LruCache 作用是,不常用的缓存对象 会被清除。
LruCache 是一种缓存策略,持有的是强引用。内部维护了一个队列,每当取出一个值,该值就会被移动到列表的尾部。每当put
使用场景 当滑动列表,如果超出最大设置的内存就把不常用的对象清除掉。把常用的对象存储到Cache中。
当缓存已满时而继续添加,会头部移除,方便GC。
LRU(Least Recently Used):最近最少使用 算法
1,LruCahce 需要设置缓存大小,一般为应用最大使用内存的 1/8 ,有2个方法。get,put.
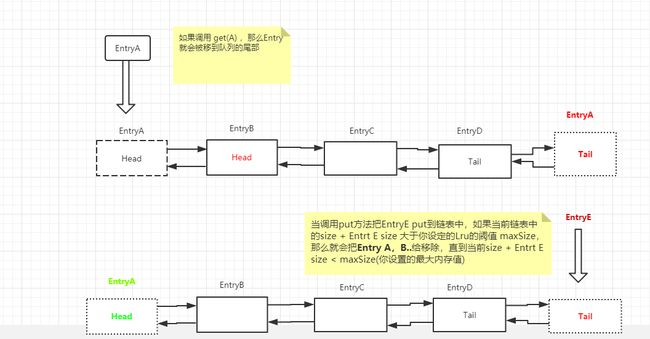
LruCache 内部维护了LikedHashMap实例对象,LikedHashMap有一个特性,每当调用get,会把当前的对象 move node to last(将节点移到最后,就是将结点移到队列的尾结点)。
而LikedHashMap 是双向链表的数据结构。
如果当put元素的时候,会被插入到列表尾结点,当队列已满时head结点会被移除。
如果一个已经存在的元素(Key)又被插入到列表中时,那么这个元素会被再次插入到尾结结点中。
也就是只要get put 元素,当前元素就会被插入到列表的尾结点
LruCache key value ,不允许为null。
看下LinkedHashMap的小栗子:
LinkedHashMap linkedHashMap = new
LinkedHashMap(12, 12L, true);
linkedHashMap.put("1", "A");
linkedHashMap.put("2", "B");
linkedHashMap.put("3", "C");
Set entry = linkedHashMap.entrySet();
for (Object o : entry) {
System.out.println(o);
}
System.out.println("--------------------------");
linkedHashMap.get("1");
Set entry1 = linkedHashMap.entrySet();
for (Object o : entry1) {
System.out.println(o);
}
打印如下:当get("1") ,此节点就最后才打印
1=A
2=B
3=C
2=B
3=C
1=A
再来看LruCache的实现
public class LruCache {
private final LinkedHashMap map;
private int size;
private int maxSize;
private int putCount;
private int createCount;
private int evictionCount;
private int hitCount;
private int missCount;
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
} else {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
//true 会调用 LinkedHashMap afterNodeAccess(e) 配置节点访问
//如果为false那么调用LinkedHashMap 的get 将不会有 插入到尾节点的功能,
this.map = new LinkedHashMap(0, 0.75F, true);
}
}
//每次put 都会重新计算缓存大小
public void resize(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
} else {
synchronized(this) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
this.trimToSize(maxSize);
}
}
@Nullable
public final V get(@NonNull K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
} else {
Object mapValue;
synchronized(this) {
//调用LinkedHashMap的get方法返回
mapValue = this.map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
++this.hitCount;
return mapValue;
}
++this.missCount;
}
V createdValue = this.create(key);
.....
}
@Nullable
public final V put(@NonNull K key, @NonNull V value) {
//不允许键值为null
if (key != null && value != null) {
//上一个元素,如果第一次put(key),则返回为null,否则返回上次的Value
Object previous;
synchronized(this) {
++this.putCount;
//计算当前的Vaule值占用的内存大小
this.size += this.safeSizeOf(key, value);
//把当前的值put 到LinkedHashMap ,获取到上次存放的Value值
previous = this.map.put(key, value);
if (previous != null) {
//上次存放的Value值 不为null了,则减去上次存放的Value值的大小
this.size -= this.safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
this.entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
this.trimToSize(this.maxSize);
return previous;
} else {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
}
//死循环,跳出循环的条件就是当前设置的内存总大小 >= 当前的内存大小
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while(true) {
Object key;
Object value;
synchronized(this) {
if (this.size < 0 || this.map.isEmpty() && this.size != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException(this.getClass().getName() + ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (this.size <= maxSize || this.map.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//获取head结点
Entry toEvict = (Entry)this.map.entrySet().iterator().next();
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
//移除这个Value,并减去当前value所占用的内存大小,直到size(当前的占用总内存) <= maxSize(初始化的时候设置总的内存大小) 跳出循环
this.map.remove(key);
this.size -= this.safeSizeOf(key, value);
++this.evictionCount;
}
this.entryRemoved(true, key, value, (Object)null);
}
}
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, @NonNull K key, @NonNull V oldValue, @Nullable V newValue) {
}
@Nullable
protected V create(@NonNull K key) {
return null;
}
private int safeSizeOf(K key, V value) {
int result = this.sizeOf(key, value);
if (result < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Negative size: " + key + "=" + value);
} else {
return result;
}
}
//我们必须重写这个方法,来告诉lru如何计算当前值的大小(比如 bitmapSize = bitmap.getByteCount())
protected int sizeOf(@NonNull K key, @NonNull V value) {
return 1;
}
LruCache利用了LinkedHashMap的特性
- 1.调用put和get方法会把当前的节点插入到链表的尾部
- 2.当调用put方法,如果当前的链表中已有这个节点那么计算出前一个节点占用的内存大小,并用当前链表所占用的内存 size - entry(Pre Node) +Entry(Cur Node) = size ,如果计算出的size > maxSize 那么就移除head节点 直到 size <= maxSize 为止。
- 3.这样LrcCache 就是可以让 当前的内存大小 保持在 一个最大阈值(maxSize),而可以有效的避免OOM。