核心:
1.1*1的kernel_size能够有效减少参数数量
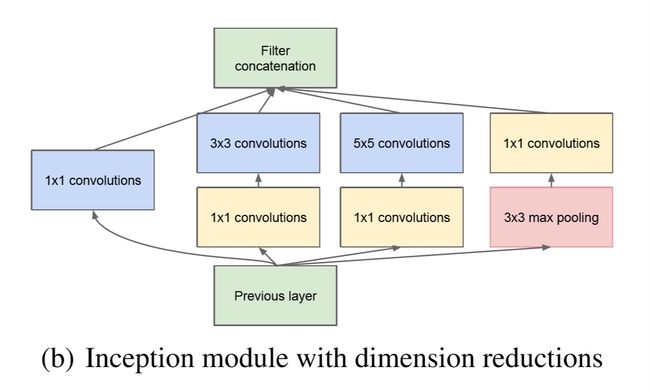
2.Inception block
Inception结构
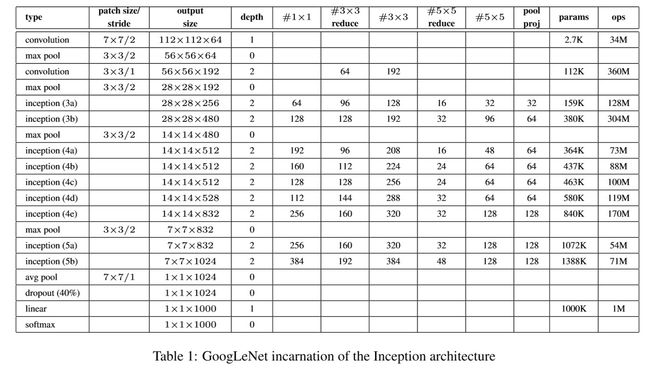
网络结构
忽略辅助分类:使用CIFAR10数据集
代码:
###author:xiaoheimiao
import torch
import torchvision
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision.transforms import transforms
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
#定义conv-bn-relu函数
def conv_relu(in_channel, out_channel, kernel, stride=1, padding=0):
conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel, stride, padding),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel, eps=1e-3),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
return conv
#定义incepion结构,见inception图
class inception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out1_1, out2_1, out2_3, out3_1, out3_5,
out4_1):
super(inception, self).__init__()
self.branch1 = conv_relu(in_channel, out1_1, 1)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
conv_relu(in_channel, out2_1, 1),
conv_relu(out2_1, out2_3, 3, padding=1))
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
conv_relu(in_channel, out3_1, 1),
conv_relu(out3_1, out3_5, 5, padding=2))
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=1, padding=1),
conv_relu(in_channel, out4_1, 1),
)
def forward(self, x):
b1 = self.branch1(x)
b2 = self.branch2(x)
b3 = self.branch3(x)
b4 = self.branch4(x)
output = torch.cat([b1, b2, b3, b4], dim=1)
return output
# 堆叠GOOGLENET,见上表所示结构
class GOOGLENET(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(GOOGLENET, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
conv_relu(3, 64, 7, 2, 3), nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, padding=0),
conv_relu(64, 64, 1), conv_relu(64, 192, 3, padding=1),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2), inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32),
inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64), nn.MaxPool2d(
3, stride=2), inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64),
inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64),
inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64),
inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64),
inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128), nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2),
inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128),
inception(832, 384, 182, 384, 48, 128, 128), nn.AvgPool2d(2))
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(9216,1024),
nn.Dropout2d(p=0.4),
nn.Linear(1024, 10))
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
out = self.classifier(x)
return out
#训练函数
def net_train():
net.train()
running_loss = 0.0
for i, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):
# 将输入传入GPU
inputs, labels = data
inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)
# 将梯度置零
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 前向传播-计算误差-反向传播-优化
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 计算误差并显示
running_loss += loss.item()
if i % 60 == 0: # print every 60 mini-batches
print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, i + 1, running_loss / 60))
running_loss = 0.0
print('Training Epoch Finished')
#测试函数
def net_test():
correct = 0
total = 0
# 关闭梯度
with torch.no_grad():
for data in testloader:
images, labels = data
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print('Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: %d %%' % (100 * correct / total))
return
#数据集函数
def net_dataloader(root, train_transform, test_transform):
trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root, train=True, transform=train_transform, download=False)
testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root, train=False, transform=test_transform, download=False)
trainloader = DataLoader(
trainset, batch_size=60, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
testloader = DataLoader(
testset, batch_size=8, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
print('Initializing Dataset...')
return trainloader, testloader
#main
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建实例并送入GPU
net = GOOGLENET().to(device)
# 选择误差
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 选择优化器
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
# 数据位置
root = './pydata/data/'
# 数据处理
train_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
test_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
# 创建数据loader
trainloader, testloader = net_dataloader(root, train_transform,
test_transform)
# run
n_epoch = 5#改变epoch
for epoch in range(n_epoch):
net_train()#每个epoch训练一次,测试一次
net_test()