Java-队列
目录
队列
双端队列
LinkList的常用方法
Queue的方法
Deque的方法
模拟实现队列
循环队列
队列的相关OJ题:
用队列实现栈
用栈实现队列
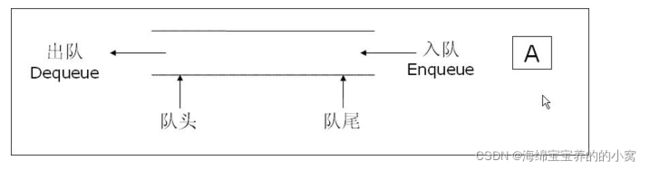
队列
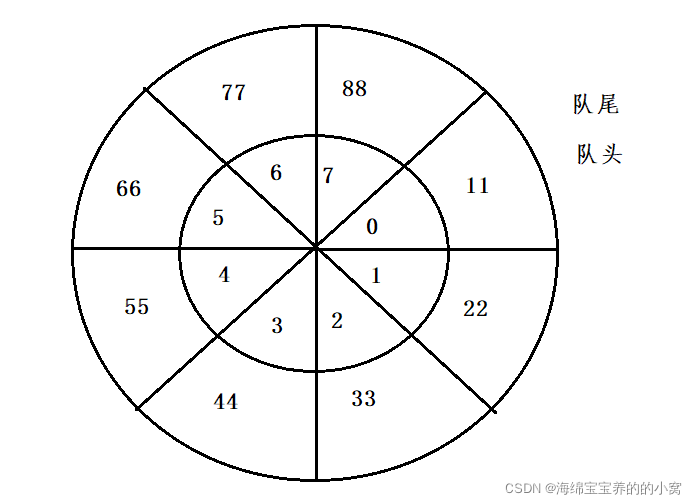
队列只允许一端插入元素,从另一端进行删除元素的特殊线性表。队列具有先进先出的特点。
入队:进入插入操作,这一端称为队尾。
出队:进行删除操作,这一端称为对头。
双端队列
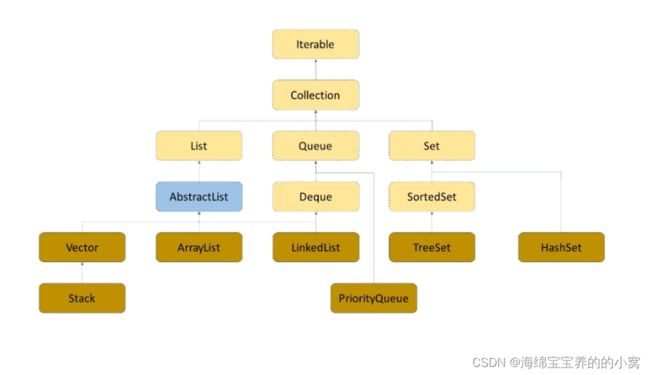
在前文集合中我们提到了Queue和Deque,一个是普通队列一个是双端队列,他们底层都是由一个双向链表LinkList实现的,当然Queue还有由一个优先级队列priorityQueue(二叉树实现)。
那么什么是双端队列呢?
双端队列是指两端都可以进行进队和出队操作的队列,将队列的两端分别称为前端和后端,两端都可以入队和出队。所以双端队列既能够当队列使用,也能当栈使用。
LinkList的常用方法
这些方法就不进行演示了,在前面的ArrayList的方法大致类似。
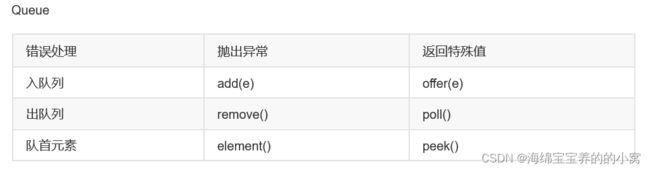
Queue的方法
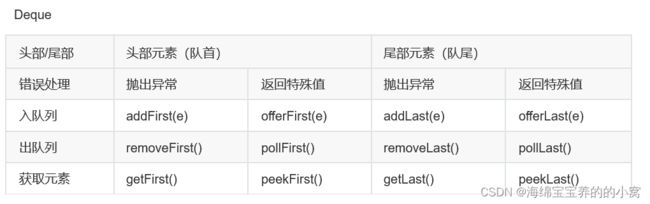
 Deque的方法
Deque的方法
这些方法也是有点区别的,这里做了些总结:
而且使用时尽量匹配着使用,比如offer、poll、peek是一组,add、remove、element是一组。
模拟实现队列
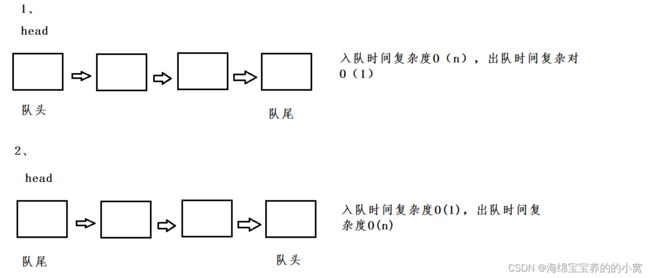
前面我们了解了队列中的一些方法,也知道了队列底层是由一个双向链表实现的。那么能不能用一个单链表实现呢?
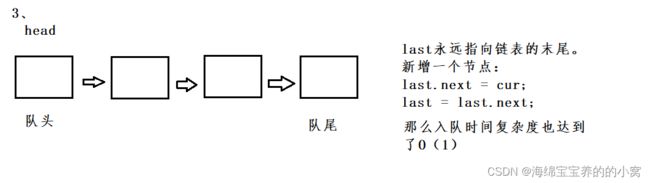
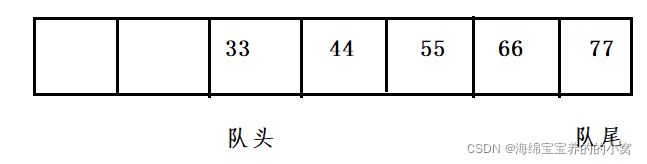
我们来分析一下,队列的入队和出队时间复杂度都是O(1)。
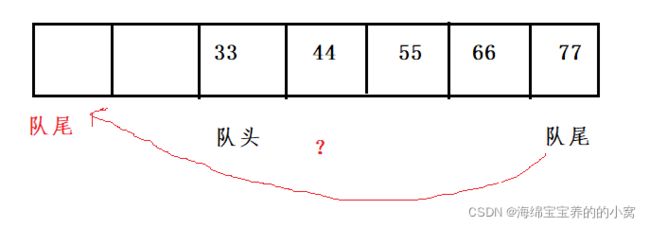
我们使用尾插法,发现两种方法都达不到要求。
但我们发现第一种方法其实是一个少了一个尾指针,如果我们为其增设一个尾指针:
由此我们可以写出以下代码:
class Node{
int val;
Node next;
public Node(int val, Node next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class myQueue {
public Node head = null;
public Node last = null;
private int size = 0;
public void offer(int val){
Node node = new Node(val);
if(head == null){
head = node;
last = node;
}else{
last.next = node;
last = last.next;
}
size++;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public int poll(){
Node node = head;
head = head.next;
size--;
return node.val;
}
public int peek(){
Node node = head;
return node.val;
}
}测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
myQueue queue = new myQueue();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}结果:
我们发现第二种方法如果想实现,似乎只能用双向链表实现了,所以如果想试着实现的可以试试哦,其实很简单的。
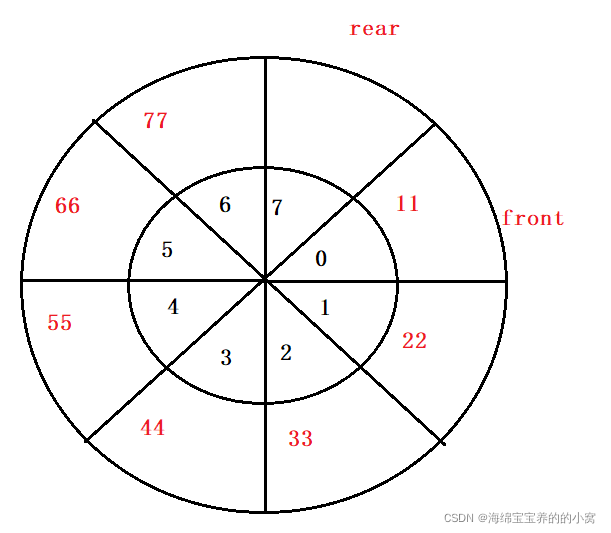
循环队列
我们原来模拟栈的时候不就是用的数组嘛,那么队列是否也可以用数组实现呢?
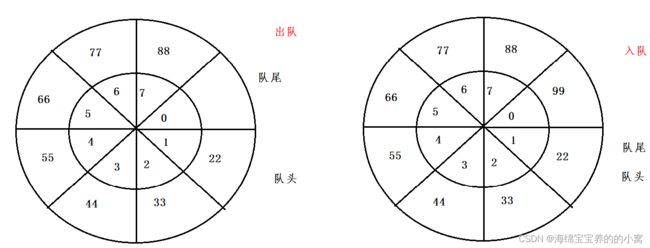
我们发现数组入队和出队时间复杂度都是O(1),那么这不是刚刚好嘛。但是有一个问题,如何判断队列是否满了。如果出现下列这种情况:
如何证明他满了?因为它前面还有两个空格?那你怎么知道它还有两个空格?
再比如现在如何插入元素,也就是说队尾如何回到数组最前方?
因此为了便于理解我们将这个数组卷起来:
回到一开始的问题,如何判断数组满了?
我们有4种解决方案:
第一种:
设立一个usedSize,入队usedSize++并且%一个数组的长度,出队usedSize--并且%一个数组长度,如果usedSize等于数组的长度则判断已满。
代码实现:
public class MyCircularQueue {
int []elem;
int rear;
int front;
int usedSize;
public MyCircularQueue() {
this.elem = new int[8];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return usedSize == 0;
}
public boolean isFull(){
return usedSize == elem.length;
}
public boolean offer(int val){
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("队列已满");
return false;
}
this.elem[rear] = val;
rear = (rear + 1) % elem.length;
usedSize++;
return true;
}
public boolean poll(){
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列为空");
return false;
}
front = (front - 1) % elem.length;
usedSize--;
return true;
}
public int front(){//查看队头元素
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列为空");
return -1;
}
return this.elem[front];
}
public int rear(){//查看队尾元素
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列为空");
return -1;
}
return this.elem[rear-1];
}
}测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCircularQueue qu = new MyCircularQueue();
qu.offer(1);
qu.offer(2);
qu.offer(3);
qu.offer(4);
System.out.println(qu.front());
System.out.println(qu.rear());
System.out.println(qu.poll());
System.out.println(qu.poll());
System.out.println(qu.poll());
System.out.println(qu.poll());
System.out.println(qu.poll());
}结果:
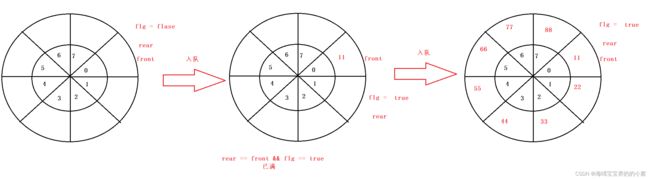
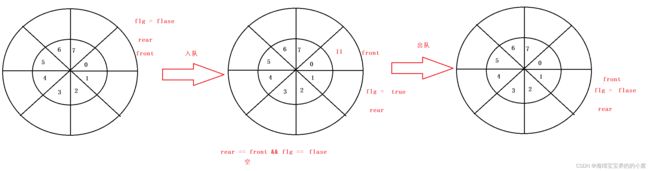
第二种:
设立一个标志位 flg ,初始值为false,入队把flg置为true,出队则把flg置为false。
思路有了,代码就不写了哈,有兴趣的可以去尝试写写。
第三种:
浪费一个空间,判断rear的下一个是不是front,如果是就代表满了
其余的思路与第一种相似。
第四种:
首先说明这个方法不是特别好,但是力扣做题时用这种方法通过了(不想说啥,只能说明力扣用例不够全)。因为rear与front相遇时不是满就是空,因此当rear与front相遇时我们判断数组是否有元素存在,不存在则不满,存在即满了。当然因为是int类型我们也不能判断元素是否为空,只能判断那个值是否是0,因为我们出队时可以把那个位置的元素置为0,(如果你一开始入队的元素全是0就没法判断是否满喽~~~)。
代码:
class MyCircularQueue {
public int []elem;
public int front;
public int rear;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.elem = new int[k];
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull())return false;
else {
this.elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty())return false;
else{
elem[front] = 0;
front = (front+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
}
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty())return -1;
else return this.elem[front];
}
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int index = -1;
if(rear == 0) {
index = elem.length-1;
}else {
index = rear-1;
}
return elem[index];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if(front == rear && elem[rear] == 0)return true;
else return false;
}
public boolean isFull() {
if(front == rear && elem[rear] != 0)return true;
else return false;
}
}力扣链接:设计循环队列 。
队列的相关OJ题:
用队列实现栈
前面我们学习了栈,现在用队列来实现下栈。
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例:
输入:
["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]解释:
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // 返回 2
myStack.pop(); // 返回 2
myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
解题思路:
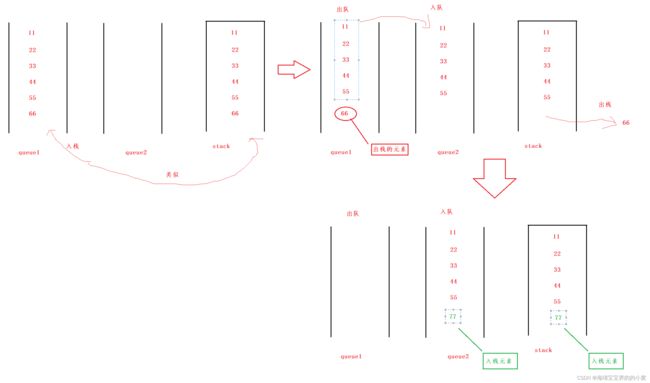
因为栈是后进先出,而队列是先进先出,一开始我们可以指定一个队列来入队,之后如果再入队就如那个不为空的队列,然后出队的话,如果哪个队列不为空,先把队列的大小赋给一个变量,然后这个队列出队的元素用另一个队列入队,最后剩的元素就是要出栈的元素
代码:
class MyStack {
Queue queue1;
Queue queue2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList();
queue2 = new LinkedList();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
if(!queue1.isEmpty()){
queue1.offer(x);
}else if(!queue2.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(x);
}else{
queue1.offer(x);
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if(empty())return -1;
if(!queue1.isEmpty()){
int size = queue1.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
return queue1.poll();
}else{
int size = queue2.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++){
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
}
return queue2.poll();
}
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
if(empty())return -1;
if(!queue1.isEmpty()){
int size = queue1.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
int val = queue1.poll();
queue2.offer(val);
return val;
}else{
int size = queue2.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++){
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
}
int val = queue2.poll();
queue1.offer(val);
return val;
}
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
}
} 力扣OJ链接:队列实现栈
用栈实现队列
队列实现栈后,我们再用栈来实现下队列吧~~
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
示例 1:
输入:
["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
解题思路:
方法与用队列实现栈类似,先用一个栈stack1存储入队的元素,如果要出队,则把栈stack1全部出栈到栈stack2中,最后出stack2中的元素,之后循环就好了,哪个栈不为空把这个栈中的元素放到另一个栈中,最后出栈栈顶元素。
代码实现:
class MyQueue {
private Stack stack1;
private Stack stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(!stack2.isEmpty()){
return stack2.pop();
}else{
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
int a = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(a);
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
public int peek() {
if(!stack2.isEmpty()){
return stack2.peek();
}else{
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
int a = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(a);
}
return stack2.peek();
}
}
public boolean empty() {
if(stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty())return true;
else return false;
}
} 力扣OJ链接:用栈实现队列
队列介绍告一段落。
本文收录专栏《数据结构》。