- React.FC的注解是有些问题的,在是否优先使用这个类型作为注解上存在一部分争议,因为这个类型破坏了JSX.LibraryManagedAttributes, 导致其忽略了函数和类组件的defaultsProps,displayName这样的参数,详见,另外,其不能像class组件一样返回props的children 详见(显式的定义children属性,或更改源码可解决这个问题)。还有一点,FC在@types/react18之前总是隐式的定义好children,即使你的Props注解并没有定义children,你仍然可以在参数里解构出它。
- 在@types/react版本16.8和18之间可以使用React.VoidFunctionComponent或React.VFC替代它,它规定要想在函数体内使用props必须显示的定义它
- 因为编译器的限制 在函数组件中,不能返回除jsx和null以外的值,如果真的需要返回除这两种之外的值,可以使用类型断言,例如
const MyArrayComponent = () => (Array(5).fill() as any) as JSX.Element4.
React.FC React.Component - 开发泛型class组件
// 在使用的时候约束它的props类型
type SelectProps = {items: T[]};
class Select extends React.Component, {}> {
}
// 使用
const Form = () => items={['a','b']}> - 开发泛型函数
function foo(x:T): T{
return x
}
// 箭头泛型函数需要用extends提示编辑器这是个泛型
const foo = >() => {} 7.React.ReactElement可以通过传入泛型,来注解类或函数组件的实例化结果
class MyAwesomeComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return Hello;
}
}
const foo: React.ReactElement = = - useState<>() . 奇淫巧技:
const [user,setUser] = React.useState(null);
const [user,setUser] = React.useState({} as IUser) - reducer函数的形参里intialState的类型注解可以直接typeOf它取出它的类型,
action参数可以使用联合类型活AnyAction注解(from ’redux‘),
泛型注解
import { Reducer } from 'redux';
export function reducer:
Reducer() {} 10.useRef<>(),奇淫巧技:
// 如果可以的话尽量使用的类型具体点
// 比如使用HTMLDivElement 就比HTMLElement好很多,比Element好更多
function Foo(){
const divRef = useRef(null);
return etc
}
11.类型断言:as/泛型注解(React里不能用)/去除null或undefined断言!
// 非空断言操作符
const fooRef = useRef(null!)
const foo = name!.chartAt(0))
- 函数的执行结果在给其他变量进行赋值,会发现该变量的注解有问题
function fn(){return ['1',false] };
type AType = string[]
let a:AType = fn() // error
// 1.将其变为 return ['1',false] as any[] 或者 return ['1',false] as string[],如果是只读的可以 as const
// 2. type Atype = (string | boolean)[],但已不符合实际意义
// 3. react团队推荐自定义钩子return两个以上的值时可以使用对象
13.createContext
type Theme = 'light' | 'dark'
const TeemeContext = React.createContext('dark')
// 创建{}用断言 const Context = React.createContext({} as ContextState);
const sampleAppContext: TeemeContext = 'light';
export const App = () => (
...
);
// 如果想创建默认值为null或undefined可以React.createContext(undefined!),不然在使用.时
// 会报没有相关api可以调用,但这样失去了类型安全,或者可以使用一个helper函数来帮助我们创建,让我们不再考虑undeined
// 的情况
function createCtx() {
const ctx = React.createContext(undefined);
function useCtx() {
const c = React.useContext(ctx);
if (c === undefined)
throw new Error("useCtx must be inside a Provider with a value");
return c;
}
return [useCtx, ctx.Provider] as const; // 'as const' makes TypeScript infer a tuple
}
// Usage:
// We still have to specify a type, but no default!
export const [useCurrentUserName, CurrentUserProvider] = createCtx();
function EnthusasticGreeting() {
const currentUser = useCurrentUserName();
return HELLO {currentUser.toUpperCase()}!;
}
function App() {
return (
);
}
//
// 整合useContext,createContext,useState为一体
export function createCtx(defaultValue: A) {
type UpdateType = React.Dispatch<
React.SetStateAction
>;
const defaultUpdate: UpdateType = () => defaultValue;
const ctx = React.createContext({
state: defaultValue,
update: defaultUpdate,
});
function Provider(props: React.PropsWithChildren<{}>) {
const [state, update] = React.useState(defaultValue);
return
);
}
export function Component() {
const { state, update } = React.useContext(TextContext);
return (
);
}
//更好的createContextApi
https://gist.github.com/sw-yx/f18fe6dd4c43fddb3a4971e80114a052
14.useImperativeHandle, forwardRef
export interface MyInputHandles {
focus(): void;
}
const MyInput: RefForwardingComponent = (props, ref) => {
const inputRef = useRef(null);
useImperativeHandle(ref, () =>({
focus: () => {
if(inputRef.current) {
inputRef.current.focus();
}
}
}))
return
}
export default forwardRef(MyInput)
- React.Component里如果为了更好的引用state可以在React.Component
和 state:MyState {}两处做注解
- props的注解不用标记readOnly 。 因为在添加到泛型组件时,会自动添加ReadOnly
- class properties
pointer: number
- getDerivedStateFromProps
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props:Props, state:State): Partial | null {
}
- 当您需要函数的返回值确定状态时可以使用ReturnType
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props:Props, state:State): Partial | null {
}
- ts中就你就可以不用写defaultProps了
21. 如何优雅的取出component的props
const GreetComponent = ({ name, age }: {name:string, age:25}) => (
{`Hello, my name is ${name}, ${age}`}
);
type ComponentProps = T extends
| React.ComponentType
| React.Component
? JSX.LibraryManagedAttributes
: never;
const TestComponent = (props: ComponentProps) => {
return ;
};
- react中常见的ts类型
type AppProps = {
message: string;
count: number;
disabled: boolean;
/** array of a type! */
names: string[];
/** string literals to specify exact string values, with a union type to join them together */
status: "waiting" | "success";
/** any object as long as you dont use its properties (NOT COMMON but useful as placeholder) */
obj: object;
obj2: {}; // almost the same as `object`, exactly the same as `Object`
/** an object with any number of properties (PREFERRED) */
obj3: {
id: string;
title: string;
};
/** array of objects! (common) */
objArr: {
id: string;
title: string;
}[];
/** a dict object with any number of properties of the same type */
dict1: {
[key: string]: MyTypeHere;
};
dict2: Record; // equivalent to dict1
/** any function as long as you don't invoke it (not recommended) */
onSomething: Function;
/** function that doesn't take or return anything (VERY COMMON) */
onClick: () => void;
/** function with named prop (VERY COMMON) */
onChange: (id: number) => void;
/** alternative function type syntax that takes an event (VERY COMMON) */
onClick(event: React.MouseEvent): void;
/** an optional prop (VERY COMMON!) */
optional?: OptionalType;
};
- react中的注解
type AppProps = {
message: string;
count: number;
disabled: boolean;
/** array of a type! */
names: string[];
/** string literals to specify exact string values, with a union type to join them together */
status: "waiting" | "success";
/** any object as long as you dont use its properties (NOT COMMON but useful as placeholder) */
obj: object;
obj2: {}; // almost the same as `object`, exactly the same as `Object`
/** an object with any number of properties (PREFERRED) */
obj3: {
id: string;
title: string;
};
/** array of objects! (common) */
objArr: {
id: string;
title: string;
}[];
/** a dict object with any number of properties of the same type */
dict1: {
[key: string]: MyTypeHere;
};
dict2: Record; // equivalent to dict1
/** any function as long as you don't invoke it (not recommended) */
onSomething: Function;
/** function that doesn't take or return anything (VERY COMMON) */
onClick: () => void;
/** function with named prop (VERY COMMON) */
onChange: (id: number) => void;
/** alternative function type syntax that takes an event (VERY COMMON) */
onClick(event: React.MouseEvent): void;
/** an optional prop (VERY COMMON!) */
optional?: OptionalType;
};
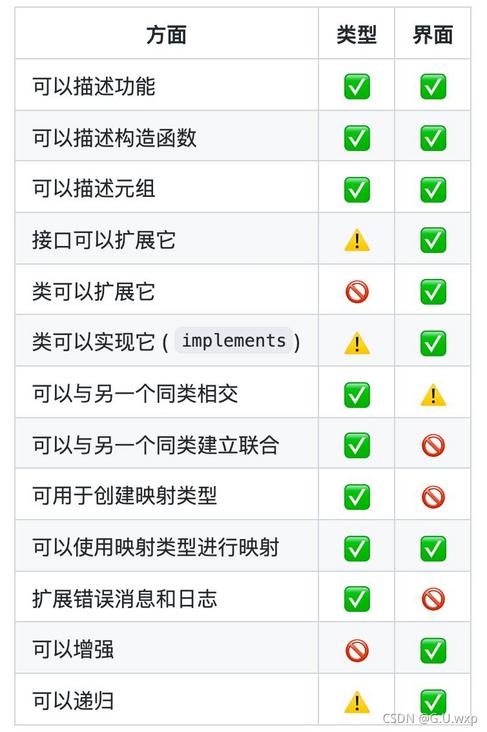
24.接口与类型别名的差异
类型别名和接口非常相似,在很多情况下你可以自由选择它们。几乎所有的功能都在interface中可用type,关键区别在于不能重新打开类型以添加新属性与始终可扩展的接口。
25.当你想要使用getDerivedStateFromProps的返回值作为组建的state注解时
// 1. 普通情况
class Comp extends React.Component<
Props,
ReturnType
> {
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props: Props) {}
}
// 2. 返回函数
type CustomValue = any;
interface Props {
propA: CustomValue;
}
interface DefinedState {
otherStateField: string;
}
type State = DefinedState & ReturnType;
function transformPropsToState(props: Props) {
return {
savedPropA: props.propA, // save for memoization
derivedState: props.propA,
};
}
class Comp extends React.PureComponent {
constructor(props: Props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
otherStateField: "123",
...transformPropsToState(props),
};
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props: Props, state: State) {
if (isEqual(props.propA, state.savedPropA)) return null;
return transformPropsToState(props);
}
}
- 表单事件
// 如果不考虑性能的话,可以使用内联处理,注解将自动正确生成
const el = (
- 事件类型列表
AnimationEvent : css动画事件
ChangeEvent:,