在一个Django应用中可以创建多个APP应用,每个APP应用都可以独立使用,在有多个APP的情况下,APP之间若数据库使用不一,如APP1使用的数据库IP与APP2使用的数据库IP不一致,或者APP1使用MYSQL,APP2使用PGSQL,那么就要对不同APP的数据库进行不同的设置。
以下为一次实际操作演示。
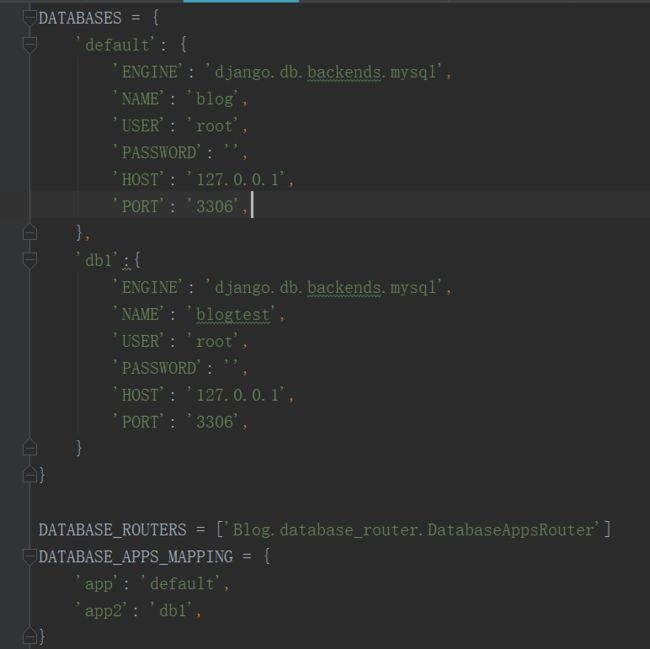
DATABASES ={
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'db.sqlite3'),
},
'db1': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'dbname1',
'USER': 'your_db_user_name',
'PASSWORD': 'yourpassword',
"HOST": "localhost",
},
'db2': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'dbname2',
'USER': 'your_db_user_name',
'PASSWORD': 'yourpassword',
"HOST": "localhost",
},
}
# use multi-database in django
# add by WeizhongTu
DATABASE_ROUTERS =['{项目名称}.database_router.DatabaseAppsRouter']
DATABASE_APPS_MAPPING ={
# example:
#'app_name':'database_name',
'app1': 'db1',
'app2': 'db2',
}
在project_name目录下创建一个database_route.py文件(即与setting.py同级的文件)
文件中写入:
fromdjango.conf importsettings
DATABASE_MAPPING =settings.DATABASE_APPS_MAPPING
classDatabaseAppsRouter(object):
"""
A router to control all database operations on models for different
databases.
In case an app is not set in settings.DATABASE_APPS_MAPPING, the router
will fallback to the `default` database.
Settings example:
DATABASE_APPS_MAPPING = {'app1': 'db1', 'app2': 'db2'}
"""
defdb_for_read(self, model, **hints):
""""Point all read operations to the specific database."""
ifmodel._meta.app_label inDATABASE_MAPPING:
return DATABASE_MAPPING[model._meta.app_label]
return None
defdb_for_write(self, model, **hints):
"""Point all write operations to the specific database."""
ifmodel._meta.app_label inDATABASE_MAPPING:
return DATABASE_MAPPING[model._meta.app_label]
return None
defallow_relation(self, obj1, obj2, **hints):
"""Allow any relation between apps that use the same database."""
db_obj1 =DATABASE_MAPPING.get(obj1._meta.app_label)
db_obj2 =DATABASE_MAPPING.get(obj2._meta.app_label)
ifdb_obj1 anddb_obj2:
ifdb_obj1 ==db_obj2:
return True
else:
return False
return None
实际操作时:
python manage.py makemigrations {app} 创建存储
python manage.py migrate 同步数据库
在代码中使用时候:
test=BlogT.objects.using('db1').get_or_create(title=title,content=content)
在object取得对象时候指定你使用的数据库 using(‘{setting的数据库}’)