之前的几篇源码分析我们分别对
Navigation、Lifecycles、ViewModel、LiveData、进行了分析,也对JetPack有了更深入的了解。但是Jetpack远不止这些组件,今天的主角---Paging,Jetpack中的分页组件,官方是这么形容它的:‘’逐步从您的数据源按需加载信息‘’
如果你对Jetpack组件有了解或者想对源码有更深入的了解,请看我之前的几篇文章:
1. Jetpack源码解析---看完你就知道Navigation是什么了?
2. Jetpack源码解析---Navigation为什么切换Fragment会重绘?
3. Jetpack源码解析---用Lifecycles管理生命周期
4. Jetpack源码解析—LiveData的使用及工作原理
5. Jetpack源码解析---ViewModel基本使用及源码解析
1. 背景
在我的Jetpack_Note系列中,对每一篇的分析都有相对应的代码片段及使用,我把它做成了一个APP,目前功能还不完善,代码我也上传到了GitHub上,参考了官方的Demo以及目前网上的一些文章,有兴趣的小伙伴可以看一下,别忘了给个Star。
https://github.com/Hankkin/JetPack_Note
今天我们的主角是Paging,介绍之前我们先看一下效果:
2. 简介
2.1 基本介绍
官方定义:
分页库Pagin Library是Jetpack的一部分,它可以妥善的逐步加载数据,帮助您一次加载和显示一部分数据,这样的按需加载可以减少网络贷款和系统资源的使用。分页库支持加载有限以及无限的list,比如一个持续更新的信息源,分页库可以与RecycleView无缝集合,它还可以与LiveData或RxJava集成,观察界面中的数据变化。
2.2 核心组件
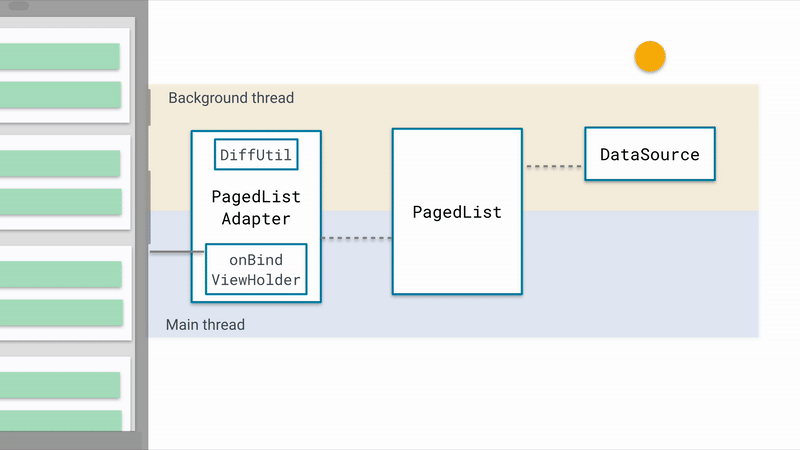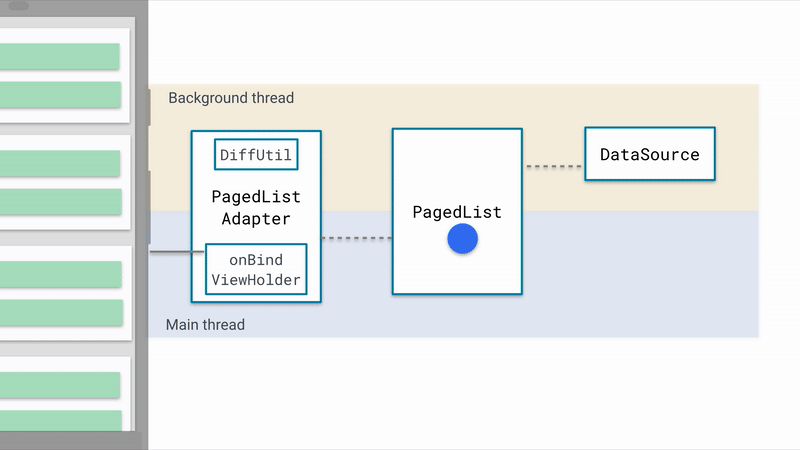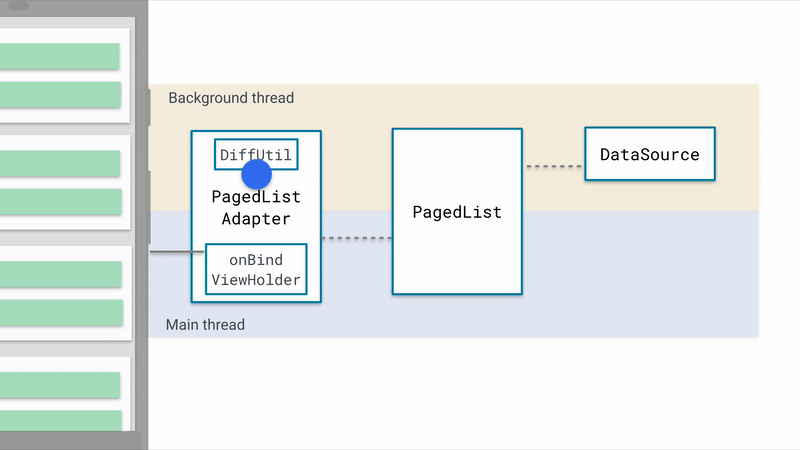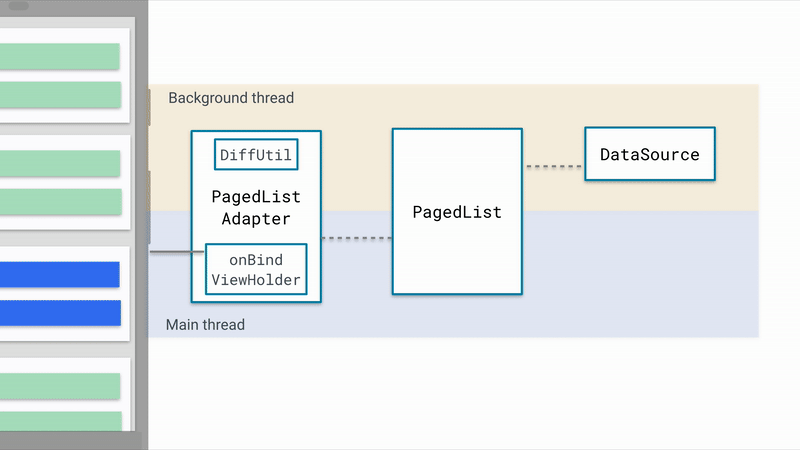
1. PagedList
PageList是一个集合类,它以分块的形式异步加载数据,每一块我们称之为页。它继承自AbstractList,支持所有List的操作,它的内部有五个主要变量:
- mMainThreadExecutor 主线程Executor,用于将结果传递到主线程
- mBackgroundThreadExecutor 后台线程,执行负载业务逻辑
- BoundaryCallback 当界面显示缓存中靠近结尾的数据的时候,它将加载更多的数据
- Config PageList从DataSource中加载数据的配置
- PagedStorage
用于存储加载到的数据
Config属性:
- pageSize:分页加载的数量
- prefetchDistance:预加载的数量
- initialLoadSizeHint:初始化数据时加载的数量,默认为pageSize*3
- enablePlaceholders:当item为null是否使用placeholder显示
PageList会通过DataSource加载数据,通过Config的配置,可以设置一次加载的数量以及预加载的数量。除此之外,PageList还可以想RecycleView.Adapter发送更新的信号,驱动UI的刷新。
2. DataSource
DataSourceKey对应加载数据的条件信息,Value对应加载数据的实体类。Paging库中提供了三个子类来让我们在不同场景的情况下使用:
- PageKeyedDataSource:如果后端API返回数据是分页之后的,可以使用它;例如:官方Demo中GitHub API中的SearchRespositories就可以返回分页数据,我们在GitHub API的请求中制定查询关键字和想要的哪一页,同时也可以指明每个页面的项数。
- ItemKeyedDataSource:如果通过键值请求后端数据;例如我们需要获取在某个特定日期起Github的前100项代码提交记录,该日期将成为DataSource的键,ItemKeyedDataSource允许自定义如何加载初始页;该场景多用于评论信息等类似请求
- PositionalDataSource:适用于目标数据总数固定,通过特定的位置加载数据,这里Key是Integer类型的位置信息,T即Value。 比如从数据库中的1200条开始加在20条数据。
3. PagedListAdapter
PageListAdapter继承自RecycleView.Adapter,和RecycleView实现方式一样,当数据加载完毕时,通知RecycleView数据加载完毕,RecycleView填充数据;当数据发生变化时,PageListAdapter会接受到通知,交给委托类AsyncPagedListDiffer来处理,AsyncPagedListDiffer是对DiffUtil.ItemCallback
3.基本使用
3.1 添加依赖包
implementation "androidx.paging:paging-runtime:$paging_version" // For Kotlin use paging-runtime-ktx
implementation "androidx.paging:paging-runtime-ktx:$paging_version" // For Kotlin use paging-runtime-ktx
// alternatively - without Android dependencies for testing
testImplementation "androidx.paging:paging-common:$paging_version" // For Kotlin use paging-common-ktx
// optional - RxJava support
implementation "androidx.paging:paging-rxjava2:$paging_version" // For Kotlin use paging-rxjava2-ktx
3.2 PagingWithRoom使用
新建UserDao
/**
* created by Hankkin
* on 2019-07-19
*/
@Dao
interface UserDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM User ORDER BY name COLLATE NOCASE ASC")
fun queryUsersByName(): DataSource.Factory
@Insert
fun insert(users: List)
@Insert
fun insert(user: User)
@Delete
fun delete(user: User)
}
创建UserDB数据库
/**
* created by Hankkin
* on 2019-07-19
*/
@Database(entities = arrayOf(User::class), version = 1)
abstract class UserDB : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun userDao(): UserDao
companion object {
private var instance: UserDB? = null
@Synchronized
fun get(context: Context): UserDB {
if (instance == null) {
instance = Room.databaseBuilder(context.applicationContext,
UserDB::class.java, "UserDatabase")
.addCallback(object : RoomDatabase.Callback() {
override fun onCreate(db: SupportSQLiteDatabase) {
fillInDb(context.applicationContext)
}
}).build()
}
return instance!!
}
/**
* fill database with list of cheeses
*/
private fun fillInDb(context: Context) {
// inserts in Room are executed on the current thread, so we insert in the background
ioThread {
get(context).userDao().insert(
CHEESE_DATA.map { User(id = 0, name = it) })
}
}
}
}
创建PageListAdapter
/**
* created by Hankkin
* on 2019-07-19
*/
class PagingDemoAdapter : PagedListAdapter(diffCallback) {
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int) =
ViewHolder(AdapterPagingItemBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.context), parent, false))
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int) {
val item = getItem(position)
holder.apply {
bind(createOnClickListener(item), item)
itemView.tag = item
}
}
private fun createOnClickListener(item: User?): View.OnClickListener {
return View.OnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(it.context, item?.name, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
class ViewHolder(private val binding: AdapterPagingItemBinding) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(binding.root) {
fun bind(listener: View.OnClickListener, item: User?) {
binding.apply {
clickListener = listener
user = item
executePendingBindings()
}
}
}
companion object {
/**
* This diff callback informs the PagedListAdapter how to compute list differences when new
* PagedLists arrive.
*
* When you add a Cheese with the 'Add' button, the PagedListAdapter uses diffCallback to
* detect there's only a single item difference from before, so it only needs to animate and
* rebind a single view.
*
* @see android.support.v7.util.DiffUtil
*/
private val diffCallback = object : DiffUtil.ItemCallback() {
override fun areItemsTheSame(oldItem: User, newItem: User): Boolean =
oldItem.id == newItem.id
/**
* Note that in kotlin, == checking on data classes compares all contents, but in Java,
* typically you'll implement Object#equals, and use it to compare object contents.
*/
override fun areContentsTheSame(oldItem: User, newItem: User): Boolean =
oldItem == newItem
}
}
}
ViewModel承载数据
class PagingWithDaoViewModel internal constructor(private val pagingRespository: PagingRespository) : ViewModel() {
val allUsers = pagingRespository.getAllUsers()
fun insert(text: CharSequence) {
pagingRespository.insert(text)
}
fun remove(user: User) {
pagingRespository.remove(user)
}
}
Activity中观察到数据源的变化后,会通知Adapter自动更新数据
class PagingWithDaoActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var viewModel: PagingWithDaoViewModel
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_paging_with_dao)
setLightMode()
setupToolBar(toolbar) {
title = resources.getString(R.string.paging_with_dao)
setDisplayHomeAsUpEnabled(true)
}
viewModel = obtainViewModel(PagingWithDaoViewModel::class.java)
val adapter = PagingDemoAdapter()
rv_paging.adapter = adapter
viewModel.allUsers.observe(this, Observer(adapter::submitList))
}
override fun onOptionsItemSelected(item: MenuItem?): Boolean {
when (item?.itemId) {
android.R.id.home -> finish()
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item)
}
}
3.3 PagingWithNetWork 使用
上面我们通过Room进行了数据库加载数据,下面看一下通过网络请求记载列表数据:
和上面不同的就是Respository数据源的加载,之前我们是通过Room加载DB数据,现在我们要通过网络获取数据:
GankRespository 干货数据源仓库
/**
* created by Hankkin
* on 2019-07-30
*/
class GankRespository {
companion object {
private const val PAGE_SIZE = 20
@Volatile
private var instance: GankRespository? = null
fun getInstance() =
instance ?: synchronized(this) {
instance
?: GankRespository().also { instance = it }
}
}
fun getGank(): Listing {
val sourceFactory = GankSourceFactory()
val config = PagedList.Config.Builder()
.setPageSize(PAGE_SIZE)
.setInitialLoadSizeHint(PAGE_SIZE * 2)
.setEnablePlaceholders(false)
.build()
val livePageList = LivePagedListBuilder(sourceFactory, config).build()
val refreshState = Transformations.switchMap(sourceFactory.sourceLiveData) { it.initialLoad }
return Listing(
pagedList = livePageList,
networkState = Transformations.switchMap(sourceFactory.sourceLiveData) { it.netWorkState },
retry = { sourceFactory.sourceLiveData.value?.retryAllFailed() },
refresh = { sourceFactory.sourceLiveData.value?.invalidate() },
refreshState = refreshState
)
}
}
可以看到getGank()方法返回了ListingListing是个什么呢?
/**
* Data class that is necessary for a UI to show a listing and interact w/ the rest of the system
* 封装需要监听的对象和执行的操作,用于上拉下拉操作
* pagedList : 数据列表
* networkState : 网络状态
* refreshState : 刷新状态
* refresh : 刷新操作
* retry : 重试操作
*/
data class Listing(
// the LiveData of paged lists for the UI to observe
val pagedList: LiveData>,
// represents the network request status to show to the user
val networkState: LiveData,
// represents the refresh status to show to the user. Separate from networkState, this
// value is importantly only when refresh is requested.
val refreshState: LiveData,
// refreshes the whole data and fetches it from scratch.
val refresh: () -> Unit,
// retries any failed requests.
val retry: () -> Unit)
Listing是我们封装的一个数据类,将数据源、网络状态、刷新状态、下拉刷新操作以及重试操作都封装进去了。那么我们的数据源从哪里获取呢,可以看到Listing的第一个参数pageList = livePageList,livePageList通过LivePagedListBuilder创建,LivePagedListBuilder需要两个参数(DataSource,PagedList.Config):
GankSourceFactory
�
/**
* created by Hankkin
* on 2019-07-30
*/
class GankSourceFactory(private val api: Api = Injection.provideApi()) : DataSource.Factory(){
val sourceLiveData = MutableLiveData()
override fun create(): DataSource {
val source = GankDataSource(api)
sourceLiveData.postValue(source)
return source
}
}
GankDataSource
/**
* created by Hankkin
* on 2019-07-30
*/
class GankDataSource(private val api: Api = Injection.provideApi()) : PageKeyedDataSource() {
private var retry: (() -> Any)? = null
val netWorkState = MutableLiveData()
val initialLoad = MutableLiveData()
fun retryAllFailed() {
val prevRetry = retry
retry = null
prevRetry?.also { it.invoke() }
}
override fun loadInitial(params: LoadInitialParams, callback: LoadInitialCallback) {
initialLoad.postValue(NetworkState.LOADED)
netWorkState.postValue(NetworkState.HIDDEN)
api.getGank(params.requestedLoadSize, 1)
.enqueue(object : Callback {
override fun onFailure(call: Call, t: Throwable) {
retry = {
loadInitial(params, callback)
}
initialLoad.postValue(NetworkState.FAILED)
}
override fun onResponse(call: Call, response: Response) {
if (response.isSuccessful) {
retry = null
callback.onResult(
response.body()?.results ?: emptyList(),
null,
2
)
initialLoad.postValue(NetworkState.LOADED)
} else {
retry = {
loadInitial(params, callback)
}
initialLoad.postValue(NetworkState.FAILED)
}
}
})
}
override fun loadAfter(params: LoadParams, callback: LoadCallback) {
netWorkState.postValue(NetworkState.LOADING)
api.getGank(params.requestedLoadSize, params.key)
.enqueue(object : Callback {
override fun onFailure(call: Call, t: Throwable) {
retry = {
loadAfter(params, callback)
}
netWorkState.postValue(NetworkState.FAILED)
}
override fun onResponse(call: Call, response: Response) {
if (response.isSuccessful) {
retry = null
callback.onResult(
response.body()?.results ?: emptyList(),
params.key + 1
)
netWorkState.postValue(NetworkState.LOADED)
} else {
retry = {
loadAfter(params, callback)
}
netWorkState.postValue(NetworkState.FAILED)
}
}
})
}
override fun loadBefore(params: LoadParams, callback: LoadCallback) {
}
}
网络请求的核心代码在GankDataSource中,因为我们的请求是分页请求,所以这里的GankDataSource我们继承自PageKeyedDataSource,它实现了三个方法:
loadInitial: 初始化加载,初始加载的数据 也就是我们直接能看见的数据
loadAfter: 下一页加载,每次传递的第二个参数 就是 你加载数据依赖的key
loadBefore: 往上滑加载的数据
可以看到我们在loadInitial中设置了initialLoad和netWorkState的状态值,同时通过RetrofitApi获取网络数据,并在成功和失败的回调中对数据和网络状态值以及加载初始化做了相关的设置,具体就不介绍了,可看代码。loadAfter同理,只不过我们在加载数据后对key也就是我们的page进行了+1操作。
Config参数就是我们对分页加载的一些配置:
val config = PagedList.Config.Builder()
.setPageSize(PAGE_SIZE)
.setInitialLoadSizeHint(PAGE_SIZE * 2)
.setEnablePlaceholders(false)
.build()
下面看我们在Activity中怎样使用:
PagingWithNetWorkActivity
class PagingWithNetWorkActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var mViewModel: PagingWithNetWorkViewModel
private lateinit var mDataBinding: ActivityPagingWithNetWorkBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
mDataBinding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this,R.layout.activity_paging_with_net_work)
setLightMode()
setupToolBar(toolbar) {
title = resources.getString(R.string.paging_with_network)
setDisplayHomeAsUpEnabled(true)
}
mViewModel = obtainViewModel(PagingWithNetWorkViewModel::class.java)
mDataBinding.vm = mViewModel
mDataBinding.lifecycleOwner = this
val adapter = PagingWithNetWorkAdapter()
mDataBinding.rvPagingWithNetwork.adapter = adapter
mDataBinding.vm?.gankList?.observe(this, Observer { adapter.submitList(it) })
mDataBinding.vm?.refreshState?.observe(this, Observer {
mDataBinding.rvPagingWithNetwork.post {
mDataBinding.swipeRefresh.isRefreshing = it == NetworkState.LOADING
}
})
mDataBinding.vm?.netWorkState?.observe(this, Observer {
adapter.setNetworkState(it)
})
}
override fun onOptionsItemSelected(item: MenuItem?): Boolean {
when (item?.itemId) {
android.R.id.home -> finish()
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item)
}
}
ViewModel中的gankList是一个LiveData,所以我们在这里给它设置一个观察,当数据变动是调用adapter.submitList(it),刷新数据,这个方法是PagedListAdapter中的,里面回去检查新数据和旧数据是否相同,也就是上面我们提到的AsyncPagedListDiffer来实现的。到这里整个流程就已经结束了,想看源码可以到Github上。
4. 总结
我们先看下官网给出的gif图:
总结一下,Paging的基本原理为:
- 使用DataSource从网络或者数据库获取数据
- 将数据保存到PageList中
- 将PageList中的数据提交给PageListAdapter
- PageListAdapter在后台线程中通过Diff对比新老数据,反馈到RecycleView中
- RecycleView刷新数据
基本原理在图上我们可以很清晰的了解到了,本篇文章的Demo中结合了ViewModel以及DataBinding进行了数据的存储和绑定。
最后代码地址:
https://github.com/Hankkin/JetPack_Note