github 地址:https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router
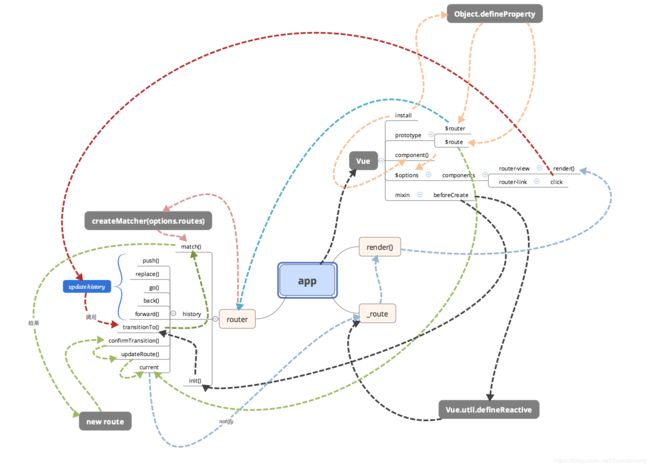
思维导图
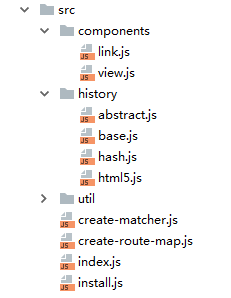
router目录
1.components下是两个组件 和
2.history是路由方式的封装,提供三种方式
3.util下主要是各种功能类和功能函数
4.create-matcher和create-router-map是生成匹配表
5.index是VueRouter类,也整个插件的入口
6.Install 提供安装的方法
先看入口文件main.js;先整体展示下vue-router使用方式,请牢记一下几步哦。
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
//注册插件 如果是在浏览器环境运行的,可以不写该方法
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 1. 定义(路由)组件。
// 可以从其他文件 import 进来
const User = { template: '用户' }
const Role = { template: '角色' }
// 2. 定义路由
// Array,每个路由应该映射一个组件。
const routes = [
{ path: '/user', component: User },
{ path: '/home', component: Home }
]
// 3. 创建 router 实例,并传 `routes` 配置
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
// 4. 创建和挂载根实例。
// 记得要通过 router 对象以参数注入Vue,
// 从而让整个应用都有路由功能
// 使用 router-link 组件来导航.
// 路由出口
// 路由匹配到的组件将渲染在这里
const app = new Vue({
router,
template: `
Basic
/ 用户 角色 /用户
分析开始
第一步
Vue是使用.use( plugins )方法将插件注入到Vue中。
use方法会检测注入插件VueRouter内的install方法,如果有,则执行install方法。
注意:如果是在浏览器环境,在index.js内会自动调用.use方法。如果是基于node环境,需要手动调用。
if (inBrowser && window.Vue) {
window.Vue.use(VueRouter)
}
Install解析 (对应目录结构的install.js)
该方法内主要做了以下三件事:
1、对Vue实例混入beforeCreate钩子操作(在Vue的生命周期阶段会被调用)
2、通过Vue.prototype定义router、router、route 属性(方便所有组件可以获取这两个属性)
3、Vue上注册router-link和router-view两个组件
export function install (Vue) {
if (install.installed && _Vue === Vue) return
install.installed = true
_Vue = Vue
const isDef = v => v !== undefined
const registerInstance = (vm, callVal) => {
let i = vm.$options._parentVnode
if (isDef(i) && isDef(i = i.data) && isDef(i = i.registerRouteInstance)) {
i(vm, callVal)
}
}
Vue.mixin({
//对Vue实例混入beforeCreate钩子操作
beforeCreate () {
if (isDef(this.$options.router)) {
this._routerRoot = this
this._router = this.$options.router
this._router.init(this)
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current)
} else {
this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this
}
registerInstance(this, this)
},
destroyed () {
registerInstance(this)
}
})
//通过Vue.prototype定义$router、$route 属性(方便所有组件可以获取这两个属性)
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$router', {
get () { return this._routerRoot._router }
})
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$route', {
get () { return this._routerRoot._route }
})
//Vue上注册router-link和router-view两个组件
Vue.component('RouterView', View)
Vue.component('RouterLink', Link)
const strats = Vue.config.optionMergeStrategies
// use the same hook merging strategy for route hooks
strats.beforeRouteEnter = strats.beforeRouteLeave = strats.beforeRouteUpdate = strats.created
}
第二步 生成router实例
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
生成实例过程中,主要做了以下两件事
1、根据配置数组(传入的routes)生成路由配置记录表。
2、根据不同模式生成监控路由变化的History对象
注:History类由HTML5History、HashHistory、AbstractHistory三类继承
history/base.js实现了基本history的操作
history/hash.js,history/html5.js和history/abstract.js继承了base,只是根据不同的模式封装了一些基本操作
在入口文件中,首先要实例化一个 VueRouter ,然后将其传入 Vue 实例的 options 中。现在继续来看在 src/index.js 中暴露出来的 VueRouter 类:
// ...
import { createMatcher } from './create-matcher'
// ...
export default class VueRouter {
// ...
constructor (options: RouterOptions = {}) {
this.app = null
this.options = options
this.beforeHooks = []
this.afterHooks = []
// 创建 match 匹配函数
this.match = createMatcher(options.routes || [])
// 根据 mode 实例化具体的 History
let mode = options.mode || 'hash'
this.fallback = mode === 'history' && !supportsHistory
if (this.fallback) {
mode = 'hash'
}
if (!inBrowser) {
mode = 'abstract'
}
this.mode = mode
switch (mode) {
case 'history':
this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base)
break
case 'hash':
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback)
break
case 'abstract':
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this)
break
default:
assert(false, `invalid mode: ${mode}`)
}
}
// ...
}
里边包含了重要的一步:创建 match 匹配函数。
match 匹配函数
匹配函数是由 src/create-matcher.js 中的 createMatcher 创建的:
/* @flow */
import Regexp from 'path-to-regexp'
// ...
import { createRouteMap } from './create-route-map'
// ...
export function createMatcher (routes: Array): Matcher {
// 创建路由 map
const { pathMap, nameMap } = createRouteMap(routes)
// 匹配函数
function match (
raw: RawLocation,
currentRoute?: Route,
redirectedFrom?: Location
): Route {
// ...
}
function redirect (
record: RouteRecord,
location: Location
): Route {
// ...
}
function alias (
record: RouteRecord,
location: Location,
matchAs: string
): Route {
// ...
}
function _createRoute (
record: ?RouteRecord,
location: Location,
redirectedFrom?: Location
): Route {
if (record && record.redirect) {
return redirect(record, redirectedFrom || location)
}
if (record && record.matchAs) {
return alias(record, location, record.matchAs)
}
return createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom)
}
// 返回
return match
}
// ...
具体逻辑后续再具体分析,现在只需要理解为根据传入的 routes 配置生成对应的路由 map,然后直接返回了 match 匹配函数。
继续来看 src/create-route-map.js 中的 createRouteMap 函数:
/* @flow */
import { assert, warn } from './util/warn'
import { cleanPath } from './util/path'
// 创建路由 map
export function createRouteMap (routes: Array): {
pathMap: Dictionary,
nameMap: Dictionary
} {
// path 路由 map
const pathMap: Dictionary = Object.create(null)
// name 路由 map
const nameMap: Dictionary = Object.create(null)
// 遍历路由配置对象 增加 路由记录
routes.forEach(route => {
addRouteRecord(pathMap, nameMap, route)
})
return {
pathMap,
nameMap
}
}
// 增加 路由记录 函数
function addRouteRecord (
pathMap: Dictionary,
nameMap: Dictionary,
route: RouteConfig,
parent?: RouteRecord,
matchAs?: string
) {
// 获取 path 、name
const { path, name } = route
assert(path != null, `"path" is required in a route configuration.`)
// 路由记录 对象
const record: RouteRecord = {
path: normalizePath(path, parent),
components: route.components || { default: route.component },
instances: {},
name,
parent,
matchAs,
redirect: route.redirect,
beforeEnter: route.beforeEnter,
meta: route.meta || {}
}
// 嵌套子路由 则递归增加 记录
if (route.children) {
// ...
route.children.forEach(child => {
addRouteRecord(pathMap, nameMap, child, record)
})
}
// 处理别名 alias 逻辑 增加对应的 记录
if (route.alias !== undefined) {
if (Array.isArray(route.alias)) {
route.alias.forEach(alias => {
addRouteRecord(pathMap, nameMap, { path: alias }, parent, record.path)
})
} else {
addRouteRecord(pathMap, nameMap, { path: route.alias }, parent, record.path)
}
}
// 更新 path map
pathMap[record.path] = record
// 更新 name map
if (name) {
if (!nameMap[name]) {
nameMap[name] = record
} else {
warn(false, `Duplicate named routes definition: { name: "${name}", path: "${record.path}" }`)
}
}
}
function normalizePath (path: string, parent?: RouteRecord): string {
path = path.replace(/\/$/, '')
if (path[0] === '/') return path
if (parent == null) return path
return cleanPath(`${parent.path}/${path}`)
}
可以看出主要做的事情就是根据用户路由配置对象生成普通的根据 path 来对应的路由记录以及根据 name 来对应的路由记录的 map,方便后续匹配对应。
实例化 History
这也是很重要的一步,所有的 History 类都是在 src/history/ 目录下,现在呢不需要关心具体的每种 History 的具体实现上差异,只需要知道他们都是继承自 src/history/base.js 中的 History 类的:
/* @flow */
// ...
import { inBrowser } from '../util/dom'
import { runQueue } from '../util/async'
import { START, isSameRoute } from '../util/route'
// 这里从之前分析过的 install.js 中 export _Vue
import { _Vue } from '../install'
export class History {
// ...
constructor (router: VueRouter, base: ?string) {
this.router = router
this.base = normalizeBase(base)
// start with a route object that stands for "nowhere"
this.current = START
this.pending = null
}
// ...
}
// 得到 base 值
function normalizeBase (base: ?string): string {
if (!base) {
if (inBrowser) {
// respect 第三步 生成vue实例
const app = new Vue({
router,
template: `
Basic
/ 用户 角色 /用户
代码执行到这,会进入Vue的生命周期,还记得第一步Vue-Router对Vue混入了beforeCreate钩子吗,此时创建一个 Vue 实例,对应的 beforeCreate 钩子就会被调用:
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
//验证vue是否有router对象了,如果有,就不再初始化了
if (isDef(this.$options.router)) { //没有router对象
//将_routerRoot指向根组件
this._routerRoot = this
//将router对象挂载到根组件元素_router上
this._router = this.$options.router
//初始化,建立路由监控
this._router.init(this)
//劫持数据_route,一旦_route数据发生变化后,通知router-view执行render方法
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current)
} else {
//如果有router对象,去寻找根组件,将_routerRoot执行根组件(解决嵌套关系时候_routerRoot指向不一致问题)
this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this
}
registerInstance(this, this)
},
destroyed () {
registerInstance(this)
}
})
代码执行到这,初始化结束,界面将显示默认首页
路由更新方式:
一、主动触发
router-link绑定了click方法,触发history.push或者history.replace,从而触发history.transitionTo。
transitionTo用于处理路由转换,其中包含了updateRoute用于更新_route。
在beforeCreate中有劫持_route的方法,当_route变化后,触发router-view的变化。
二、地址变化(如:在浏览器地址栏直接输入地址)
HashHistory和HTML5History会分别监控hashchange和popstate来对路由变化作对用的处理 。
HashHistory和HTML5History捕获到变化后会对应执行push或replace方法,从而调用transitionTo
,剩下的就和上面主动触发一样啦。
总结
1、安装插件
混入beforeCreate生命周期处理,初始化_routerRoot,_router,_route等数据
全局设置vue静态访问router和router和route,方便后期访问
完成了router-link和 router-view 两个组件的注册,router-link用于触发路由的变化,router-view作 为功能组件,用于触发对应路由视图的变化
2、根据路由配置生成router实例
根据配置数组生成路由配置记录表
生成监控路由变化的hsitory对象
3、将router实例传入根vue实例
根据beforeCreate混入,为根vue对象设置了劫持字段_route,用户触发router-view的变化
调用init()函数,完成首次路由的渲染,首次渲染的调用路径是 调用history.transitionTo方法,根据router的match函数,生成一个新的route对象
接着通过confirmTransition对比一下新生成的route和当前的route对象是否改变,改变的话触发updateRoute,更新hsitory.current属性,触发根组件的_route的变化,从而导致组件的调用render函数,更新router-view
另外一种更新路由的方式是主动触发
router-link绑定了click方法,触发history.push或者history.replace,从而触发history.transitionTo
同时会监控hashchange和popstate来对路由变化作对用的处理