api
1.SparkConf
1.1作用
--是Spark应用的配置对象。用来加载Spark的各种配置参数,用户也可以使用这个对象设置自定义的参数!自定义的参数有更高的优先级!
--使用链式编程,调用setter方法!
1.2 创建
①new SparkConf
1.3 常见方法
- setMaster:
master一般理解为分布式系统的管理进程!setMaster设置当前的Job需要提交到哪个集群!
通常写的是集群master的提交的url(和master通信的Url)
- setAppName:
设置当前的应用名称
| masterurl | 模式 |
|---|---|
| local / local[n] / local[*] | 本地 |
| spark://master所在主机名:master所绑定的rpc端口 | 独立模式(standalone) |
| yarn | YARN模式 |
2.SparkContext(帮忙提交driver)
2.1 作用
- 使用Spark功能的核心入口
- 代表和Spark集群的连接
- 可以用来创建RDD,累加器,广播变量等编程需要的模型
注意: 在一个JVM中,只能创建一个SparkContext!
可以调用Stop,在创建新的SparkContext之前!
2.2 创建
class SparkContext(config: SparkConf)
2.3 常见方法
| API | 介绍 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| def textFile( path: String, minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions): RDD[String] | 从HDFS或本地文件系统读取文本数据 | 将文本中的每一行内容作为集合中的元素返回! |
| def collect(): Array[T] | 将RDD中的每个元素以数组形式返回 | |
2.4 WordCount:
--单词统计!
准备数据!数据的路径,可以使用绝对路径,还可以使用相对路径!
相对路径:
main : 相对路径相对于 project
test : 相对路径相对于 module
2.4.1 Hadoop与Spark的写法区别
- Hadoop
Hadoop MR:
Driver : 完成Job的提交! 初始化Job提交的应用上下文!
Configuration conf= new Configuration() : Job的各种配置!
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf)
job.setXXX // 各种设置
job.waitForCompletion------> 初始化
JobContextImpl(应用上下文)对象
应用上下文: Job运行的环境!
Mapper.map(key,value,Context)
Reducer.reduce(key,value,Context)
mapreduce.framework.name
默认 local
yarn
编程模型:
Mapper ,Reducer ,Combiner
- Spark
Spark MR :
Driver : 完成Job的提交! 初始化Job提交的应用上下文!
SparkConf : Job的各种配置!
基于配置,创建一个Job运行的上下文环境,称为SparkContext
调用算子编程!
setMaster: 设置job运行的集群
//编程模型:
RDD(集合)s, accumulators and broadcast variables
Spark就是使用scala写的! Spark提供的方法,本质上就是scala提供的api!
2.4.2 代码
wordcount : ①读文件,一行一行读
②将每行进行 切分,切分为每个单词
③ 单词 ----> (单词,1)
④ 将单词分组
(单词 , {
(单词,1),(单词,1),(单词,1),(单词,1)...})
⑤统计相同单词的values 个数
(单词 , 5)
2.4.3 SparkContext的解释作用
--源码:
Main entry point for Spark functionality. A SparkContext represents the connection to a Spark
cluster, and can be used to create RDDs, accumulators and broadcast variables on that cluster.
@note Only one `SparkContext` should be active per JVM. You must `stop()` the
active `SparkContext` before creating a new one.
@param config a Spark Config object describing the application configuration. Any settings in
this config overrides the default configs as well as system properties.
--作用:
1、Spark功能的主要入口点。
2、用于Spark集群的连接
3、并可用于在该集群上创建RDD、累加器和广播变量。
4、@note每个JVM只能有一个“SparkContext”处于活动状态。在创建新的“SparkContext”之前,必须调用 stop(),在创建新的SparkContext
5、@param config描述应用程序配置的Spark config对象中的任何设置
此配置覆盖默认配置以及系统属性。
--注意
①在一个JVM中,只能创建一个Sparkcontext,
②可以调用Stop,在创建新的SparkContext之前!
2.5 编程模型及其获取
1、什么是RDD、累加器、广播变量?
涉及到编程模型:
(1)编程模型含义,job里面写的类需要继承编程模型,然后编程模型提供一个模板,job也就是实现模型里 面的mapper和reducer方法,
(2)hadoop的编程模型:Mapper,Reducer,Combiner
(3)Spark的编程模型:RDD、累加器、广播变量
spark的编程模型怎么获取?
(1)先有SparkContext,才能由它创建编程模型,之后才能进行编程
三、安装Spark
3.1 本地模式
3.1.1 linux的本地模式
-
安装:将spark-3.0.0-bin-hadoop3.2.tgz解压到非中文无空格目录!
-
测试:
spark-shell:交互环境
println(sc.textFile("/home/atguigu/input")
.flatMap(_.split(" "))
.map((_, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
.collect().mkString(","))
spark-submit:用来提交jar包
# spark-submit [options] jar包 jar包中类的参数
/opt/module/spark-local/bin/spark-submit
--master local #通过本地服务将job提交到集群上
--class com.atguigu.spark.WordCount1 #调用jar包的哪个类
/home/atguigu/wc.jar
/home/atguigu/input
3.2 独立模式 =>(standalone是spark提供的一个独立集群)
3.2.1 介绍
--standalone是spark提供的一个独立(不依赖任何第三方框架)集群!
- 两种进程:
1.master :
类比为 ResourceManager ,负责整个集群资源的管理和调度,与worker进行通信,向worker分配任务,处理客户端提交的Job的请求,为Job申请资源!
2.worker :
类比为 NodeManager ,负责单个机器资源的管理和调度,和master进行通信!处理master分配的任务!
3.2.2 安装
-
配置需要在哪些机器启动worker!
①在一台机器安装spark
②编辑$SPARK_HOME/conf/slaves#在哪些机器启动worker hadoop102 hadoop103 hadoop104 -
告诉worker,Master在哪个进程,通过哪个端口号可以和master通信
③编辑 $SPARK_HOME/conf/spark-env.sh
#告诉每个worker,集群中的master在哪个机器 SPARK_MASTER_HOST=hadoop103 ##告诉每个worker,集群中的master绑定的rpc端口号 SPARK_MASTER_PORT=7077④分发到集群
⑤启动
# 在当前机器启动master,必须在master配置的那台机器启动 sbin/start-all.sh⑥查看是否启动
hadoop103:80803.2.3 常见的端口号
| 进程 | 端口号 | 协议 |
|---|---|---|
| master | 7077 | RPC |
| master | 8080 | HTTP |
| worker | 8081 | HTTP |
| Job运行时监控(job在那个机器运行就在哪监控) | 4040 | HTTP |
3.2.4 测试
-
spark-shell:交互环境(是一个RPEL环境,能够立刻出结果,一般用于调试)
启动:bin/spark-shell --master spark://hadoop103:7077
println(sc.textFile("hdfs://hadoop102:8020/input")
.flatMap(_.split(" "))
.map((_, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _,3)
.reduceByKey(_ + _,2)
.collect().mkString(","))
-
spark-submit:用来提交jar包
用法: spark-submit [options] jar包 jar包中类的参数
/opt/module/spark-local/bin/spark-submit
--master spark://hadoop103:7077 #通过Hadoop103的7077端口将job提交到集群上
--class com.atguigu.spark.WordCount1 #调用jar包的哪个类,要执行程序的主类
/home/atguigu/wc.jar #程序主类所在的jar
/home/atguigu/input
=故障处理=
3.2.5 --deploy-mode(很重要)
- client(默认): 会在Client本地启动Driver程序!
bin/spark-submit
--master spark://hadoop103:7077
--class com.atguigu.spark.day01.WordCount1
/opt/module/spark-local/bin/spark-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar hdfs://hadoop102:9820/input
- cluster: 会在集群中选择其中一台机器启动Driver程序!
bin/spark-submit
--master spark://hadoop103:7077
--deploy-mode cluster
--class com.atguigu.spark.day01.WordCount1
/opt/module/spark-standalone/bin/spark-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar hdfs://hadoop102:9820/input
区别:
①Driver程序运行位置的不同会影响结果的查看!
client: 将某些算子的结果收集到client端!
要求client端Driver不能中止!
cluster(生产): 需要在Driver运行的executor上查看日志!
②client: jar包只需要在client端有!
cluster: 保证jar包可以在集群的任意台worker都可以读到!
===================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-84reymjU-1603267550451)(Spark0621.assets/image-20200922002641049.png)]
其中将结果打印这一步的collect()方法:(将RDD中的元素转成数组,在driver中打包成array)
Return an array that contains all of the elements in this RDD.
解释为:该方法返回一个数组,数组里面包含了RDD里面所有的元素
举个例子:
result是最后运算的结果,所有RDD相关的都在executor上运行。executor都在集群里面,
result运行结束之后,要运行将结果打印出来那段代码,这段代码在driver里面
(sparkcontext在哪driver就在哪)
在driver端打印一段数组前提是啥?
前提是result这个RDD肯定是在一个exector上,即executor上有这个result
现在有一个driver,我们说了根据模式不一样,driver所在位置不一样
--如果是client模式,
就在客户端,那么客户端就需要将result的结果打印,就需要将result的结果发给我才能打印,此时这个结果打印在客户端
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-XCiemgIn-1603267550454)(Spark0621.assets/image-20200922004259681.png)]
--如果是集群模式
则result在某个集群上打印,但客户端在client(假设为103)上提交,如果此时该客户端上执行了一个sparksubmint命令,此时103就是客户端,但是driver有可能在102,此时在客户端无法看见结果,只有client模式才能看见,这个时候你就需要找,找driver运行的exeecutor才能看见结果
此时找到集群,Hadoop103:8080找到102的8081上
====================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
3.3 配置历史服务
3.3.1 作用
在Job离线期间,依然可以通过历史服务查看之前生成的日志!
3.3.2 原理
Job在运行期间,将产生的日志,保存到你指定的目录中!参考下述①步骤
启动一个历史服务(进程),由此进程读取日志保存目录中的信息,提供UI界面,允许用户访问此界面,查看之前保存的历史服务!参考下述②步骤!
3.3.3 过程
①配置 SPARK_HOME/conf/spark-defaults.conf 类比(mapred-site.xml)
影响的是启动的spark应用sql
spark.eventLog.enabled true
#日志保存目录需要手动创建
spark.eventLog.dir hdfs://hadoop102:8020/sparklogs
②配置 SPARK_HOME/conf/spark-env.sh**
影响的是spark的历史服务进程
export SPARK_HISTORY_OPTS="
-Dspark.history.ui.port=18080
-Dspark.history.fs.logDirectory=hdfs://hadoop102:8020/sparklogs
-Dspark.history.retainedApplications=30"
③分发以上文件,重启集群
④启动历史服务进程
sbin/start-historyserver.sh
3.4 spark on yarn
YARN: 集群!
Spark: 相对于YARN来说,就是一个客户端,提交Job到YARN上运行!
MR ON YARN提交流程:
①Driver 请求 RM,申请一个applicatiion
②RM接受请求,此时,RM会首先准备一个Container运行 ApplicationMaster
③ ApplicationMaster启动完成后,向RM进行注册,向RM申请资源运行
其他任务
Hadoop MR : 申请Container运行MapTask,ReduceTask
Spark: 申请Container运行 Executor
只需要选择任意一台可以连接上YARN的机器,安装Spark即可!
3.4.1 配置
确认下YARN的 yarn-site.xml配置中
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.pmem-check-enabledname>
<value>falsevalue>
property>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.vmem-check-enabledname>
<value>falsevalue>
property>
<property>
<name>yarn.log.server.urlname>
<value>http://hadoop102:19888/jobhistory/logsvalue>
property>
分发 yarn-site.xml,重启YARN!
编辑 SPARK_HOME/conf/spark-env.sh
YARN_CONF_DIR=/opt/module/hadoop/etc/hadoop
export SPARK_HISTORY_OPTS="
-Dspark.history.ui.port=18080
-Dspark.history.fs.logDirectory=hdfs://hadoop102:8020/sparklogs
-Dspark.history.retainedApplications=30"
编辑 SPARK_HOME/conf/spark-defaults.conf
spark.eventLog.enabled true
#需要手动创建
spark.eventLog.dir hdfs://hadoop102:8020/sparklogs
#spark历史服务的地址和端口
spark.yarn.historyServer.address=hadoop103:18080
spark.history.ui.port=18080
3.4.2 测试
spark-shell --master yarn: 交互式环境
println(sc.textFile("hdfs://hadoop102:8020/input")
.flatMap(_.split(" "))
.map((_, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _,3)
.collect().mkString(","))
spark-submit: 用来提交jar包
用法: spark-submit [options] jar包 jar包中类的参数
spark-on-yarn client模式:
/opt/module/spark-yarn/bin/spark-submit --class com.atguigu.spark.WordCount1 /home/atguigu/wc.jar hdfs://hadoop102:8020/input
spark-on-yarn cluster模式:
/opt/module/spark-yarn/bin/spark-submit --deploy-mode cluster --class com.atguigu.spark.WordCount1 /home/atguigu/wc.jar hdfs://hadoop102:8020/input
3.4.3 修改队列中的AM个数
AM:Application master
yarn上每提交一个job,就要启自己的application master,只允许启动一个master则只能有一个job
解决方法一:直接杀死前一个进程
解决方法二:修改一下配置
cd /opt/module/hadoop/etc/hadoop/
vim capacity-scheduler.xml
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.maximum-am-resource-percent</name>
<value>"0.5"</value>
<description>
Maximum percent of resources in the cluster which can be used to run
application masters i.e. controls number of concurrent running
applications.
</description>
</property>
xsync capacity-scheduler.xml
重启动yarn
调度和运行是两回事
四、提交流程
4.1 SparkOnYarn Client模式提交流程:
https://www.processon.com/view/link/5f60e3fb6376894e32710fd4
4.2 SparkOnYarn Cluster模式提交流程:
https://www.processon.com/view/link/5f4876d46376890e62f62889
运行spark-submit命令【当前是client模式,在client端运行driver】
启动Driver
向ResourceManager提交应用,同时启动ApplicationMaster(ExecutorLaunchar)【在yarn上运行需要appmaster】
ExecutorLaunchar启动之后,需要向ResourceMAnager注册,告诉ResourceMAnager我启动好了
之后ExecutorLaunchar向NodeManager申请container【container是由nodemanager分配的】
于是就和nodemanager通信,告诉nodemanager把container准备好,我要启动了
于是nodemanager就启动了YarnCoarseGraindExecutorBackend(Executor)【executor是负责task运算的,但task谁发给我呢,driver发给我】
于是通知driver我启动好了,然后driver就给我new了一个executor【这是一个对象,这个对象负责运算task】
此时又向driver发申请,申请给我发任务
driver向executor发送任务(offer)
然后executor这个线程接收到task,会启动许多个线程,来运行task
----
运行框架
--目前明白几个东西:
1.Sparkcontext所在的程序称为driver程序
2.有一个集群,driver程序把job提交到集群上后,会在集群上启动executor(类似于maptask,reducertask)
3.executor这个进程会有很多线程算RDD的算子
提交模式
--Standalone模式
集群是master和worker,在worker上启executor
--YARN模式
在nodemanager上准备一个container,在container上其executor
*driver会监控每个计算节点(Executor),如果计算时某个节点任务报错了,他会将这个出错订单任务继续发到别的计算节点(Executor)上继续运算*
4.3 Job提交运行的大致流程:
https://www.processon.com/view/link/5f699d387d9c087da1bbf254
分区数增多一定会shuffer,shuffer不一定分区增加,就数据需要重新分区的时候会shuffer,即分区之间交换数据也会shuffer
比如有两个行动算子,提交了两个job任务,
--提交的job任务通过DAGScheduler划分出不同的阶段,
以job1为例,这里job1这个任务有四个算子,其中第三个算子运算的时候会进行数据的重新分配,产生新的分区,RDD3到RDD4就是shuffle阶段,这个job1就被分成了两个阶段(stage0和stage1),其中RDD1,RDD2,RDD3在第一个阶段,每个阶段会有任务,至于这个任务是怎么运算的,(以task0为例,task0只算o号阶段0号分区的数据,只算Rdd3的0号分区的数据,调用的是RDD3的compute方法,compute计算的话就是需要数据和逻辑,数据就是0号区的数据,RDD3的0号分区数据是从哪来的呢,是从上一个算子的0号分区来的,这些RDD之间通过依赖关系找父RDD,那么最原始的数据从哪里来的呢,我们调用了textFile这个算子,从hdfs上拿到了数据,RDD0的0号分区调用computer,compute通过计算0号分区的数据,得到了RDD2的0分区的数据,再拿RDD3的compute方法的计算逻辑得到我自己的0号分区的数据数据)stage0的最后一个算子有两个分区,就意味着这个阶段每个算子都有两个分区,每个分区由一个task任务进行计算,stage1有三个分区,便有三个task进行计算,job一共有5个task。
--通过TaskScheduler进行调度,通过Task的本地化级别,负载均衡,黑名单等综合考虑调度
--将Task任务发送给集群上的Executor
假设这里有两个Executor进程,其中Executor1收到了三个Task任务,Executor2收到了两个Task任务,每个Task会启动一个线程,这里Executor1启动三个线程,Executor2启动两个线程,每个线程启动的顺序是不一样的,Executor先收到哪个Task,就先启动那个任务对应的线程,
又stage0和stage1这两个阶段之间会有shuffer,stage0上的task这里类比为maptask,stage1上的task这里类比为reducetask,maptask需要将结果溢写到磁盘(至于怎么写的,就涉及到下一个阶段),这里的下一个阶段就是stage1这个阶段,这个阶段有三个分区,就需要将stage0上的task重新分配成三个分区,接着就是reducer阶段,这里就是stage1上的Task0任务找到stage0上的task重新分配成的三个分区的第一个分区,重新分配结束之后,最后的结果就有三个区,RDD4有一个collect方法,将分成的三个区的数据收集到一个数组上,在driver上打印出来。
五、核心概念
5.1 partition
MapReduce: 有shuffle
MapTask: context.write(k,v)------>分区------>排序-------->溢写…
combine
分区的目的:①分类,将相同的数据分到一个区
每个ReduceTask都会处理一个分区的数据
②并行运算
Kafka: 有Topic,有Partition
分区的目的: ①方便主题的扩展
②分区多,同时运行多个消费者线程并行消费,提升消费速率
Spark: 分区。 RDD(数据的集合),对集合进行分区!
分区的目的: ①分类(使用合适的分区器)
②并行运算(主要目的)
5.2 术语
| 概念 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| client | 申请运行Job任务的设备或程序 |
| server | 处理客户端请求,响应结果 |
| master | 集群的管理者,负责处理提交到集群上的Job,类比为RM |
| worker | 工作者!实际负责接受master分配的任务,运行任务,类比为NM |
| driver | 创建SparkContext的程序,称为Driver程序 |
| executor | 计算器,计算者。是一个进程,负责Job核心运算逻辑的运行! |
| task | 计算任务! task是线程级别!在一个executor中可以同时运行多个task。一个Task负责一个Stage中一个分区数据的计算! |
| 并行度 | 取决于executor申请的core数 |
| application | 可以提交SparkJob的应用程序,在一个application中,可以调用多次行动算子,每个行动算子都是一个Job! |
| Job | 一个Spark的任务,在一个Job中,Spark又会将Job划分为若干阶段(stage),在划分阶段时,会使用DAG调度器,将算子按照特征(是否shuffle)进行划分。 |
| stage | 阶段。一个Job的stage的数量= shuffle算子的个数+1。 只要遇到会产生shuffle的算子,就会产生新的阶段! 阶段划分的意义: 同一个阶段的每个分区的数据,可以交给1个Task进行处理! |
======================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
- 客户端:就是命令用来干嘛的。在哪提交job哪就是客户端
- 服务端:就是你那块集群
- master:standalone模式的两个进程之一,在集群上
- worker:standalone模式的两个进程之一,在集群上
- driver:叫做驱动,在哪创建SparkContext
--因为job要提交(driver主要完成job提交的)
--就要有一个集群通信,sparkcontext就是维持一个集群的连接,无它就不能提交,
--所以sparkcontext在哪那就是driver
-
executor:计算器,计算者。是一个进程,负责Job核心运算逻辑的运行!
一个负责计算的进程
类似于hadoop中的
MapTask – > 运行mapper里面的map方法
ReduceTask --> 运行rducer里面的reduce方法
map方法和reduce方法都是编程模型
分布式运算:
--executor是一个进程,负责运行spark的编程模型,spark的编程模型RDD
--所有调用RDD的,都在exector端运行,Exector端在集群里面
--所以客户端可以任意机器,例如102,103,104,甚至110,只要110能够联上功能集群,
--此时RDD里面的这堆算子就在集群里面算,这叫分布式运算
7.stage:阶段。一个Job的stage的数量= shuffle算子的个数+1。 只要遇到会产生shuffle的算子,就会产生新的阶段! 阶段划分的意义: 同一个阶段的每个分区的数据,可以交给1个Task进行处理!
===============================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
转换算子(方法):
将一个RDD 转换为 另一个RDD
方法传入RDD,返回RDD,就是转换算子!
行动算子:
将一个RDD提交为一个Job
方法传入RDD,返回值不是RDD,通常都是行动算子!
只有行动算子会提交Job!
六、核心编程------RDD
6.1 RDD的介绍
RDD: RDD在Driver中封装的是计算逻辑,而不是数据!
--以下几点
1.使用RDD编程后,调用了行动算子后,此时会提交一个job,在提交job时,会划分Stage,划分之后,将每个阶段的每个分区使用一个Task进行计算处理!
2.Task封装的就是计算逻辑!
3.Driver将Task发送给Executor执行,Driver只将计算逻辑发送给Executor!Executor在执行计算逻辑时。此时发现,我们需要读取某个数据,举例(textFile)
4.RDD真正被创建是在Executor端!
5.移动计算而不是移动数据,如果读取的数据时HDFS上的数据时,此时HDFS上的数据以block的形式存储在DataNode所在的机器!
6.如果当前Task要计算那片数据,恰好就是对应的那块数据,那块数据在102,当前job在102,104启动了Executor,当前Task发送给102更合适!省略数据的网络传输,直接从本地读取块信息!
6.1.1 什么是RDD?
弹性分布式数据集,一种数据处理的"模型"&"数据结构","可以理解为在java中我们创建了一个类,在类中构建了很多属性和方法,然后最后使用一个行动算子,将这些方法全部启动运行,并将运行的结果返回",是一个抽象类。如汽车模型,航母模型、手机模型等。
6.1.2 RDD的特点:
1. 可分区:提高消费能力,更适合并发计算,类似kafka的消费者消费数据,"一个分区对应一个task,在executor中,一个core对应一个task,这样就体现了并发计算"。
2. 弹性:变化,可变。
a、存储弹性:可以在磁盘和内存之间自动切换;"shuffle阶段,就会将数据存入磁盘中,避免数据量过大,导致任务失败。一个任务分很多个阶段,每个阶段内的运行,则是基于内存的。"
b、容错弹性:数据丢失可以自动恢复;
c、计算弹性:计算出错后重试机制;
d、分区弹性: 根据计算结果动态改变分区的数量。"每次计算以后,可能数据会减少,这样一来,就会造成数据倾斜的状况,通过动态修改分区的数量,这样就可以数据使尽量均匀分布在不同的分区内。"
3. 不可变:类似不可变集合
RDD只存储计算的逻辑,不存储数据,计算的逻辑是不可变的,一旦改变,则会创建新的RDD;
4. RDD :一个抽象类,需要子类具体实现,说明有很多种数据处理方式
===============================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
RDD的getpartition方法可以设置分区,
computer函数是在Task调用,executor里的task
===============================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
6.2 RDD的核心特征
一组分区(只要创建RDD,RDD里就有很多分区)
分区是RDD的一个属性,这个分区是通过getPartitions进行分区的
每个类型的RDD就有多个不同的分区策略
- A list of partitions
private var partitions_ : Array[Partition] = _
#计算分区,生成一个数组,总的分区数
protected def getPartitions: Array[Partition]
每个Task通过compute方法读取分区的数据(读完数据放在jvm里面)
* - A function for computing each split
def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T]
记录依赖于其他RDD的依赖关系,用于容错时,重建数据
* - A list of dependencies on other RDDs
针对RDD[(k,v)],有分区器!
* - Optionally, a Partitioner for key-value RDDs (e.g. to say that the RDD is hash-partitioned)
针对一些数据源,可以设置数据读取的偏好位置,用来将task发送给指定的节点,可选的
* - Optionally, a list of preferred locations to compute each split on (e.g. block locations for
* an HDFS file)
RDD源码解释
/**
* A Resilient Distributed Dataset (RDD), the basic abstraction in Spark. Represents an immutable,
* partitioned collection of elements that can be operated on in parallel. This class contains the
* basic operations available on all RDDs, such as `map`, `filter`, and `persist`. In addition,
* [[org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions]] contains operations available only on RDDs of key-value
* pairs, such as `groupByKey` and `join`;
* [[org.apache.spark.rdd.DoubleRDDFunctions]] contains operations available only on RDDs of
* Doubles; and
* [[org.apache.spark.rdd.SequenceFileRDDFunctions]] contains operations available on RDDs that
* can be saved as SequenceFiles.
* All operations are automatically available on any RDD of the right type (e.g. RDD[(Int, Int)])
* through implicit.
*
* Internally, each RDD is characterized by five main properties:
*
* - A list of partitions
* - A function for computing each split
* - A list of dependencies on other RDDs
* - Optionally, a Partitioner for key-value RDDs (e.g. to say that the RDD is hash-partitioned)
* - Optionally, a list of preferred locations to compute each split on (e.g. block locations for
* an HDFS file)
*
* All of the scheduling and execution in Spark is done based on these methods, allowing each RDD
* to implement its own way of computing itself. Indeed, users can implement custom RDDs (e.g. for
* reading data from a new storage system) by overriding these functions. Please refer to the
* Spark paper
* for more details on RDD internals.
*/
6.3 创建RDD
RDD怎么来: ①new
直接new
调用SparkContext提供的方法
②由一个RDD转换而来
6.3.1 从集合中创建RDD(makeRDD)
源码:在SparkContext.scala这个文件下
/** Distribute a local Scala collection to form an RDD.
*
* This method is identical to `parallelize`.
* @param seq Scala collection to distribute
* @param numSlices number of partitions to divide the collection into
* @return RDD representing distributed collection
*/
译文:
/*分发本地Scala集合以形成RDD。
*此方法与`parallelize`相同。
* @param(参数一) seq Scala集合以分发
* @param(参数二) numSlices将集合划分为的分区数
* @return(返回值) RDD代表分布式集合* /
// 返回ParallelCollectionRDD
def makeRDD[T: ClassTag](
seq: Seq[T], //数据来源,一个集合
numSlices: Int = defaultParallelism) : RDD[T] = withScope {
parallelize(seq, numSlices) //将集合划分到这些分区数上
}
从集合中创建RDD
val rdd1: RDD[Int] = sparkContext.makeRDD(list)
//等价
val rdd2: RDD[Int] = sparkContext.parallelize(list)
6.3.1.1 分区数
设置分区数可以有以下方法:
①:makeRDD的时候传参:在会产生shuffle的算子后面传【自己制定分区数】
例如:.reduceByKey(_ + _,"numPartitions:3") //见双引号部分
②:直接修改默认并行度:【配置默认并行度】
例如:
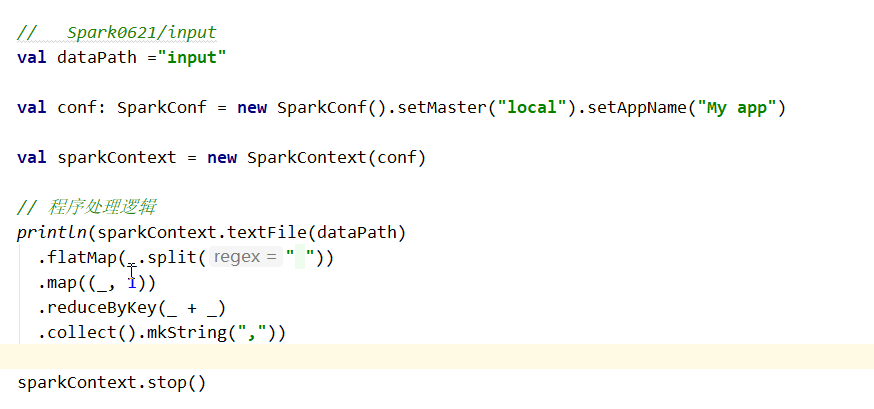
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf()
.setMaster("local[*]")
.setAppName("My app")
.set("spark.default.parallelism","需要设置的数量")
③:以上都没配就看当前cpu申请的总的核数,setMaster(“local[*]”)设置
例如:
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf()
.setMaster("local[*]") //这里[]里可以设置cpu数
.setAppName("My app")
.set("spark.default.parallelism","需要设置的数量")
numSlices:控制集合创建几个分区
由makeRDD方法知道,如果不设置numSlices,会有一个默认的并行度(defaultParallelism)
--并行和并发的区别:
1.并行:多个线程可以同时进行 两个CPU每个cpu一个线程
2.并发:两个线程抢同一个资源
提交一个job的最大并行度是啥呢?
job在提交时会运行一个executor,executor这个进程在container上运行,container容器里面有cpu和内存资源,
假设一个executor申请的每个container都有2个cpu,一共起了10个executor,就有20个cpu,那么最大并行度就是20,意味着可以有20个task同时运行
Executor的个数 X Executor申请的cpu的个数 = 最大并行度
疑问?
怎么决定job的提交到底申请几个executor呢
/**
Default level of parallelism to use when not given by user (e.g. parallelize and makeRDD). 用户未指定时要使用的默认并行度
*/
def defaultParallelism: Int = {
assertNotStopped()
taskScheduler.defaultParallelism //任务调度器的参数
}
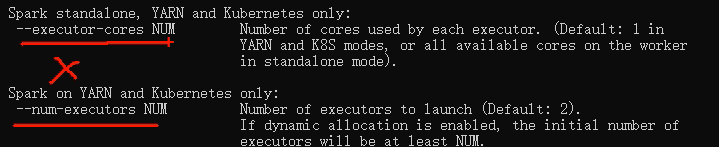
输入命令spark-submit 后面是可以写参数的,最大并行度如下图
本地提交的默认最大并行度如何找?如下==============================================================
进入defaultParallelism方法如下:
// Get the default level of parallelism to use in the cluster, as a hint for sizing jobs.
def defaultParallelism(): Int //是抽象的,那么就要找实现类,它只有一个实现类
可见defaultParallelism是抽象的,那么就要找实现类,它只有一个实现类TaskSchedulerImpl,找该类的defaultParallelism方法,如下:
override def defaultParallelism(): Int = backend.defaultParallelism()
它调用了defaultParallelism(),此方法在SchedulerBackend下,代码见下:
def defaultParallelism(): Int
可见它又是一个抽象的,SchedulerBackend有以下实现类:
SchedulerBackend
--> CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend
--> StandaloneSchedulerBackend 【如果往Standalone上提交找这个类】
--> LocalSchedulerBackend 【如果往本地提交找这个类】
至于在哪提交,查看setMaster()参数,我们这里是本地,
继续查看LocalSchedulerBackend这个类的LocalSchedulerBackend这个方法,如下:
override def defaultParallelism(): Int =
scheduler.conf.getInt("spark.default.parallelism", totalCores)
综上:=====================================================================================================
在本地提交时,defaultParallelism(默认并行度)由以下参数决定:
override def defaultParalleism():Int =
// 默认的 SparkConf中没有设置spark.default.parallelism
scheduler.conf.getInt("spark.default.parallelism",totalCores)
可见我们可以设置最大并行度:
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf()
.setMaster("local[*]")
.setAppName("My app")
.set("spark.default.parallelism","需要设置的数量") //这最后一行这块是设置默认最大并行度的
默认defaultParallelism=totalCores是不配的,默认等于一
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf()
.setMaster("local[*]")
//上面这行local[]里面填cpu个数,填的是几,那么total就代表是几,就是默认最大并行度是几
.setAppName("My app")
.set("spark.default.parallelism","需要设置的数量")
默认defaultParallelism=totalCores(当前本地集群可以用的总核数),目的为了最大限度并行运行!
standalone / YARN模式, totalCores是Job申请的总的核数!
本地集群总的核数取决于 : Local[N]
local: 1核
local[2]: 2核
local[*] : 所有核,多少个线程就有多少个cpu
6.3.1.2 分区策略
makeRDD方法:
第二个参数numSlices决定分区数,可见numSlices走的是parallelize方法
def makeRDD[T: ClassTag](
seq: Seq[T], //数据来源,一个集合
numSlices: Int = defaultParallelism): RDD[T] = withScope {
parallelize(seq, numSlices) //将集合划分到这些分区数上
}
parallelize方法:
该方法new 了一个ParallelCollectionRDD(并行的集合RDD)
def parallelize[T: ClassTag](
seq: Seq[T],
numSlices: Int = defaultParallelism): RDD[T] = withScope {
assertNotStopped()
new ParallelCollectionRDD[T](this, seq, numSlices, Map[Int, Seq[String]]())
}
此时创建的RDD就是ParallelCollectionRDD类型
那么找分区策略的话就找这个RDD对应的分区策略
找ParallelCollectionRDD.scala这个文件的getPartitions方法
override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = {
val slices = ParallelCollectionRDD.slice(data, numSlices).toArray
slices.indices.map(i => new ParallelCollectionPartition(id, i, slices(i))).toArray
}
/*
这个方法又调用了ParallelCollectionRDD的slice方法,传了两个参数,一个数据,一个分区数,然后toArray得到slices,slices又调用indices.map方法,将slices又作为一个数组返回了
*/
我们再看slice方法
/**
* Slice a collection into numSlices sub-collections. One extra thing we do here is to treat Range
* collections specially, encoding the slices as other Ranges to minimize memory cost. This makes
* it efficient to run Spark over RDDs representing large sets of numbers. And if the collection
* is an inclusive Range, we use inclusive range for the last slice.
*/
①先看这:
def slice[T: ClassTag](seq: Seq[T], numSlices: Int): Seq[Seq[T]] = {
// seq:就是传入的数据
// numSlices:就是分区数
// 检查分区数是否合法
if (numSlices < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Positive number of partitions required")
}
// Sequences need to be sliced at the same set of index positions for operations
// like RDD.zip() to behave as expected
/*length:5
numSlices:2
*/
def positions(length: Long, numSlices: Int): Iterator[(Int, Int)] = {
/*
(0 until numSlices) = [0,2)
0: (0,2)
1: (2,5)
*/
(0 until numSlices).iterator.map {
i =>
val start = ((i * length) / numSlices).toInt
val end = (((i + 1) * length) / numSlices).toInt
(start, end)
}
}
②再看
seq match {
//这里是seq为range
case r: Range =>
positions(r.length, numSlices).zipWithIndex.map {
case ((start, end), index) =>
// If the range is inclusive, use inclusive range for the last slice
if (r.isInclusive && index == numSlices - 1) {
new Range.Inclusive(r.start + start * r.step, r.end, r.step)
}
else {
new Range(r.start + start * r.step, r.start + end * r.step, r.step)
}
}.toSeq.asInstanceOf[Seq[Seq[T]]]
//适用于Long,Double,BigInteger等范围
case nr: NumericRange[_] =>
// For ranges of Long, Double, BigInteger, etc
val slices = new ArrayBuffer[Seq[T]](numSlices)
var r = nr
for ((start, end) <- positions(nr.length, numSlices)) {
val sliceSize = end - start
slices += r.take(sliceSize).asInstanceOf[Seq[T]]
r = r.drop(sliceSize)
}
slices
=======================================看下面代码=======================================
..我们是list.... 对range类型进行特殊处理
// 非Range,按此方法处理
case _ =>
//Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val array = seq.toArray // To prevent O(n^2) operations for List etc将list转成array
// 返回 {(0,2),(2,5)}
//
positions(array.length, numSlices) //这里的positions方法在上面
.map {
case (start, end) =>
// Array(1,2,3,4,5).slice
// (0,2) => (1,2)
// (2,5) => (3,4,5)
array.slice(start, end).toSeq
}.toSeq
}
**总结: **
ParallelCollectionRDD在对集合中的元素进行分区时,大致是平均分。如果不能整除,后面的分区会多分!
6.3.2 从外部存储(文件)创建RDD( textfile)
源码在SparkContext.scala这个文件下
/**
* Read a text file from HDFS, a local file system (available on all nodes), or any
* Hadoop-supported file system URI, and return it as an RDD of Strings.
* The text files must be encoded as UTF-8.
*
* @param path path to the text file on a supported file system
* @param minPartitions suggested minimum number of partitions for the resulting RDD
* @return RDD of lines of the text file
*/
译文
/*
*从HDFS,本地文件系统(在所有节点上都可用)或任何Hadoop支持的文件系统URI中读取文本文件,并将其作为字符串的 RDD 返回。文本文件必须编码为UTF-8。
* @param path --> 所支持文件系统上文本文件的路径
* @param minPartitions --> 建议生成的RDD的最小分区数
* @返回文本文件行的RDD
*/
def textFile(
path: String,
minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions): RDD[String] = withScope {
assertNotStopped()
hadoopFile(
path,
classOf[TextInputFormat],
classOf[LongWritable],
classOf[Text],
minPartitions
).map(pair => pair._2.toString).setName(path)
}
从外部存储创建RDD
@Test
def testHadoopRDD() = {
val rdd:RDD[String] = sparkContext.textFile("input",4)
rdd.saveAsTextFile("output")
}
6.3.2.1 分区数
def textFile(
path: String,
minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions): RDD[String] = withScope {
assertNotStopped()
hadoopFile(path, classOf[TextInputFormat], classOf[LongWritable], classOf[Text],
minPartitions).map(pair => pair._2.toString).setName(path)
}
defaultMinPartitions:
// 使用defaultParallelism(默认集群的核数) 和 2取最小
def defaultMinPartitions: Int = math.min(defaultParallelism, 2)
defaultMinPartitions和minPartitions 不是最终 分区数,但是会影响最终分区数!
最终分区数,取决于切片数!
6.3.2.2 分区策略
源码创建如下:
def textFile(
path: String,
minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions): RDD[String] = withScope {
assertNotStopped()
hadoopFile(
path,
classOf[TextInputFormat],
classOf[LongWritable],
classOf[Text],
minPartitions
).map(pair => pair._2.toString).setName(path)
}
由源码可知,textFile方法,需要传两个参数,一个是数据存储路径,另一个就是建议生成的RDD的最小分区数,调用的是hadoopFile这个方法,进入hadoopFile方法,如下
minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions): RDD[(K, V)] = withScope {
assertNotStopped()
// This is a hack to enforce loading hdfs-site.xml.
// See SPARK-11227 for details.
FileSystem.getLocal(hadoopConfiguration)
// A Hadoop configuration can be about 10 KiB, which is pretty big, so broadcast it.
val confBroadcast = broadcast(new SerializableConfiguration(hadoopConfiguration))
val setInputPathsFunc = (jobConf: JobConf) => FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(jobConf, path)
new HadoopRDD(
this,
confBroadcast,
Some(setInputPathsFunc),
inputFormatClass,
keyClass,
valueClass,
minPartitions).setName(path)
}
HadoopRDD中的getPartitions方法
可知该方法就是new了一个 HadoopRDD,具体的分区策略。需要看HadoopRDD是怎么运行的,进入HadoopRDD,找到getPartitions这个方法,代码如下
override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = {
val jobConf = getJobConf()
// add the credentials here as this can be called before SparkContext initialized
SparkHadoopUtil.get.addCredentials(jobConf)
try {
/*
①调用输入格式
getInputFormat做两件事:
第一个切片
第二个RecordReder,将每段数据封装成K,V
(org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat)进行切片,切片时, minPartitions=2
*/
val allInputSplits = getInputFormat(jobConf).getSplits(jobConf, minPartitions)
/*
②是否过滤空切片后的切片集合,要么是原先的切片
*/
val inputSplits = if (ignoreEmptySplits) {
allInputSplits.filter(_.getLength > 0)
} else {
allInputSplits
}
/*
③如果切的是1片,且是针对文件的切片,做特殊处理
FileSplit:对接的数据源不同。生成的切片就不一样,对接的是文本 或者文件数据,生成的切片都叫FileSplit
*/
if (inputSplits.length == 1 && inputSplits(0).isInstanceOf[FileSplit]) {
val fileSplit = inputSplits(0).asInstanceOf[FileSplit]
val path = fileSplit.getPath
if (fileSplit.getLength > conf.get(IO_WARNING_LARGEFILETHRESHOLD)) {
val codecFactory = new CompressionCodecFactory(jobConf)
if (Utils.isFileSplittable(path, codecFactory)) {
logWarning(s"Loading one large file ${path.toString} with only one partition, " +
s"we can increase partition numbers for improving performance.")
} else {
logWarning(s"Loading one large unsplittable file ${path.toString} with only one " +
s"partition, because the file is compressed by unsplittable compression codec.")
}
}
}
/*
④分区数=过滤后的切片数
inputSplits有多少我的长度就有多少
*/
val array = new Array[Partition](inputSplits.size)
for (i <- 0 until inputSplits.size) {
array(i) = new HadoopPartition(id, i, inputSplits(i))
}
array
} catch {
case e: InvalidInputException if ignoreMissingFiles =>
logWarning(s"${jobConf.get(FileInputFormat.INPUT_DIR)} doesn't exist and no" +
s" partitions returned from this path.", e)
Array.empty[Partition]
}
切的片数,等于我的分区数,看看ignoreEmptySplits这个值是true还是false,点击ignoreEmptySplits,如下:
private val ignoreEmptySplits = sparkContext.conf.get(HADOOP_RDD_IGNORE_EMPTY_SPLITS)
点击HADOOP_RDD_IGNORE_EMPTY_SPLITS,代码如下:
private[spark] val HADOOP_RDD_IGNORE_EMPTY_SPLITS =
ConfigBuilder("spark.hadoopRDD.ignoreEmptySplits")
.internal()
.doc("When true, HadoopRDD/NewHadoopRDD will not create partitions for empty input splits.")
.version("2.3.0")
.booleanConf
.createWithDefault(false)
我们看到值默认为false
所以源代码中
/*
②是否过滤空切片后的切片集合,要么是原先的切片
*/
val inputSplits = if (ignoreEmptySplits) {
allInputSplits.filter(_.getLength > 0)
} else {
allInputSplits
}
ignoreEmptySplits默认为空,所以allInputSplits被返回了
综上结论·:在HadoopRDD中切片数等于分区数
接下来看具体时间怎么切的
首先看看HadoopRDD介绍
/**
* :: DeveloperApi ::
* An RDD that provides core functionality for reading data stored in Hadoop (e.g., files in HDFS,
* sources in HBase, or S3), using the older MapReduce API (`org.apache.hadoop.mapred`).
*
* @param sc The SparkContext to associate the RDD with.
* @param broadcastedConf A general Hadoop Configuration, or a subclass of it. If the enclosed
* variable references an instance of JobConf, then that JobConf will be used for the Hadoop job.
* Otherwise, a new JobConf will be created on each slave using the enclosed Configuration.
* @param initLocalJobConfFuncOpt Optional closure used to initialize any JobConf that HadoopRDD
* creates.
* @param inputFormatClass Storage format of the data to be read.
* @param keyClass Class of the key associated with the inputFormatClass.
* @param valueClass Class of the value associated with the inputFormatClass.
* @param minPartitions Minimum number of HadoopRDD partitions (Hadoop Splits) to generate.
*
* @note Instantiating this class directly is not recommended, please use
* `org.apache.spark.SparkContext.hadoopRDD()`
*/
译文:
DeveloperApi ::
*一个RDD,它使用较旧的MapReduce API(`org.apache.hadoop.mapred`)提供核心功能,以读取Hadoop中存储的数据(例如HDFS中的文件,HBase或S3中的源)。 )。
/*HadoopRDD用的是老的包(org.apache.hadoop.mapred)下的输入格式*/
* * @param sc与RDD关联的SparkContext。
* @param broadcastedConf常规Hadoop配置或其子类。如果附带的
*变量引用JobConf的实例,则该JobConf将用于Hadoop作业。
*否则,将使用随附的配置在每个从站上创建一个新的JobConf。
* @param initLocalJobConfFuncOpt可选闭包,用于初始化HadoopRDD创建的任何JobConf。
* @param inputFormatClass要读取的数据的存储格式。
* @param keyClass与inputFormatClass关联的键的类。
* @param valueClass与inputFormatClass关联的值的类。
* @param minPartitions要生成的HadoopRDD分区(Hadoop拆分)的最小数量。
* @note不建议直接实例化此类,请使用
*`org.apache.spark.SparkContext.hadoopRDD()`
调试
val allInputSplits = getInputFormat(jobConf).getSplits(jobConf, minPartitions)
//此处打断点
第一次进去,进的是getInputFormat,代码如下
protected def getInputFormat(conf: JobConf): InputFormat[K, V] = {
val newInputFormat = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(inputFormatClass.asInstanceOf[Class[_]], conf)
.asInstanceOf[InputFormat[K, V]]
newInputFormat match {
case c: Configurable => c.setConf(conf)
case _ =>
}
newInputFormat
}
HadoopRDD中的getSplits方法:
出来,再进,进去的是getSplits,代码如下:
package org.apache.hadoop.mapred;
/** Splits files returned by {@link #listStatus(JobConf)} when
* they're too big.*/
public InputSplit[] getSplits(JobConf job, int numSplits)
throws IOException {
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch().start();
FileStatus[] files = listStatus(job);
发现他是老的包下面的(即是:HadoopRDD调用的是mapred包下旧的API)
默认的输入格式:
TextInputFormat exterends FileInputFormat,
它并没有重写getSplit方法,
因此TextInputFormat 依然使用父类也就是FileInputFormat的getSplit方法进行切片
切片(getSplits在FilInputFormat文件下)完整源码如下:
/*11111111111111111111*/
public InputSplit[] getSplits(JobConf job, int numSplits)
throws IOException {
//①统计当前切片的数据的总大小
long totalSize = 0; // compute total size
for (FileStatus file: files) {
// check we have valid files
if (file.isDirectory()) {
throw new IOException("Not a file: "+ file.getPath());
}
totalSize += file.getLen();
}
断点处=================================
// ②计算 goalsize(期望每片大小)
long goalSize = totalSize / ("numSplits" == 0 ? 1 : numSplits);
问?其中的numsplits从哪来的,见getSplits方法传的参数的红色部分
public InputSplit[] getSplits(JobConf job, int "numSplits")
throws IOException {
那么numSplits又是谁传过去的呢
来到它的父方法HadoopRDD文件里的getPartitions方法
val allInputSplits = getInputFormat(jobConf).getSplits(jobConf, minPartitions)
可见minPartitions就是numSplits,那么在HadoopRDD文件minPartitions又是哪来的呢?本文件的头部,如下
class HadoopRDD[K, V](
sc: SparkContext,
broadcastedConf: Broadcast[SerializableConfiguration],
initLocalJobConfFuncOpt: Option[JobConf => Unit],
inputFormatClass: Class[_ <: InputFormat[K, V]],
keyClass: Class[K],
valueClass: Class[V],
minPartitions: Int)
可见最后一个属性就是minPartitions,构造HadoopRDD的时候已经将minPartitions传过来了
那么是怎么构造的呢?
进入textFile方法,如下
def textFile(
path: String,
minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions): RDD[String] = withScope {
assertNotStopped()
hadoopFile(path, classOf[TextInputFormat], classOf[LongWritable], classOf[Text],
minPartitions).map(pair => pair._2.toString).setName(path)
}
发现minPartitions等于defaultMinPartitions
/*
minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions (不传时默认为2)
defaultMinPartitions = math.min(defaultParallelism, 2)
numSplits = minPartitions
*/
回到断点处===============
/*222222222222222222*/
// ②计算 goalsize(期望每片大小)
long goalSize = totalSize / (numSplits == 0 ? 1 : numSplits);
// 默认为1,调节 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input. FileInputFormat.SPLIT_MINSIZE, 改变minSize
我们知道numSplits默认为2,就不是0,就走后边,
接着有统计一个minSize值,minSize怎么算呢,如下
/*3333333333333333333*/
long minSize = Math.max(job.getLong(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.
FileInputFormat.SPLIT_MINSIZE, 1), minSplitSize);
//minSplitSize默认为1
接着new了一个数组,数组里放的是每一个切片,接着for循环,取出每一个文件,如下:切片以文件为单位切
/*44444444444444444444444444444444*/
// generate splits
ArrayList<FileSplit> splits = new ArrayList<FileSplit>(numSplits);
NetworkTopology clusterMap = new NetworkTopology();
// 切片以文件为单位切片
for (FileStatus file: files) {
Path path = file.getPath();
long length = file.getLen();
如果文件不为空,源码如下:
判断文件长度是否为0,不为0,判断嫩肤不能切,能切再计算块大小
/*555555555555555555555555555*/
if (length != 0) {
FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job);
BlockLocation[] blkLocations;
if (file instanceof LocatedFileStatus) {
blkLocations = ((LocatedFileStatus) file).getBlockLocations();
} else {
blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length);
}
if (isSplitable(fs, path)) {
// 获取文件的块大小,块大小在上传文件时,指定,如果不指定,默认 128M
long blockSize = file.getBlockSize();
// 计算片大小 一般等于 blockSize()
long splitSize = computeSplitSize(goalSize, minSize, blockSize);
/*
computeSplitSize方法如下:
protected long computeSplitSize(long goalSize, long minSize,
long blockSize) {
// 在处理大数据时,一般情况下,blockSize作为片大小
//那么goalSize受什么影响呢,numSplits和totalSize,
//同时numSplits又受minPartitions影响
return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(goalSize, blockSize));
}
*/
long bytesRemaining = length;
// 循环切片
while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) {
String[][] splitHosts = getSplitHostsAndCachedHosts(blkLocations,
length-bytesRemaining, splitSize, clusterMap);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize,
splitHosts[0], splitHosts[1]));
bytesRemaining -= splitSize;
}
// 剩余部分 <=片大小1.1倍,整体作为1片
if (bytesRemaining != 0) {
String[][] splitHosts = getSplitHostsAndCachedHosts(blkLocations, length
- bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining, clusterMap);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length - bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining,
splitHosts[0], splitHosts[1]));
}
} else {
//如果文件不可切,整个文件作为1片
// 不是压缩格式,都可切,如果是压缩格式,继续判断是否是可切的压缩格式(bzip2,lzo)
// 看文件的后缀,如果文件后缀是 .deflate, .gzip , .snappy都不可切
// 否则都可切
String[][] splitHosts = getSplitHostsAndCachedHosts(blkLocations,0,length,clusterMap);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, splitHosts[0], splitHosts[1]));
}
}
这里看一下isSplitable方法:
protected boolean isSplitable(FileSystem fs, Path filename) {
return true;
}
protected boolean isSplitable(FileSystem fs, Path file) {
final CompressionCodec codec = compressionCodecs.getCodec(file);
if (null == codec) {
return true;
}
return codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec;
}
看getCodec方法
/**
* Find the relevant compression codec for the given file based on its
* filename suffix.
* @param file the filename to check
* @return the codec object
* 根据文件名后缀找到给定文件的相关压缩编解码器。
* @param文件要检查的文件名
* @返回编解码器对象* /
*/
public CompressionCodec getCodec(Path file) {
CompressionCodec result = null;
if (codecs != null) {
String filename = file.getName();
String reversedFilename =
new StringBuilder(filename).reverse().toString();
SortedMap<String, CompressionCodec> subMap =
codecs.headMap(reversedFilename);
if (!subMap.isEmpty()) {
String potentialSuffix = subMap.lastKey();
if (reversedFilename.startsWith(potentialSuffix)) {
result = codecs.get(potentialSuffix);
}
}
}
return result;
}
回去,所以不是压缩格式都能切
如果文件长度为空,源码如下:
/*6666666666666666666666666*/
else {
// 文件长度为0,创建一个空切片
//Create empty hosts array for zero length files
//这个splits就是上面new的数组
splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0]));
/*
这一块makeSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0])就相当于new一个FileSplit对象
*/
}
怎么new一个FileSplit对象呢?点击makeSplit,进入该方法,在FileInputFormat文件下
/**
* A factory that makes the split for this class. It can be overridden
* by sub-classes to make sub-types
*/
protected FileSplit makeSplit(Path file, long start, long length,
String[] hosts) {
return new FileSplit(file, start, length, hosts);
}
说明文件为空也是切一片
/*7777777777777777777777777777777*/
sw.stop();
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Total # of splits generated by getSplits: " + splits.size()
+ ", TimeTaken: " + sw.now(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
return splits.toArray(new FileSplit[splits.size()]);
}
long splitSize = computeSplitSize(goalSize, minSize, blockSize);
// 在处理大数据时,一般情况下,blockSize作为片大小
return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(goalSize, blockSize));