Springboot自定义注解,支持SPEL表达式
举例,自定义redis模糊删除注解
1.自定义注解
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface CacheEvictFuzzy {
/**
* redis key集合,模糊删除
* @return
*/
String[] key() default "";
}
2.使用AOP拦截方法,解析注解参数
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Set;
@Aspect
@Order(1)
@Component
public class CacheCleanFuzzyAspect {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private RedisUtil redis;
//指定要执行AOP的方法
@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(cacheEvictFuzzy)")
public void pointCut(CacheEvictFuzzy cacheEvictFuzzy){}
// 设置切面为加有 @RedisCacheable注解的方法
@Around("@annotation(cacheEvictFuzzy)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, CacheEvictFuzzy cacheEvictFuzzy){
return doRedis(proceedingJoinPoint, cacheEvictFuzzy);
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "@annotation(cacheEvictFuzzy)", throwing = "error")
public void afterThrowing (Throwable error, CacheEvictFuzzy cacheEvictFuzzy){
logger.error(error.getMessage());
}
/**
* 删除缓存
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @param cacheEvictFuzzy
* @return
*/
private Object doRedis (ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, CacheEvictFuzzy cacheEvictFuzzy){
Object result = null;
//得到被切面修饰的方法的参数列表
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
// 得到被代理的方法
Method method = ((MethodSignature) proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod();
String[] keys = cacheEvictFuzzy.key();
Set keySet = null;
String realkey = "";
for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(keys[i])){
continue;
}
realkey = parseKey(keys[i], method, args);
keySet = redis.keys("*"+realkey+"*");
if (null != keySet && keySet.size()>0){
redis.delKeys(keySet);
logger.debug("拦截到方法:" + proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName() + "方法");
logger.debug("删除的数据key为:"+keySet.toString());
}
}
try {
result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}finally {
return result;
}
}
/**
* 获取缓存的key
* key 定义在注解上,支持SPEL表达式
* @return
*/
private String parseKey(String key, Method method, Object [] args){
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) return null;
//获取被拦截方法参数名列表(使用Spring支持类库)
LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer u = new LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer();
String[] paraNameArr = u.getParameterNames(method);
//使用SPEL进行key的解析
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
//SPEL上下文
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
//把方法参数放入SPEL上下文中
for(int i=0;i
完事啦!
大家可以注意到关键方法就是parseKey
/**
* 获取缓存的key
* key 定义在注解上,支持SPEL表达式
* @return
*/
private String parseKey(String key, Method method, Object [] args){
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) return null;
//获取被拦截方法参数名列表(使用Spring支持类库)
LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer u = new LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer();
String[] paraNameArr = u.getParameterNames(method);
//使用SPEL进行key的解析
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
//SPEL上下文
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
//把方法参数放入SPEL上下文中
for(int i=0;i
自定义注解结合切面和spel表达式
在我们的实际开发中可能存在这么一种情况,当方法参数中的某些条件成立的时候,需要执行一些逻辑处理,比如输出日志。而这些代码可能都是差不多的,那么这个时候就可以结合自定义注解加上切面加上spel表达式进行处理。就比如在spring中我们可以使用@Cacheable(key="#xx")实现缓存,这个#xx就是一个spel表达式。
需求:我们需要将service层方法中方法的某个参数的值大于0.5的方法,输出方法执行日志。(需要了解一些spel表达式的语法)
实现步骤:
1、自定义一个注解Log
2、自定义一个切面,拦截所有方法上存在@Log注解修饰的方法
3、写一个service层方法,方法上标注@Log注解
难点:
在切面中需要拿到具体执行方法的方法名,可以使用spring提供的LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer来获取到
自定义一个注解
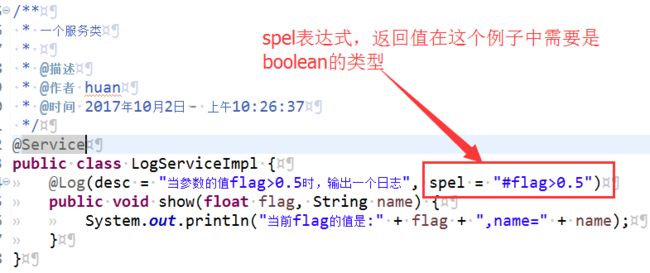
注意:注解中的spel的值是必须的,且spel表达式返回的结果应该是一个布尔值
/**
* 记录日志信息,当spel表但是中的值为true时,输出日志信息
*
* @描述
* @作者 huan
* @时间 2017年10月2日 - 上午10:25:39
*/
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Log {
String spel();
String desc() default "描述";
}
自定义一个service类,在需要拦截的方法上加上@Log注解
写一个自定义切面
注意一下解析spel表达式中context的设值即可
/**
* 日志切面,当条件满足时输出日志.
*
* @描述
* @作者 huan
* @时间 2017年10月2日 - 上午10:32:16
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogAspect {
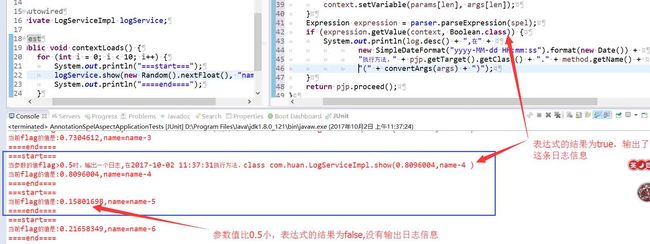
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer discoverer = new LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer();
@Around("@annotation(log)")
public Object invoked(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, Log log) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
Method method = ((MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature()).getMethod();
String spel = log.spel();
String[] params = discoverer.getParameterNames(method);
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
for (int len = 0; len < params.length; len++) {
context.setVariable(params[len], args[len]);
}
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression(spel);
if (expression.getValue(context, Boolean.class)) {
System.out.println(log.desc() + ",在" + new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()) + "执行方法," + pjp.getTarget().getClass() + "." + method.getName()
+ "(" + convertArgs(args) + ")");
}
return pjp.proceed();
}
private String convertArgs(Object[] args) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (Object arg : args) {
if (null == arg) {
builder.append("null");
} else {
builder.append(arg.toString());
}
builder.append(',');
}
builder.setCharAt(builder.length() - 1, ' ');
return builder.toString();
}
}
pom文件的依赖
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-parent 1.5.2.RELEASE UTF-8 UTF-8 1.8 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-aop org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-test test org.springframework.boot spring-boot-maven-plugin
测试
增加内容
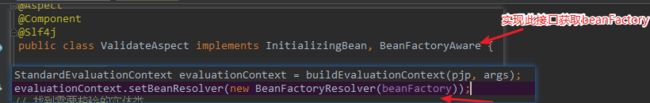
1、当我们想在自己写的spel表达式中调用spring bean 管理的方法时,如何写。spel表达式支持使用 @来引用bean,但是此时需要注入BeanFactory
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。