- 内存保护学习(一):tc27x的内存保护MPU设置浅析(个人理解)
剑从东方起
链接文件及功能安全开发语言c语言
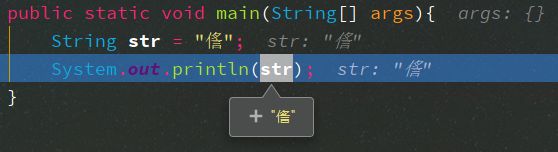
目录一、背景二、Tc27x相关寄存器1、注意点2、注意几个强相关寄存器1)、数据保护范围寄存器2)、代码保护范围寄存器3)、保护集启用寄存器命名约定4)、PSW(每个核都有一个)5)、SYSCON三、使用方法1、内存方面2、在ECUM里面初始化MPU3、OS回调CBK检查4、机理5、补充点一、背景根据低ASIL等级开发的软件组件可能会错误地访问具有较高ASIL等级的软件组件的内存区域,从而产生干扰
- Scanpy源码浅析之pp.normalize_total
何物昂
版本导入Scanpy,其版本为'1.9.1',如果你看到的源码和下文有差异,其可能是由于版本差异。importscanpyasscsc.__version__#'1.9.1'例子函数pp.normalize_total用于Normalizecountspercell,其源代码在scanpy/preprocessing/_normalization.py我们通过一个简单例子来了解该函数主要功能:将一
- python使用MD5
18.程序员
哈希算法算法
一、要使用Python进行MD5加密,可以使用Python标准库中的hashlib模块。二、案例importhashlibstring="Hello,World!"#要进行加密的字符串hash_object=hashlib.md5(string.encode())#将字符串编码并进行MD5加密hash_hex=hash_object.hexdigest()#获取加密后的十六进制字符串print(h
- 浅析IM即时通讯开发中TCP协议层KeepAlive保活机制
wecloud1314
tcp/ip网络服务器
对于IM这种应用而言,应用层的网络保活的最直接办法就是心跳机制,比如主流的IM里有微信、QQ、钉钉、易信等等,可能代码实现细节有所差异,但理论上无一例外都是这样实现。(PS:没错,当初微信跟运营商间的“信令危机”就是跟这个有关)所谓的网络心跳,通常是客户端每隔一小段时间向服务器发送一个数据包(即心跳包),通知服务器自己仍然在线(心跳包中同时可能传输一些必要的数据)。发送心跳包,从通信层面来说就是为
- 浅析MYSQL的事务和锁
胡萝卜、
mysql数据库java
1.MySQL的事务和锁1.1事务的介绍:概念:事务指逻辑上的一组操作,组成这个操作的单元,要么全部成功执行,要么全部执行失败个人理解:某个业务执行更新语句,整个业务下得sql语句(单指更新)全部成功执行,或者执行全部失败常见的mysql执行命令:starttransaction开启事务rollback回滚事务commit提交事务showvariableslike'%commit';查询是否为自动
- 浅析‖医疗行业数据安全
等保星视界
最近小编接触到了医疗行业,猛然发觉信息化技术当前真的是深入应用到了医院的日常经营发展中,医院整体的管理运营全都面向系统化,让医院的管理效率、质量都纷纷得以提升。这也使得信息安全管理工作占据了更加重要的位置。小编总结了下医院信息安全管理的主要工作大概包括这几点:l信息系统网络安全l备份信息记录安全l计算机设备病毒防治l医院信息管理系统平台安全等想必大家也都有所了解,医疗记录包含大量敏感信息:如病患的
- 2020-01-28
ab96a7f92f71
中西医对病毒性肺病诊治差别(浅析1)ab96a7f92f71字数289·阅读02020-01-2814:05西医除了追溯疾病症状与体征之外,更多借助于各种化验、检测手段和影像学,尤其是血常规和胸部高清CT影像加以诊断,还必须做咽拭子或下呼吸道分泌物寻找出病原体,例如有针对病毒核酸检测或培养测序和抗体滴度测试等。当然还进行全面身体测试数据发现以往的基础病或体质状态。中医主要运用望闻问切传统手段来辨别
- Spring源码浅析の循环依赖
西岭千秋雪_
源码分析springjava后端springboot
AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean:尝试获取bean如果bean是单例的:if(mbd.isSingleton()){//尝试获取beansharedInstance=getSingleton(beanName,()->{try{//获取不到就创建returncreateBean(beanName,mbd,args);}catch(BeansExceptionex){//E
- 从中国小说叙述学的角度浅析《酒国》叙述结构
花里胡哨_0ac9
“长篇小说的结构是长篇小说艺术的重要组成部分,是作家丰沛想象力的表现。好的结构,能够凸现故事的意义,也能够改编故事的单一意义。好的结构,可以超越故事,也可以解构故事”一、结构突破的合理性莫言曾提到:“结构就是政治”,证明他在长篇小说的谋篇布局方面下了很大的工夫,这一点在《酒国》里面体现得尤为突出。本文试图运用赵毅衡先生提出的叙述学观点与方法,对《酒国》做一个较浅略的分析。在这个层面上,我们仅对叙述
- 浅析网页不安装插件播放RTSP/FLV视频的方法
点量云实时渲染-小芹
云流化像素流云渲染音视频rtsp无插件网页播放rtmpflv视频网页播放webrtc
早期很多摄像头视频流使用的是RTSP、RTMP协议,播放这类协议的视频通常是在网页上安装插件。但现在越来越多的用户,对于网页安装插件比较反感,且随着移动设备的普及,用户更多的希望使用手机、平板等移动设备,直接可以查看这些协议的视频。那是否有什么方案可以直接网页打开RTSP、RTMP协议的视频,直接观看不用安装插件呢?而且对于摄像头的数据,尽可能低延迟的获取实时画面。其实很多摄像头厂家也注意到这个问
- 浅析大数据Hadoop之YARN架构
haotian1685
python数据清洗人工智能大数据大数据学习深度学习大数据大数据学习YARNhadoop
1.YARN本质上是资源管理系统。YARN提供了资源管理和资源调度等机制1.1原HadoopMapReduce框架对于业界的大数据存储及分布式处理系统来说,Hadoop是耳熟能详的卓越开源分布式文件存储及处理框架,对于Hadoop框架的介绍在此不再累述,读者可参考Hadoop官方简介。使用和学习过老Hadoop框架(0.20.0及之前版本)的同仁应该很熟悉如下的原MapReduce框架图:1.2H
- B站1.18亿元收购甬易支付,获得支付牌照——浅析支付牌照
d488c517aee9
一、B站1.18亿元收购甬易支付宁波市公共资源交易中心网站消息,11月19日,宁波恒舜拍卖有限公司发布余姚中国塑料城物流有限公司产权交易项目成交公告。公告显示,浙江甬易电子支付有限公司65.5%的国有股权,由B站运营主体上海宽娱数码科技有限公司拍得,成交价为人民币11796.55万元。据了解,甬易支付成立于2011年7月,于2012年6月首次获得《支付业务许可证》,2017年6月成功获得续展,续展
- 「浅析系列」《论语》(八佾篇)(1)
霜月洞天
文(3.1)与文(3.2)、文(3.6)【联】文(3.10)与文(3.22)提:中心词(概括)为“底线”。底线有不同的种类,譬如人性底线,三观底线,认知底线,行事底线等,而各底线种类又各自分为多种底线实质,也即在某一种种类之下,到底存在怎样的规矩。点:此四节内容都指出了底线当中“僭越身份”的种类以及礼乐(礼节)中的实质。点2:1、文(3.1):底线→僭越身份(种类:天子与大夫【季孙作为大夫僭越了天
- 【算法】浅析贪心算法
Ustinian_310
算法贪心算法python
贪心算法:高效解决问题的策略1.引言在计算机科学和优化领域,贪心算法是一种常用的解决问题的策略。它以当前情况为基础,做出最优选择,从而希望最终结果也是最优的。本文将带你了解贪心算法的原理、使用方法及其在实际应用中的意义,并通过代码示例和图示帮助大家更好地理解。2.贪心算法简介2.1定义贪心算法(GreedyAlgorithm)是一种在每一步选择中都采取当前状态下最优(即最有利)的选择,从而希望导致
- 使用Vue组件的watch监听-简单计算器
编程初学者01
vue.jsvue.js前端javascript前端框架
Vue组件的初探一、浅析这里做了一个全局的组件vue.component('mycomp',{})在中写组件,将id=comp1script中直接template:"#copm1"其他的部分就是之前所讲的watch来实现简易计算器差不多组件watch监听-计算(CQNU-ZJW)+=varcom=Vue.component('mycomp',{template:"#comp1",data(){re
- 2024年高教社杯数学建模国赛赛题浅析——助攻快速选题
BZD数模社
数学建模
一图流——一张图读懂国赛总体概述:A题偏几何与运动学模型,适合有几何与物理背景的队伍,数据处理复杂性中等。B题侧重统计和优化,适合有运筹学和经济学背景的队伍,数据处理较为直接但涉及多步骤的决策优化。C题属于优化类问题,涉及复杂的多变量优化与不确定性分析,数据处理难度大。D题涉及概率和优化,特别是几何概率模型的推导,理论难度较高。E题数据量较大,重点在于大规模交通数据的分析与优化,适合擅长交通工程和
- ur5在gazebo中仿真的官方源码浅析
Ecalpal
机器人其他
一复现好久之前初学ros+gazebo机械臂仿真的时候总有些懵,用的是ur5机械臂,现在回过头来看好像看懂了一些,故重新理清了一下功能包的逻辑,方便查阅。官方源码本文参考ubuntu16.04安装UR3/UR5/UR10机械臂的ROS驱动并实现gazebo下Moveit运动规划仿真以及真实UR3机械臂的运动控制(1)1.1roslaunchur_gazebour5.launch1.1.1找gaze
- Objective-C高级特性浅析与实践指南
小鹿撞出了脑震荡
objective-c学习
OC的学习笔记(二)文章目录OC的学习笔记(二)@property访问控制符点语法自定义`init`方法内存管理retain和release@class处理发生异常的方法NSSrting的常用方法类方法对象方法lengthcharacterAtIndexisEuqalStringcompare@autorelease和自动释放池自动释放池Category类别与扩展category的运用NSNumb
- socks代理和http代理的区别_浅析socks代理如何使用TCP和UDP协议
weixin_39640414
udp接受
SOCKS是一种网络传输协议,主要用于客户端与外网服务器之间通讯的中间传递。sock5协议没有规定加密,所以是明文传输,当然也可以搭配ssl加密。由于网上的信息传输都是运用tcp或udp进行的,所以使用socks5代理可以办到网上所能办到的一切,因为sock5既支持TCP协议又支持UDP协议。当然,socks5对这两种协议的使用是有区别的,以下分类说明。如何用代理TCP协议:1、向服务器的1080
- 2024最好的传奇手游打金服推荐 传奇手游打金服排行榜大全
会飞滴鱼儿
传奇游戏熟悉的背景音乐和爽快的攻击体验,凭借着这些元素,成为许多80后童年时光的最佳伴侣。面对当今市场上丰富的游戏资源,不少人依然留恋这款可以联机、高自由度玩法的传奇游戏。那么,让我们一同回顾一下2024年最值得一玩的传奇手游打金服,并浅析它们的特点以及全网热度情况。传奇手游延续至今,已经接近二十年的历史了,而这些年走过来,被诟病最多的就是其“内部号”的事情,本期小编也给大家整理了一份资料:但是现
- 浅析事件驱动Reactor
不适合写代码的程序员
服务器C/C++IO多路复用事件驱动Reactor设计模式
文章目录前言1、Reactor模式的核心概念2、Reactor模式的工作流程3、典型的Reactor模型架构4、优缺点分析5、实际应用中的Reactor6、使用示例前言事件驱动的Reactor模式是一种设计模式,广泛应用于高性能网络服务器和I/O密集型应用中。它的核心思想是通过事件驱动的方式管理和处理多个并发连接或I/O操作,而不需要为每个连接或操作创建单独的线程。这种模式能够极大地提高系统的可扩
- 产品经理那些事
Judy_Lily
牵引力教育浅析产品经理的价值众所周知,产品经理常被称为公司里轻量级的“CEO”,很多事都离不开产品经理,作为互联网时代的产品运营官,产品经理的“价值”无论从发展前景还是薪酬方面,都是非常可观的。那么,产品经理具体是做什么的呢?一位合格的产品经理要涉及很多方面:专业知识、行业常识、市场行情、竞争格局等等。专业知识:虽然产品经理不要求会算法,但是了解一定的专业知识是与算法研发工程师沟通的基础,否则产品
- 浅析STM32外部中断易死机解决
brotherwyz
stm32嵌入式硬件单片机
本案例stm32死机或程序跑飞是实际产品中出现的,初步怀疑是外部中断口,有极强的干扰所致,于是拿着信号发生器实测,当信号发生器产生300KHz的信号,甚至到12MHz的信号时,期间,程序跑飞或死机。看门狗也无法重启。解决点:1、初始化时,先关闭总中断,初始化完成后,再开启总中断/*Resetofallperipherals,InitializestheFlashinterfaceandtheSys
- 2021西邮LINUX兴趣小组纳新题浅析
大专er
c语言
4.考察位运算intmain(intargc,char*argv[]){charch='A';inti=65;unsignedintf=33554433;*(int*)&f>>=24;*(int*)&f=*(int*)&f+'?';printf("ch=%ci=%cf=%c\n",ch,i,*(int*)&f);return0;}*(int*)&f>>=24;这一行将f由无符号整数强制转换为整数,
- 闲聊 | 浅析《寂静之地2》三幕式剧作结构
端木胥
纪念第一次在影院看恐怖片。三幕式戏剧结构,最早可追溯到亚里士多德在《诗学》中总结的戏剧理论,即戏剧应包含开始、中间、结尾三个部分。著名编剧悉德·菲尔德则对这一理论加以扩充和具象化,他的概念模式放在电影剧本中,可分为以下三幕:第一幕是铺陈,占电影的四分之一。目的在于为整部电影的叙述架构基本的框架,交代故事发生的主要背景和事件,介绍主要的人物关系;第二幕是冲突,占电影的一半。这一阶段通过冲突的演变推动
- linux 进程映射空间 libc,linux进程地址空间布局浅析
钟程杰
linux进程映射空间libc
此文章是围绕该文章的思路进行总结的,原文记录的笔记详尽,在此基础上,我总结了本身的一下(想对浅显)。若是对具体细节想要了解的,能够访问这篇文章,在文章最后付了一段代码,跟该成程序的内存映射图,若是有哪里写的不正确,欢迎补充和指正。linux程序是什么抽象的来讲当咱们打开电脑点击应用程序图标,一个程序就运行起来了,可是在操做系统层面来看,实际上是产生了一个进程,这是一个程序的实体。ios接下来以li
- 线程和进程 linux,浅析 Linux 进程与线程
邹世辉
线程和进程linux
简介进程与线程是所有的程序员都熟知的概念,简单来说进程是一个执行中的程序,而线程是进程中的一条执行路径。进程是操作系统中基本的抽象概念,本文介绍Linux中进程和线程的用法以及原理,包括创建、消亡等。进程创建与执行Linux中进程的创建与执行分为两个函数,分别是fork和exec,如下代码所示:intmain(){pid_tpid;if((pid=fork()<0){printf("forkerr
- 浅析《可可西里》的电影美学:藏羚羊的血泪史是人与自然的对立性
你的能很能
文|bethlyn“可可西里”是蒙古语,意为“青色的山梁”,后经过一定艺术处理,延伸成广为接受的“美丽的青山,美丽的少女”。个中文化交错或许在寓意上有所出入,不过既都是美好,也大可不必纠结了。08年奥运会在北京举行,藏羚羊当选为奥运会吉祥物“迎迎”,陆川表示藏羚羊的“申吉”成功与自己的《可可西里》有抹不开的联系。《可可西里》是近年来我看过的最有力量的片子,写实性的剧本,写实性的拍摄手法,写实性的演
- 完成标准(DOD)浅析
众易
2016-03-0520:55:28Bonnie-Wu阅读数4649更多分类专栏:研发管理版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循CC4.0BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/wubijuan/article/details/50810671最近,我的团队问我一个问题:“为什么我安排下去的每个迭代任务,总是做不完?”经过沟通,我发现团
- 密码之浅析Diffie–Hellman
right_33cb
转:https://www.cnblogs.com/hyddd/p/7689132.html这个密钥交换方法,由惠特菲尔德·迪菲(BaileyWhitfieldDiffie)、马丁·赫尔曼(MartinEdwardHellman)于1976年发表。它是一种安全协议,让双方在完全没有对方任何预先信息的条件下通过不安全信道建立起一个密钥,这个密钥一般作为“对称加密”的密钥而被双方在后续数据传输中使用。
- 面向对象面向过程
3213213333332132
java
面向对象:把要完成的一件事,通过对象间的协作实现。
面向过程:把要完成的一件事,通过循序依次调用各个模块实现。
我把大象装进冰箱这件事为例,用面向对象和面向过程实现,都是用java代码完成。
1、面向对象
package bigDemo.ObjectOriented;
/**
* 大象类
*
* @Description
* @author FuJian
- Java Hotspot: Remove the Permanent Generation
bookjovi
HotSpot
openjdk上关于hotspot将移除永久带的描述非常详细,http://openjdk.java.net/jeps/122
JEP 122: Remove the Permanent Generation
Author Jon Masamitsu
Organization Oracle
Created 2010/8/15
Updated 2011/
- 正则表达式向前查找向后查找,环绕或零宽断言
dcj3sjt126com
正则表达式
向前查找和向后查找
1. 向前查找:根据要匹配的字符序列后面存在一个特定的字符序列(肯定式向前查找)或不存在一个特定的序列(否定式向前查找)来决定是否匹配。.NET将向前查找称之为零宽度向前查找断言。
对于向前查找,出现在指定项之后的字符序列不会被正则表达式引擎返回。
2. 向后查找:一个要匹配的字符序列前面有或者没有指定的
- BaseDao
171815164
seda
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
public class BaseDao {
public Conn
- Ant标签详解--Java命令
g21121
Java命令
这一篇主要介绍与java相关标签的使用 终于开始重头戏了,Java部分是我们关注的重点也是项目中用处最多的部分。
1
- [简单]代码片段_电梯数字排列
53873039oycg
代码
今天看电梯数字排列是9 18 26这样呈倒N排列的,写了个类似的打印例子,如下:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class 电梯数字排列_S3_Test {
public static void main(S
- Hessian原理
云端月影
hessian原理
Hessian 原理分析
一. 远程通讯协议的基本原理
网络通信需要做的就是将流从一台计算机传输到另外一台计算机,基于传输协议和网络 IO 来实现,其中传输协议比较出名的有 http 、 tcp 、 udp 等等, http 、 tcp 、 udp 都是在基于 Socket 概念上为某类应用场景而扩展出的传输协
- 区分Activity的四种加载模式----以及Intent的setFlags
aijuans
android
在多Activity开发中,有可能是自己应用之间的Activity跳转,或者夹带其他应用的可复用Activity。可能会希望跳转到原来某个Activity实例,而不是产生大量重复的Activity。
这需要为Activity配置特定的加载模式,而不是使用默认的加载模式。 加载模式分类及在哪里配置
Activity有四种加载模式:
standard
singleTop
- hibernate几个核心API及其查询分析
antonyup_2006
html.netHibernatexml配置管理
(一) org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration类
读取配置文件并创建唯一的SessionFactory对象.(一般,程序初始化hibernate时创建.)
Configuration co
- PL/SQL的流程控制
百合不是茶
oraclePL/SQL编程循环控制
PL/SQL也是一门高级语言,所以流程控制是必须要有的,oracle数据库的pl/sql比sqlserver数据库要难,很多pl/sql中有的sqlserver里面没有
流程控制;
分支语句 if 条件 then 结果 else 结果 end if ;
条件语句 case when 条件 then 结果;
循环语句 loop
- 强大的Mockito测试框架
bijian1013
mockito单元测试
一.自动生成Mock类 在需要Mock的属性上标记@Mock注解,然后@RunWith中配置Mockito的TestRunner或者在setUp()方法中显示调用MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);生成Mock类即可。二.自动注入Mock类到被测试类 &nbs
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(11)开发子程序
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
*开发子程序
*/
--子程序目是指被命名的PL/SQL块,这种块可以带有参数,可以在不同应用程序中多次调用
--PL/SQL有两种类型的子程序:过程和函数
--开发过程
--建立过程:不带任何参数
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE out_time
IS
BEGIN
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line(systimestamp);
E
- 【EhCache一】EhCache版Hello World
bit1129
Hello world
本篇是EhCache系列的第一篇,总体介绍使用EhCache缓存进行CRUD的API的基本使用,更细节的内容包括EhCache源代码和设计、实现原理在接下来的文章中进行介绍
环境准备
1.新建Maven项目
2.添加EhCache的Maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>ne
- 学习EJB3基础知识笔记
白糖_
beanHibernatejbosswebserviceejb
最近项目进入系统测试阶段,全赖袁大虾领导有力,保持一周零bug记录,这也让自己腾出不少时间补充知识。花了两天时间把“传智播客EJB3.0”看完了,EJB基本的知识也有些了解,在这记录下EJB的部分知识,以供自己以后复习使用。
EJB是sun的服务器端组件模型,最大的用处是部署分布式应用程序。EJB (Enterprise JavaBean)是J2EE的一部分,定义了一个用于开发基
- angular.bootstrap
boyitech
AngularJSAngularJS APIangular中文api
angular.bootstrap
描述:
手动初始化angular。
这个函数会自动检测创建的module有没有被加载多次,如果有则会在浏览器的控制台打出警告日志,并且不会再次加载。这样可以避免在程序运行过程中许多奇怪的问题发生。
使用方法: angular .
- java-谷歌面试题-给定一个固定长度的数组,将递增整数序列写入这个数组。当写到数组尾部时,返回数组开始重新写,并覆盖先前写过的数
bylijinnan
java
public class SearchInShiftedArray {
/**
* 题目:给定一个固定长度的数组,将递增整数序列写入这个数组。当写到数组尾部时,返回数组开始重新写,并覆盖先前写过的数。
* 请在这个特殊数组中找出给定的整数。
* 解答:
* 其实就是“旋转数组”。旋转数组的最小元素见http://bylijinnan.iteye.com/bl
- 天使还是魔鬼?都是我们制造
ducklsl
生活教育情感
----------------------------剧透请原谅,有兴趣的朋友可以自己看看电影,互相讨论哦!!!
从厦门回来的动车上,无意中瞟到了书中推荐的几部关于儿童的电影。当然,这几部电影可能会另大家失望,并不是类似小鬼当家的电影,而是关于“坏小孩”的电影!
自己挑了两部先看了看,但是发现看完之后,心里久久不能平
- [机器智能与生物]研究生物智能的问题
comsci
生物
我想,人的神经网络和苍蝇的神经网络,并没有本质的区别...就是大规模拓扑系统和中小规模拓扑分析的区别....
但是,如果去研究活体人类的神经网络和脑系统,可能会受到一些法律和道德方面的限制,而且研究结果也不一定可靠,那么希望从事生物神经网络研究的朋友,不如把
- 获取Android Device的信息
dai_lm
android
String phoneInfo = "PRODUCT: " + android.os.Build.PRODUCT;
phoneInfo += ", CPU_ABI: " + android.os.Build.CPU_ABI;
phoneInfo += ", TAGS: " + android.os.Build.TAGS;
ph
- 最佳字符串匹配算法(Damerau-Levenshtein距离算法)的Java实现
datamachine
java算法字符串匹配
原文:http://www.javacodegeeks.com/2013/11/java-implementation-of-optimal-string-alignment.html------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- 小学5年级英语单词背诵第一课
dcj3sjt126com
englishword
long 长的
show 给...看,出示
mouth 口,嘴
write 写
use 用,使用
take 拿,带来
hand 手
clever 聪明的
often 经常
wash 洗
slow 慢的
house 房子
water 水
clean 清洁的
supper 晚餐
out 在外
face 脸,
- macvim的使用实战
dcj3sjt126com
macvim
macvim用的是mac里面的vim, 只不过是一个GUI的APP, 相当于一个壳
1. 下载macvim
https://code.google.com/p/macvim/
2. 了解macvim
:h vim的使用帮助信息
:h macvim
- java二分法查找
蕃薯耀
java二分法查找二分法java二分法
java二分法查找
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
蕃薯耀 2015年6月23日 11:40:03 星期二
http:/
- Spring Cache注解+Memcached
hanqunfeng
springmemcached
Spring3.1 Cache注解
依赖jar包:
<!-- simple-spring-memcached -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.simple-spring-memcached</groupId>
<artifactId>simple-s
- apache commons io包快速入门
jackyrong
apache commons
原文参考
http://www.javacodegeeks.com/2014/10/apache-commons-io-tutorial.html
Apache Commons IO 包绝对是好东西,地址在http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/,下面用例子分别介绍:
1) 工具类
2
- 如何学习编程
lampcy
java编程C++c
首先,我想说一下学习思想.学编程其实跟网络游戏有着类似的效果.开始的时候,你会对那些代码,函数等产生很大的兴趣,尤其是刚接触编程的人,刚学习第一种语言的人.可是,当你一步步深入的时候,你会发现你没有了以前那种斗志.就好象你在玩韩国泡菜网游似的,玩到一定程度,每天就是练级练级,完全是一个想冲到高级别的意志力在支持着你.而学编程就更难了,学了两个月后,总是觉得你好象全都学会了,却又什么都做不了,又没有
- 架构师之spring-----spring3.0新特性的bean加载控制@DependsOn和@Lazy
nannan408
Spring3
1.前言。
如题。
2.描述。
@DependsOn用于强制初始化其他Bean。可以修饰Bean类或方法,使用该Annotation时可以指定一个字符串数组作为参数,每个数组元素对应于一个强制初始化的Bean。
@DependsOn({"steelAxe","abc"})
@Comp
- Spring4+quartz2的配置和代码方式调度
Everyday都不同
代码配置spring4quartz2.x定时任务
前言:这些天简直被quartz虐哭。。因为quartz 2.x版本相比quartz1.x版本的API改动太多,所以,只好自己去查阅底层API……
quartz定时任务必须搞清楚几个概念:
JobDetail——处理类
Trigger——触发器,指定触发时间,必须要有JobDetail属性,即触发对象
Scheduler——调度器,组织处理类和触发器,配置方式一般只需指定触发
- Hibernate入门
tntxia
Hibernate
前言
使用面向对象的语言和关系型的数据库,开发起来很繁琐,费时。由于现在流行的数据库都不面向对象。Hibernate 是一个Java的ORM(Object/Relational Mapping)解决方案。
Hibernte不仅关心把Java对象对应到数据库的表中,而且提供了请求和检索的方法。简化了手工进行JDBC操作的流程。
如
- Math类
xiaoxing598
Math
一、Java中的数字(Math)类是final类,不可继承。
1、常数 PI:double圆周率 E:double自然对数
2、截取(注意方法的返回类型) double ceil(double d) 返回不小于d的最小整数 double floor(double d) 返回不大于d的整最大数 int round(float f) 返回四舍五入后的整数 long round