tensorflow 以及keras常用API记录
tensorflow 常用API
-
- 1. Python 和 NumPy 实用程序(keras)
-
- 1.1 to_categorical
- 1.2 get_file
- 1.3 Sequence
- 1.4 tf.keras.layers.DenseFeatures
- 1.5 tf.keras.layers.Embedding
- 1.6 tf.keras.layers.Dropout
- 1.7 tf.keras.callbacks
-
- 1.7.1 tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping()
- 1.7.2 tf.keras.callbacks.History()
- 2. tf.data
-
- 2.1 tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset
- 3. tf.feature_column
-
- 3.1 tf.feature_column.indicator_column
- 3.2 tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity
- 3.3 tf.feature_column.embedding_column
1. Python 和 NumPy 实用程序(keras)
1.1 to_categorical
tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y, num_classes=None, dtype="float32")`
将类向量(整数)转换为二进制类矩阵。例如,与 categorical_crossentropy 一起使用。
a = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical([0, 1, 2, 3], num_classes=4)
>>> a = tf.constant(a, shape=[4, 4])
>>> print(a)
tf.Tensor(
[[1. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 1.]], shape=(4, 4), dtype=float32)
b = tf.constant([.9, .04, .03, .03,
.3, .45, .15, .13,
.04, .01, .94, .05,
.12, .21, .5, .17],
shape=[4, 4])
>>> loss = tf.keras.backend.categorical_crossentropy(a, b)
>>> print(np.around(loss, 5))
[0.10536 0.82807 0.1011 1.77196]
1.2 get_file
tf.keras.utils.get_file(
fname=None,
origin=None,
untar=False,
md5_hash=None,
file_hash=None,
cache_subdir="datasets",
hash_algorithm="auto",
extract=False,
archive_format="auto",
cache_dir=None,
)
如果文件不在缓存中,则从 URL 下载文件。
默认情况下,url 处的文件origin被下载到 cache_dir ~/.keras,放置在 cache_subdir 中datasets,并给出文件名fname。example.txt因此,文件的最终位置 将是~/.keras/datasets/example.txt.
path_to_downloaded_file = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
"flower_photos",
"https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz",
untar=True)
1.3 Sequence
tf.keras.utils.Sequence()
用于拟合数据序列(例如数据集)的基础对象。
Sequence必须实现__getitem__和__len__方法。如果你想在不同时期之间修改你的数据集,你可以实现 on_epoch_end. 该方法__getitem__应该返回一个完整的批次。
from skimage.io import imread
from skimage.transform import resize
import numpy as np
import math
# Here, `x_set` is list of path to the images
# and `y_set` are the associated classes.
class CIFAR10Sequence(Sequence):
def __init__(self, x_set, y_set, batch_size):
self.x, self.y = x_set, y_set
self.batch_size = batch_size
def __len__(self):
return math.ceil(len(self.x) / self.batch_size)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
batch_x = self.x[idx * self.batch_size:(idx + 1) *
self.batch_size]
batch_y = self.y[idx * self.batch_size:(idx + 1) *
self.batch_size]
return np.array([
resize(imread(file_name), (200, 200))
for file_name in batch_x]), np.array(batch_y)
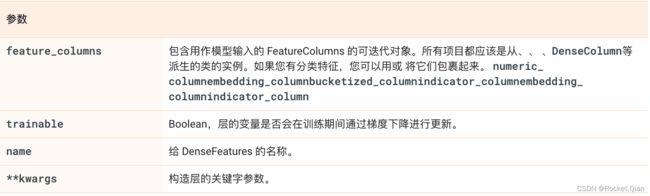
1.4 tf.keras.layers.DenseFeatures
tf.keras.layers.DenseFeatures(
feature_columns, trainable=True, name=None, **kwargs
)
通常,使用 FeatureColumns 描述训练数据中的单个示例。在模型的第一层,这个面向列的数据应该被转换为单个Tensor.
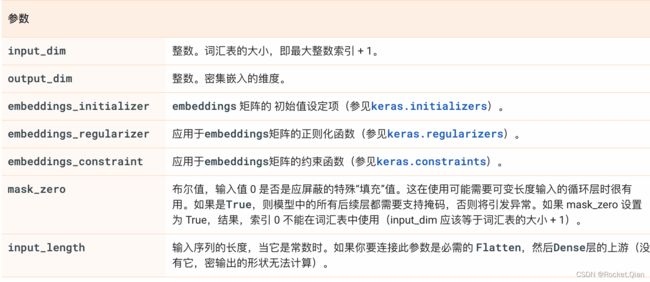
1.5 tf.keras.layers.Embedding
tf.keras.layers.Embedding(
input_dim, output_dim, embeddings_initializer='uniform',
embeddings_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
embeddings_constraint=None, mask_zero=False, input_length=None, **kwargs
)
1.6 tf.keras.layers.Dropout
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(
rate, noise_shape=None, seed=None, **kwargs
)
1.7 tf.keras.callbacks
1.7.1 tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping()
tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss', min_delta=0, patience=0, verbose=0,
mode='auto', baseline=None, restore_best_weights=False
)
1.7.2 tf.keras.callbacks.History()
此回调会自动应用于每个 Keras 模型。该History对象被用返回fit的模型方法。
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)])
model.compile(tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(), loss='mse')
history = model.fit(np.arange(100).reshape(5, 20), np.zeros(5),
epochs=10)
print(history.params)
# check the keys of history object
print(history.history.keys())
2. tf.data
2.1 tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset
tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset(
file_pattern, batch_size, column_names=None, column_defaults=None,
label_name=None, select_columns=None, field_delim=',',
use_quote_delim=True, na_value='', header=True, num_epochs=None,
shuffle=True, shuffle_buffer_size=10000, shuffle_seed=None,
prefetch_buffer_size=None, num_parallel_reads=None, sloppy=False,
num_rows_for_inference=100, compression_type=None, ignore_errors=False
)
dataset 中的每个条目都是一个批次,用一个元组(多个样本,多个标签)表示。样本中的数据组织形式是以列为主的张量(而不是以行为主的张量),每条数据中包含的元素个数就是批次大小。
3. tf.feature_column
3.1 tf.feature_column.indicator_column
3.2 tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity
3.3 tf.feature_column.embedding_column
tf.feature_column.embedding_column(
categorical_column, dimension, combiner='mean', initializer=None,
ckpt_to_load_from=None, tensor_name_in_ckpt=None, max_norm=None, trainable=True,
use_safe_embedding_lookup=True
)