前言
之前有幸跟公司大神聊Spring Boot,大神跟我聊了很多关于Spring Boot相关的知识,其中有一个就是Spring Boot框架下批处理的解决方案,考虑到批处理在实际应用场景中使用率还是有的,好奇的我,决定拿下它!
项目代码已上传Git Hub,欢迎取阅:
- https://github.com/dylanz666/spring-batch-demo
批处理框架
Spring Batch是一款基于 Spring 的企业批处理应用框架,可以帮助我们构建出健壮的批处理应用。
实现批处理的整体步骤
- 添加依赖;
- Spring Boot基本概念介绍;
- 编写批处理过程代码;
- 批处理任务调度;
1. 添加依赖;
在项目pom.xml文件的dependencies节点下添加以下依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-batch
2. Spring Boot基本概念介绍;
在实现批处理之前我们需要了解一些Spring Batch的基本概念:
1). Item Reader;
表示对资源的读处理,如从数据库查询、从文件读取、从变量读取等;
2). Item Processor;
表示对读取的数据进行处理,开发者可以实现自己的业务逻辑操作来对数据处理,如对数据进行计算、逻辑处理、格式转换等;
3). Item Writer;
表示对资源的写处理,如写入数据库、写入文件、打印log等;
4). Step;
代表一个完整的批处理步骤,一个Step由Item Reader、 Item Processor、Item Writer三部分组成;
-
Step与Item Reader、 Item Processor、Item Writer的关系:
5). Job;
代表一个完整的批处理过程,一个Job由一个或多个Step组成:
-
Job与Step的关系:
-
批处理过程整体结构:
6). Listener;
监听。Spring Batch中还有个监听的功能,与其他地方的监听类似,用于对Step、Job状态进行监听,我们可以实现监听方法,对其进行一些逻辑处理,如打印log等;
7). JobLauncher;
JobLauncher负责启动job;
3. 编写批处理过程代码;
假设我们要解决的问题是,批量读取数组中的数据,并对数据做一些后续的处理。我会写2个Job,一个是单个Step的Job,一个是2个Step的Job,并且2个Step的Job,第1个Step的处理后的数据要给第2个Step使用。
过程代码的整体步骤:
1). 编写ItemReader;
2). 编写ItemProcessor;
3). 编写ItemWriter;
4). 编写JobExecutionListener;
5). 装配Job;
6). 使用数据库源;
7). 修改Spring Boot入口类;
1). 编写ItemReader;
- ItemReaderService
package com.github.dylanz666.service;
import org.springframework.batch.item.ItemReader;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author : dylanz
* @since : 08/25/2020
*/
@Service
public class ItemReaderService implements ItemReader {
//在此处进行数据读取操作,如从数据库查询、从文件中读取、从变量中读取等,本例从变量中读取;
private String[] message = {"message 1", "message 2", "message 3", "message 4", "message 5"};
private int count = 0;
public String read() throws Exception {
if (count < message.length) {
return message[count++];
}
count = 0;
return null;
}
}
- ItemReaderService2
package com.github.dylanz666.service;
import org.springframework.batch.item.ItemReader;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author : dylanz
* @since : 08/26/2020
*/
@Service
public class ItemReaderService2 implements ItemReader {
private int count = 0;
public String read() throws Exception {
if (ItemProcessorService.message != null && count < ItemProcessorService.message.length) {
return ItemProcessorService.message[count++];
}
count = 0;
return null;
}
}
2). 编写ItemProcessor;
- ItemProcessorService
package com.github.dylanz666.service;
import org.springframework.batch.item.ItemProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author : dylanz
* @since : 08/25/2020
*/
@Service
public class ItemProcessorService implements ItemProcessor {
public static String[] message;
//在此处进行数据处理操作,如进行计算、逻辑处理、格式转换等,本例将数据变成全大写数据;
public String process(String data) throws Exception {
//存储处理过的数据,可供下一个step使用
List list = new ArrayList<>();
if (message != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < message.length; i++) {
list.add(message[i]);
}
}
list.add(data.toUpperCase());
message = list.toArray(new String[list.size()]);
return data.toUpperCase();
}
}
- ItemProcessorService2
package com.github.dylanz666.service;
import org.springframework.batch.item.ItemProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author : dylanz
* @since : 08/26/2020
*/
@Service
public class ItemProcessorService2 implements ItemProcessor {
public String process(String data) throws Exception {
return data + " dylanz";
}
}
3). 编写ItemWriter;
package com.github.dylanz666.service;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.batch.item.ItemWriter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author : dylanz
* @since : 08/25/2020
*/
@Service
public class ItemWriterService implements ItemWriter {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
//在此处进行数据输出操作,如写入数据库、写入文件、打印log等,本例为打印log;
public void write(List messages) throws Exception {
for (String message : messages) {
logger.info("Writing data: " + message);
}
}
}
4). 编写JobExecutionListener;
我们对Job运行前后进行监听,并打印相应log:
package com.github.dylanz666.service;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.batch.core.BatchStatus;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobExecution;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobExecutionListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author : dylanz
* @since : 08/25/2020
*/
@Service
public class JobListener implements JobExecutionListener {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
public void beforeJob(JobExecution jobExecution) {
logger.info("JOB IS STARTED.");
}
public void afterJob(JobExecution jobExecution) {
if (jobExecution.getStatus() == BatchStatus.FAILED) {
logger.info("JOB IS EXECUTED FAILED.");
return;
}
if (jobExecution.getStatus() == BatchStatus.COMPLETED) {
logger.info("JOB IS EXECUTED SUCCESSFULLY.");
}
}
}
5). 装配Job;
在config包底下创建BathConfig.java类(名字随意),我们装配2个Job,一个为单Step Job,一个为2个Step Job,同时在每个job上设置监听:
package com.github.dylanz666.config;
import com.github.dylanz666.service.*;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Job;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobExecutionListener;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Step;
import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.JobBuilderFactory;
import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.StepBuilderFactory;
import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.RunIdIncrementer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author : dylanz
* @since : 08/25/2020
*/
@Configuration
public class BatchConfig {
@Autowired
private JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory;
@Autowired
private StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory;
@Autowired
private ItemReaderService itemReaderService;
@Autowired
private ItemReaderService2 itemReaderService2;
@Autowired
private ItemProcessorService itemProcessorService;
@Autowired
private ItemProcessorService2 itemProcessorService2;
@Autowired
private ItemWriterService itemWriterService;
@Autowired
private JobListener jobListener;
@Bean
public Job singleStepJob() {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("singleStepJob")
.incrementer(new RunIdIncrementer())
.listener(listener())
.start(uppercaseStep())
.build();
}
@Bean
public Job multiBoundStepsJob() {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("multiBoundStepsJob")
.incrementer(new RunIdIncrementer())
.listener(listener())
.start(uppercaseStep())
.next(addMessageStep())
.build();
}
@Bean
public Step uppercaseStep() {
return stepBuilderFactory.get("uppercaseStep")
.chunk(1)
.reader(itemReaderService)
.processor(itemProcessorService)
.writer(itemWriterService).build();
}
@Bean
public Step addMessageStep() {
return stepBuilderFactory.get("addMessageStep")
.chunk(1)
.reader(itemReaderService2)
.processor(itemProcessorService2)
.writer(itemWriterService).build();
}
@Bean
public JobExecutionListener listener() {
return jobListener;
}
}
6). 使用数据库源(非必需);
- 不使用数据库存储批处理job的元数据及执行信息;
默认是不需要任何改动的,此时不保存元数据及执行信息;
如果遇到提示数据源缺失问题,也可尝试在Spring Boot启动类的@SpringBootApplication注解添加属性:exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class},即:
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
- 使用数据存储批处理job的元数据及执行信息;
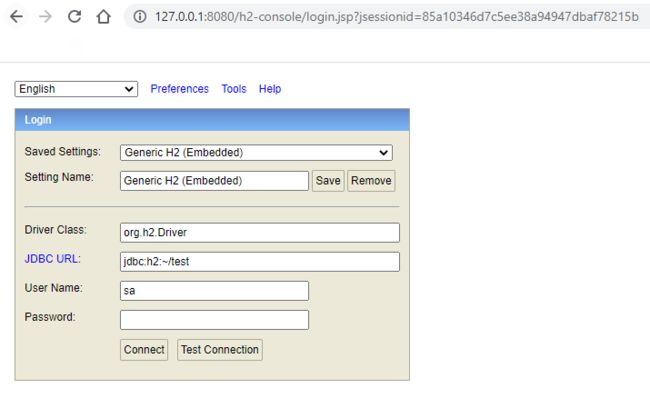
该方式可以随时跟踪执行进度,重新执行失败记录等,我们可以使用mysql等数据库,另外一种更常用、简单的方式是使用嵌入式数据库H2 Database。
使用H2 Database只需在src/main/resources/application.properties添加以下配置即可:(前提是要移除启动类@SpringBootApplication注解的属性:exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
server.port=8080
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:~/test
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
#初次密码可随意
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.h2.console.path=/h2-console
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
7). 修改Spring Boot入口类;
在Spring Boot项目入口类上添加注解@EnableBatchProcessing即可,如:
package com.github.dylanz666;
import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.EnableBatchProcessing;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @author : dylanz
* @since : 08/25/2020
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableBatchProcessing
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
- 启动项目后,我们可访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/h2-console 查看元数据和执行信息:
- 输入密码并点击Connect按钮链接H2数据库后:
- 可在H2 数据库中执行sql进行元数据和执行信息的查询等操作;
4. 批处理任务调度;
批处理任务调度常见的几种方式:
1). 项目启动时自启动(一次性执行所有批处理任务);
默认启动项目时会一次性执行所有批处理任务。
如果我们不想在项目启动时执行所有批处理任务,那么需要在application.properties添加配置项:
spring.batch.job.enabled=false
2). 通过接口调用方式把任务调度交给客户端;
- 在controller包下编写2个批处理任务调度接口:
package com.github.dylanz666.controller;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Job;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobParameters;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobParametersBuilder;
import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.JobLauncher;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author : dylanz
* @since : 08/25/2020
*/
@RestController
public class BatchController {
@Autowired
private Job singleStepJob;
@Autowired
private Job multiBoundStepsJob;
@Autowired
private JobLauncher jobLauncher;
@GetMapping("/job/step")
public String invokeStep() throws Exception {
JobParameters jobParameters = new JobParametersBuilder().addLong("time", System.currentTimeMillis())
.toJobParameters();
jobLauncher.run(singleStepJob, jobParameters);
return "The job is proceed.";
}
@GetMapping("/job/steps")
public String invokeSteps() throws Exception {
JobParameters jobParameters = new JobParametersBuilder().addLong("time", System.currentTimeMillis())
.toJobParameters();
jobLauncher.run(multiBoundStepsJob, jobParameters);
return "The multi bound steps job is proceed.";
}
}
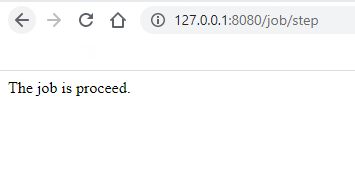
- 项目启动后,调用任务调度接口,如本例使用的2个接口:
(1). http://127.0.0.1:8080/job/step
(2). http://127.0.0.1:8080/job/steps
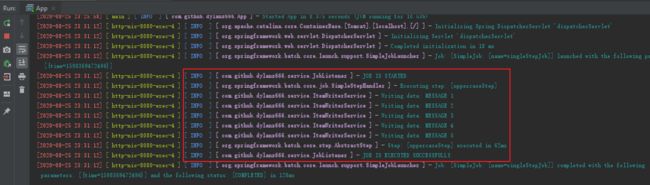
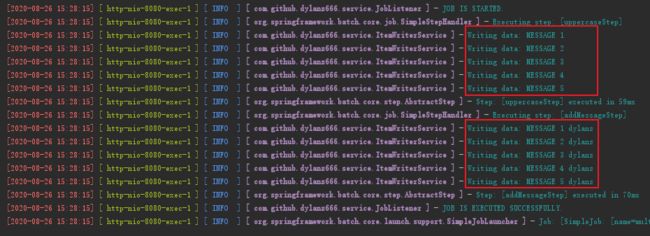
通过log我们会发现,http://127.0.0.1:8080/job/steps这个API,使用的Job multiBoundStepsJob,先执行了uppercaseStep()方法,把字符串转成大写,然后在这基础上,执行了addMessageStep()方法,在字符串尾部添加" dylanz"字符串,其中关键点是:
[1]. 我们在ItemProcessorService方法中用static成员变量String[] message保存ItemProcessorService处理后的数据;
[2]. 在itemReaderService2中使用static成员变量String[] message作为数据源;
[3]. 在multiBoundStepsJob中使用了uppercaseStep和addMessageStep这2个Step;
这个是2个关联Step间数据传递的一种方法;
我们也可以设置一个Job,包含多个互不关联的Step,只需要在编写Step时使用链式写法:
.start(xxx)
.next(xxx)
.next(xxx)
....
.build()
3). 定期调度批处理任务;
由于Spring Batch只是一个批处理应用框架,而不是调度框架,它只关注批处理相关的问题,并不提供调度功能,因此,我们需要借助其他调度框架实现定期调度。
我了解到的Spring Boot框架内常用、成熟的调度方式、调度框架有:
(1). Spring Boot自带的@Scheduled;
(2). Quartz;
(1). Spring Boot自带的@Scheduled
@Scheduled有3种执行方式:
//1. 按照指定的cron表达式,一旦符合cron表示的时间,则执行任务,如,//每5秒中执行一次任务:
@Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * ?")
//2. 以固定频率执行任务,如每1分钟执行一次任务;
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000)
//3. 任务执行完成后再延迟固定时间后再执行下一次,如延迟1分钟再执行任务;
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 60000)
cron表达式可以参考网上的介绍:https://www.jianshu.com/p/e9ce1a7e1ed1
cron表达式也可以使用在线生成工具:https://cron.qqe2.com/
[1]. 编写Schedule类,如:
package com.github.dylanz666.config;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Job;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobParameters;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobParametersBuilder;
import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.JobLauncher;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author : dylanz
* @since : 08/25/2020
*/
@Component
public class SpringScheduledConfig {
@Autowired
private Job singleStepJob;
@Autowired
private JobLauncher jobLauncher;
@Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * ?")
public void demoScheduled() throws Exception {
JobParameters jobParameters = new JobParametersBuilder().addLong("time", System.currentTimeMillis())
.toJobParameters();
jobLauncher.run(singleStepJob, jobParameters);
}
}
[2]. 项目启动类增加注解:
- @EnableScheduling
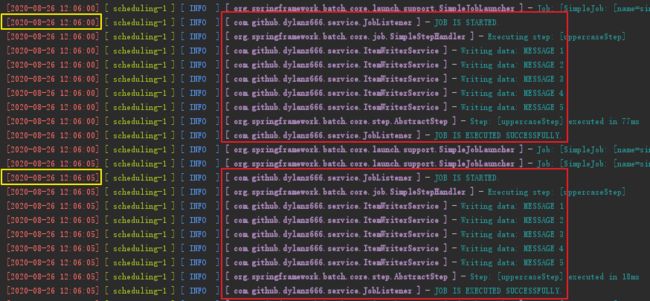
[3]. 实际运行效果:
这整个过程还是非常简单的,但cron疑似在支持年份时有问题。
(2). 批处理调度框架Quartz
Quartz是OpenSymphony开源组织在Job scheduling领域又一个开源项目,完全由Java开发,可以用来执行定时任务,类似于java.util.Timer。但是相较于Timer, Quartz增加了很多功能:
- 持久性作业 - 就是保持调度定时的状态;
- 作业管理 - 对调度作业进行有效的管理;
Quartz依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-quartz
我的理解是Quartz不仅是批处理调度框架,同时也是批处理应用框架。由于Quartz相对灵活,换句话说就是使用起来相对复杂些,我们就参考其他人的文章,改日再叙:
- https://www.cnblogs.com/imyanger/p/11828301.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/noaman_wgs/article/details/80984873
如果本文对您有帮助,麻烦动动手指点点赞?
谢谢!