何为架构?
架构(Architecture):软件开发中的设计方案,类与类之间的关系、模块与模块之间的关系、客户端与服务端的关系。
经常听到的架构名词:MVC、MVP、MVVM、VIPER、CDD、三层架构、四层架构等。
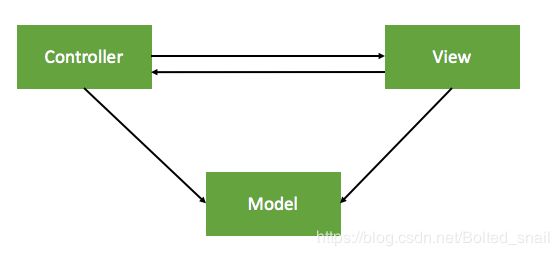
MVC - Apple版
Model-View-Controller
是iOS开发中常用的模式 ,Model和View之间没有任何直接到关系,通过Controller作为桥梁将二者联系起来。(Controller可初始化数据并将数据传递给Model;Model可以将数据传递给Controller,Controller将这些数据赋给View展示;View可以传递事件给Controller,Controller通过事件判断区出来数据Model)。
优点:View、Model可以重复利用,可以独立使用
缺点:Controller的代码过于臃肿。
Model-View-Controller 苹果官方文档
MVC – 变种
Model-View-Controller
变种的MVC,每一个view对应一个Model,只要Controller设置View的Model,就可直接展示对应的示图(常见的cell添加一个model属性就是这种模式)。
优点:对Controller进行瘦身,将View内部的细节封装起来了,外界不知道View内部的具体实现;
缺点:View依赖于Model。
MVP
Model-View-Presenter
MVP中的V在iOS中指的是ViewController和View。MVP将MVC的ViewController进行拆分:视图数据逻辑处理部分为P,ViewController剩余部分与View合并成V,V和P之间通过Protocol进行通信。
MVP实现了各模块的解藕,具有更好的可测试性。但是总体代码量比MVC大。
另外,iOS MVC更适用于快速开发,即代码规模较小的项目。因此将简单的MVC的Demo改成MVP,反而会显得笨拙。
#import "MJAppPresenter.h"
#import "MJApp.h"//Model
#import "MJAppView.h"//View
@interface MJAppPresenter()
@property (weak, nonatomic) UIViewController *controller;
@end
@implementation MJAppPresenter
- (instancetype)initWithController:(UIViewController *)controller
{
if (self = [super init]) {
self.controller = controller;
// 创建View
MJAppView *appView = [[MJAppView alloc] init];
appView.frame = CGRectMake(100, 100, 100, 150);
appView.delegate = self;
[controller.view addSubview:appView];
// 加载模型数据
MJApp *app = [[MJApp alloc] init];
app.name = @"QQ";
app.image = @"QQ";
// 赋值数据
[appView setName:app.name andImage:app.image];
}
return self;
}
#pragma mark - MJAppViewDelegate
- (void)appViewDidClick:(MJAppView *)appView
{
NSLog(@"presenter 监听了 appView 的点击");
}
@end
#import "ViewController.h"
#import "MJAppPresenter.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@property (strong, nonatomic) MJAppPresenter *presenter;
//@property (strong, nonatomic) MJOtherPresenter *presenter1;
//@property (strong, nonatomic) MJNewsPresenter *presenter2;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.presenter = [[MJAppPresenter alloc] initWithController:self];
}
可以看出View和Model的都是直接和Presenter传递值和交互的,时间处理也在Presenter中,不同的View和Model可以给Controller添加不同的Presenter属性即可,Controller不再直接是View和Model的桥梁。
MVVM
Model-View-ViewModel
Model-View-ViewModel for iOS
MVVM 模式将 Presenter 改名为 ViewModel,基本上与 MVP 模式完全一致。 唯一的区别是,它采用双向绑定(data-binding);当被绑定对象某个值的变化时,绑定对象会自动感知,无需被绑定对象主动通知绑定对象。可以使用KVO和RAC实现。例如在Label中显示倒计时,是V绑定了包含定时器的VM。
双向绑定在MVVM中指的是V和VM之间相互绑定。例如TextField的text长度达到阈值,另一个Button改变背景颜色。这个过程中首先VM感知V中TextField的text属性长度变化,V感知VM中对应的状态属性。一旦V中TextField的text属性长度超出VM中的阈值,VM中的状态属性改变,触发V中Button的背景色发生改变。
MVVM的优点:
1.低耦合。视图(View)可以独立于Model变化和修改,一个ViewModel可以绑定到不同的"View"上,当View变化的时候Model可以不变,当Model变化的时候View也可以不变。
2.可重用性。你可以把一些视图逻辑放在一个ViewModel里面,让很多view重用这段视图逻辑。
3.独立开发。开发人员可以专注于业务逻辑和数据的开发(ViewModel),设计人员可以专注于页面设计。
4.可测试。界面素来是比较难于测试的,而现在测试可以针对ViewModel来写。
facebook的KVOController九可以用来双向绑定,其github地址为:KVOController
//View
#import
@class MJAppView, MJAppViewModel;
@protocol MJAppViewDelegate
@optional
- (void)appViewDidClick:(MJAppView *)appView;
@end
@interface MJAppView : UIView
@property (weak, nonatomic) MJAppViewModel *viewModel;
@property (weak, nonatomic) id
@end
#import "MJAppView.h"
#import "NSObject+FBKVOController.h"
@interface MJAppView()
@property (weak, nonatomic) UIImageView *iconView;
@property (weak, nonatomic) UILabel *nameLabel;
@end
@implementation MJAppView
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame
{
if (self = [super initWithFrame:frame]) {
UIImageView *iconView = [[UIImageView alloc] init];
iconView.frame = CGRectMake(0, 0, 100, 100);
[self addSubview:iconView];
_iconView = iconView;
UILabel *nameLabel = [[UILabel alloc] init];
nameLabel.frame = CGRectMake(0, 100, 100, 30);
nameLabel.textAlignment = NSTextAlignmentCenter;
[self addSubview:nameLabel];
_nameLabel = nameLabel;
}
return self;
}
- (void)setViewModel:(MJAppViewModel *)viewModel
{
_viewModel = viewModel;
__weak typeof(self) waekSelf = self;
//监听viewModel的name和image属性变化,一旦变化就给view赋值
[self.KVOController observe:viewModel keyPath:@"name" options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew block:^(id _Nullable observer, id _Nonnull object, NSDictionary
waekSelf.nameLabel.text = change[NSKeyValueChangeNewKey];
}];
[self.KVOController observe:viewModel keyPath:@"image" options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew block:^(id _Nullable observer, id _Nonnull object, NSDictionary
waekSelf.iconView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:change[NSKeyValueChangeNewKey]];
}];
}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet
{
if ([self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(appViewDidClick:)]) {
[self.delegate appViewDidClick:self];
}
}
@end
//ViewModel
#import
@interface MJAppViewModel : NSObject
- (instancetype)initWithController:(UIViewController *)controller;
@end
#import "MJAppViewModel.h"
#import "MJApp.h"
#import "MJAppView.h"
@interface MJAppViewModel()
@property (weak, nonatomic) UIViewController *controller;
@property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name;
@property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *image;
@end
@implementation MJAppViewModel
- (instancetype)initWithController:(UIViewController *)controller
{
if (self = [super init]) {
self.controller = controller;
// 创建View
MJAppView *appView = [[MJAppView alloc] init];
appView.frame = CGRectMake(100, 100, 100, 150);
appView.delegate = self;
appView.viewModel = self;//双向绑定
[controller.view addSubview:appView];
// 加载模型数据
MJApp *app = [[MJApp alloc] init];
app.name = @"QQ";
app.image = @"QQ";
// 设置数据
self.name = app.name;
self.image = app.image;
}
return self;
}
#pragma mark - MJAppViewDelegate
- (void)appViewDidClick:(MJAppView *)appView
{
NSLog(@"viewModel 监听了 appView 的点击");
}
@end
//Controller
#import "ViewController.h"
#import "MJAppViewModel.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@property (strong, nonatomic) MJAppViewModel *viewModel;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.viewModel = [[MJAppViewModel alloc] initWithController:self];
}
@end
可以看出Controller 中只添加了ViewModel,不再与View和Model有任何关系,ViewModel初始化了View和Model,并将Model数据绑定给自己;而View绑定了ViewModel属性,并监听器值得变化,一旦有变化设置相应的控件;ViewModel为View代理,响应view的一些事件。
设计模式
设计模式(Design Pattern)
是一套被反复使用、代码设计经验的总结
使用设计模式的好处是:可重用代码、让代码更容易被他人理解、保证代码可靠性
一般与编程语言无关,是一套比较成熟的编程思想
设计模式可以分为三大类
创建型模式:对象实例化的模式,用于解耦对象的实例化过程
单例模式、工厂方法模式,等等
结构型模式:把类或对象结合在一起形成一个更大的结构
代理模式、适配器模式、组合模式、装饰模式,等等
行为型模式:类或对象之间如何交互,及划分责任和算法
观察者模式、命令模式、责任链模式,等等
作者:iOS弗森科
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/864e65605ea4
来源:
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。