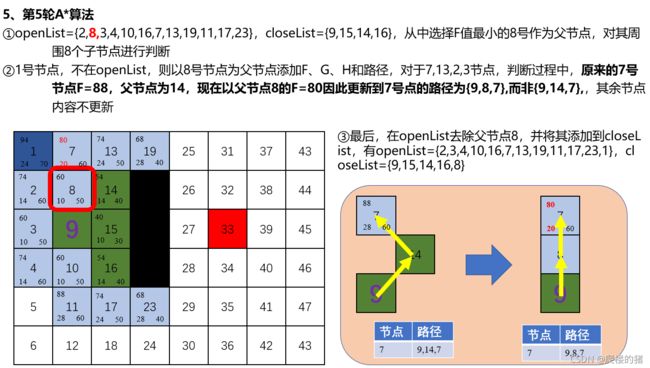
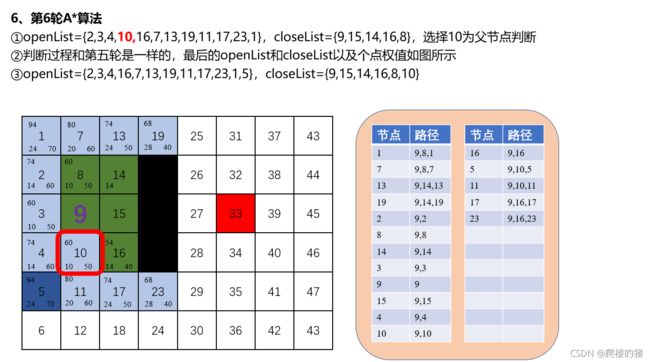
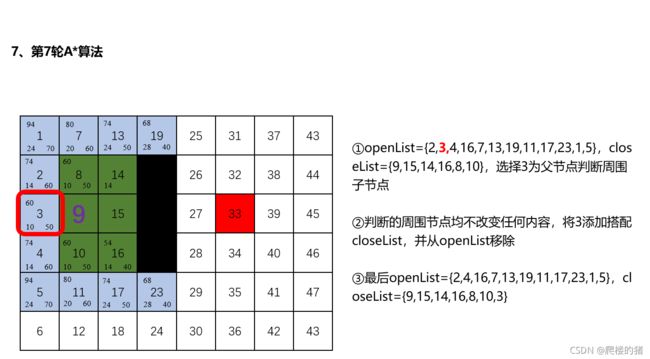
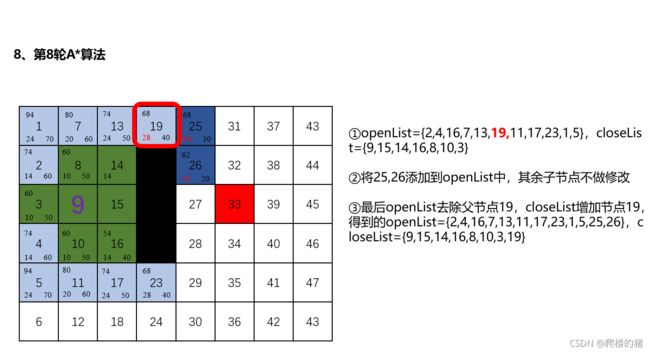
3 移动机器人路径规划(4- A*路径规划算法)
3 移动机器人路径规划
- 4.1 Astat路径规划算法原理
- 4.2 Astat路径规划例子示例
- 4.3 Astat路径规划算法MATLAB代码
-
- 4.3.1 MATLAB代码示例
- 4.3.2 主代码:Astat.m
- 4.3.3 函数代码:Astat_NextNode.m
- 4.4 Astat路径规划算法Python代码
4.1 Astat路径规划算法原理
A-Star算法是一种静态路网中求解最短路径最有效的直接搜索方法,也是许多其他问题的常用启发式算法。注意其是最有效的直接搜索算法,之后涌现了很多预处理算法(如ALT,CH,HL等等),在线查询效率是A*算法的数千甚至上万倍。
- 公式表示为: f(n)=g(n)+h(n),
- 其中, f(n) 是从初始状态经由状态n到目标状态的最小代价估计,
- g(n) 是在状态空间中从初始状态到状态n的最小代价,
- h(n) 是从状态n到目标状态的路径的最小估计代价。对于路径搜索问题,状态就是图中的节点,代价就是距离)
参考文档
Astat算法-百度百科
Astat中文博客
Astat最火英文博客
4.2 Astat路径规划例子示例
4.3 Astat路径规划算法MATLAB代码
4.3.1 MATLAB代码示例
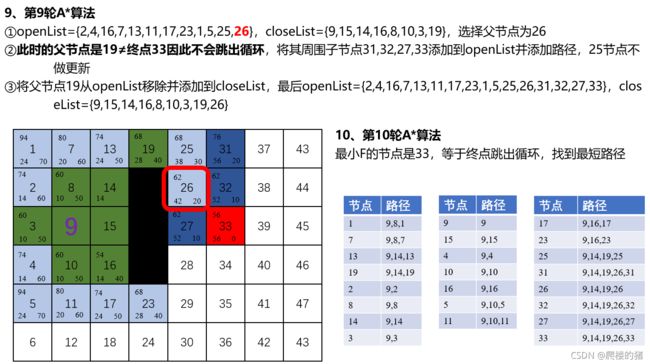
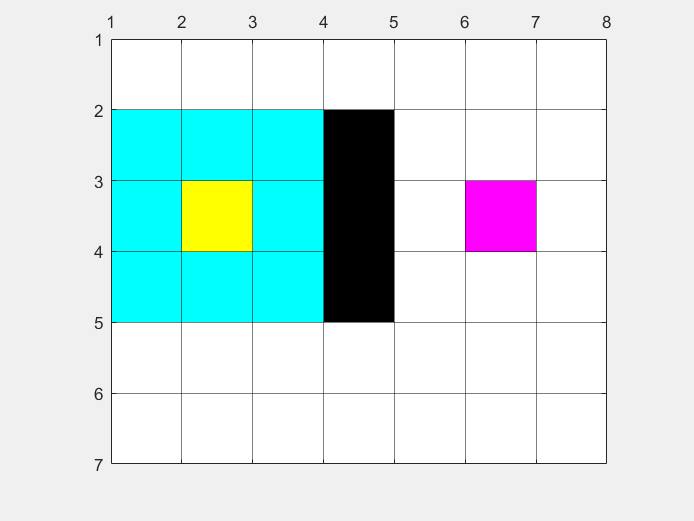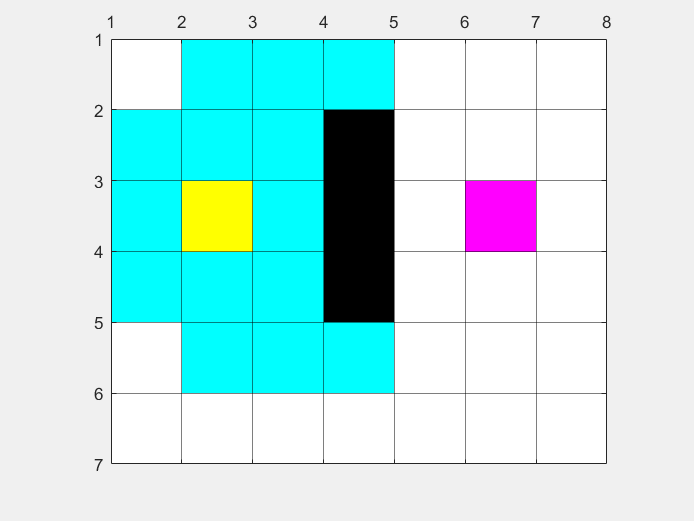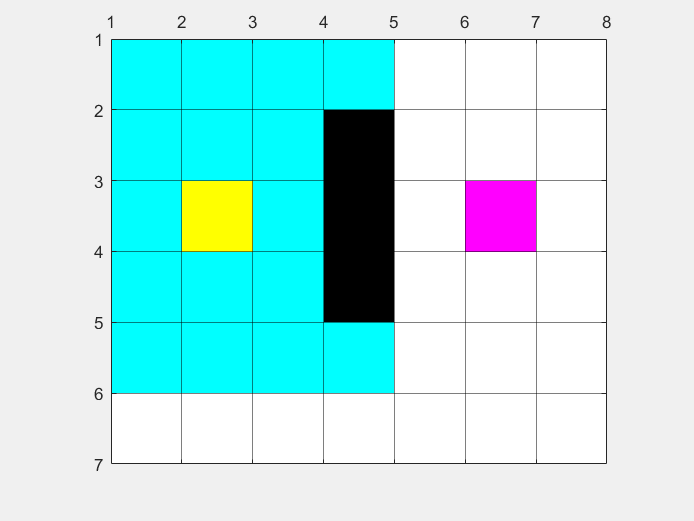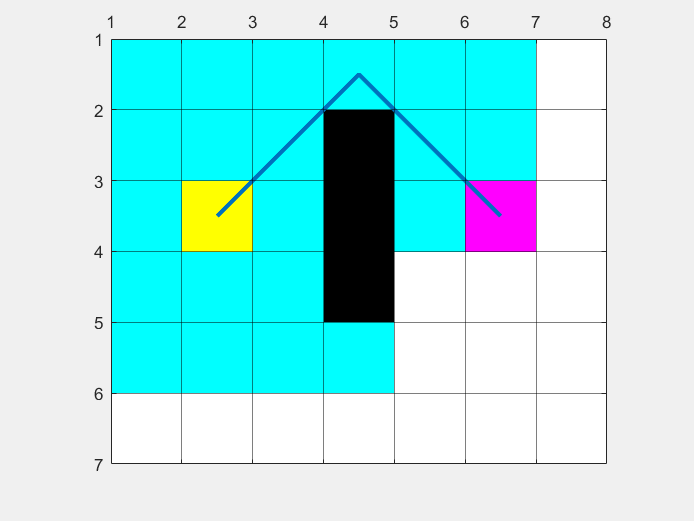
地图信息和示例是一致的,最后得到的最短路径,和搜寻的地图区域如图所示:
4.3.2 主代码:Astat.m
%% 定义基础数据,包括地图行列的长度,起点位置等
clc;clear;close all
rows = 6;cols = 7; % 地图的尺寸
dy_SearchArea =[]; % 动态绘制搜索区域
searchHead = 2;searchEnd = searchHead; % 动态绘制搜索区域的速度
startSub = [3,2]; % 起点行列位置
goalSub = [3,6]; % 终点行列位置
obsSub = [2,4;3,4;4,4]; % 障碍物行列位置(n*2)
%% 定义栅格地图,并初始化,此部分以后内容,均不用修改-------------------------------------------------
% 初始化地图数值为1,代表全空白区域
field = ones(rows, cols);
% 起点、终点、障碍物区域的权值
% Tips:对于单个点,Filed(x,y) = 2是可以的,但是多个点需要转成索引数组才能
field(startSub(1),startSub(2)) = 4;
field(goalSub(1),goalSub(2)) = 5;
% 后续路径规划算法,对于点的位置,均用索引值进行表示(输入变量只需要一个就行)
obsR = obsSub(:,1);obsC = obsSub(:,2);
obsIndex = sub2ind([rows,cols],obsR,obsC);
startIndex = sub2ind([rows,cols],startSub(1),startSub(2));
goalIndex = sub2ind([rows,cols],goalSub(1),goalSub(2));
field(obsIndex) = 2;
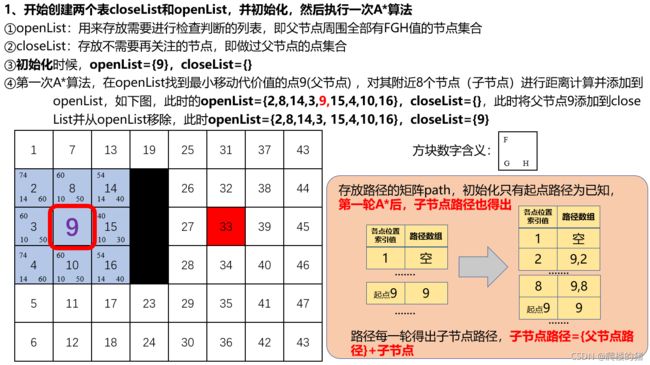
%% ******建立openList(n*4)和closeList(n*2)并初始化************************************
% 初始时,openList只有起点,closeList为空
% openList(n*4),分别记录记录点的位置信息,G、H、F值
openList = [startIndex,0,0,0];
% closeList(n*2)记录位置信息和距离权值F值,初始化时候为空
closeList = [];
%% *************初始化path,即从起点到地图任意点的路径矩阵(n*2)***************************
for i = 1:rows*cols
path{
i,1} = i; % 存放地图任意点的索引
path{
i,2} = []; % 存放起点到该点的路径
end
% 对于起点,其路径是已知的,写入起点路径
path{
startIndex,2} = startIndex;
%% 绘制地图--------------------------------------------------------------------------
% 定义函数,列数,以及障碍物坐标
cmap = [1 1 1; ... % 1-白色-空地
0 0 0; ... % 2-黑色-静态障碍
1 0 0; ... % 3-红色-动态障碍
1 1 0;... % 4-黄色-起始点
1 0 1;... % 5-品红-目标点
0 1 0; ... % 6-绿色-到目标点的规划路径
0 1 1]; % 7-青色-动态规划的路径
colormap(cmap);
image(1.5,1.5,field);
% 设置栅格属性------------------------------------------------------------------------------
grid on;hold on;
set(gca,'gridline','-','gridcolor','k','linewidth',0.5,'GridAlpha',0.5);
set(gca,'xtick',1:cols+1,'ytick',1:rows+1);
set(gca, 'XAxisLocation','top')
axis image;
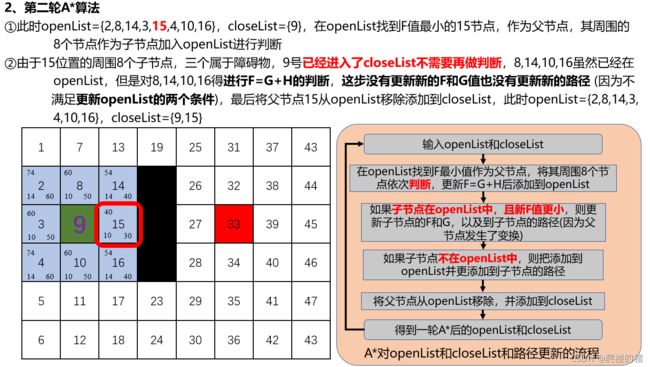
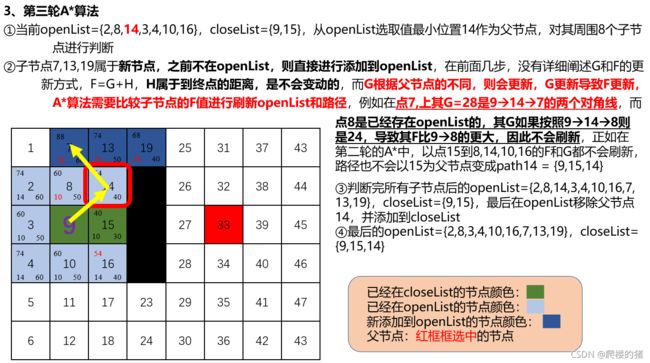
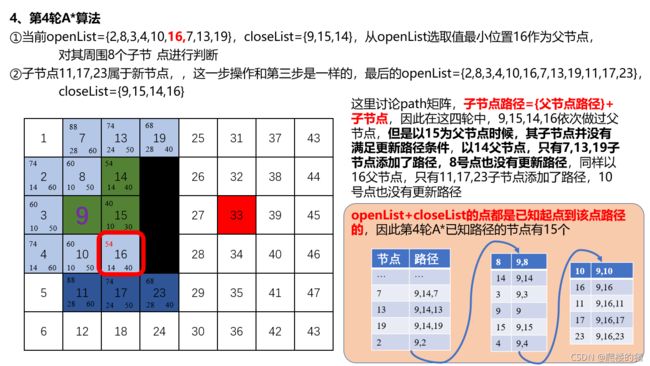
%% ******A*算法*************************************************************************
while true
% 1、从openList开始搜索移动代价最小的节点,min函数返回值为[值,位置]
[~,idxNode] = min(openList(:,4));
node = openList(idxNode,1);
% 2、判断是否搜索到终点
if node == goalIndex
break
end
% ******3、在openList选中最小的F值点作为父节点
nextNodes = Astat_NextNode(field,closeList,node);
% *******4、判断父节点周围子节点情况,并将子节点依次添加或者更新到openList中
for i = 1:length(nextNodes)
% 需要判断的子节点
nextNode = nextNodes(i);
% 计算代价函数
[rowNode,colNode] = ind2sub([rows, cols], node);
[row_nextNode,col_nextNode] = ind2sub([rows, cols], nextNode);
[row_goalPos,col_goalPos] = ind2sub([rows, cols],goalIndex);
g = openList(idxNode,2) + norm( [rowNode,colNode] -[row_nextNode,col_nextNode]);
h = abs(row_goalPos - row_nextNode) + abs(col_goalPos - col_nextNode);
f = g + h;
% 判断该子节点是否存在在openList中
[inOpen,idx_nextNode] = ismember(nextNode, openList(:,1));
% ******如果存在,则需要比较F值,取F值小的更新F和G、H同时更新路径
if inOpen && f < openList(idx_nextNode,4)
openList(idx_nextNode,2) = g;
openList(idx_nextNode,3) = h;
openList(idx_nextNode,4) = f;
path{
nextNode,2} = [path{
node,2}, nextNode];
end
% *******如果不存在,则添加到openList表中
if ~inOpen
openList(end+1,:) = [nextNode,g,h,f];
path{
nextNode,2} = [path{
node,2}, nextNode];
end
end
% 将父节点从openList中移除,添加到closeList中
closeList(end+1,: ) = [openList(idxNode,1), openList(idxNode,4)];
openList(idxNode,:)= [];
% =======绘制动态搜索区域
dy_SearchArea = [openList(:,1)',closeList(:,1)']; % 添加节点到动态区域中
field(dy_SearchArea) = 7; % 动态区域的颜色
field(startIndex) = 4; % 起点颜色保持不变
field(goalIndex) = 5; % 终点颜色保持不变
if mod(searchHead,searchEnd) == 0 % 控制动图绘制速度
image(1.5,1.5,field); % 联合drawnow函数绘制动态效果
drawnow;
end
searchHead = searchHead + 1;
end
%% 绘制最优路径的折线图*******************************************************************
% 由于绘图函数plot针对的窗口是x,y,它们与row,col是的先后顺序是相反的,即X对应col,y对应row
image(1.5,1.5,field); % 将动画速度未显示完的搜索区域全部显示
field(dy_SearchArea) = 1; % 最后将搜索区域的值改回为空白值
optPath = path{
goalIndex,2}; % 最优路径
[plotr,plotc] = ind2sub([rows,cols],optPath);
plot(plotc+0.5,plotr+0.5,'LineWidth',2.5);
% % function nextNodes = Astat_NextNode(field,closeList,node)
% % % ASTAT_NEXTNODE 对父节点周围的8个节点进行判断
% % % 判断内容需要排除超过边界之外的、位于障碍区的、位于closeList中的三大类
% %
% % [rows, cols] = size(field); % 获取地图尺寸
% % [r,c] = ind2sub([rows, cols], node); % 得到父节点行列值,方便进行上下左右移动
% % movePos = [-1,1;0,1;1,1;-1,0;1,0;-1,-1;0,-1;1,-1]; % 移动方向矩阵
% % nextNodes = []; % 存放子节点线性索引位置的的矩阵(1*n)
% %
% % % closeList内第一列存放点的索引值,单独拎出第一列来进行判断是否在closeList中
% % closenode = []; % 初始化时候closeList为空,不能执行(:,1)操作,
% % % 故函数中的closenode作为临时变量初始为空
% % if ~isempty(closeList) % if的目的就是为了保证初始的closeList=[]也有效
% % closenode = closeList(:,1);
% % end
% %
% % for i = 1:8
% % if 0 < r+movePos(i,1) && r+movePos(i,1) <= rows && 0 < c+movePos(i,2) && c+movePos(i,2) <= cols
% % nextSub = [r + movePos(i,1), c + movePos(i,2)];
% % nextIndex = sub2ind([rows, cols], nextSub(1), nextSub(2));
% % if field(nextSub(1), nextSub(2)) ~= 2
% % if ~ismember(nextIndex, closenode)
% % nextNodes(end+1) = nextIndex;
% % end
% % end
% % end
% % end
4.3.3 函数代码:Astat_NextNode.m
function nextNodes = Astat_NextNode(field,closeList,node)
% ASTAT_NEXTNODE 对父节点周围的8个节点进行判断
% 判断内容需要排除超过边界之外的、位于障碍区的、位于closeList中的三大类
[rows, cols] = size(field); % 获取地图尺寸
[r,c] = ind2sub([rows, cols], node); % 得到父节点行列值,方便进行上下左右移动
movePos = [-1,1;0,1;1,1;-1,0;1,0;-1,-1;0,-1;1,-1]; % 移动方向矩阵
nextNodes = []; % 存放子节点线性索引位置的的矩阵(1*n)
% closeList内第一列存放点的索引值,单独拎出第一列来进行判断是否在closeList中
closenode = []; % 初始化时候closeList为空,不能执行(:,1)操作,
% 故函数中的closenode作为临时变量初始为空
if ~isempty(closeList) % if的目的就是为了保证初始的closeList=[]也有效
closenode = closeList(:,1);
end
for i = 1:8
if 0 < r+movePos(i,1) && r+movePos(i,1) <= rows && 0 < c+movePos(i,2) && c+movePos(i,2) <= cols
nextSub = [r + movePos(i,1), c + movePos(i,2)];
nextIndex = sub2ind([rows, cols], nextSub(1), nextSub(2));
if field(nextSub(1), nextSub(2)) ~= 2
if ~ismember(nextIndex, closenode)
nextNodes(end+1) = nextIndex;
end
end
end
end
4.4 Astat路径规划算法Python代码
暂时参照PythonRobotics:(https://github.com/redglassli/PythonRobotics#a-algorithm)
"""
A* grid planning
author: Atsushi Sakai(@Atsushi_twi)
Nikos Kanargias ([email protected])
See Wikipedia article (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A*_search_algorithm)
"""
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
show_animation = True
class AStarPlanner:
def __init__(self, ox, oy, reso, rr):
"""
Initialize grid map for a star planning
ox: x position list of Obstacles [m]
oy: y position list of Obstacles [m]
reso: grid resolution [m]
rr: robot radius[m]
"""
self.reso = reso
self.rr = rr
self.calc_obstacle_map(ox, oy)
self.motion = self.get_motion_model()
class Node:
def __init__(self, x, y, cost, pind):
self.x = x # index of grid
self.y = y # index of grid
self.cost = cost
self.pind = pind
def __str__(self):
return str(self.x) + "," + str(self.y) + "," + str(
self.cost) + "," + str(self.pind)
def planning(self, sx, sy, gx, gy):
"""
A star path search
input:
sx: start x position [m]
sy: start y position [m]
gx: goal x position [m]
gy: goal y position [m]
output:
rx: x position list of the final path
ry: y position list of the final path
"""
nstart = self.Node(self.calc_xyindex(sx, self.minx),
self.calc_xyindex(sy, self.miny), 0.0, -1)
ngoal = self.Node(self.calc_xyindex(gx, self.minx),
self.calc_xyindex(gy, self.miny), 0.0, -1)
open_set, closed_set = dict(), dict()
open_set[self.calc_grid_index(nstart)] = nstart
while 1:
if len(open_set) == 0:
print("Open set is empty..")
break
c_id = min(
open_set,
key=lambda o: open_set[o].cost + self.calc_heuristic(ngoal,
open_set[
o]))
current = open_set[c_id]
# show graph
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.plot(self.calc_grid_position(current.x, self.minx),
self.calc_grid_position(current.y, self.miny), "xc")
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(
0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
if len(closed_set.keys()) % 10 == 0:
plt.pause(0.001)
if current.x == ngoal.x and current.y == ngoal.y:
print("Find goal")
ngoal.pind = current.pind
ngoal.cost = current.cost
break
# Remove the item from the open set
del open_set[c_id]
# Add it to the closed set
closed_set[c_id] = current
# expand_grid search grid based on motion model
for i, _ in enumerate(self.motion):
node = self.Node(current.x + self.motion[i][0],
current.y + self.motion[i][1],
current.cost + self.motion[i][2], c_id)
n_id = self.calc_grid_index(node)
# If the node is not safe, do nothing
if not self.verify_node(node):
continue
if n_id in closed_set:
continue
if n_id not in open_set:
open_set[n_id] = node # discovered a new node
else:
if open_set[n_id].cost > node.cost:
# This path is the best until now. record it
open_set[n_id] = node
rx, ry = self.calc_final_path(ngoal, closed_set)
return rx, ry
def calc_final_path(self, ngoal, closedset):
# generate final course
rx, ry = [self.calc_grid_position(ngoal.x, self.minx)], [
self.calc_grid_position(ngoal.y, self.miny)]
pind = ngoal.pind
while pind != -1:
n = closedset[pind]
rx.append(self.calc_grid_position(n.x, self.minx))
ry.append(self.calc_grid_position(n.y, self.miny))
pind = n.pind
return rx, ry
@staticmethod
def calc_heuristic(n1, n2):
w = 1.0 # weight of heuristic
d = w * math.hypot(n1.x - n2.x, n1.y - n2.y)
return d
def calc_grid_position(self, index, minp):
"""
calc grid position
:param index:
:param minp:
:return:
"""
pos = index * self.reso + minp
return pos
def calc_xyindex(self, position, min_pos):
return round((position - min_pos) / self.reso)
def calc_grid_index(self, node):
return (node.y - self.miny) * self.xwidth + (node.x - self.minx)
def verify_node(self, node):
px = self.calc_grid_position(node.x, self.minx)
py = self.calc_grid_position(node.y, self.miny)
if px < self.minx:
return False
elif py < self.miny:
return False
elif px >= self.maxx:
return False
elif py >= self.maxy:
return False
# collision check
if self.obmap[node.x][node.y]:
return False
return True
def calc_obstacle_map(self, ox, oy):
self.minx = round(min(ox))
self.miny = round(min(oy))
self.maxx = round(max(ox))
self.maxy = round(max(oy))
print("minx:", self.minx)
print("miny:", self.miny)
print("maxx:", self.maxx)
print("maxy:", self.maxy)
self.xwidth = round((self.maxx - self.minx) / self.reso)
self.ywidth = round((self.maxy - self.miny) / self.reso)
print("xwidth:", self.xwidth)
print("ywidth:", self.ywidth)
# obstacle map generation
self.obmap = [[False for i in range(self.ywidth)]
for i in range(self.xwidth)]
for ix in range(self.xwidth):
x = self.calc_grid_position(ix, self.minx)
for iy in range(self.ywidth):
y = self.calc_grid_position(iy, self.miny)
for iox, ioy in zip(ox, oy):
d = math.hypot(iox - x, ioy - y)
if d <= self.rr:
self.obmap[ix][iy] = True
break
@staticmethod
def get_motion_model():
# dx, dy, cost
motion = [[1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1],
[-1, 0, 1],
[0, -1, 1],
[-1, -1, math.sqrt(2)],
[-1, 1, math.sqrt(2)],
[1, -1, math.sqrt(2)],
[1, 1, math.sqrt(2)]]
return motion
def main():
print(__file__ + " start!!")
# start and goal position
sx = 10.0 # [m]
sy = 10.0 # [m]
gx = 50.0 # [m]
gy = 50.0 # [m]
grid_size = 2.0 # [m]
robot_radius = 1.0 # [m]
# set obstacle positions
ox, oy = [], []
for i in range(-10, 60):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(-10.0)
for i in range(-10, 60):
ox.append(60.0)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(-10, 61):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(60.0)
for i in range(-10, 61):
ox.append(-10.0)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(-10, 40):
ox.append(20.0)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(0, 40):
ox.append(40.0)
oy.append(60.0 - i)
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.plot(ox, oy, ".k")
plt.plot(sx, sy, "og")
plt.plot(gx, gy, "xb")
plt.grid(True)
plt.axis("equal")
a_star = AStarPlanner(ox, oy, grid_size, robot_radius)
rx, ry = a_star.planning(sx, sy, gx, gy)
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.plot(rx, ry, "-r")
plt.show()
plt.pause(0.001)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()