零基础学习cJSON 源码详解与应用 (四)cJSON_Parse();解析json字符串
文章目录
-
- 一,解析json字符串示例
- 二,代码解析
-
- 2.1 parse_buffer 结构体
- 2.2 skip_utf8_bom();
- 2.3 buffer_skip_whitespace();
- 2.4 parse_value();
- 小结
cJSON系列:
- 零基础学习cJSON 源码详解与应用(一)如何学习cJSON
- 零基础学习cJSON 源码详解与应用(二)创建json数据
- 零基础学习cJSON 源码详解与应用 (三)cJSON_Print();打印json
- 零基础学习cJSON 源码详解与应用 (四)cJSON_Parse();解析json字符串
零基础学习cJSON 源码详解与应用 (五)修改,复制,比较cjson
上一章介绍了从cjson结构体到json字符串的过程,这一章是逆过程,就是将json字符串转换成cjson结构体。逆过程与上一章思路上是一脉相承的。紧紧围绕着cjson结构体与json的格式。
一,解析json字符串示例
还记得在第一章第二节的应用场景示例吗,通过http接口获取到天气的json数据,这些json数据是通过http协议发送到我们客户端,一般是以字符串形式放在body里。客户端想要从中读取所需信息,就必须将字符串解析成cjson结构体,然后由键读取其中的值。
用以下例子来说明如何使用cjson解析字符串:
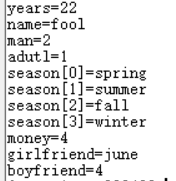
代码解析了json字符串,然后从cjson中提取每个item的值并打印出来。
//非格式化的json字符串
char *json = "{\"years\":22,\"name\":\"fool\",\"man\":true,\"adult\":false,\"season\":[\"spring\",\"summer\",\"fall\",\"winter\"],\"money\":null,\"child\":{\"girlfriend\":\"june\",\"boyfriend\":null}}";
cJSON *root = cJSON_Parse(json);
cJSON *item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "years");
int years = years->valuedouble;
printf("years=%d \r\n", years);
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "name");
char *name = cJSON_GetStringValue(item);
printf("name=%s \r\n", name);
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "man");
int man = item->type;
printf("man=%d \r\n", man);
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "adult");
int adult = item->type;
printf("adutl=%d \r\n", adult);
//获取数组item
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "season");
int arry_size = cJSON_GetArraySize(item);
for (int i = 0; i < arry_size;i++)
{
//打印数组里的所有item
char *season = cJSON_GetStringValue(cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, i));
printf("season[%d]=%s \r\n",i, season);
}
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "money");
int money = item->type;
printf("money=%d \r\n", money);
//获取嵌套的json
cJSON *child = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "child");
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(child, "girlfriend");
char *girlfriend = cJSON_GetStringValue(item);
printf("girlfriend=%s \r\n", girlfriend);
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(child, "boyfriend");
int boyfriend = item->type;
printf("boyfriend=%d \r\n", boyfriend);
//记得删除json
cJSON_Delete(root);
二,代码解析
cJSON_Parse();调用了cJSON_ParseWithOpts(),只是后两个输入参数为0。这对我们的分析影响不大。先大概看一下cJSON_ParseWithOpts();
/*
* 解析json字符串
* value:字符串
* 成功则返回cjson结构体
*/
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_ParseWithOpts(const char *value, const char **return_parse_end, cJSON_bool require_null_terminated)
{
//暂存json字符串的buff
parse_buffer buffer = { 0, 0, 0, 0, { 0, 0, 0 } };
//成功返回的item
cJSON *item = NULL;
/* reset error position */
//用于记录错误的全局变量
global_error.json = NULL;
global_error.position = 0;
if (value == NULL)
{
goto fail;
}
//初始化字符串buffer
buffer.content = (const unsigned char*)value; //json字符串内容
buffer.length = strlen((const char*)value) + sizeof(""); //长度
buffer.offset = 0; //已经解析的长度为0
buffer.hooks = global_hooks; //老朋友了,内存管理大师
//创建一个空item对象
item = cJSON_New_Item(&global_hooks);
if (item == NULL) /* memory fail */
{
goto fail;
}
//跳过json字符串中的bom和空格等特殊字符,然后再解析字符串
if (!parse_value(item, buffer_skip_whitespace(skip_utf8_bom(&buffer))))
{
/* parse failure. ep is set. */
goto fail;
}
/* if we require null-terminated JSON without appended garbage, skip and then check for a null terminator */
//require_null_terminated 和 return_parse_end为0,先不管了
if (require_null_terminated)
{
buffer_skip_whitespace(&buffer);
if ((buffer.offset >= buffer.length) || buffer_at_offset(&buffer)[0] != '\0')
{
goto fail;
}
}
if (return_parse_end)
{
*return_parse_end = (const char*)buffer_at_offset(&buffer);
}
//返回成功的item
return item;
fail:
//失败了,先释放内存
if (item != NULL)
{
cJSON_Delete(item);
}
//检查字符串出错的位置,可供用户分析错误
if (value != NULL)
{
error local_error;
local_error.json = (const unsigned char*)value;
local_error.position = 0;
if (buffer.offset < buffer.length)
{
local_error.position = buffer.offset;
}
else if (buffer.length > 0)
{
local_error.position = buffer.length - 1;
}
if (return_parse_end != NULL)
{
*return_parse_end = (const char*)local_error.json + local_error.position;
}
global_error = local_error;
}
return NULL;
}
这个代码有几个重要的函数skip_utf8_bom(),buffer_skip_whitespace(),parse_value()同时还有一个重要的结构体parse_buffer。下面从这几个方面入手,深入理解代码。
2.1 parse_buffer 结构体
//parsebuffer 一个item的字符串内容
typedef struct
{
const unsigned char *content; //json字符串
size_t length; //字符串的字节总长度
size_t offset; //当前解析的位置
size_t depth; //json对象嵌套的深度
internal_hooks hooks; //分配内存用到的函数
} parse_buffer;
有没有一种熟悉的味道,与上一章print_buffer功能上接近,他将陪伴我们渡过解析字符串的全过程。
为了更好的使用parse_buffer,cjson提供了几个宏来方便操作,简单理解这些宏的作用,在接下来的代码中,他们会经常出现。
//检查buffer能否读取从offset开始size个字节的数据
#define can_read(buffer, size) ((buffer != NULL) && (((buffer)->offset + size) <= (buffer)->length))
//检查buffer能否读取从offset起index个字节的数据
#define can_access_at_index(buffer, index) ((buffer != NULL) && (((buffer)->offset + index) < (buffer)->length))
#define cannot_access_at_index(buffer, index) (!can_access_at_index(buffer, index))
//返回buffer的offset的指针
#define buffer_at_offset(buffer) ((buffer)->content + (buffer)->offset)
2.2 skip_utf8_bom();
uft-8不需要bom表明字节顺序,但可以用BOM来表示编码方式,windows就是采用bom来标记文本文件的编码方式的。解析的时候跳过这些无用的字符。
/*
* 跳过buffer中表示bom的字符\xEF\xBB\xBF
* 成功返回buffer
*/
static parse_buffer *skip_utf8_bom(parse_buffer * const buffer)
{
if ((buffer == NULL) || (buffer->content == NULL) || (buffer->offset != 0))
{
return NULL;
}
//先判断buffer中是否能读取4个字节的数据,再比较这4个数据与bom的字符串
if (can_access_at_index(buffer, 4) && (strncmp((const char*)buffer_at_offset(buffer), "\xEF\xBB\xBF", 3) == 0))
{
//是bom字符,offset跳过这三个字符
buffer->offset += 3;
}
return buffer;
}
上面的代码使用了宏,进一步理解宏can_access_at_index和buffer_at_offset的作用。如果没有检查buffer的内存大小,则可能导致内存读取错误。
注意通过移动offset来跳过content的字符或是标记已经解析过的字符。
2.3 buffer_skip_whitespace();
该函数用于跳过没有利用价值的特殊符号。
/*
* 跳过cr(回车),lf(换行)和空格 直到遇到普通的字符
*/
static parse_buffer *buffer_skip_whitespace(parse_buffer * const buffer)
{
if ((buffer == NULL) || (buffer->content == NULL))
{
return NULL;
}
//ascii码小于32的都是不可显示的,作特殊功能的码
while (can_access_at_index(buffer, 0) && (buffer_at_offset(buffer)[0] <= 32))
{
//使用offset来表示跳过
buffer->offset++;
}
//更新offset
if (buffer->offset == buffer->length)
{
buffer->offset--;
}
return buffer;
}
2.4 parse_value();
该函数在结构上与print_value()有异曲同工之妙。解析不同类型item的内容。
对于简单的null,true,false只需要判断字符串是否相等;
对于其他类型的item,判断第一个字符:
字符串类型的item,则判断是否有双引号;
数组则是[]
json则看{}
/*
* 解析input_buff字符串里的内容到item中
*/
static cJSON_bool parse_value(cJSON * const item, parse_buffer * const input_buffer)
{
if ((input_buffer == NULL) || (input_buffer->content == NULL))
{
return false; /* no input */
}
//解析不同类型的item,通过字符串比较函数strncmp
/* null */
if (can_read(input_buffer, 4) && (strncmp((const char*)buffer_at_offset(input_buffer), "null", 4) == 0))
{
//确定item类型,offset前进4(null占了四个字符)
item->type = cJSON_NULL;
input_buffer->offset += 4;
return true;
}
/* false */
if (can_read(input_buffer, 5) && (strncmp((const char*)buffer_at_offset(input_buffer), "false", 5) == 0))
{
//确定item类型,offset前进5(false占了四个字符)
item->type = cJSON_False;
input_buffer->offset += 5;
return true;
}
/* true */
if (can_read(input_buffer, 4) && (strncmp((const char*)buffer_at_offset(input_buffer), "true", 4) == 0))
{
//确定item类型,offset前进4(true占了四个字符)
item->type = cJSON_True;
item->valueint = 1;
input_buffer->offset += 4;
return true;
}
/* string 检查的是双引号*/
if (can_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) && (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] == '\"'))
{
//解析字符串
return parse_string(item, input_buffer);
}
/* number 由符号及ascii码判断*/
if (can_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) && ((buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] == '-') || ((buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] >= '0') && (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] <= '9'))))
{
//进入解析数字
return parse_number(item, input_buffer);
}
/* array 由数组的标志符号[]判断*/
if (can_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) && (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] == '['))
{
//进入解析数组
return parse_array(item, input_buffer);
}
/* object 由json标志符号{}判断*/
if (can_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) && (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] == '{'))
{
//进入解析json
return parse_object(item, input_buffer);
}
return false;
}
1,parse_string(); 从字符串解析字符串
在代码同样要注意特殊符号的处理。例如,假设item的内容是:
“item”: “hello world\r\n”
解析的时候就会把\r\n转换成真正的回车和换行,而不是简单的字符串复制
/*
* 解析input_buffer里的字符串,并给item赋值
*/
static cJSON_bool parse_string(cJSON * const item, parse_buffer * const input_buffer)
{
const unsigned char *input_pointer = buffer_at_offset(input_buffer) + 1; //input_pointer此时跳过了"
const unsigned char *input_end = buffer_at_offset(input_buffer) + 1;
unsigned char *output_pointer = NULL;
unsigned char *output = NULL;
/* 检查是不是字符串*/
if (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] != '\"')
{
goto fail;
}
{
/* calculate approximate size of the output (overestimate) */
//计算大概的输出字节大小
size_t allocation_length = 0; //内存分配所需字节
size_t skipped_bytes = 0; //一些特殊符号需要跳过
//检查所有的buff,计算需要跳过的字节,并找到字符串结束的"的指针
while (((size_t)(input_end - input_buffer->content) < input_buffer->length) && (*input_end != '\"'))
{
/* is escape sequence */
//如果是转义字符\,对解析无用,则跳过该字符
if (input_end[0] == '\\')
{
//防止当最后一个是反斜杠时,内存溢出
if ((size_t)(input_end + 1 - input_buffer->content) >= input_buffer->length)
{
/* prevent buffer overflow when last input character is a backslash */
goto fail;
}
skipped_bytes++;
input_end++;
}
input_end++;
}
//正确情况下,input_end此时应该是结尾的",且长度不该超length 再次检查
if (((size_t)(input_end - input_buffer->content) >= input_buffer->length) || (*input_end != '\"'))
{
goto fail; /* string ended unexpectedly */
}
/* This is at most how much we need for the output */
//计算大概所需内存为字符串尾部-头部-跳过的字节数
allocation_length = (size_t) (input_end - buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)) - skipped_bytes;
//分配所需内存
output = (unsigned char*)input_buffer->hooks.allocate(allocation_length + sizeof(""));
if (output == NULL)
{
goto fail; /* allocation failure */
}
}
//复制字符串内的有效内容到output
output_pointer = output;
/* loop through the string literal */
//从头复制input内容
while (input_pointer < input_end)
{
//如果不是特殊字符,直接复制到output_pointer
if (*input_pointer != '\\')
{
*output_pointer++ = *input_pointer++;
}
/* escape sequence */
else //存在特殊符号
{
//input_pointer[0]='\\'
unsigned char sequence_length = 2;
//到字符串尾部
if ((input_end - input_pointer) < 1)
{
goto fail;
}
//将大小两个字符的特殊符号,转化成一个字节的对应符号
switch (input_pointer[1])
{
case 'b':
*output_pointer++ = '\b';
break;
case 'f':
*output_pointer++ = '\f';
break;
case 'n':
*output_pointer++ = '\n';
break;
case 'r':
*output_pointer++ = '\r';
break;
case 't':
*output_pointer++ = '\t';
break;
case '\"':
case '\\':
case '/':
*output_pointer++ = input_pointer[1];
break;
/* UTF-16 literal */
case 'u':
sequence_length = utf16_literal_to_utf8(input_pointer, input_end, &output_pointer);
if (sequence_length == 0)
{
/* failed to convert UTF16-literal to UTF-8 */
goto fail;
}
break;
default:
goto fail;
}
//移动input_pointer指针
input_pointer += sequence_length;
}
}
/* zero terminate the output */
//字符串结束符,使output_pointer结束
*output_pointer = '\0';
//将解析出的字符串指针赋值给item,并更新offset
item->type = cJSON_String;
item->valuestring = (char*)output;
input_buffer->offset = (size_t) (input_end - input_buffer->content);
input_buffer->offset++;
return true;
fail:
//失败则释放内存
if (output != NULL)
{
input_buffer->hooks.deallocate(output);
}
//更新offset
if (input_pointer != NULL)
{
input_buffer->offset = (size_t)(input_pointer - input_buffer->content);
}
return false;
}
2,parse_number();从字符串中解析数字
例如:把字符串"520"转换成 “我爱你” 520.
/*
* 解析字符串中的数字
*/
static cJSON_bool parse_number(cJSON * const item, parse_buffer * const input_buffer)
{
double number = 0; //存放数字结果 520
unsigned char *after_end = NULL;
unsigned char number_c_string[64]; //暂存数字字符串"520"
unsigned char decimal_point = get_decimal_point(); //小数点的字符
size_t i = 0;
if ((input_buffer == NULL) || (input_buffer->content == NULL))
{
return false;
}
//判断最后63个字符是否是数字或小数点
for (i = 0; (i < (sizeof(number_c_string) - 1)) && can_access_at_index(input_buffer, i); i++)
{
switch (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[i])
{
case '0':
case '1':
case '2':
case '3':
case '4':
case '5':
case '6':
case '7':
case '8':
case '9':
case '+':
case '-':
case 'e':
case 'E':
//以上情况直接将input_buffer的数字复制到数组
number_c_string[i] = buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[i];
break;
case '.':
number_c_string[i] = decimal_point;
break;
//不是数字或小数点,说明数字已经结束
default:
goto loop_end;
}
}
loop_end:
//给字符数组打上大结局
number_c_string[i] = '\0';
//strtod()将数字字符串转成浮点数,after_end为转换结尾的地址
number = strtod((const char*)number_c_string, (char**)&after_end);
//若结尾地址==字符串头,肯定错了
if (number_c_string == after_end)
{
return false; /* parse_error */
}
//将解析到的数字赋值给item
item->valuedouble = number;
/*限制number的大小,防止内存溢出*/
if (number >= INT_MAX)
{
item->valueint = INT_MAX;
}
else if (number <= (double)INT_MIN)
{
item->valueint = INT_MIN;
}
else
{
//最后放到valueint
item->valueint = (int)number;
}
//完善item的信息
item->type = cJSON_Number;
input_buffer->offset += (size_t)(after_end - number_c_string);
return true;
}
3, parse_array();从字符串中解析数组
数组的起始和结束标志很好理解,就是[]符号。
在之前的章节里讲过,cjson里的数组表示起始就是一个以item为节点的链表,所以在代码中嵌套调用了parse_value();这里是值得思考一下的。
例如:
"[1,2,3,4,5]"转换成cjson为节点的链表,一个有5个节点,每个节点的类型都是number,进入parse_value()后都是往parse_number()里钻。
/*
* 解析json数组,数组是以链表连接一起的
*/
static cJSON_bool parse_array(cJSON * const item, parse_buffer * const input_buffer)
{
cJSON *head = NULL; //链表的头item
cJSON *current_item = NULL;
//json深度有限制
if (input_buffer->depth >= CJSON_NESTING_LIMIT)
{
return false; /* to deeply nested */
}
input_buffer->depth++;
//数组是以[开始
if (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] != '[')
{
/* not an array */
goto fail;
}
input_buffer->offset++;
//跳过特殊字符
buffer_skip_whitespace(input_buffer);
if (can_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) && (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] == ']'))
{
/* empty array */
//空数组
goto success;
}
/* 检查我们是不是跳过头,跳到buffer尾部 */
if (cannot_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0))
{
input_buffer->offset--;
goto fail;
}
/* 做人留一线,日后好相见 */
input_buffer->offset--;
/* loop through the comma separated array elements */
//在循环中,构建数组,也就是item链表
do
{
/* allocate next item */
cJSON *new_item = cJSON_New_Item(&(input_buffer->hooks));
if (new_item == NULL)
{
goto fail; /* allocation failure */
}
/* attach next item to list */
if (head == NULL)
{
//确定链表头
current_item = head = new_item;
}
else
{
//将新成员依次插入链表
current_item->next = new_item;
new_item->prev = current_item;
current_item = new_item;
}
//解析新的子节点item的内容
input_buffer->offset++;
//跳过特殊字符
buffer_skip_whitespace(input_buffer);
//进入解析(嵌套调用了)
if (!parse_value(current_item, input_buffer))
{
goto fail; /* failed to parse value */
}
buffer_skip_whitespace(input_buffer);
}
//逗号存在表示有下一个item,无则退出
while (can_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) && (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] == ','));
//正确的情况下,数组最后一个元素解析完后 下一个字符就是]
if (cannot_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) || buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] != ']')
{
goto fail; /* expected end of array */
}
success:
input_buffer->depth--;
//将item链表头连接到父节点的child 完善item
item->type = cJSON_Array;
item->child = head;
input_buffer->offset++;
return true;
//失败了就释放内存
fail:
if (head != NULL)
{
cJSON_delete(head);
}
return false;
}
4,parse_object();从字符串中解析json
这个函数与上一个代码上非常相似,不同之处在于,解析json对象时,当解析完 { 后,需要先解析出item的键,再嵌套调用parse_value();解析item的值。
/*
* 解析json对象,得到一个json类型的链表赋值给父json
*/
static cJSON_bool parse_object(cJSON * const item, parse_buffer * const input_buffer)
{
cJSON *head = NULL; //json数据里的第一个item
cJSON *current_item = NULL;
//json深度限制
if (input_buffer->depth >= CJSON_NESTING_LIMIT)
{
return false; /* to deeply nested */
}
input_buffer->depth++;
//json对象是以{}包含起来
if (cannot_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) || (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] != '{'))
{
goto fail; /* not an object */
}
input_buffer->offset++;
buffer_skip_whitespace(input_buffer);
if (can_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) && (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] == '}'))
{
//空的json!amazing!
goto success; /* empty object */
}
/* check if we skipped to the end of the buffer */
if (cannot_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0))
{
input_buffer->offset--;
goto fail;
}
/* step back to character in front of the first element */
input_buffer->offset--;
/* loop through the comma separated array elements */
//解析json数据,{ 之后一定是 "key"键,所以先解析出键
do
{
/* allocate next item */
//创建新的json item
cJSON *new_item = cJSON_New_Item(&(input_buffer->hooks));
if (new_item == NULL)
{
goto fail; /* allocation failure */
}
/* attach next item to list */
if (head == NULL)
{
/* start the linked list */
current_item = head = new_item;
}
else
{
/* add to the end and advance */
current_item->next = new_item;
new_item->prev = current_item;
current_item = new_item;
}
/* parse the name of the child */
input_buffer->offset++;
buffer_skip_whitespace(input_buffer);
//此时的input_buff解析出来的是json的key值
if (!parse_string(current_item, input_buffer))
{
goto fail; /* failed to parse name */
}
buffer_skip_whitespace(input_buffer);
//parse_string()把解析的字符串存放在item的valuestring,需要赋值到item的string成员
current_item->string = current_item->valuestring;
current_item->valuestring = NULL;
//检查key值后是否是冒号,若不是则出错
if (cannot_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) || (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] != ':'))
{
goto fail; /* invalid object */
}
//正常解析item的value
input_buffer->offset++;
buffer_skip_whitespace(input_buffer);
if (!parse_value(current_item, input_buffer))
{
goto fail; /* failed to parse value */
}
buffer_skip_whitespace(input_buffer);
}
//每个item之间由逗号分隔,最后一个item没有逗号
while (can_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) && (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] == ','));
//检查大括号有没有关上
if (cannot_access_at_index(input_buffer, 0) || (buffer_at_offset(input_buffer)[0] != '}'))
{
goto fail; /* expected end of object */
}
//将item链表头连接给父节点json
success:
input_buffer->depth--;
item->type = cJSON_Object;
item->child = head;
input_buffer->offset++;
return true;
fail:
if (head != NULL)
{
cJSON_Delete(head);
}
return false;
}