JavaScript -面向对象 内置对象 JavaScript BOM
1、JavaScript面向对象
1.1、面向对象介绍
在 Java 中我们学习过面向对象,核心思想是万物皆对象。在 JavaScript 中同样也有面向对象。思想类似。
1.2、类的定义和使用
- 结构说明
-
代码实现
<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>类的定义和使用title> head> <body> body> <script> //定义Person类 class Person{ //构造方法 constructor(name,age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } //show方法 show(){ document.write(this.name + "," + this.age + "
"); } //eat方法 eat(){ document.write("吃饭..."); } } //使用Person类 let p = new Person("张三",23); p.show(); p.eat(); script> html>1.3、字面量类的定义和使用
-
结构说明
-
代码实现
<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>字面量定义类和使用title> head> <body> body> <script> //定义person let person = { name : "张三", age : 23, hobby : ["听课","学习"], eat : function() { document.write("吃饭..."); } }; //使用person document.write(person.name + "," + person.age + "," + person.hobby[0] + "," + person.hobby[1] + "
"); person.eat(); script> html>
1.3、继承
-
继承:让类与类产生子父类的关系,子类可以使用父类有权限的成员。
-
继承关键字:extends
-
顶级父类:Object
<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>继承title> head> <body> body> <script> //定义Person类 class Person{ //构造方法 constructor(name,age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } //eat方法 eat(){ document.write("吃饭..."); } } //定义Worker类继承Person class Worker extends Person{ constructor(name,age,salary){ super(name,age); this.salary = salary; } show(){ document.write(this.name + "," + this.age + "," + this.salary + "
"); } } //使用Worker let w = new Worker("张三",23,10000); w.show(); w.eat(); script> html>
1.4、小结
-
面向对象
把相关的数据和方法组织为一个整体来看待,从更高的层次来进行系统建模,更贴近事物的自然运行模式。
-
类的定义
class 类{} 字面量定义
-
类的使用
let 对象名 = new 类名(); 对象名.变量名 对象名.方法名()
-
继承
让类和类产生子父类关系,提高代码的复用性和维护性。
子类 extends 父类
Object 顶级父类
2、JavaScript内置对象
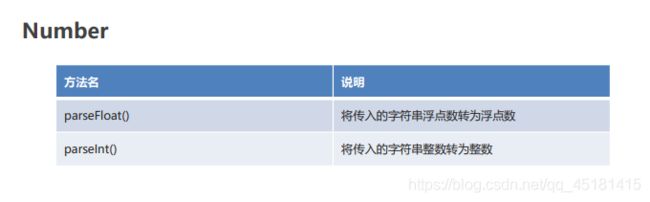
2.1、Number
- 方法介绍
- 代码实现
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Numbertitle>
head>
<body>
body>
<script>
//1. parseFloat() 将传入的字符串浮点数转为浮点数
document.write(Number.parseFloat("3.14") + "
");
//2. parseInt() 将传入的字符串整数转为整数
document.write(Number.parseInt("100") + "
");
document.write(Number.parseInt("200abc") + "
"); // 从数字开始转换,直到不是数字为止
script>
html>
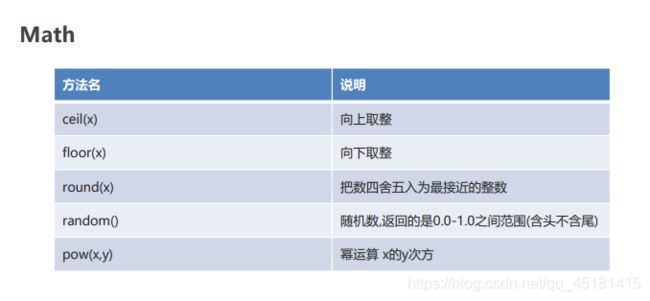
2.2、Math
- 方法介绍
- 代码实现
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Mathtitle>
head>
<body>
body>
<script>
//1. ceil(x) 向上取整
document.write(Math.ceil(4.4) + "
"); // 5
//2. floor(x) 向下取整
document.write(Math.floor(4.4) + "
"); // 4
//3. round(x) 把数四舍五入为最接近的整数
document.write(Math.round(4.1) + "
"); // 4
document.write(Math.round(4.6) + "
"); // 5
//4. random() 随机数,返回的是0.0-1.0之间范围(含头不含尾)
document.write(Math.random() + "
"); // 随机数
//5. pow(x,y) 幂运算 x的y次方
document.write(Math.pow(2,3) + "
"); // 8
script>
html>
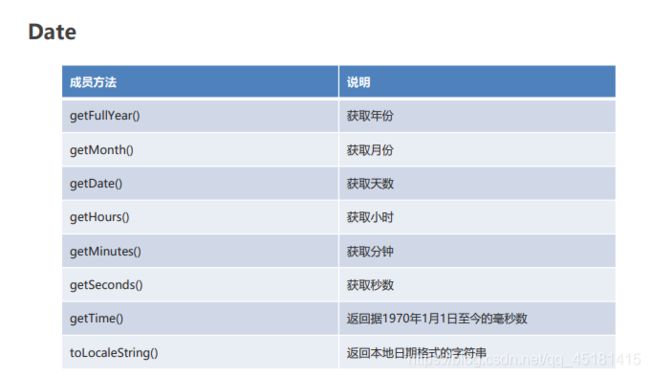
2.3、Date
-
方法说明
- 构造方法
- 成员方法
- 代码实现
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Datetitle>
head>
<body>
body>
<script>
//构造方法
//1. Date() 根据当前时间创建对象
let d1 = new Date();
document.write(d1 + "
");
//2. Date(value) 根据指定毫秒值创建对象
let d2 = new Date(10000);
document.write(d2 + "
");
//3. Date(year,month,[day,hours,minutes,seconds,milliseconds]) 根据指定字段创建对象(月份是0~11)
let d3 = new Date(2222,2,2,20,20,20);
document.write(d3 + "
");
//成员方法
//1. getFullYear() 获取年份
document.write(d3.getFullYear() + "
");
//2. getMonth() 获取月份
document.write(d3.getMonth() + "
");
//3. getDate() 获取天数
document.write(d3.getDate() + "
");
//4. toLocaleString() 返回本地日期格式的字符串
document.write(d3.toLocaleString());
script>
html>
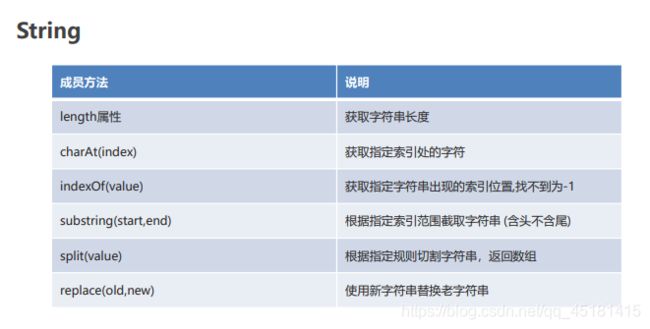
2.4、String
-
方法说明
- 构造方法
- 成员方法
- 代码实现
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Stringtitle>
head>
<body>
body>
<script>
//1. 构造方法创建字符串对象
let s1 = new String("hello");
document.write(s1 + "
");
//2. 直接赋值
let s2 = "hello";
document.write(s2 + "
");
//属性
//1. length 获取字符串的长度
document.write(s2.length + "
");
//成员方法
//1. charAt(index) 获取指定索引处的字符
document.write(s2.charAt(1) + "
");
//2. indexOf(value) 获取指定字符串出现的索引位置
document.write(s2.indexOf("l") + "
");
//3. substring(start,end) 根据指定索引范围截取字符串(含头不含尾)
document.write(s2.substring(2,4) + "
");
//4. split(value) 根据指定规则切割字符串,返回数组
let s3 = "张三,23,男";
let arr = s3.split(",");
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
document.write(arr[i] + "
");
}
//5. replace(old,new) 使用新字符串替换老字符串
let s4 = "你会不会跳伞啊?让我落地成盒。你妹的。";
let s5 = s4.replace("你妹的","***");
document.write(s5 + "
");
script>
html>
2.5、RegExp
正则表达式:是一种对字符串进行匹配的规则。
-
方法说明
- 构造方法&成员方法
- 规则
- 代码实现
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>RegExptitle>
head>
<body>
body>
<script>
//1.验证手机号
//规则:第一位1,第二位358,第三到十一位必须是数字。总长度11
let reg1 = /^[1][358][0-9]{9}$/;
document.write(reg1.test("18688888888") + "
");
//2.验证用户名
//规则:字母、数字、下划线组成。总长度4~16
let reg2 = /^[a-zA-Z_0-9]{4,16}$/;
document.write(reg2.test("zhang_san123"));
script>
html>
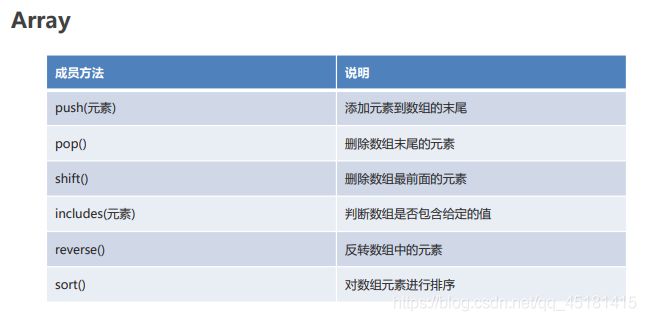
2.6、Array
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Arraytitle>
head>
<body>
body>
<script>
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5];
//1. push(元素) 添加元素到数组的末尾
arr.push(6);
document.write(arr + "
");
//2. pop() 删除数组末尾的元素
arr.pop();
document.write(arr + "
");
//3. shift() 删除数组最前面的元素
arr.shift();
document.write(arr + "
");
//4. includes(元素) 判断数组中是否包含指定的元素
document.write(arr.includes(2) + "
");
//5. reverse() 反转数组元素
arr.reverse();
document.write(arr + "
");
//6. sort() 对数组元素排序
arr.sort();
document.write(arr + "
");
script>
html>
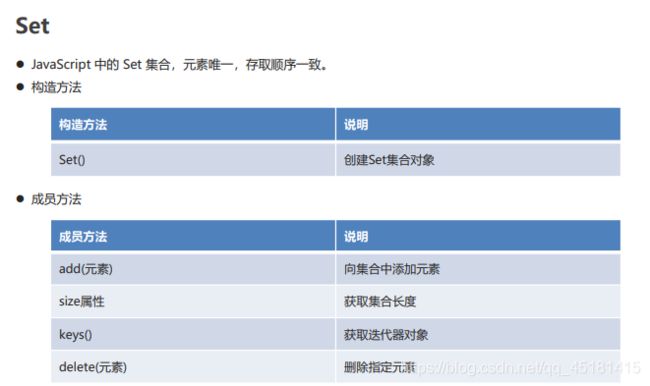
2.7、Set
JavaScript 中的 Set 集合,元素唯一,存取顺序一致。
- 方法说明
- 代码实现
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Settitle>
head>
<body>
body>
<script>
// Set() 创建集合对象
let s = new Set();
// add(元素) 添加元素
s.add("a");
s.add("b");
s.add("c");
s.add("c");
// size属性 获取集合的长度
document.write(s.size + "
"); // 3
// keys() 获取迭代器对象
let st = s.keys();
for(let i = 0; i < s.size; i++){
document.write(st.next().value + "
");
}
// delete(元素) 删除指定元素
document.write(s.delete("c") + "
");
let st2 = s.keys();
for(let i = 0; i < s.size; i++){
document.write(st2.next().value + "
");
}
script>
html>
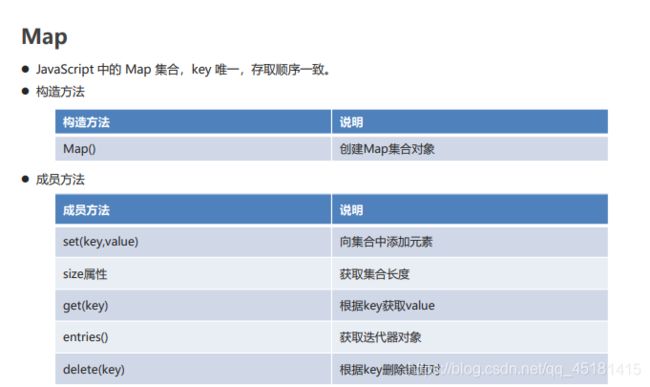
2.8、Map
JavaScript 中的 Map 集合,key 唯一,存取顺序一致。
- 方法说明
- 代码实现
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Maptitle>
head>
<body>
body>
<script>
// Map() 创建Map集合对象
let map = new Map();
// set(key,value) 添加元素
map.set("张三",23);
map.set("李四",24);
map.set("李四",25);
// size属性 获取集合的长度
document.write(map.size + "
");
// get(key) 根据key获取value
document.write(map.get("李四") + "
");
// entries() 获取迭代器对象
let et = map.entries();
for(let i = 0; i < map.size; i++){
document.write(et.next().value + "
");
}
// delete(key) 根据key删除键值对
document.write(map.delete("李四") + "
");
let et2 = map.entries();
for(let i = 0; i < map.size; i++){
document.write(et2.next().value + "
");
}
script>
html>
2.9、Json
- JSON(JavaScript Object Notation):是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。
- 它是基于 ECMAScript 规范的一个子集,采用完全独立于编程语言的文本格式来存储和表示数据。
- 简洁和清晰的层次结构使得 JSON 成为理想的数据交换语言。易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于计算机解析和 生成,并有效的提升网络传输效率。
- 方法说明
- 代码实现
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>JSONtitle>
head>
<body>
body>
<script>
//定义天气对象
let weather = {
city : "北京",
date : "2088-08-08",
wendu : "10° ~ 23°",
shidu : "22%"
};
//1.将天气对象转换为JSON格式的字符串
let str = JSON.stringify(weather);
document.write(str + "
");
//2.将JSON格式字符串解析成JS对象
let weather2 = JSON.parse(str);
document.write("城市:" + weather2.city + "
");
document.write("日期:" + weather2.date + "
");
document.write("温度:" + weather2.wendu + "
");
document.write("湿度:" + weather2.shidu + "
");
script>
html>
2.10、表单校验
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>表单校验title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">link>
head>
<body>
<div class="login-form-wrap">
<h1>程序员h1>
<form class="login-form" action="#" id="regist" method="get" autocomplete="off">
<label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" placeholder="Username..." value="">
label>
<label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" placeholder="Password..." value="">
label>
<input type="submit" value="注册">
form>
div>
body>
<script>
//1.为表单绑定提交事件
document.getElementById("regist").onsubmit = function() {
//2.获取填写的用户名和密码
let username = document.getElementById("username").value;
let password = document.getElementById("password").value;
//3.判断用户名是否符合规则 4~16位纯字母
let reg1 = /^[a-zA-Z]{4,16}$/;
if(!reg1.test(username)) {
alert("用户名不符合规则,请输入4到16位的纯字母!");
return false;
}
//4.判断密码是否符合规则 6位纯数字
let reg2 = /^[\d]{6}$/;
if(!reg2.test(password)) {
alert("密码不符合规则,请输入6位纯数字的密码!");
return false;
}
//5.如果所有条件都不满足,则提交表单
return true;
}
script>
html>
2.11、小结
- 内置对象是 JavaScript 提供的带有属性和方法的特殊数据类型。
- 数字日期 Number Math Date
- 字符串 String RegExp
- 数组集合 Array Set Map
- 结构化数据 JSON
3、JavaScript BOM
- BOM(Browser Object Model):浏览器对象模型。
- 将浏览器的各个组成部分封装成不同的对象,方便我们进行操作。
3.1、Windows窗口对象
- 定时器
- 唯一标识 setTimeout(功能,毫秒值):设置一次性定时器。
- clearTimeout(标识):取消一次性定时器。
- 唯一标识 setInterval(功能,毫秒值):设置循环定时器。
- clearInterval(标识):取消循环定时器。
- 加载事件
- window.onload:在页面加载完毕后触发此事件的功能。
- 代码实现
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>window窗口对象title>
<script>
//一、定时器
function fun(){
alert("该起床了!");
}
//设置一次性定时器
//let d1 = setTimeout("fun()",3000);
//取消一次性定时器
//clearTimeout(d1);
//设置循环定时器
//let d2 = setInterval("fun()",3000);
//取消循环定时器
//clearInterval(d2);
//加载事件
window.onload = function(){
let div = document.getElementById("div");
alert(div);
}
script>
head>
<body>
<div id="div">dddddiv>
body>
html>
3.2、Location地址栏对象
-
href 属性
就是浏览器的地址栏。我们可以通过为该属性设置新的 URL,使浏览器读取并显示新的 URL 的内容。
- 代码实现
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>location地址栏对象title>
<style>
p{
text-align: center;
}
span{
color: red;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<p>
注册成功!<span id="time">5span>秒之后自动跳转到首页...
p>
body>
<script>
//1.定义方法。改变秒数,跳转页面
let num = 5;
function showTime() {
num--;
if(num <= 0) {
//跳转首页
location.href = "index.html";
}
let span = document.getElementById("time");
span.innerHTML = num;
}
//2.设置循环定时器,每1秒钟执行showTime方法
setInterval("showTime()",1000);
script>
html>
3.3、案例-动态广告
- 案例分析和实现
<img src="img/ad_big.jpg" id="ad_big" width="100%"/>
- 在 css 样式中,display 属性可以控制元素是否显示
style="display: none;"
- 设置定时器,3 秒后显示广告图片
//1.设置定时器,3秒后显示广告图片
setTimeout(function(){
let img = document.getElementById("ad_big");
img.style.display = "block";
},3000);
- 设置定时器,3 秒后隐藏广告图片
//2.设置定时器,3秒后隐藏广告图片
setTimeout(function(){
let img = document.getElementById("ad_big");
img.style.display = "none";
},6000);
3.4、小结
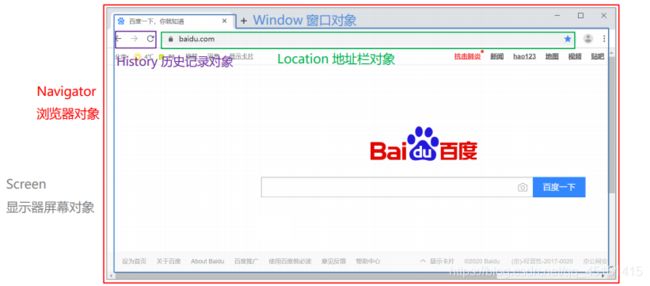
- **BOM(Browser Object Model):**浏览器对象模型。
- 将浏览器的各个组成部分封装成不同的对象,方便我们进行操作。
- Window:窗口对象
- Location:地址栏对象
- Navigator:浏览器对象
- History:当前窗口历史记录对象
- Screen:显示器屏幕对象
- Window 窗口对象
- setTimeout()、clearTimeout():一次性定时器
- setInterval()、clearInterval():循环定时器
- onload 事件:页面加载完毕触发执行功能
- Location 地址栏对象 href 属性:跳转到指定的 URL 地址
4、JavaScript封装
封装思想
-
**封装:**将复杂的操作进行封装隐藏,对外提供更加简单的操作。
-
获取元素的方法
- document.getElementById(id值):根据 id 值获取元素
- document.getElementsByName(name值):根据 name 属性值获取元素们
- document.getElementsByTagName(标签名):根据标签名获取元素们
-
代码实现
<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>封装title> head> <body> <div id="div1">div1div> <div name="div2">div2div> body> <script src="my.js">script> <script> let div1 = getById("div1"); alert(div1); // let div1 = document.getElementById("div1"); // alert(div1); // let divs = document.getElementsByName("div2"); // alert(divs.length); // let divs2 = document.getElementsByTagName("div"); // alert(divs2.length); script> html>js封装
function getById(id){ return document.getElementById(id); } function getByName(name) { return document.getElementsByName(name); } function getByTag(tag) { return document.getElementsByTagName(tag); }
我们之前的操作都是基于原生 JavaScript 的,比较繁琐。 JQuery 是一个前端框架技术,针对 JavaScript 进行了一系列的封装,使得操作变得非常简单! 期待吧……