uni的vue代码是如何在微信小程序里面执行的,对此比较感兴趣所以去调试学习了一波.
准备工作
// 在vue.config.js里打开非压缩的代码
module.exports = {
configureWebpack: config => {
config.devtool = 'none'
config.mode = 'development'
}
}
// 运行时代码路径 node_modules\@dcloudio\uni-mp-weixin\dist\index.js
// uni修改过后的vue代码路径 node_modules\@dcloudio\vue-cli-plugin-uni\packages\mp-vue\dist\mp.runtime.esm.js
页面初始化
不管是页面还是组件,uni都是通过微信提供的全局component方法来实现的,uni在原生的conponent基础上做了一层代理
const MPPage = Page;
const MPComponent = Component;
if (!MPPage.__$wrappered) {
MPPage.__$wrappered = true;
// page 也做了代理,但是没有使用(至少正常配置没有使用)
Page = function (options = {}) {
initHook('onLoad', options);
return MPPage(options)
};
Page.after = MPPage.after;
Component = function (options = {}) {
initHook('created', options);
return MPComponent(options)
};
}
对外暴露了createComponent, createPage 这2个方法,在生成的vue文件里会调用这2个方法,这2个方法的核心都是parseComponent
function createPage (vuePageOptions) {
{
// Component 是被包裹一次的wx原生方法
return Component(parsePage(vuePageOptions))
}
}
function parsePage (vuePageOptions) {
return parseBasePage(vuePageOptions, {
isPage,
initRelation
})
}
function createComponent (vueOptions) {
{
return Component(parseComponent(vueOptions))
}
}
function parseBasePage (vuePageOptions, {
isPage,
initRelation
}) {
const pageOptions = parseComponent(vuePageOptions);
initHooks(pageOptions.methods, hooks$1, vuePageOptions);
pageOptions.methods.onLoad = function (query) {
this.options = query;
const copyQuery = Object.assign({}, query);
delete copyQuery.__id__;
this.$page = {
fullPath: '/' + (this.route || this.is) + stringifyQuery(copyQuery)
};
this.$vm.$mp.query = query; // 兼容 mpvue
this.$vm.__call_hook('onLoad', query);
};
return pageOptions
}
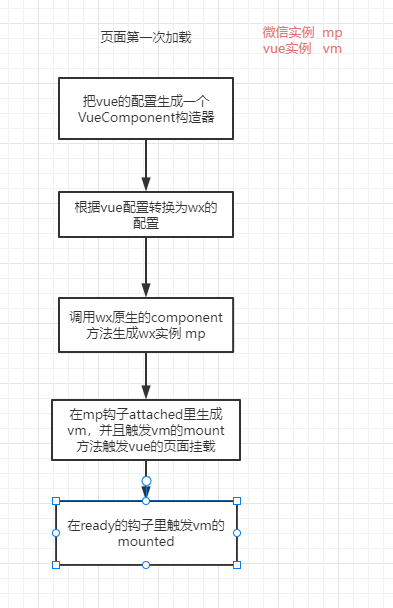
parseComponent的parseBaseComponent方法是把vue配置初始化为微信的配置文件(上面的代码贴出来不看都无所谓这里才真正的开始),把你vue的配置转换为微信小程序的配置
function parseComponent (vueComponentOptions) {
return parseBaseComponent(vueComponentOptions, {
isPage,
initRelation
})
}
function parseBaseComponent (vueComponentOptions, {
isPage,
initRelation
} = {}) {
// Vue.extend(vueComponentOptions); 核心就是通过vue的extend方法生成一个构造器
const [VueComponent, vueOptions] = initVueComponent(Vue, vueComponentOptions);
const options = {
multipleSlots: true,
addGlobalClass: true,
...(vueOptions.options || {})
};
// 这个option就是微信用来生成组件的option
const componentOptions = {
options,
// vue的data和methods都会合并然后放在wx的data里
data: initData(vueOptions, Vue.prototype),
// vue的mixins extends behaviors都合并然后变成wx的behaviors
behaviors: initBehaviors(vueOptions, initBehavior),
// vue的props转换而成
properties: initProperties(vueOptions.props, false, vueOptions.__file),
lifetimes: {
attached () {
// 获取到微信实例的props
const properties = this.properties;
const options = {
mpType: isPage.call(this) ? 'page' : 'component',
mpInstance: this,
propsData: properties
};
// 初始化 vue 实例
this.$vm = new VueComponent(options);
// 执行vue实例的mount,这一步很特别,vue实例其实是没有任何的render,因为vue的template
// 已经在打包的过程中变成wxml,给wx实例使用了,所以这个vue的实例的页面内容其实是空的,
// 那如何处理vue的渲染watch呢,uni对vue的源码做了处理,在patch的时候,新建了一个空对象
// 然后把data和computed里面的所有属性都复制给了新对象,从而达到了渲染watch的监听效果
// 也就是说在uni里面的vue,所有的data和computed都是在渲染watch里面使用了的,可能对排除
// 某些问题有所帮助
this.$vm.$mount();
},
ready () {
// 当组件 props 默认值为 true,初始化时传入 false 会导致 created,ready 触发, 但 attached 不触发
// https://developers.weixin.qq.com/community/develop/doc/00066ae2844cc0f8eb883e2a557800
if (this.$vm) {
this.$vm._isMounted = true;
// 在微信实例的ready钩子里 触发vue的挂载钩子
this.$vm.__call_hook('mounted');
this.$vm.__call_hook('onReady');
}
},
detached () {
this.$vm && this.$vm.$destroy();
}
},
pageLifetimes: {
show (args) {
this.$vm && this.$vm.__call_hook('onPageShow', args);
},
hide () {
this.$vm && this.$vm.__call_hook('onPageHide');
},
resize (size) {
this.$vm && this.$vm.__call_hook('onPageResize', size);
}
},
methods: {
__l: handleLink,
__e: handleEvent
}
};
if (isPage) {
return componentOptions
}
return [componentOptions, VueComponent]
}
用一张图来快速理解
uni的和vue的区别
一 computed是立即执行,且所有data和computed都会成为渲染依赖
二 vue的组件其实是没有任何页面的,页面都是微信组件的
三 wx的实例是通过微信的component来生成的,不是page方法