Android平台有很多优秀的开源库,OkHttp绝对是其中的佼佼者,它是Square出品的一个网络通讯库,功能强大、稳定可靠,以至于Google也在4.4以后用OkHttp来实现HttpURLConnectiond的底层功能,本文将通过阅读项目的源码,一步步构建OkHttp的项目架构,了解这个强大的通讯库是如何设计的。
简单用例
我们先看看OkHttp的基本使用方法
Get请求:
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
String run(String url) throws IOException {
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(url)
.build();
Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
return response.body().string();
}
Post请求:
public static final MediaType JSON
= MediaType.parse("application/json; charset=utf-8");
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
String post(String url, String json) throws IOException {
RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(JSON, json);
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(url)
.post(body)
.build();
Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
return response.body().string();
}
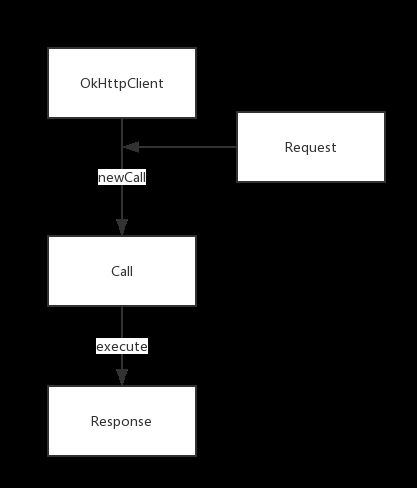
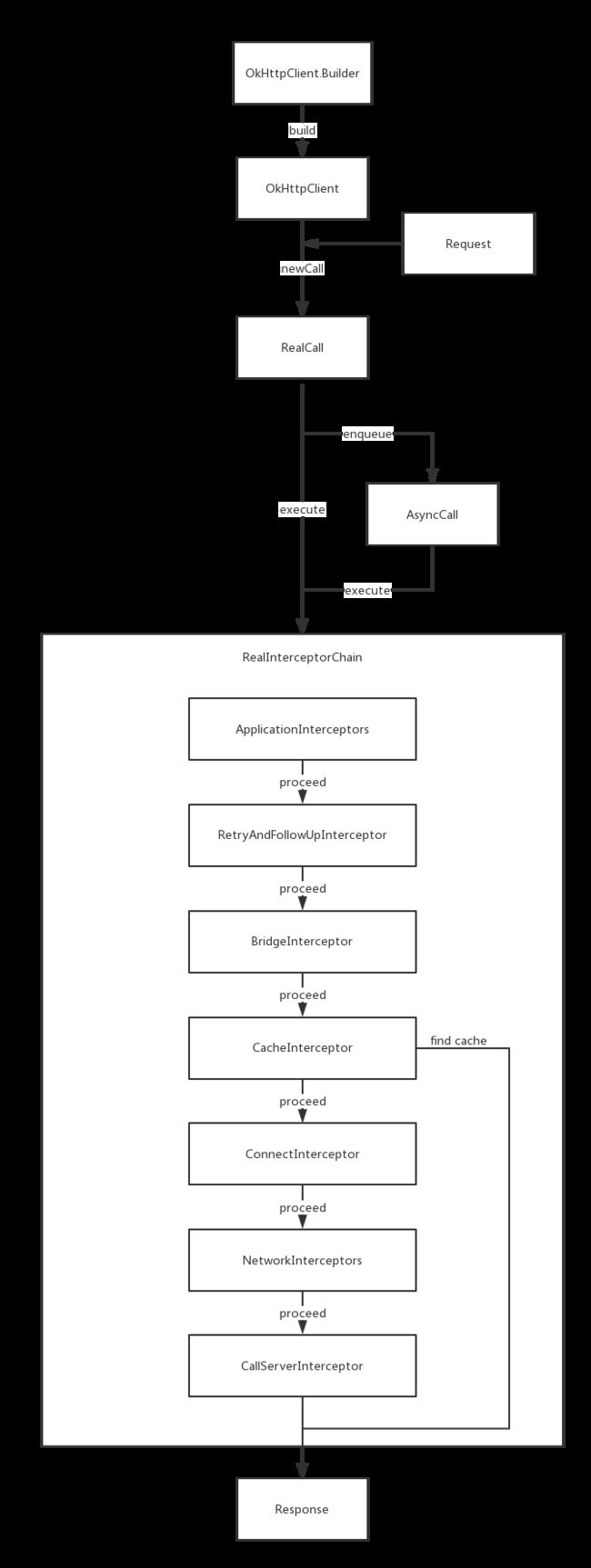
发送请求需要首先构建一个担当客户端角色的OkHttpClient,再构建我们要发送的请求Request,填充好url和body后,通过OkHttpClient把Request发送出去,获取并返回Response,这个流程如下图:
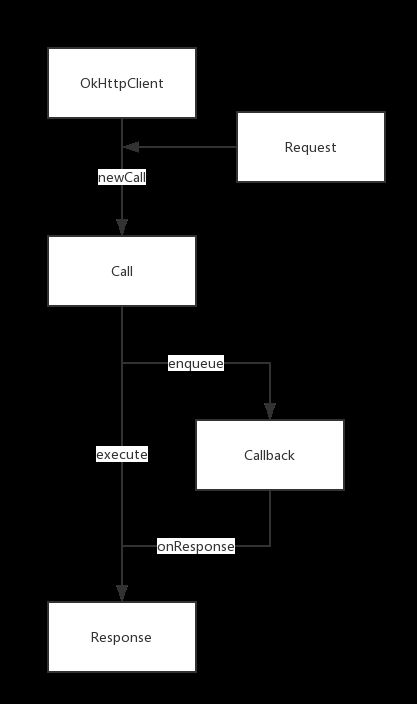
OkHttp还支持异步请求,异步请求的使用方式:
client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
System.out.println(response.body().string());
}
});
异步请求会通过Callback来监听异步请求结果,加上异步请求的流程图如下:
以上是OkHttp的基本用例,接下来我们要进入到源码来分析它究竟是怎么工作的。
构建OkHttpClient
OkHttpClient可以使用Builder来配置超时、代理、DNS等各种参数,之后调用builder()来生成OkHttpClient对象。
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addNetworkInterceptor(new LoggingInterceptor())
...... //各种配置
.build();
查看源码可以看到,OkHttpClient的无参构造方法实际上也是通过调用Builder方法来构建,只是省略了配置参数的过程。
public OkHttpClient() {
this(new Builder());
}
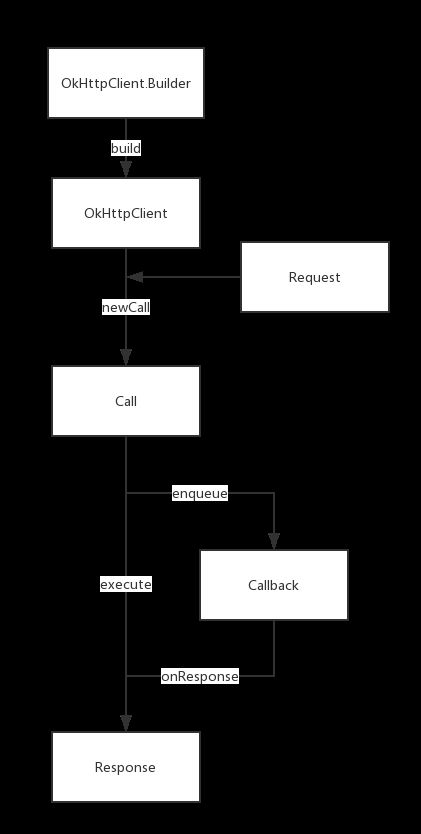
之后,Builder的各个配置会保存在Client中,供后面的操作来读取使用。加上Builder的流程图如下:
发送请求
无论是同步还是异步请求,都需要先调用newCall方法获取Call对象,而Call对象是什么呢?
public interface Call extends Cloneable {
Request request();
Response execute() throws IOException;
void enqueue(Callback responseCallback);
void cancel();
boolean isExecuted();
boolean isCanceled();
Call clone();
interface Factory {
Call newCall(Request request);
}
}
Call是一个已经准备好执行的请求,值得注意的是,它是工厂模式的一个产物,OkHttpClient就是一个继承了Call.Factory接口的工厂类。
public class OkHttpClient implements Cloneable, Call.Factory, WebSocket.Factory {
...
@Override public Call newCall(Request request) {
return RealCall.newRealCall(this, request, false);
}
...
}
在OkHttpClient的newCall方法中,创建的是一个RealCall对象,RealCall才是实现核心通讯功能的主角。
我们先看RealCall的execute同步执行方法。
@Override public Response execute() throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);
try {
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled");
return result;
} catch (IOException e) {
eventListener.callFailed(this, e);
throw e;
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
在执行的时候,RealCall先检查自身是否已经执行过,然后执行eventListener的回调并在dispatcher中通知client自己的状态改变,关键的发送请求操作是在getResponseWithInterceptorChain方法中实现的。
再看看RealCall的enqueue异步执行方法。
@Override public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);
client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));
}
final class AsyncCall extends NamedRunnable {
...
@Override protected void execute() {
boolean signalledCallback = false;
try {
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (signalledCallback) {
// Do not signal the callback twice!
Platform.get().log(INFO, "Callback failure for " + toLoggableString(), e);
} else {
eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, e);
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);
}
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
异步请求通过构建一个AsyncCall来实现,OkHttpClient的Dispatcher会在适当的时机调用AsyncCall,在AsyncCall中我们也能看到getResponseWithInterceptorChain的身影,事实上,所有请求操作都是在getResponseWithInterceptorChain中实现的,想要知道请求的发送过程,还是要看getResponseWithInterceptorChain的实现方式。
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
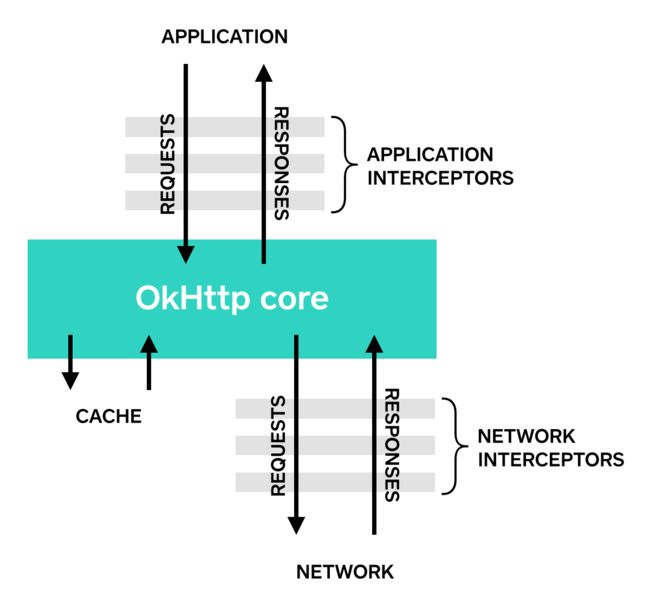
getResponseWithInterceptorChain中生成了一个Interceptor的列表,并根据这个列表维护一个Interceptor链,每一个Interceptor都实现了一部分功能,发送请求就是按顺序执行这个Interceptor链的过程。
- RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor负责失败重试和重定向请求
- BridgeInterceptor负责桥接应用和网络间的请求和响应
- CacheInterceptor负责管理网络缓存
- ConnectInterceptor负责和服务器建立连接
- CallServerInterceptor负责发起请求
除此之外,RealCall还会在合适的时机插入开发者定义的ApplicationInterceptors和NetworkInterceptor,两种Interceptor的主要差别在于是否一定会被执行和执行的次数(wiki
),从这两种Interceptor插入时机来看,我们就不难理解他们是怎么实现的。
Interceptor是OkHttp最核心的设计(也是我认为最优雅的设计),它把请求、缓存、桥接等各个功能都解耦成一个个的Interceptor,然后用一条责任链完美地串联在一起。
接下来我们关注发送请求的两个关键步骤:建立连接和发送数据
建立连接
ConnectInterceptor的代码:
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
Request request = realChain.request();
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation();
// We need the network to satisfy this request. Possibly for validating a conditional GET.
boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks = !request.method().equals("GET");
HttpCodec httpCodec = streamAllocation.newStream(client, chain, doExtensiveHealthChecks);
RealConnection connection = streamAllocation.connection();
return realChain.proceed(request, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection);
}
ConnectInterceptor的职责很简单,就是构造一个HttpCodec并放入Interceptor链中,HttpCodec是一个负责对请求和响应进行编码和解码操作的抽象类,所有IO操作都由它来封装实现。ConnectInterceptor会使用RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor生成的StreamAllocation,找到可用的 RealConnection,根据HTTP版本构造对应的HttpCodec实体对象,提供给后面的Interceptor使用。
发送数据
CallServerInterceptor的代码,省略了部分:
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
HttpCodec httpCodec = realChain.httpStream();
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation();
RealConnection connection = (RealConnection) realChain.connection();
Request request = realChain.request();
// 发送Request的Header
httpCodec.writeRequestHeaders(request);
Response.Builder responseBuilder = null;
// 判断是否需要发送Body
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(request.method()) && request.body() != null)
if ("100-continue".equalsIgnoreCase(request.header("Expect"))) {
httpCodec.flushRequest();
// 100-coutinue的处理
responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(true);
}
if (responseBuilder == null) {
// 发送Request的Body
long contentLength = request.body().contentLength();
CountingSink requestBodyOut =
new CountingSink(httpCodec.createRequestBody(request, contentLength));
BufferedSink bufferedRequestBody = Okio.buffer(requestBodyOut);
request.body().writeTo(bufferedRequestBody);
bufferedRequestBody.close();
} else if (!connection.isMultiplexed()) {
streamAllocation.noNewStreams();
}
}
httpCodec.finishRequest();
if (responseBuilder == null) {
// 读取Response的Header
responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(false);
}
Response response = responseBuilder
.request(request)
.handshake(streamAllocation.connection().handshake())
.sentRequestAtMillis(sentRequestMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
int code = response.code();
// 读取Response的Body
if (forWebSocket && code == 101) {
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.build();
} else {
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(httpCodec.openResponseBody(response))
.build();
}
if ("close".equalsIgnoreCase(response.request().header("Connection"))
|| "close".equalsIgnoreCase(response.header("Connection"))) {
streamAllocation.noNewStreams();
}
return response;
}
CallServerInterceptor使用前面Interceptor生成的产物,一步步发送Request的Header和Body,再接收Response的Header和Body,最后返回构建好的Response。CallServerInterceptor作为Interceptor链的最后一环,最终实现了Http通讯功能。
总结
最后再总结一下OkHttp的流程,首先用OkHttpClient.Builder构建OkHttpClient,通过newCall方法把配置好的Request转换为可执行的RealCall,根据同步或异步使用不同的调度方式,构建Chain按顺序执行每个Interceptor的操作,最终返回Response。
OkHttp的架构简单优雅,拓展性也因为Interceptor的设计而异常强大,和Retrofit结合使用的话还能发挥更强大的功力。这次对OkHttp的源码简析还有很多地方没有仔细说明,比如RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor失败和重定向的操作、CacheInterceptor的缓存方案等等,感兴趣的同学可以下载OkHttp的源码学习。