Python+Opencv实现图像匹配——模板匹配
1、原理
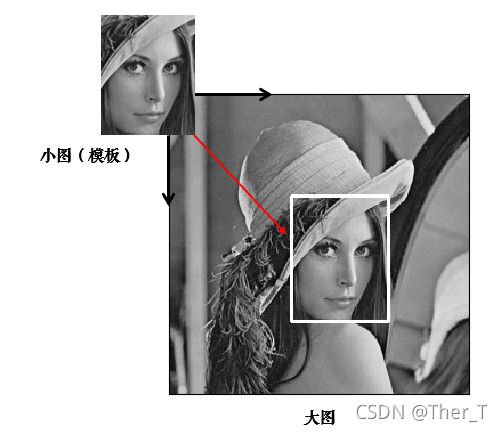
简单来说,模板匹配就是拿一个模板(图片)在目标图片上依次滑动,每次计算模板与模板下方的子图的相似度,最后就计算出了非常多的相似度;
如果只是单个目标的匹配,那只需要取相似度最大值所在的位置就可以得出匹配位置;
如果要匹配多个目标,那就设定一个阈值,就是说,只要相似度大于比如0.8,就认为是要匹配的目标。
1.1 相似度度量指标
- 差值平方和匹配 CV_TM_SQDIFF
- 标准化差值平方和匹配 CV_TM_SQDIFF_NORMED
- 相关匹配 CV_TM_CCORR
- 标准相关匹配 CV_TM_CCORR_NORMED
- 相关匹配 CV_TM_CCOEFF
- 标准相关匹配 CV_TM_CCOEFF_NORMED
1.2 计算步骤
- 有一张模板图像Templa和一张较大的待搜索图像Image,模板匹配是一种用于在较大图像中搜索和查找模板图像位置的方法。
- 具体就是将模板图像滑动到输入图像上(就像在卷积操作一样),然后在模板图像下比较模板和输入图像的子图的相似度。
- 它返回一个灰度图像,其中每个像素表示该像素的邻域与模板匹配的相似度。如果输入图像的大小(WxH)和模板图像的大小(wxh),则输出图像的大小将为(W-w+ 1,H-h + 1)。 获得相似度图像之后,在其上查找最大相似度所在的像素。将其作为匹配区域矩形的左上角,并以(w,h)作为矩形的宽度和高度。该矩形是与模板匹配的区域。
2、代码实现
2.1 单模板匹配单个目标
代码实现一如下:
# 相关系数匹配方法: cv2.TM_CCOEFF
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img, template, cv2.TM_CCOEFF)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
left_top = max_loc # 左上角
right_bottom = (left_top[0] + w, left_top[1] + h) # 右下角
cv2.rectangle(img, left_top, right_bottom, 255, 2) # 画出矩形位置
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(res, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Matching Result'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Detected Point'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
代码实现二如下:
#opencv模板匹配----单目标匹配
import cv2
#读取目标图片
target = cv2.imread("target.jpg")
#读取模板图片
template = cv2.imread("template.jpg")
#获得模板图片的高宽尺寸
theight, twidth = template.shape[:2]
#执行模板匹配,采用的匹配方式cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED
result = cv2.matchTemplate(target,template,cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED)
#归一化处理
cv2.normalize( result, result, 0, 1, cv2.NORM_MINMAX, -1 )
#寻找矩阵(一维数组当做向量,用Mat定义)中的最大值和最小值的匹配结果及其位置
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
#匹配值转换为字符串
#对于cv2.TM_SQDIFF及cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED方法min_val越趋近与0匹配度越好,匹配位置取min_loc
#对于其他方法max_val越趋近于1匹配度越好,匹配位置取max_loc
strmin_val = str(min_val)
#绘制矩形边框,将匹配区域标注出来
#min_loc:矩形定点
#(min_loc[0]+twidth,min_loc[1]+theight):矩形的宽高
#(0,0,225):矩形的边框颜色;2:矩形边框宽度
cv2.rectangle(target,min_loc,(min_loc[0]+twidth,min_loc[1]+theight),(0,0,225),2)
#显示结果,并将匹配值显示在标题栏上
cv2.imshow("MatchResult----MatchingValue="+strmin_val,target)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
2.2 单模板匹配多个目标
目标照片:mario.jpg
代码如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
img_rgb = cv2.imread('mario.jpg')
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rgb, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
template = cv2.imread('mario_coin.jpg', 0)
h, w = template.shape[:2]
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img_gray, template, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
threshold = 0.8
# 取匹配程度大于%80的坐标
loc = np.where(res >= threshold)
#np.where返回的坐标值(x,y)是(h,w),注意h,w的顺序
for pt in zip(*loc[::-1]):
bottom_right = (pt[0] + w, pt[1] + h)
cv2.rectangle(img_rgb, pt, bottom_right, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imwrite("img.jpg",img_rgb)
cv2.imshow('img', img_rgb)
cv2.waitKey(0)
3、算法精度优化
- 多尺度模板匹配
- 旋转目标模板匹配
- 非极大值抑制
通过上图可以看到对同一个图有多个框标定,需要去重,只需要保留一个
解决方案:对于使用同一个待检区域使用NMS(非极大值抑制)进行去掉重复的矩形框
NMS 原理
对于Bounding Box的列表B及其对应的置信度S,采用下面的计算方式。选择具有最大score的检测框M,将其从B集合中移除并加入到最终的检测结果D中。通常将B中剩余检测框中与M的IoU大于阈值Nt的框从B中移除,重复这个过程,直到B为空。
ps. 重叠率(重叠区域面积比例IOU)常用的阈值是 0.3 ~ 0.5.
代码如下:
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
def py_nms(dets, thresh):
"""Pure Python NMS baseline."""
#x1、y1、x2、y2、以及score赋值
# (x1、y1)(x2、y2)为box的左上和右下角标
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = dets[:, 4]
#每一个候选框的面积
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
#order是按照score降序排序的
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
# print("order:",order)
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
#计算当前概率最大矩形框与其他矩形框的相交框的坐标,会用到numpy的broadcast机制,得到的是向量
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
#计算相交框的面积,注意矩形框不相交时w或h算出来会是负数,用0代替
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
#计算重叠度IOU:重叠面积/(面积1+面积2-重叠面积)
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
#找到重叠度不高于阈值的矩形框索引
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
# print("inds:",inds)
#将order序列更新,由于前面得到的矩形框索引要比矩形框在原order序列中的索引小1,所以要把这个1加回来
order = order[inds + 1]
return keep
def template(img_gray,template_img,template_threshold):
'''
img_gray:待检测的灰度图片格式
template_img:模板小图,也是灰度化了
template_threshold:模板匹配的置信度
'''
h, w = template_img.shape[:2]
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img_gray, template_img, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
start_time = time.time()
loc = np.where(res >= template_threshold)#大于模板阈值的目标坐标
score = res[res >= template_threshold]#大于模板阈值的目标置信度
#将模板数据坐标进行处理成左上角、右下角的格式
xmin = np.array(loc[1])
ymin = np.array(loc[0])
xmax = xmin+w
ymax = ymin+h
xmin = xmin.reshape(-1,1)#变成n行1列维度
xmax = xmax.reshape(-1,1)#变成n行1列维度
ymax = ymax.reshape(-1,1)#变成n行1列维度
ymin = ymin.reshape(-1,1)#变成n行1列维度
score = score.reshape(-1,1)#变成n行1列维度
data_hlist = []
data_hlist.append(xmin)
data_hlist.append(ymin)
data_hlist.append(xmax)
data_hlist.append(ymax)
data_hlist.append(score)
data_hstack = np.hstack(data_hlist)#将xmin、ymin、xmax、yamx、scores按照列进行拼接
thresh = 0.3#NMS里面的IOU交互比阈值
keep_dets = py_nms(data_hstack, thresh)
print("nms time:",time.time() - start_time)#打印数据处理到nms运行时间
dets = data_hstack[keep_dets]#最终的nms获得的矩形框
return dets
if __name__ == "__main__":
img_rgb = cv2.imread('mario.jpg')#需要检测的图片
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rgb, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)#转化成灰色
template_img = cv2.imread('mario_coin.jpg', 0)#模板小图
template_threshold = 0.8#模板置信度
dets = template(img_gray,template_img,template_threshold)
count = 0
for coord in dets:
cv2.rectangle(img_rgb, (int(coord[0]),int(coord[1])), (int(coord[2]),int(coord[3])), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imwrite("result.jpg",img_rgb)


