为程序员写的Reed-Solomon码解释
英文原文:Reed–Solomon codes for coders
翻译参照: Felix021
参考:AN2407.pdf
WIKI:里德-所罗门码
实现:Pypi ReedSolo
译注:最近看到了RS码,发现还挺有意思的,找了一些资料学习了下,发现对于程序员来说,从这篇看起会比较容易。看完以后想着翻译一下试试,看看自己到底看懂了多少,于是就有了这篇。本文有部分错误,以及一些排版不对的地方,有兴趣的还是看原文更好:)
Reed-Solomon纠错码(以下简称RS码)广泛用于数据存储(如CD)和传输应用中。然而,在这些应用中,码字是藏在了电子设备里,所以无法一窥它们的模样以及它们是如何生效的。有些复杂的条形码设计也采用了RS码,能够暴露出所有的细节,对于想要获得这种技术如何生效的第一手技术的爱好者,这是一种很有趣的方式。
在这篇文章里,我是试图从程序员的视角(而不是数学家的视角)来介绍RS码的基本原理。我会用以当下流行的QR码作为例子来介绍。我选择了Python(主要是因为写出来的代码看起来整洁美观),但是我也会介绍一些不那么显而易见的Python特性,以便那些不熟悉Python的人也能看懂。里头涉及到的数学知识对读者有一定要求,并且一般是大学才教授的,但是应当能让对高中代数掌握较好的人看懂。
1. QR码结构
这一节详细介绍QR码的结构。本节的信息不完整,这是有意为之,只介绍了一个小的21x21的QR码(也被称为version 1)的常见特征。有关二维码的更多信息,请参考附录(appendix)。
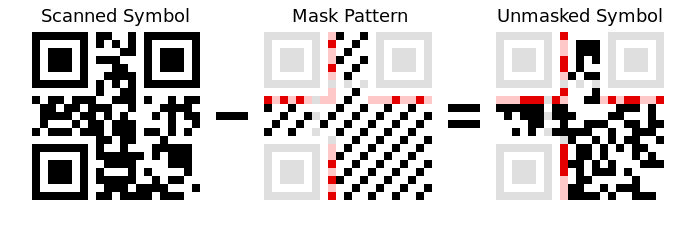
这是一个用于当例子的QR码。它由深色和浅色的方格组成,在条形码领域被称为“模块”(module)。在角落的3个方形定位器模式是QR码的典型可见特征。原图
1.1 掩码
之所以需要掩码处理,是为了避免数据区域中出现诸如类似定位器模式的形状,或者是大片的空白区域等,可能会使扫描器混淆、错乱。掩码处理逆转某些模块(白色变成黑色,黑色变成白色),保留其他模块不变。
参考下面的图示,红色区域使用一个固定的掩码模式编码,保存了数据区域(黑白部分)的掩码格式信息。当QR码被创建的时候,编码器通过尝试,选择使得不期望出现特征出现最少的那个掩码模式。被选择的掩码模式信息会被保存在格式信息(红色区域)中,使得解码器知道该用哪个。浅灰色的区域是不包含任何信息的固定模式。此外,在定位器模式中,还包含由交错的黑白模块组成的标尺(timing patterns 参考解释)。原图
使用异或运算(XOR,eXclusive-or,通常在变成语言中用 ^ 来表示),掩码过程可以很容易地被加载/移除。对格式信息的反掩码操作如下所示。逆时针读取左上角的定位器模式,我们能够得到下面的比特序列,白色表示0,黑色表示1。
-
Input 101101101001011 -
Mask ^ 101010000010010 -
Output 000111101011001
1.2 格式信息
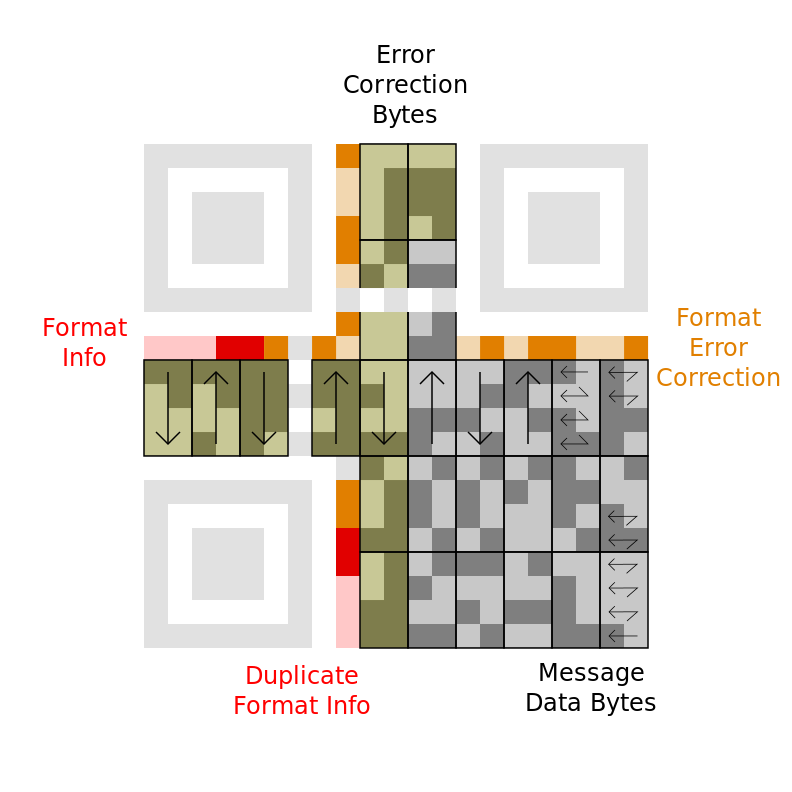
格式信息有另一份可辨别的副本,因此即使其中一份被毁坏,也仍然有机会被识别。副本被分成两个部分,分别放在另外两个定位器的边上,同样也是逆时针方向阅读(沿着左下角定位器往上,然后是右上角定位器边缘从左往右)。
格式信息的前2 bits 给出了用于数据的纠错级别。这个尺寸的QR码包含26字节(bytes,1 byte = 8 bits )信息,其中一些用于保存原数据,一些用于保存校验码,如下表所示。左边第一列只是给纠错级别起了个简单的名字。
| 纠错级别 | 级别指示器 | 纠错码字节数 | 原数据字节数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | 01 | 7 | 19 |
| M | 00 | 10 | 16 |
| Q | 11 | 13 | 13 |
| H | 10 | 17 | 9 |
格式信息中的接下来3 bits用于指定对数据区域使用的掩码模式。模式使用6x6放歌的方式定义,根据需要不断重复以覆盖整个区域。模式如下所示,包含了对应的数学公式指明(掩码中的)每个模块是否是黑色(i和j分别是行列从0开始的编号,从左上角开始算起)原图
格式信息中剩下的10 bits 是用于对格式信息本身的错误校验,会在后续章节中解释。
1.3 数据
下图展示了经过反掩码操作后的放大了的图样。不同的区域被标记出来了,包括数据区域的边缘。原图
数据比特从右下角开始,沿着最右边的两列向上走“之”字形。前三个字节分别是 01000000 11010010 01110101(译注:可参见图中右下角的小箭头)。接下来两列从上向下读取,因此接下来的字节是 01000111 。当读取到底部后,再反过来从下往上读取接下来两列……按照这种方式一直读到最左边的列(如果有必要,跳过timing pattern)。下面是完整的十六进制表示的数据:
原始信息: 40 d2 75 47 76 17 32 06 27 26 96 c6 c6 96 70 ec
错误纠正: bc 2a 90 13 6b af ef fd 4b e0
1.4 解码
最后的步骤是将信息解码成可读格式。前4 bits 指明了信息是如何编码的。QR码使用几种不同的编码方案,使得不同类型的信息可以更高效地被存储,可参见下表的总结。在方案指示器之后是“长度”字段,告诉解码器保存了多少个字符。字符的长度取决于指定的编码方案。
| 方案名称 | 模式指示器 | 长度字节数 | 数据字节数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 数字 | 0001 | 10 | 10 bits per 3 digits |
| 字母数字 | 0010 | 9 | 11 bits per 2 characters |
| 字节 | 0100 | 8 | 8 bits per character |
| 汉字 | 1000 | 8 | 13 bits per character |
长度字节数只对小的QR码有效
我们的样例数据开头是 0100 ,表明接下来是每个字符8 bits 。接下来8 bits 是长度字段,00001101(10进制的13),表明有13个字符。之后才是数据字符。前两个是00100111和01010100(对于ASCII字符 ' 和 T)。有兴趣的读者可以自行解码后续的字符。(译注:用微信二维码扫扫就行了。。。)
在数据 bit 之后是另外一个4 bit 模式指示器,可以跟前一个不同,从而允许在一个QR码中混合多个编码方案。如果没有其他数据了,用 0000 来标记结尾(注意,标准允许忽略这个标记,如果存储空间不够的话)。
2. BCH码
格式信息是用BCH码编码的,能够纠正一定数量的 bit 错误。BCH码是RS码的普遍形式(所有的RS码都是BCH码)。在QR二维码中,BCH码只用于格式信息,比数据信息中用到的RS码要简单得多,因此我们可以先从这里开始。
2.1 BCH错误检测
用于检测编码信息的过程类似整数除法,但是使用异或来代替减法。格式串应该能够被称为“生成子”(generator)的码“整除”。QR码使用 10100110111 这个生成子。下面使用前述格式串 000111101011001 演示了这个过程:
-
00011 -
----------------- -
10100110111 ) 000111101011001 -
^ 10100110111 -
--------------- -
010100110111 -
^ 10100110111 -
------------- -
00000000000
下面这个Python函数实现了这个过程
-
def qr_check_format(fmt): -
g = 0x537 # = 0b10100110111 in python 2.6+ -
for i in range(4,-1,-1): -
if fmt & (1 << (i+10)): # 判断是否为1 -
fmt ^= g << i -
return fmt
Python注记1:range函数可能对于非python程序猿来说不够明确。它产生一个数字序列 [4, 3, 2, 1, 0]。源于C的语言中,它类似于 for (i = 4; i >= 0; i--); 在pascal类语言中则类似于 for i := 4 downto 0 。
Python注记2:&操作符是“按位与”,<<操作符是左移位,与C类语言一致。
译注:这个函数的返回值是参数 fmt 除以生成子的余数
这个函数也可以被用于编码 5-bit 的格式信息:
-
encoded_format = (format<<10) ^ qr_check_format(format<<10)
译注:由于format左移了10个bit,因此这里用 ^ 和用 + 是等价的。实际上因为这里的 + 是按位加(其实也就是异或了),所以它也等同于 - ,这一点对于理解它很重要。如果记格式信息为F,生成子为G,(F<<10)/G的商为Q、余数为R (即F<<10 == QG + R),则最终的编码信息 C = (F << 10) ^ ((F << 10) mod G) = (QG + R) - R = Q*G,从而C应当是能够被G整除的。如果收到的C不能被G整除,说明传输出错了。
读者也许会对修改此函数让它能除以不同数字感兴趣。例如,更大些的QR码包含6 bits的版本信息和12个错误校验码,并使用生成子 1111100100101 。
使用数学的规范格式,这些二进制数字可以用一个系数为"整数模2"(译注:参考链接第三段内容理解)的多项式来描述。数字中的每一个 bit 是多项式中对应一项的系数(译注:该项的幂等于该bit在数字中的位置)。例如:
-
10100110111 = 1 x^10 + 0 x^9 + 1 x^8 + 0 x^7 + 0 x^6 + 1 x^5 -
+ 1 x^4 + 0 x^3 + 1 x^2 + 1 x^1 + 1 -
= x^10 + x^8 + x^5 + x^4 + x^2 + x^1 + 1
2.2 BCH纠错
如果qr_check_format(fmt)得到的余数不是0,那么这个码被损坏或者是读取错误了(译注:即使是0也不能100%保证就对了)。下一步是要找出哪一个格式码最可能是原数据。虽然对于BCH码有许多复杂的解码算法,但是在这里杀鸡用不上牛刀。因为总共只有32个格式串(译注:15 bits 中前5个是原信息,后10个是根据原信息生成的),因此遍历找出所有码字中与fmt不同位数最小的那个会更简单(这个被称为汉明距离, hamming distance)
-
def hamming_weight(x): #不同bit的数量 -
weight = 0 -
while x > 0: -
weight += x & 1 -
x >>= 1 -
return weight -
def qr_decode_format(fmt): -
best_fmt = -1 -
best_dist = 15 -
for test_fmt in range(0,32): -
test_code = (test_fmt<<10) ^ qr_check_format(test_fmt<<10) -
test_dist = hamming_weight(fmt ^ test_code) -
if test_dist < best_dist: -
best_dist = test_dist -
best_fmt = test_fmt -
elif test_dist == best_dist: #如多个码字与fmt距离相同,则都不选 -
best_fmt = -1 -
return best_fmt
如果发现fmt不能被唯一地解码,则函数qr_decode_format返回-1。这种情况是由于有多个码字与fmt具有相同的距离。
-
>>> print(qr_decode_format(int("000111101011001",2))) # no errors -
3 -
>>> print(qr_decode_format(int("111111101011001",2))) # 3 bit-errors -
3 -
>>> print(qr_decode_format(int("111011101011001",2))) # 4 bit-errors -
-1
3. 有限域理论
在讲解用于编码数据的RS码之前,还需要介绍一点数学。类似于乘法和除法,我们定义两个对应的操作,应用于 8-bit 字节(译注:这里应该指的是整数,下同),且其结果也是 8-bit 字节。许多类似的算术规则对于新的定义也仍然有效,例如,任意元素乘以1(幺元)结果不变,任意元素乘以0(零元)得0,不允许除以0。其他有用的数学属性(例如分布率)也仍然有效。(基于这些操作的元素集合)被称为一个有限域(finite field),或者叫伽罗华域(Galois field)。更多关于GF(2^w)的意义
3.1 乘法
乘法是基于上面定义的多项式。以多项式的形式把输入写下来,然后像我们熟悉的那样,用乘法分配率来计算。我们用 10001001 x 00101010 来举例:
(x^7 + x^3 + 1) * (x^5 + x^3 + x^1)= x^7 * (x^5 + x^3 + x^) + x^3 * (x^5 + x^3 + x^1) + 1 * (x^5 + x^3 + x^1)= x^12 + x^10 + x^6 + x^5 + x^4 + x^3 + x^1
译注:由于最后的加法是异或(模2加),因此系数为偶数的项都消去了。
相同的结果也可以通过竖式计算的一个修改版得到,只要把其中的加改成异或即可:
-
10001001 -
* 00101010 -
------------- -
10001001 -
^ 10001001 -
^ 10001001 -
------------- -
1010001111010
下面这个Python函数实现了这个多项式乘法。
-
def poly_mult(x,y): -
z = 0 -
i = 0 -
while (y>>i) > 0: -
if y & (1< -
z ^= x< -
i += 1 -
return z
当然,由于结果不能用8-bit来表示了(在这个例子里结果是13 bits ),所以我们在得到最终结果之前还需要一个步骤:模100011101,使用前面提到的除法过程。在本例中,最终的结果是 11000011。
上述的乘法运算也可以直接用100011101进行异或运算:
-
1010001111010 -
^ 100011101 -
---------------- -
0010110101010 -
^ 100011101 -
---------------- -
00111011110 -
^ 100011101 -
--------------- -
011000011
下面的python代码用来实现上述等效乘法的异或运算:
-
def gf_mult_noLUT(x, y, prim=0): -
#GF域乘法,无预算查询表(precomputed look-up table)辅助,速度较慢 -
#通过使用标准的无进位乘法和不可约多项式规约实现 -
def cl_mult(x,y): -
'''二进制无进位整数乘法''' -
z = 0 -
i = 0 -
while (y>>i) > 0: -
if y & (1< -
z ^= x< -
i += 1 -
return z -
def bit_length(n): -
# 计算整数最高有效位(整数二进制格式第一位). 等效于 int.bit_length() -
bits = 0 -
while n >> bits: bits += 1 -
return bits -
def cl_div(dividend, divisor=None): -
'''二进制无进位整数除法,返回余数''' -
dl1 = bit_length(dividend) -
dl2 = bit_length(divisor) -
# 余数<除数 -
if dl1 < dl2: -
return dividend -
# 余数>=除数, 通过移位对齐除数与余数的最高有效位 -
for i in range(dl1-dl2,-1,-1): -
# 检查余数是否可除(为下一次循环铺垫) -
if dividend & (1 << i+dl2-1): -
# 可除,则对齐最高有效位并执行异或运算(无进位减法) -
dividend ^= divisor << i -
return dividend -
### 调用GF域乘法 ### -
result = cl_mult(x,y) -
# 用不可约多项式规约,保证结果仍然在GF域内 -
if prim > 0: -
result = cl_div(result, prim) -
return result
测试结果:
-
>>> a = 0b10001001 -
>>> b = 0b00101010 -
>>> print(bin(gf_mult_noLUT(a, b, 0))) # multiplication only -
0b1010001111010 -
>>> print(bin(gf_mult_noLUT(a, b, 0x11d))) # multiplication + modular reduction -
0b11000011
至于为什么要用100011101作为约数进行规约(reduction),其数学原理较为复杂,简单来说,100011101所代表的GF(2^8)多项式是一个“不可约(irreducible)”多项式,也叫“本原多项式”。100011101(0x11d)是Reed-Solomon (RS)码中常用的本原多项式。
译注:从概念上讲,本原多项式和不可约多项式并不等价,但在本文适用的范畴内是可以等价理解的,而且完全可以和整数中的素数做类比来理解,只不过这个是在多项式的范畴内。
上面的乘法代码效率较差,下面是不同算法实现的更高效率的版本:
-
def gf_mult_noLUT(x, y, prim=0, field_charac_full=256, carryless=True): -
'''采用 Russian Peasant 算法实现GF域整数乘法 (主要使用位运算, 比上面的方法快). -
当设定参数prim = 0 且 carryless=False 时, 返回普通整数乘法(进位乘法)计算结果.''' -
r = 0 -
while y: # y > 0 -
if y & 1: r = r ^ x if carryless else r + x #原文有注释, 似懂非懂, 译不了, 同样的情况后面用*****表示 -
y = y >> 1 # 等价于 y // 2 -
x = x << 1 # 等价于 x*2 -
if prim > 0 and x & field_charac_full: x = x ^ prim #***** -
return r
3.2 基于对数的乘法
上述过程并不是最适合用来计算伽罗华域乘法的方法。对两个数进行乘法的过程需要8次循环,除法的过程也需要8次循环,然而我们实际上可以通过使用查表的方式来避免循环。一个科学的结果是在内存中建立完整的乘法表,但是那需要创建64k大小的表格(译注:256×256)。下面给出的结果要简洁许多。
首先,注意到使用00000010(=2)来进行乘法是相当简单的(通常把它记为α或 generator number ),只需要向左移1位,然后与100011101进行异或操作(如果有必要)。下面是α的前几次幂:
α^0 = 00000001 α^4 = 00010000 α^8 = 00011101 α^12 = 11001101
α^1 = 00000010 α^5 = 00100000 α^9 = 00111010 α^13 = 10000111
α^2 = 00000100 α^6 = 01000000 α^10 = 01110100 α^14 = 00010011
α^3 = 00001000 α^7 = 10000000 α^11 = 11101000 α^15 = 00100110
译注: α^7 * α超过了8-bit,需要与100011101异或得到α^8,依此类推。
如果这个表格依次类推,α的i次幂不会重复,直到α^255=00000001。由此,这个域中的每个元素,除了0之外,都是α的某次幂。α被称为伽罗华域的本原元素(primitive element)或者生成子(generator)。
仔细观察,可以发现另一种实现乘法的方法:把α的幂加起来。
10001001 * 00101010 = α^74 * α^142 = α^74 + 142 = α^216 = 11000011
问题是,我们怎么计算10001001是α的几次幂呢?这个问题被称为离散对数(discrete logarithm),目前没有已知的高效解法。然而,因为域中只有256个元素,我们可以很容易地建立起一个指数表;而同时,对应的对数表也也有用。
-
gf_exp = [0] * 512 #512个元素的列表. Python 2.6+可以考虑使用bytearray类型 -
gf_log = [0] * 256 -
def init_tables(prim=0x11d): -
#使用参数prim给的本原多项式计算指数表和对数表备用 -
global gf_exp, gf_log -
gf_exp = [0] * 512 # anti-log (exponential指数) table -
gf_log = [0] * 256 # log(对数) table -
# 计算每一个GF(2^8)域内正整数的指数和对数 -
x = 1 -
for i in range(0, 255): -
gf_exp[i] = x # 存储指数表 -
gf_log[x] = i # 存储对数表 -
# 更一般的情况用下面这行,不过速度较慢 -
#x = gf_mult_noLUT(x, 2, prim) -
# 只用到 generator==2 或指数底为 2的情况下,用下面的代码速度快过上面的 gf_mult_noLUT(): -
x <<= 1 -
if x & 0x100: # 等效于 x >= 256, 但要更快些 (because 0x100 == 256,位运算速度优势) -
x ^= prim # substract the primary polynomial to the current value (instead of 255, so that we get a unique set made of coprime numbers), this is the core of the tables generation -
# Optimization: 双倍指数表大小可以省去为了不出界而取模255的运算 (因为主要用这个表来计算GF域乘法,仅此而已). -
for i in range(255, 512): -
gf_exp[i] = gf_exp[i - 255] -
return [gf_log, gf_exp]
表gf_exp的冗余(实际只需要256,但是重复了一遍)是为了简化乘法。这样我们就不用保证gf_log[x]和gf_log[y]会超出表的范围。
-
def gf_mul(x,y): -
if x==0 or y==0: -
return 0 -
return gf_exp[gf_log[x] + gf_log[y]] # should be gf_exp[(gf_log[x]+gf_log[y])%255] if gf_exp wasn't oversized
3.3 除法
实现对数表的另一个好处是可以使用幂的差来定义除法。在下面的代码里,加上255是为了保证差不是负数。
-
def gf_div(x,y): -
if y==0: -
raise ZeroDivisionError() -
if x==0: -
return 0 -
return gf_exp[(gf_log[x] + 255 - gf_log[y]) % 255]
Python注记:raise语句抛出一个异常从而终止gf_div函数的执行。
使用这种方式来实现除法,对于任意x和非0元素y,gf_div(gf_mul(x, y), y) == x。
3.4 指数运算和逆运算
对数表的方法同时还可以简化并加速指数运算和逆运算:
-
def gf_pow(x, power): -
return gf_exp[(gf_log[x] * power) % 255] -
def gf_inverse(x): -
return gf_exp[255 - gf_log[x]] # gf_inverse(x) == gf_div(1, x)
3.5 多项式
继续介绍RS码之前,我们需要定义一些伽罗华域多项式(系数属于伽罗华域)的操作。这可能会带来一点混淆,因为伽罗华域的元素本身也是多项式(译注:是系数仅为0、1的多项式)。我的建议是不要想太多。更混乱的是,x也被用来当作占位符(多项式里的未知数)。这个x和前面提到的多项式的x没有任何关系,因此别把它们混起来。
前面给出的伽罗华域元素的二进制表示发在这里用起来会很罗嗦,因此我换成十六进制。
00000001 x^4 + 00001111 x^3 + 00110110 x^2 + 01111000 x^1 + 01000000= 01 x^4 + 0f x^3 + 36 x^2 + 78 x^1 + 40
在Python里,多项式可以按x的幂递减的list来表示,list中的元素是对于项的系数,从而上述多项式变成了[0x01, 0x0f, 0x36, 0x78, 0x40]。(实现中也可以用反过来的顺序,各有优劣。)
第一个函数将一个多项式和一个标量相乘:
-
def gf_poly_scale(p,x): -
r = [0] * len(p) -
for i in range(0, len(p)): -
r[i] = gf_mul(p[i], x) -
return r
Python程序员注意:这个函数不是用Pythonic的方式实现的,它可以用列表推导式(list comprehension)更优雅地实现(译注:指的是可以用return [gf_mul(i, x) for i in p] 来实现)。但是我限制使用这些语言特性以便它可以更方便地被转换成其他语言。
这个函数将两个多项式"加"起来(照旧使用异或操作)
-
def gf_poly_add(p,q): -
r = [0] * max(len(p),len(q)) -
for i in range(0,len(p)): -
r[i+len(r)-len(p)] = p[i] -
for i in range(0,len(q)): -
r[i+len(r)-len(q)] ^= q[i] -
return r
下一个函数将两个多项式乘起来:
-
def gf_poly_mul(p,q): -
r = [0] * (len(p)+len(q)-1) -
for j in range(0, len(q)): -
for i in range(0, len(p)): -
r[i+j] ^= gf_mul(p[i], q[j]) -
return r
最后,我们需要对一个多项式求值,给定某个x值,求出其标量结果。我们引入秦九韶算法(Horner Scheme, 霍纳算法,中国人很牛逼有没有!)来避免计算x的n次幂:
01 x^4 + 0f x^3 + 36 x^2 + 78 x^1 + 40= (((01 x^ + 0f) x^ + 36) x^ + 78) x^ + 40
-
def gf_poly_eval(p,x): -
y = p[0] -
for i in range(1, len(p)): -
y = gf_mul(y,x) ^ p[i] -
return y
还剩一个相对复杂的多项式除法没有讲到,留待下一节与RS码一块讲。
4 RS码
好了,背景知识都介绍完了,我们可以开始看看RS码了。 *译注吐槽:终于进入重点了。
4.1 洞察编码原理
前面费了这么大的篇幅介绍有限域和多项式,是因为它们是纠错编码技术的基础。通过有限域和多项式的算法,我们给数据添加了一种结构。尽管信息不变,但是数据的结构化允许我们通过定义其上的规则操作数据,这种独立于数据的结构让我们可以通过它来恢复损坏的数据。
4.2 编码
4.2.1 简介
类似于BCH编码,RS码通过生成(irreducible generator)和分解(dividing)多项式来表达信息,分解余下的多项式(remainder)就是RS码,最后我们将RS码附加在原信息后。
BCH编码乃至其它大多数的纠错码编码原则是:采用有限的字典(limited dictionary)存储差异最大的信息元,越长的信息元差异往往越大。在上述RS编码方式中,我们通过将RS码后缀在原信息码后面的方式,加长了原码长;而RS码基本是独一无二的,通过巧妙的算法,可以用RS码来推断原信息。
通俗的讲,类比加密的过程,生成多项式(generator polynomial)就是我们编码用的字典,而用它除原信息多项式的运算就是我们加密(RS编码)的过程。
4.2.2 错误处理(同python,略)
4.2.3 RS生成多项式
RS码使用类似BCH码的生成多项式,将 (x - α^n) 乘起来。例如:
g(x) = (x - α^0) (x - α^1) (x - α^2) (x - α^3) = 01 x^4 + 0f x^3 + 36 x^2 + 78 x^1 + 40
下面这个函数计算对于给定数量nsym个校验符号的RS码需要的生成多项式:
-
def rs_generator_poly(nsym): -
g = [1] -
for i in range(0,nsym): -
# g = gf_poly_mul(g, [1, gf_pow(2, i)]) # 指数运算,跟下面等效 -
g = gf_poly_mul(g, [1, gf_exp[i]]) -
return g
这个函数不是很高效,因为它在每次循环中陆续分配了更大的数组给g;但是在实际应用中它并不是瓶颈,优化癖读者有兴趣的话可以重写它,让它只给g分配一次。
4.2.4 多项式除法
现成的多项式除法算法中,最简单的是类似整数除法的算法。下面的例子展示了数据 12 34 56 (注记:这是16进制表示的)是如何被编码的:
-
12 da df -
--------------------- -
01 0f 36 78 40 ) 12 34 56 00 00 00 00 -
^ 12 ee 2b 23 f4 -
---------------- -
da 7d 23 f4 00 -
^ da a2 85 79 84 -
----------------- -
df a6 8d 84 00 -
^ df 91 6b fc d9 -
---------------- -
37 e6 78 d9
余数和原数据连起来得到编码后的数据 12 34 56 37 e6 78 d9。这种整数除法由于算法实现中需要用的很多的规约循环导致算法效率低下。综合除法(synthetic division)是一种更高效的算法。下面的代码是该算法对GF(2^p)多项式的一个扩展实现:
-
def gf_poly_div(dividend, divisor): -
'''适用于GF(2^p)域的快速多项式除法.''' -
# 注意: 多项式系数需要按幂次由高到低排序. 例如: 1 + 2x + 5x^2 = [5, 2, 1], 而非 [1, 2, 5] -
msg_out = list(dividend) # 复制被除数(尾部后缀ecc字节, 用0填充) -
#normalizer = divisor[0] # precomputing for performance -
for i in range(0, len(dividend) - (len(divisor)-1)): -
#msg_out[i] /= normalizer -
coef = msg_out[i] -
if coef != 0: # 避免log(0)未定义错误. -
for j in range(1, len(divisor)): # 因为多项式的首位都是1, (1^1==0)所以可以跳过 -
if divisor[j] != 0: # log(0) is undefined -
msg_out[i + j] ^= gf_mul(divisor[j], coef) # 等价于数学表达式:msg_out[i + j] += -divisor[j] * coef ,但异或运高效 -
# msg_out 包含商和余数, 余数的最高幂次( == length-1)和除数一样, 下面计算分断点. -
separator = -(len(divisor)-1) -
return msg_out[:separator], msg_out[separator:] # 返回商, 余数.
4.2.5 编码函数
下面的这个函数实现了编码过程(译注:可以参考2.1的BCH编码过程 (fmt<<10) ^ qr_check_format(fmt << 10),那里有个译注解释为什么这么编码):
-
def rs_encode_msg(msg_in, nsym): -
'''Reed-Solomon main encoding function''' -
gen = rs_generator_poly(nsym) -
# 后缀ecc字节位用0填充, 之后用生成子(irreducible generator polynomial)除 -
_, remainder = gf_poly_div(msg_in + [0] * (len(gen)-1), gen) -
# 余数就是 RS 码! 后缀到原信息之后形成全部编码 -
msg_out = msg_in + remainder -
# Return the codeword -
return msg_out
简单吧!事实上,RS编码流程中,最后的编码是最简单的步骤,它只是一个多项式除法运算。而解码才是RS码中最难的步骤,因为根据你需要的不同,你能找到很多种不同的算法来实现。(译注:选择恐惧症怕怕!!!)解码的部分我们以后再讲。将之前的多项式综合除法的代码和上面的编码函数内联在一起,得到的下面的代码就是在很多RS编码软件库中你将看到的样子:
-
def rs_encode_msg(msg_in, nsym): -
'''Reed-Solomon main encoding function, using polynomial division (algorithm Extended Synthetic Division)''' -
if (len(msg_in) + nsym) > 255: raise ValueError("Message is too long (%i when max is 255)" % (len(msg_in)+nsym)) -
gen = rs_generator_poly(nsym) -
# 用msg_in值初始化 msg_out 并后缀ecc字节, 用0填充. -
msg_out = [0] * (len(msg_in) + len(gen)-1) -
msg_out[:len(msg_in)] = msg_in -
# Synthetic division main loop -
for i in range(len(msg_in)): -
coef = msg_out[i] -
if coef != 0: # 避免log(0) 未定义错误 -
for j in range(1, len(gen)): # 因为多项式的首位都是1, (1^1==0)所以可以跳过 -
msg_out[i+j] ^= gf_mul(gen[j], coef) # equivalent to msg_out[i+j] += gf_mul(gen[j], coef) -
# 除完之后, msg_out 包含商 msg_out[:len(msg_in)],余数 msg_out[len(msg_in):]. -
#RS码只用到余数, 所以我们用原信息覆盖商得到完整编码. -
msg_out[:len(msg_in)] = msg_in -
return msg_out
下面这个例子演示了编码函数如何对第一节的样例QR码中的数据进行编码。它计算出的结果中的第二行(译注:输出的第二行)与样例QR码中解码出来的纠错码相符
-
>>> gf_exp = [0] * 512; gf_log = [0] * 256; -
>>> init_tables(); -
>>> msg_in = [ 0x40, 0xd2, 0x75, 0x47, 0x76, 0x17, 0x32, 0x06, -
... 0x27, 0x26, 0x96, 0xc6, 0xc6, 0x96, 0x70, 0xec ] -
>>> msg = rs_encode_msg(msg_in, 10) -
>>> for i in range(0,len(msg)): -
... print(hex(msg[i]), end=' ') -
... -
0x40 0xd2 0x75 0x47 0x76 0x17 0x32 0x6 0x27 0x26 0x96 0xc6 0xc6 -
0x96 0x70 0xec0xbc 0x2a 0x90 0x13 0x6b 0xaf 0xef 0xfd 0x4b 0xe0
Python版本注记:这是Python 3.0+的例子,因为print的语法变了。早版本的Python可以用这句来代替:“print hex(msg[i]), ” (包含末尾的逗号)
4.3 解码
4.3.1 简介
RS解码是从可能损毁的经过RS编码处理的信息中还原信息的过程。
尽管RS编码的过程是不变的,但是却有多种解码方法,相应的就有多种解码算法。
RS解码流程大致可以分为5个步骤:
- 计算伴随式(syndromes polynomial). 这个方法需要我们通过Berlekamp-Massey等算法分析哪些字符是错误的,或者快速判断输入的信息是否完全损坏。
- 由伴随式计算错误定位式(erasure/error locator polynomial). 用Berlekamp-Massey算法探测哪些字符损毁。
- 由前两式计算错误判别式(evaluator polynomial). 判断有多少字符被篡改的必要步骤。
- 由前三式计算错误等级式(magnitude polynomial). 这个式子保存了有哪些值需要从原信息中减去,所以也叫损毁式。换个角度讲,在这一步我们提取错误的信息保存到这个式子中。
- 修复输入信息. 通过将原输入信息中的错误信息减去来完成修复。
下面我们分步骤讲解。
4.3.2 伴随式(Syndrome)计算
(译注:这个要怎么翻译啊。。Syndrome是症状的意思,这里的确也是在计算收到的RS码码字的症状,从而判断是否接受到了错误的码字。)(译注:后来看了各种文档以后,得知一般都翻译为“伴随式”)
RS码的译码操作需要多个步骤。第一个步骤就是计算数据的伴随式。把数据当成一个多项式,使用x = α^0, α^1, α^2, ..., α^n对其求值(译注:得到n个伴随式的值)。因为这些x值使得生成多项式的值为0,因此如果读取到的数据没有损坏,结果应当是0。如果不是,这些伴随式里就包含了完成纠错所必需的信息。计算伴随式的实现很简单:
-
def rs_calc_syndromes(msg, nsym): -
'''给定原信息和纠错标记数,计算伴随式 -
从数学角度看,这个过程就是一个傅里叶变换 (Chien搜索刚好相反). -
''' -
synd = [0] * nsym -
for i in range(0, nsym): -
synd[i] = gf_poly_eval(msg, gf_pow(2,i)) -
return [0] + synd # pad with one 0 for mathematical precision (else we can end up with weird calculations sometimes)
继续上面的例子,我们可以看到(编码后的)数据的伴随式的确都是0;而引入一个错误以后就会得到非零伴随式。
-
>>> synd = rs_calc_syndromes(msg, 10) -
>>> print(synd)[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] -
>>> msg[0] = 0 # deliberately damage the message -
>>> synd = rs_calc_syndromes(msg, 10) -
>>> print(synd) -
[64, 192, 93, 231, 52, 92, 228, 49, 83, 245]
下面的代码用来自动检查信息是否有误:
-
def rs_check(msg, nsym): -
'''Returns true if the message + ecc has no error, false otherwise ''' -
return ( max(rs_calc_syndromes(msg, nsym)) == 0 )
=== 译注开始 ===
收到的数据 r(x) 是由编码后的数据(RS码的码字) c(x) 和错误 e(x) 组合得到的:
r(x) = c(x) + e(x)
记v=nsym由于c(x)在α^0, α^1, α^2, ..., α^(v-1)都是生成多项式的根(去看生成多项式的定义就知道了,注意+实际上也是-),而c(x)能够表示为 q(x) * g(x) (不明白的话可以参看2.1节的译注),所以这里对c(x)求值的结果必然都是0。
如果对r(x)的求值都是0,说明e(x)也都是0,说明要么是没问题,要么就是错到根本发现不出来(正好是另一个码字)。如果r(x)不等于0,那么伴随式S正好就是所有e(x)的值:
S[0] = e(1), S[1] = e(α^1), S[2] = e(α^2), ..., S[v-1] = e(α^(v-1))
如果错误的码字个数不超过v/2,通过S是可以还原信息的。
=== 译注结束 ===
4.3.3 消除(erasure)纠正
如果错误的位置是已知的(译注:某些信道可以预知,比如BEC信道,wiki这么说的,我也不知道是啥;不过QR码是另一个例子),纠正它是最简单的。这被称为消除纠正。对于每一个添加的纠错码,都可以纠正一个消除(译注:这里应该是说,添加的n个纠错码能够保证纠正n个消除码字)。如果错误位置未知,那么对于一个错误,需要2个错误校验符号。这在实际应用中非常有用,比如QR码的某些位置被覆盖或被剪掉什么的。扫描器很难知道发生了什么,所以不是所有的QR码扫描器都能纠正消除。
有了伴随式,接下来计算定位式:
-
def rs_find_errata_locator(e_pos): -
'''误码定位 -
eg:"_"为误码,"h_ll_ worldxxxxxxxxx"中误码位置应为: n-1 - [1, 4] = [18, 15] = erasures_loc.''' -
e_loc = [1] # 初始化为1而非0是因为要计算乘法 -
# erasures_loc = product(1 - x*alpha**i) for i in erasures_pos and where alpha is the alpha chosen to evaluate polynomials. -
for i in e_pos: -
e_loc = gf_poly_mul( e_loc, gf_poly_add([1], [gf_pow(2, i), 0]) ) -
return e_loc
接下来计算错误判别式(erasure/error evaluator polynomial),通过一个多项式乘法而后一个多项式除法来实现:
-
def rs_find_error_evaluator(synd, err_loc, nsym): -
'''Compute the error (or erasures if you supply sigma=erasures locator polynomial, or errata) evaluator polynomial Omega -
from the syndrome and the error/erasures/errata locator Sigma.''' -
# Omega(x) = [ Synd(x) * Error_loc(x) ] mod x^(n-k+1) -
_, remainder = gf_poly_div( gf_poly_mul(synd, err_loc), ([1] + [0]*(nsym+1)) ) # 除法运算只是为了截短 -
# Faster way that is equivalent -
#remainder = gf_poly_mul(synd, err_loc) # 乘法 -
#remainder = remainder[len(remainder)-(nsym+1):] # 截短 -
return remainder
最后,Forney算法实现第4步,下面的函数包含了该算法,实现纠正消除:
-
def rs_correct_errata(msg_in, synd, err_pos): # err_pos is a list of the positions of the errors/erasures/errata -
'''Forney algorithm, computes the values (error magnitude) to correct the input message.''' -
# 结合前面的定位结果进行错误判别(errata locator polynomial) -
coef_pos = [len(msg_in) - 1 - p for p in err_pos] # 位置换算为多项式系数 (eg: 由 [0, 1, 2] 换算为 [len(msg)-1, len(msg)-2, len(msg) -3]) -
err_loc = rs_find_errata_locator(coef_pos) -
# 计算 errata evaluator polynomial (术语叫 Omega 或 Gamma) -
err_eval = rs_find_error_evaluator(synd[::-1], err_loc, len(err_loc)-1)[::-1] -
# Chien 算法搜索 err_pos 得到误码位置 X (the roots of the error locator polynomial, ie, where it evaluates to 0) -
X = [] # will store the position of the errors -
for i in range(0, len(coef_pos)): -
l = 255 - coef_pos[i] -
X.append( gf_pow(2, -l) ) -
# Forney algorithm: compute the magnitudes -
E = [0] * (len(msg_in)) # 用来保存误码数据. This is sometimes called the error magnitude polynomial. -
Xlength = len(X) -
for i, Xi in enumerate(X): -
Xi_inv = gf_inverse(Xi) -
# 用errata locator的形式导数(formal derivative)作为Forney算法的分母(denominator), 则第i个error值为: error_evaluator(gf_inverse(Xi)) / error_locator_derivative(gf_inverse(Xi)). -
err_loc_prime_tmp = [] -
for j in range(0, Xlength): -
if j != i: -
err_loc_prime_tmp.append( gf_sub(1, gf_mul(Xi_inv, X[j])) ) -
# 下面的乘法计算Forney算法所需的分母 (errata locator derivative) -
err_loc_prime = 1 -
for coef in err_loc_prime_tmp: -
err_loc_prime = gf_mul(err_loc_prime, coef) -
# 等价于: err_loc_prime = functools.reduce(gf_mul, err_loc_prime_tmp, 1) -
# Compute y (evaluation of the errata evaluator polynomial) -
# 更直白的Forney算法实现: -
# Yl = omega(Xl.inverse()) / prod(1 - Xj*Xl.inverse()) for j in len(X) -
y = gf_poly_eval(err_eval[::-1], Xi_inv) # Forney 算法的分子 -
y = gf_mul(gf_pow(Xi, 1), y) -
# Compute the magnitude -
magnitude = gf_div(y, err_loc_prime) # magnitude value of the error, calculated by the Forney algorithm -
E[err_pos[i]] = magnitude # store the magnitude for this error into the magnitude polynomial -
# 纠正误码! (纠错码也会被修正!) -
# (这里并不是Forney 算法, 只是直接套用了解码结果) -
msg_in = gf_poly_add(msg_in, E) # 等价于Ci = Ri - Ei ; Ci 为正确信息, Ri 为包含错误的信息, Ei 为修正量表(errata magnitudes) . -
return msg_in
Python注记:这个函数使用[::-1]来反转列表元素的顺序。
译注:这个算法我没去看,有兴趣的读者可以看本文提到的另一篇讲解AN2407.pdf。
代码测试如下:
-
>>> msg[0] = 0 -
>>> synd = rs_calc_syndromes(msg, 10) -
>>> rs_correct_errata(msg, synd, [0]) # [0] is the list of the erasures locations, here it's the first character, at position 0 -
>>> print(hex(msg[0])) -
0x40
4.3.4 错误(error)纠正
更可能的情况是未知位置的错误,所以第一步是找出它们。Berlekamp-Massey算法(通常简称为BM算法)用来计算错误定位多项式。然后我们只需要计算这个(错误定位)多项式的零点(译注:应该就是指多项式的根),这标志了错误的位置。
-
def rs_find_error_locator(synd, nsym, erase_loc=None, erase_count=0): -
'''Find error/errata locator and evaluator polynomials with Berlekamp-Massey algorithm''' -
# 使用BM算法迭代计算error locator polynomial.计算差异项 Delta, 由此判断是否更新 error locator polynomial. -
# Init the polynomials -
if erase_loc: -
err_loc = list(erase_loc) -
old_loc = list(erase_loc) -
else: -
err_loc = [1] # Sigma(errors/errata locator polynomial) . -
old_loc = [1] # BM 是一个迭代算法,需要对比新旧值(Sigma)来判断哪些变量需要更新。 -
synd_shift = 0 -
if len(synd) > nsym: synd_shift = len(synd) - nsym -
for i in range(0, nsym-erase_count): -
if erase_loc: # if an erasures locator polynomial was provided to init the errors locator polynomial, then we must skip the FIRST erase_count iterations (not the last iterations, this is very important!) -
K = erase_count+i+synd_shift -
else: # if erasures locator is not provided, then either there's no erasures to account or we use the Forney syndromes, so we don't need to use erase_count nor erase_loc (the erasures have been trimmed out of the Forney syndromes). -
K = i+synd_shift -
# Compute the discrepancy Delta -
# 计算 Delta: error locator和 the syndromes进行多项式乘法运算。 -
#delta = gf_poly_mul(err_loc[::-1], synd)[K] # 严格的讲应该是 gf_poly_add(synd[::-1], [1])[::-1] , 但对于正确解码而言并不必要. -
# 而且同时还能优化效率: 我们只计算第K项的多项式乘法. 避免套嵌循环. -
delta = synd[K] -
for j in range(1, len(err_loc)): -
delta ^= gf_mul(err_loc[-(j+1)], synd[K - j]) . -
#print("delta", K, delta, list(gf_poly_mul(err_loc[::-1], synd))) # debugline -
# Shift polynomials to compute the next degree -
old_loc = old_loc + [0] -
# 计算 the errata locator and evaluator polynomials -
if delta != 0: # delta非0才更新 -
if len(old_loc) > len(err_loc): -
# 计算 Sigma(errata locator polynomial) -
new_loc = gf_poly_scale(old_loc, delta) -
old_loc = gf_poly_scale(err_loc, gf_inverse(delta)) # err_loc * 1/delta = err_loc // delta -
err_loc = new_loc -
# 更新Delta -
err_loc = gf_poly_add(err_loc, gf_poly_scale(old_loc, delta)) -
# 查看结果是否正确, 或者错误太多无法修复 -
while len(err_loc) and err_loc[0] == 0: del err_loc[0] # 排除前面的0 -
errs = len(err_loc) - 1 -
if (errs-erase_count) * 2 + erase_count > nsym: -
raise ReedSolomonError("Too many errors to correct") # 错误太多 -
return err_loc
接下来,我们用一种简单直接的试验方法,通过这个定位式来定位多项式中的0,进而定位错误位置。代码如下:
-
def rs_find_errors(err_loc, nmess): # nmess is len(msg_in) -
'''Find the roots (ie, where evaluation = zero) of error polynomial by brute-force trial, this is a sort of Chien's search -
(but less efficient, Chien's search is a way to evaluate the polynomial such that each evaluation only takes constant time).''' -
errs = len(err_loc) - 1 -
err_pos = [] -
for i in range(nmess): # normally we should try all 2^8 possible values, but here we optimize to just check the interesting symbols -
if gf_poly_eval(err_loc, gf_pow(2, i)) == 0: # It's a 0? Bingo, it's a root of the error locator polynomial, -
# in other terms this is the location of an error -
err_pos.append(nmess - 1 - i) -
# Sanity check: the number of errors/errata positions found should be exactly the same as the length of the errata locator polynomial -
if len(err_pos) != errs: -
# couldn't find error locations -
raise ReedSolomonError("Too many (or few) errors found by Chien Search for the errata locator polynomial!") -
return err_pos
译注:这个算法我也没细看,大体上,它用到了牛顿恒等式(根据4.3.3计算的伴随式)来生成错误定位多项式,然后求值得到错误的位置。更详细一点的信息可参考AN2407.pdf
这样的方法效率不高,Chien搜索是一种更高效的算法。
下面是一个纠正了编码后数据中3个错误的例子:
-
>>> print(hex(msg[10])) -
0x96 -
>>> msg[0] = 6 -
>>> msg[10] = 7 -
>>> msg[20] = 8 -
>>> synd = rs_calc_syndromes(msg, 10) -
>>> pos = rs_find_errors(synd, len(msg)) -
>>> print(pos) -
[20, 10, 0] -
>>> rs_correct_errata(msg, synd, pos) -
>>> print(hex(msg[10])) -
0x96
4.3.5 消除和错误纠正
为了能够纠正错误和消除,我们需要让已知的消除不影响查找错误位置。这可以通过计算Forney syndrome来实现,如下所示:
-
def rs_forney_syndromes(synd, pos, nmess): -
# Compute Forney syndromes, which computes a modified syndromes to compute only errors (erasures are trimmed out). 别混淆Forney syndromes 和 Forney algorithm(根据错误位置纠正信息的算法). -
erase_pos_reversed = [nmess-1-p for p in pos] # prepare the coefficient degree positions (instead of the erasures positions) -
# Optimized method, all operations are inlined -
fsynd = list(synd[1:]) # make a copy and trim the first coefficient which is always 0 by definition -
for i in range(0, len(pos)): -
x = gf_pow(2, erase_pos_reversed[i]) -
for j in range(0, len(fsynd) - 1): -
fsynd[j] = gf_mul(fsynd[j], x) ^ fsynd[j + 1] -
# 上述算法是进过优化之后的, 等价的理论算法应该是: fsynd = (erase_loc * synd) % x^(n-k) -
#erase_loc = rs_find_errata_locator(erase_pos_reversed, generator=generator) # computing the erasures locator polynomial -
#fsynd = gf_poly_mul(erase_loc[::-1], synd[1:]) # then multiply with the syndrome to get the untrimmed forney syndrome -
#fsynd = fsynd[len(pos):] # 删除(trim)没用的前 erase_pos 个系数. 似乎没必要, 不过能降低后面BM算法的计算量. -
return fsynd
Forney syndrome可以用来替换常规错误位置查找中的syndrome。
下面的这个rs_correct_errata函数给出了完整的过程,在msg_in被消除的位置中使用-1来表示。
-
def rs_correct_msg(msg_in, nsym, erase_pos=None): -
'''Reed-Solomon main decoding function''' -
if len(msg_in) > 255: # can't decode, message is too big -
raise ValueError("Message is too long (%i when max is 255)" % len(msg_in)) -
msg_out = list(msg_in) # copy of message -
# erasures: 为了解码是debug方便, 设置为 null (不必要) -
if erase_pos is None: -
erase_pos = [] -
else: -
for e_pos in erase_pos: -
msg_out[e_pos] = 0 -
# check if there are too many erasures to correct (beyond the Singleton bound) -
if len(erase_pos) > nsym: raise ReedSolomonError("Too many erasures to correct") -
# prepare the syndrome polynomial using only errors. -
synd = rs_calc_syndromes(msg_out, nsym) -
# 查验 codeword中是否有误码. 如果没有 (伴随式全部系数为 0), codeword原样返回. -
if max(synd) == 0: -
return msg_out[:-nsym], msg_out[-nsym:] # no errors -
# compute the Forney syndromes, which hide the erasures from the original syndrome (so that BM will just have to deal with errors, not erasures) -
fsynd = rs_forney_syndromes(synd, erase_pos, len(msg_out)) -
# compute the error locator polynomial using Berlekamp-Massey -
err_loc = rs_find_error_locator(fsynd, nsym, erase_count=len(erase_pos)) -
# locate the message errors using Chien search (or brute-force search) -
err_pos = rs_find_errors(err_loc[::-1] , len(msg_out)) -
if err_pos is None: -
raise ReedSolomonError("Could not locate error") # error location failed -
# Find errors values and apply them to correct the message -
# compute errata evaluator and errata magnitude polynomials, then correct errors and erasures -
msg_out = rs_correct_errata(msg_out, synd, (erase_pos + err_pos)) # note that we here use the original syndrome, not the forney syndrome -
# (because we will correct both errors and erasures, so we need the full syndrome) -
# check if the final message is fully repaired -
synd = rs_calc_syndromes(msg_out, nsym) -
if max(synd) > 0: -
raise ReedSolomonError("Could not correct message") # message could not be repaired -
# return the successfully decoded message -
return msg_out[:-nsym], msg_out[-nsym:] # also return the corrected ecc block so that the user can check()
Python注记:erase_pos和err_pos这两个数组用 + 运算连接起来。
这是实现一个全功能的错误/消除纠正RS解码器所需的最后一个片段。如果想进一步深究,原作者推荐了一本书,《Algebraic Codes for Data Transmission》
5 打包一个实例
下面的例子展示了如何使用上文中的代码进行编码和解码:
-
# Configuration of the parameters and input message -
prim = 0x11d -
n = 20 # set the size you want, it must be > k, the remaining n-k symbols will be the ECC code (more is better) -
k = 11 # k = len(message) -
message = "hello world" # input message -
# Initializing the log/antilog tables -
init_tables(prim) -
# Encoding the input message -
mesecc = rs_encode_msg([ord(x) for x in message], n-k) -
print("Original: %s" % mesecc) -
# Tampering 6 characters of the message (over 9 ecc symbols, so we are above the Singleton Bound) -
mesecc[0] = 0 -
mesecc[1] = 2 -
mesecc[2] = 2 -
mesecc[3] = 2 -
mesecc[4] = 2 -
mesecc[5] = 2 -
print("Corrupted: %s" % mesecc) -
# Decoding/repairing the corrupted message, by providing the locations of a few erasures, we get below the Singleton Bound -
# Remember that the Singleton Bound is: 2*e+v <= (n-k) -
corrected_message, corrected_ecc = rs_correct_msg(mesecc, n-k, erase_pos=[0, 1, 2]) -
print("Repaired: %s" % (corrected_message+corrected_ecc)) -
print(''.join([chr(x) for x in corrected_message]))
应该得到如下的输出:
-
Original: [104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 119, 111, 114, 108, 100, 145, 124, 96, 105, 94, 31, 179, 149, 163] -
Corrupted: [ 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 119, 111, 114, 108, 100, 145, 124, 96, 105, 94, 31, 179, 149, 163] -
Repaired: [104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 119, 111, 114, 108, 100, 145, 124, 96, 105, 94, 31, 179, 149, 163] -
hello world
6 总结(略)
译注:"Bobmath"将上述代码整合以后提交到了pypi,包名叫reedsolo,可以在https://pypi.python.org/pypi/reedsolo找到。稍微要注意的一点是,上述的所有代码实际上是针对GF(256)上面的RS码实现的,且使用了固定的生成多项式,所以并不是完全通用。